Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
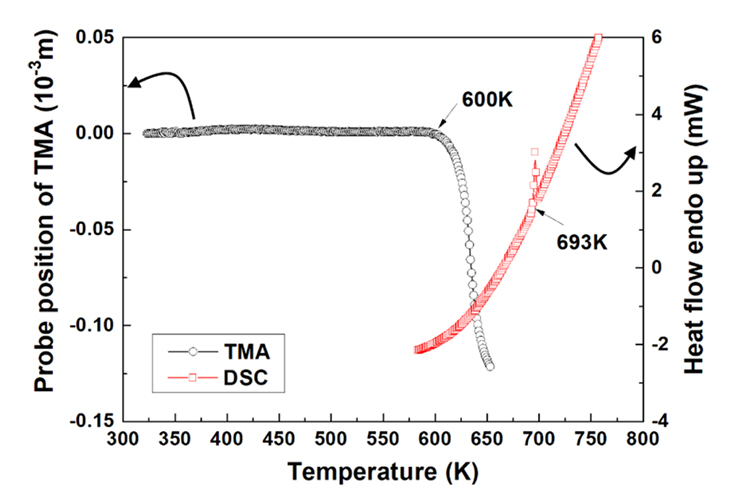
- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
- Young Soo Lim, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):50-56. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.50
- 1,045 View
- 20 Download
- [Korean]
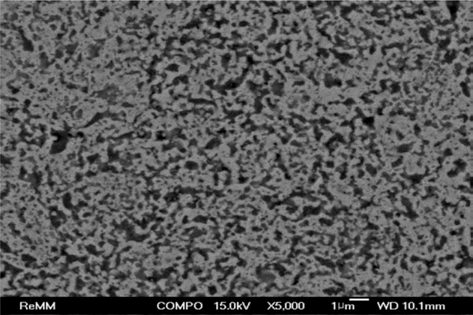
- Sintering of Fe-30 wt% TiC Composite Powders Fabricated from (Fe, TiH2, C) Powder Mixture
- Byunghoon Lee, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):356-361. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.356
- 851 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-30 wt% TiC composite powders are fabricated by in situ reaction synthesis after planetary ball milling of (Fe, TiH2, Carbon) powder mixture. Two sintering methods of a pressureless sintering and a spark-plasma sintering are tested to densify the Fe-30 wt% TiC composite powder compacts. Pressureless sintering is performed at 1100, 1200 and 1300°C for 1-3 hours in a tube furnace under flowing argon gas atmosphere. Spark-plasma sintering is carried out under the following condition: sintering temperature of 1050°C, soaking time of 10 min, sintering pressure of 50 MPa, heating rate of 50°C/min, and in a vacuum of 0.1 Pa. The curves of shrinkage and its derivative (shrinkage rate) are obtained from the data stored automatically during sintering process. The densification behaviors are investigated from the observation of fracture surface and cross-section of the sintered compacts. The pressureless-sintered powder compacts are not densified even after sintering at 1300°C for 3 h, which shows a relative denstiy of 66.9%. Spark-plasma sintering at 1050°C for 10 min exhibits nearly full densification of 99.6% relative density under the sintering pressure of 50 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Abrasive Wear Performance of Spherical Hierarchical Structured TiC/High-Manganese Steel Composites
Tao He, Shengnian Zhao, Dehong Lu, Yehua Jiang, Mojin Zhou
Materials.2024; 18(1): 130. CrossRef - Effect of TiC particle size on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiC reinforced stainless steel
Yeong-Hwan Lee, Sungmin Ko, Hyeonjae Park, Donghyun Lee, Sangmin Shin, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Yangdo Kim, Seungchan Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 480: 951. CrossRef - Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Heebong Kim, Hyuk-Tae Kwon, Sang-Kwan Lee, Sang-Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 155. CrossRef
- Abrasive Wear Performance of Spherical Hierarchical Structured TiC/High-Manganese Steel Composites
- [Korean]
- Pressureless Sintering and Spark-Plasma Sintering of Fe-TiC Composite Powders
- B. H. Lee, S. W. Bae, S. W. Bae, H. X. Khoa, J. S. Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):283-288. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.283

- 764 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Two sintering methods of a pressureless sintering and a spark-plasma sintering are tested to densify the Fe- TiC composite powders which are fabricated by high-energy ball-milling. A powder mixture of Fe and TiC is prepared in a planetary ball mill at a rotation speed of 500 rpm for 1h. Pressureless sintering is performed at 1100, 1200 and 1300°C for 1-3 hours in a tube furnace under flowing argon gas atmosphere. Spark-plasma sintering is carried out under the following condition: sintering temperature of 1050°C, soaking time of 10 min, sintering pressure of 50 MPa, heating rate of 50°C, and in a vacuum of 0.1 Pa. The curves of shrinkage and its derivative (shrinkage rate) are obtained from the data stored automatically during sintering process. The densification behaviors are investigated from the observation of fracture surface and cross-section of the sintered compacts. The pressureless-sintered powder compacts show incomplete densification with a relative denstiy of 86.1% after sintering at 1300°C for 3h. Spark-plasma sintering at 1050°C for 10 min exhibits nearly complete densification of 98.6% relative density under the sintering pressure of 50 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experimental investigation on thermal behaviour of copper-added P/M iron materials at different sintering temperatures
