Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Modulation of Microstructure and Energy Storage Performance in (K,Na)NbO3-Bi(Ni,Ta)O3 Ceramics through Zn Doping
- Jueun Kim, Seonhwa Park, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):509-515. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.509
- 788 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
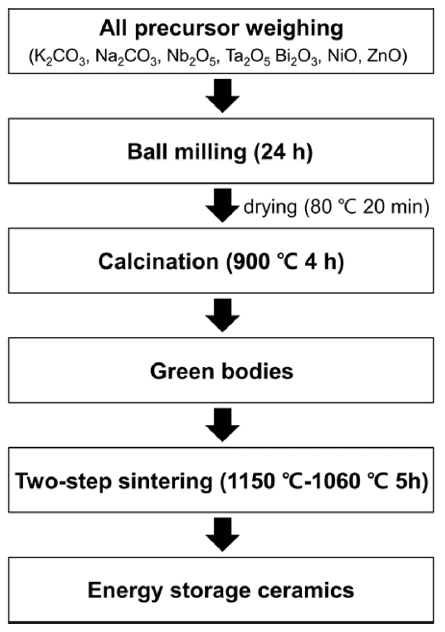
PDF Lead-free perovskite ceramics, which have excellent energy storage capabilities, are attracting attention owing to their high power density and rapid charge-discharge speed. Given that the energy-storage properties of perovskite ceramic capacitors are significantly improved by doping with various elements, modifying their chemical compositions is a fundamental strategy. This study investigated the effect of Zn doping on the microstructure and energy storage performance of potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics. Two types of powders and their corresponding ceramics with compositions of (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3 (KNN-BNT) and (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni1/3Zn1/3Ta1/3) O3 (KNN-BNZT) were prepared via solid-state reactions. The results indicate that Zn doping retards grain growth, resulting in smaller grain sizes in Zn-doped KNN-BNZT than in KNN-BNT ceramics. Moreover, the Zn-doped KNNBNZT ceramics exhibited superior energy storage density and efficiency across all x values. Notably, 0.9KNN-0.1BNZT ceramics demonstrate an energy storage density and efficiency of 0.24 J/cm3 and 96%, respectively. These ceramics also exhibited excellent temperature and frequency stability. This study provides valuable insights into the design of KNNbased ceramic capacitors with enhanced energy storage capabilities through doping strategies.
