Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Mechanical Properties in WC–Mo₂C–Co Cemented Carbides via Dual Hard-Phase Based Heterogeneous Microstructure Design
- Jinwoo Seok, Jong Tae Kim, Juree Jung, SongYi Kim, Bin Lee, Junhee Han, Leeseung Kang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):428-436. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00297
- 530 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
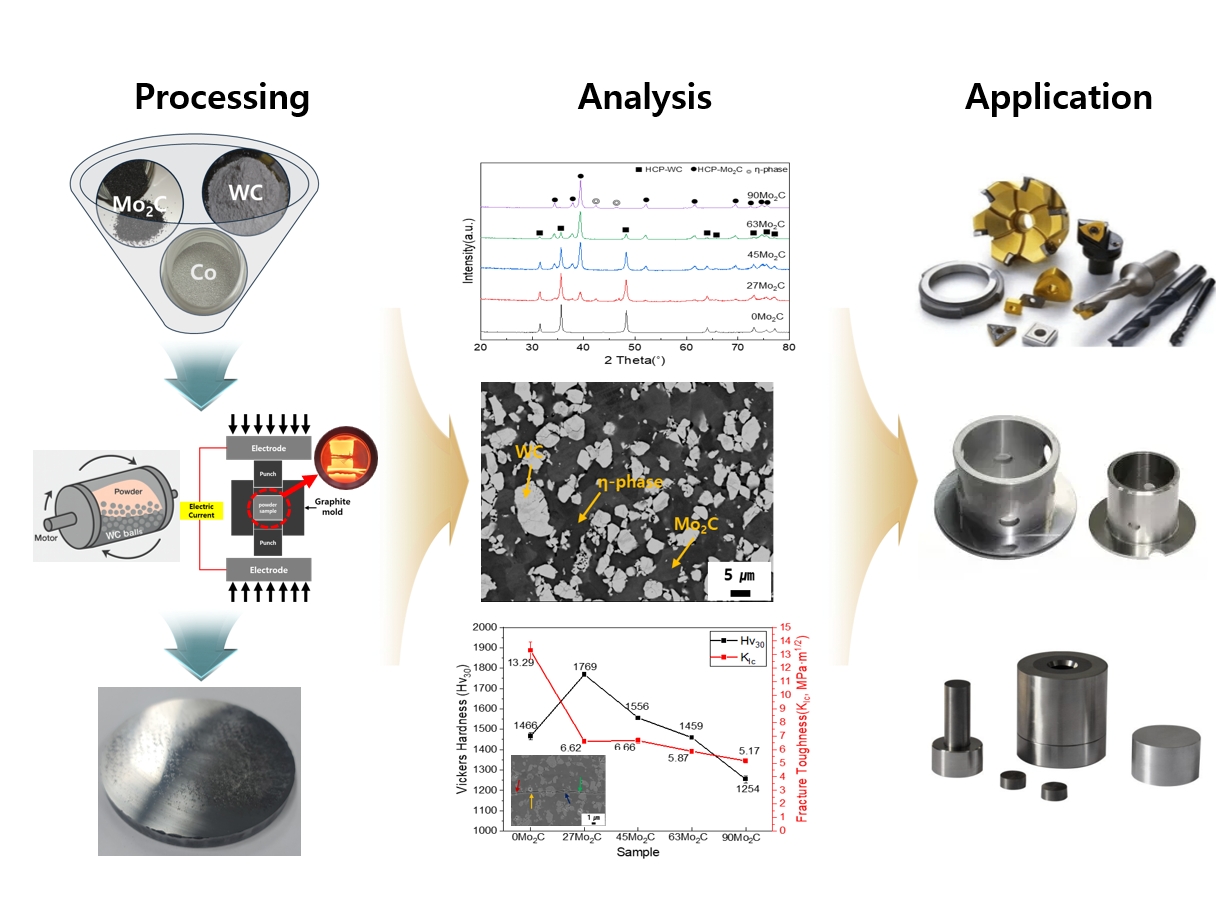
PDF - WC–Mo₂C–Co cemented carbides were fabricated to investigate the effects of Mo₂C addition on microstructure and mechanical properties. Dual hard-phase design using WC and Mo₂C was employed to optimize the balance between hardness and toughness. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) was conducted at various temperatures after ball milling, and 1300 °C for 5 min was identified as the optimized sintering condition, achieving complete densification and phase stability. The addition of Mo₂C refined the microstructure by suppressing abnormal WC grain growth through preferential dissolution of Mo₂C into the Co binder. Hardness increased up to 1769 Hv30 due to grain refinement and solid-solution strengthening, while promoted η-phase formation and reduced fracture toughness.The 27Mo₂C composition exhibited the most balanced combination of hardness and toughness. These results demonstrate that controlled Mo₂C addition enables dual hard-phase strengthening and microstructure optimization in WC–Mo₂C–Co carbides for advanced cutting and forming applications.
- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
- Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
- 501 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
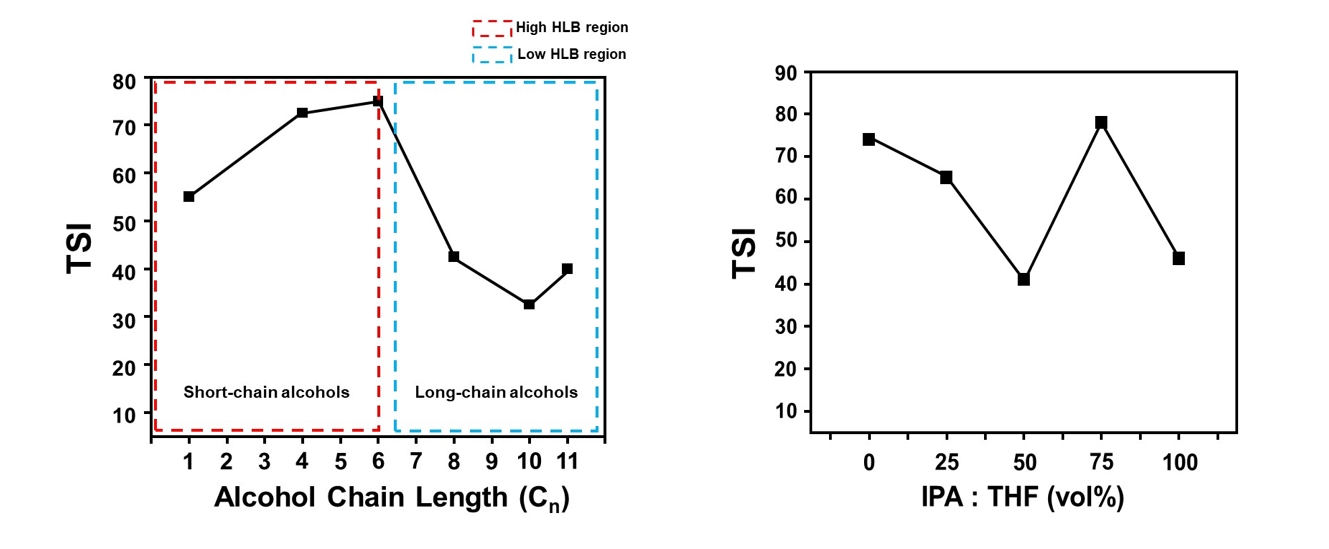
PDF - This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00444
- 977 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
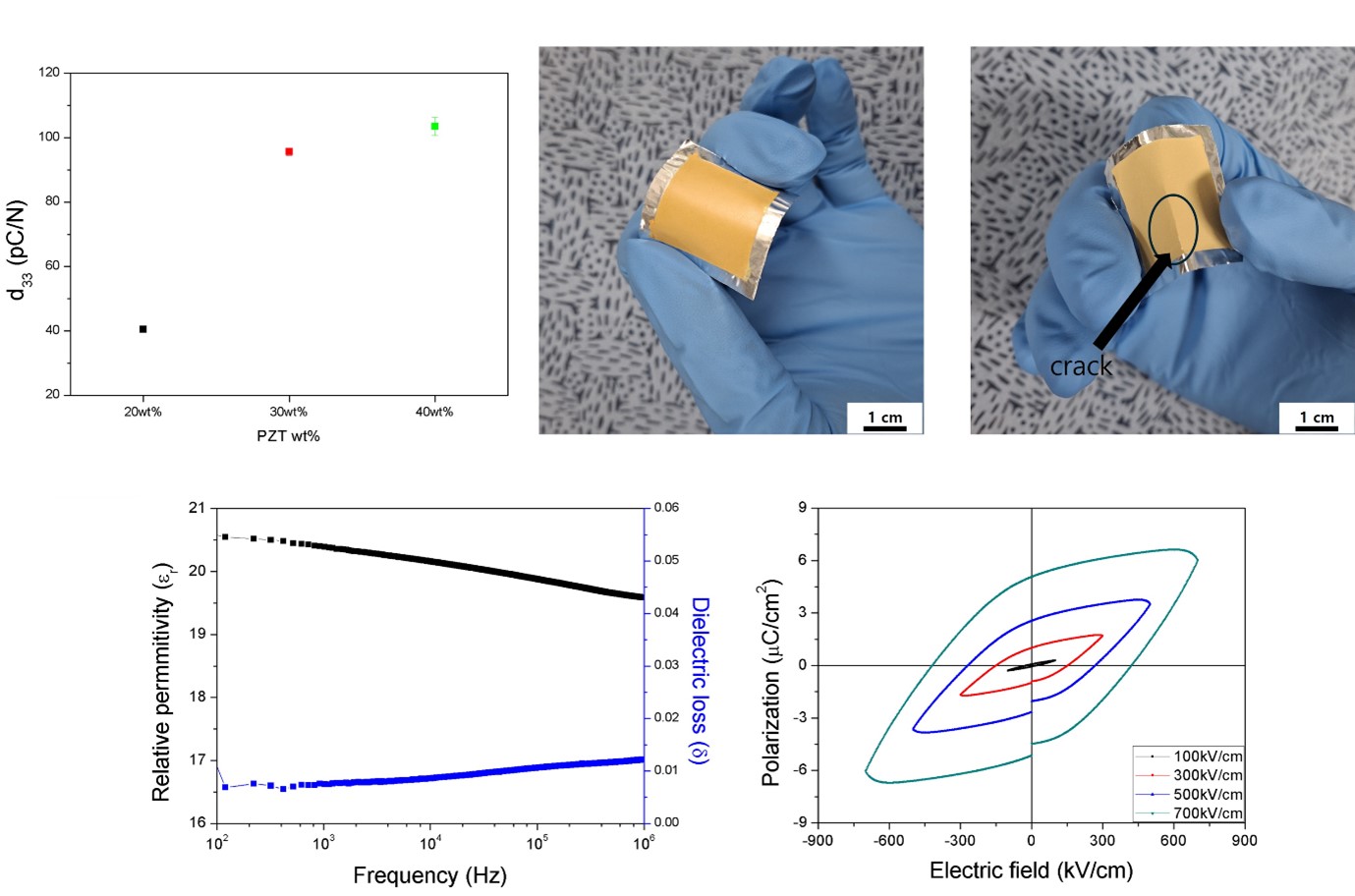
PDF - Piezoelectric composites have attracted significant research interest as sustainable power sources for electronic devices due to their high mechanical stability and electrical output characteristics. This study investigated the optimal processing conditions for fabricating a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester based on Pb(Zr,Ti)O₃ (PZT) powder and a polyimide (PI) matrix composite. Various parameters, including the optimal mixing ratio of PI/PZT, ultrasonic treatment, homogenization, vacuum oven, and UV/O₃ treatment, were optimized to achieve a uniform piezoelectric composite. A PZT content of 30 wt% and 20 minutes of homogenization were identified as the most effective conditions for increasing the uniformity of the composite. The optimized composite exhibited a high piezoelectric coefficient, a typical P-E hysteresis loop, and dielectric properties, exhibiting a voltage output that adjusts in response to variations in the applied touch force. This study provides foundational data for the uniform fabrication of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters and next-generation miniaturized electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Additive Manufacturing Optimization of Directed Energy Deposition-Processed Ti-6Al-4V Alloy using Energy Density and Powder Deposition Density
- Yukyeong Lee, Eun Sung Kim, Se-Ho Chun, Jae Bok Seol, Hyokyung Sung, Jung Seok Oh, Hyoung Seop Kim, Taekyung Lee, Tae-Hyun Nam, Jung Gi Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):491-496. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.491
- 1,040 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The process optimization of directed energy deposition (DED) has become imperative in the manufacture of reliable products. However, an energy-density-based approach without a sufficient powder feed rate hinders the attainment of an appropriate processing window for DED-processed materials. Optimizing the processing of DEDprocessed Ti-6Al- 4V alloys using energy per unit area (Eeff) and powder deposition density (PDDeff) as parameters helps overcome this problem in the present work. The experimental results show a lack of fusion, complete melting, and overmelting regions, which can be differentiated using energy per unit mass as a measure. Moreover, the optimized processing window (Eeff = 44~47 J/mm2 and PDDeff = 0.002~0.0025 g/mm2) is located within the complete melting region. This result shows that the Eeff and PDDeff-based processing optimization methodology is effective for estimating the properties of DED-processed materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


