Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Zone Annealing Velocity on the directional Recrystallization in a Ni base Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Alloys
- Young-Kyun Kim, Seong-June Yoon, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):331-335. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.331
- 677 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
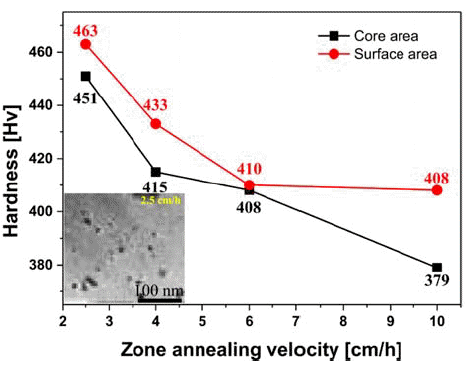
PDF This study investigates the directional recrystallization behavior of Ni based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloy according to the zone annealing velocity. The zone annealing temperature is set as 1390°C, while the zone velocities are set as 2.5, 4, 6, and 10 cm/h, respectively. The initial microstructure observation of the as-extruded sample shows equiaxed grains of random orientation, with an average grain size of 530 nm. On the other hand, the zone annealed samples show a large deviation in grain size depending on the zone velocities. In particular, grains with a size of several millimeters are observed at 2.5-cm/h zone velocity. It is also found that the preferred orientation varies with the zone annealing velocity. On the basis of these results, this study discusses the role of zone velocities in the directional recrystallization of Ni base ODS alloy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Directional recrystallisation processing: a review
Chao Yang, Ian Baker
International Materials Reviews.2021; 66(4): 256. CrossRef
- Directional recrystallisation processing: a review
- [Korean]
- The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Y2O3-Dispersed Fe-C and Fe-CNT Sintered Steels
- Jin Young Lim, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):298-301. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.298
- 626 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
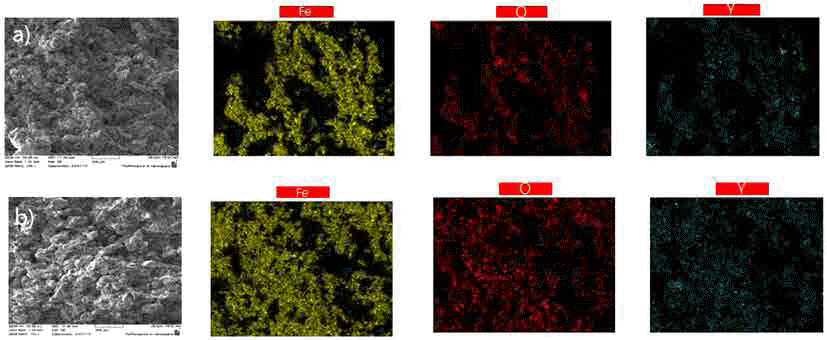
PDF In the present work, we use multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) as the starting material for the fabrication of sintered carbon steel. A comparison is made with conventionally sintered carbon steel, where graphite is used as the starting material. Milling is performed using a horizontal mill sintered in a vacuum furnace. We analyze the grain size, number of pores, X-ray diffraction patterns, and microstructure. Changes in the physical properties are determined by using the Archimedes method and Vickers hardness measurements. The result shows that the use of MWCNTs instead of graphite significantly reduces the size and volume of the pores as well as the grain size after sintering. The addition of Y2O3.to the Fe-MWCNT samples further inhibits the growth of grains.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