- [Korean]
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
- Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
- 792 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
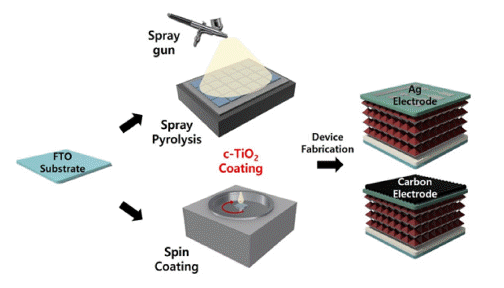
PDF This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend of Luminescent Nanomaterials
- Hyewon Jeong, Jae Sung Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):170-177. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.170
- 1,059 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
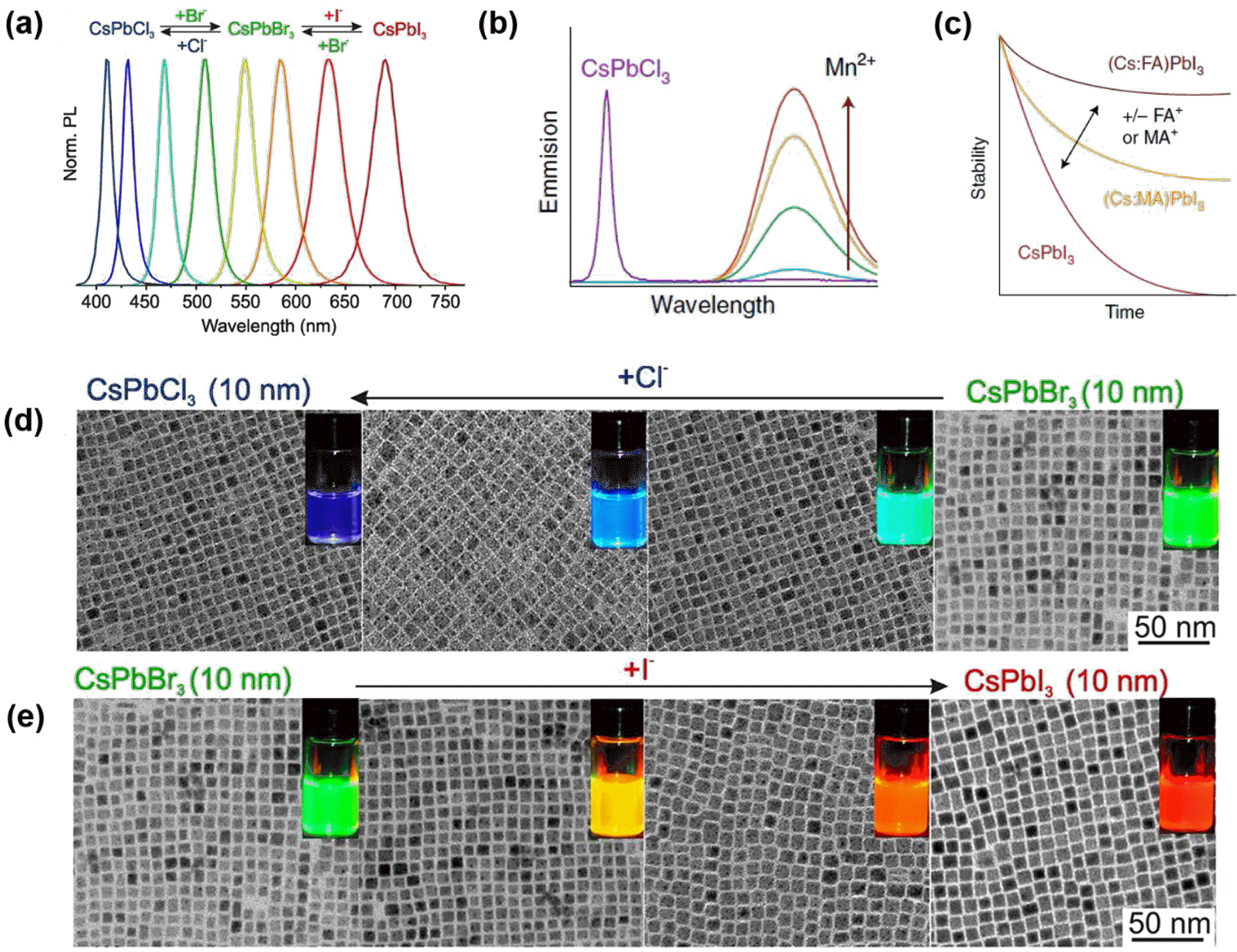
PDF Colloidally synthesized luminescent nanocrystals (NCs) have attracted tremendous attention due to their unique nanoscale optical and electronic properties. The emission properties of these NCs can be precisely tuned by controlling their size, shape, and composition as well as by introducing appropriate dopant impurities. Nowadays, these NCs are actively utilized for various applications such as optoelectronic devices including light emitting diodes (LEDs), lasers, and solar cells, and bio-medical applications such as imaging agents and bio-sensors. In this review, we classify luminescent nanomaterials into quantum dots (QDs), upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), and perovskite NCs and present their intrinsic emission mechanism. Furthermore, the recently emerging issues of efficiency, toxicity, and durability in these materials are discussed for better understanding of industry demands. As well, the future outlook will be offered for researchers to guide the direction of future research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
Jinhee Gong
The Journal of Korean Institute of Information Technology.2020; 18(4): 121. CrossRef
- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