T. K. Kandavel, S. Dhasarathy
Australian Journal of Mechanical Engineering.2021; 19(1): 57. CrossRef
- Experimental investigation on thermal behaviour of copper-added P/M iron materials at different sintering temperatures
- [Korean]
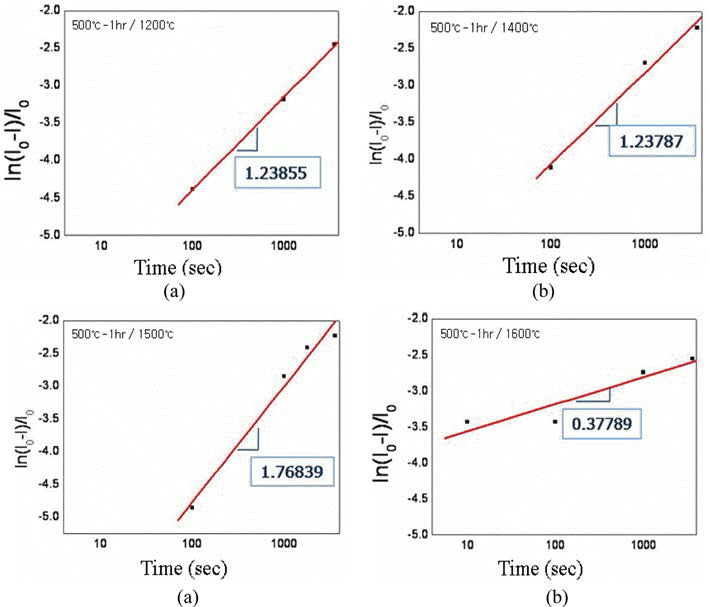
- Effect of Oxygen Content in the Tungsten Powder Fabricated by Electrical Explosion of Wire Method on the Behavior of Spark-Plasma Sintering
- Cheol-Hee Kim, Seong Lee, Byung-Kee Kim, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):447-453. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.447
- 623 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Effect of oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powder fabricated by electrical explosion of wire method on the behvior of spark plasma sintering was investigated. The initial oxygen content of 6.5 wt% of as-fabricated tungsten powder was reduced to 2.3 and 0.7 wt% for the powders which were reduction-treated at 400°C for 2 hour and at 500°C for 1h in hydrogen atmosphere, respectively. The reduction-treated tungsten powders were spark-plasma sintered at 1200-1600°C for 100-3600 sec. with applied pressure of 50 MPa under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Maximun sindered density of 97% relative density was obtained under the condition of 1600°C for 1h from the tungsten powder with 0.7 wt% oxygen. Sintering activation energy of 95.85 kJ/mol−1 was obtained, which is remarkably smaller than the reported ones of 380~460 kJ/mol−1 for pressureless sintering of micron-scale tungsten powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(5): 384. CrossRef
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
- [Korean]
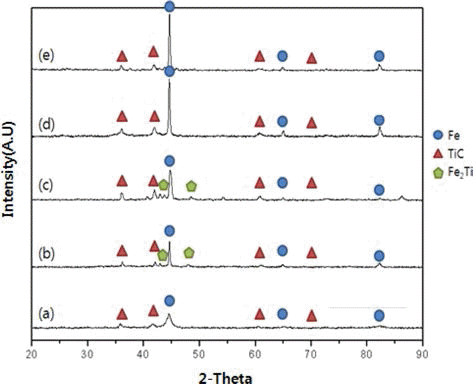
- Spark Plasma Sintering of Fe-TiC Composite Powders
- Yong-Heui Lee, Xuan-Khoa Hyunh, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):382-388. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.382
- 887 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-TiC composite powder was fabricated by high-energy milling of powder mixture of (Fe, TiC) and (FeO, TiH2, C) as starting materials, respectively. The latter one was heat-treated for reaction synthesis of TiC phase after milling. Both powders were spark-plasma sintered at various temperatures of 680-1070°C for 10 min. with sintering pressure of 70 MPa and the heating rate of 50°C/min. under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Density and hardness of the sintered compact was investigated. Fe-TiC composite fabricated from (FeO, TiH2, C) as starting materials showed better sintered properties. It seems to be resulted from ultra-fine TiC particle size and its uniform distribution in Fe-matrix compared to the simply mixed (Fe, TiC) powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative study of Ni-TaC composites via high-energy ball milling activation and spark plasma sintering: Reinforcement, densification, oxidation resistance, and mechanical property
Bum-Soon Park, Jeong-Han Lee, Jae-Cheol Park, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 984: 173900. CrossRef - Effect of TiC particle size on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiC reinforced stainless steel
Yeong-Hwan Lee, Sungmin Ko, Hyeonjae Park, Donghyun Lee, Sangmin Shin, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Yangdo Kim, Seungchan Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 480: 951. CrossRef - Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Heebong Kim, Hyuk-Tae Kwon, Sang-Kwan Lee, Sang-Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 155. CrossRef
- Comparative study of Ni-TaC composites via high-energy ball milling activation and spark plasma sintering: Reinforcement, densification, oxidation resistance, and mechanical property
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


