Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- A Study of Various SiO2 Coating Control on White TiO2 Pigment for Cosmetic Applications
- Minsol Park, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):207-212. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.207
- 1,102 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
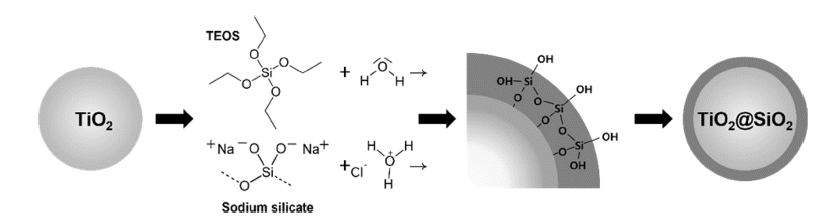
PDF Nanosized rutile titanium dioxide (TiO2) is used in inorganic pigments and cosmetics because of its high whiteness and duality. The high quality of the white pigments depends on their surface coating technique via the solgel process. SiO2 coatings are required to improve the dispersibility, UV-blocking, and whiteness of TiO2. Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is an important coating precursor owing to its ability to control various thicknesses and densities. In addition, we use Na2SiO3 (sodium silicate) as a precursor because of its low cost. Compared to TEOS, which controls the pH using a basic catalyst, Na2SiO3 controls the pH using an acid catalyst, giving a uniform coating. The coating thickness of TiO2 is controlled using a surface modifier, cetrimonium bromide, which is used in various applications. The shape and thickness of the nanosized coating layer on TiO2 are analyzed using transmission electron microscopy, and the SiO2 nanoparticle behavior in terms of the before-and-after size distribution is measured using a particle size analyzer. The color measurements of the SiO2 pigment are performed using UV-visible spectroscopy.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Uniform TiO2 Blocking Layers for Prevention of Electron Recombination in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
- Ju-won Bae, Bon-Ryul Koo, Tae-Kuen Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):1-6. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.1
- 756 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
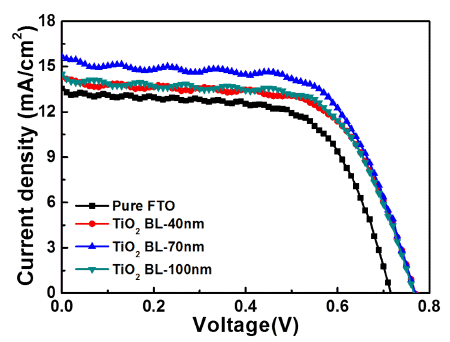
PDF Uniform TiO2 blocking layers (BLs) are fabricated using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis deposition (USPD) method. To improve the photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), the BL thickness is controlled by using USPD times of 0, 20, 60, and 100 min, creating TiO2 BLs of 0, 40, 70, and 100 nm, respectively, in average thickness on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass. Compared to the other samples, the DSSC containing the uniform TiO2 BL of 70 nm in thickness shows a superior power conversion efficiency of 7.58±0.20% because of the suppression of electron recombination by the effect of the optimized thickness. The performance improvement is mainly attributed to the increased open-circuit voltage (0.77±0.02 V) achieved by the increased Fermi energy levels of the working electrodes and the improved short-circuit current density (15.67±0.43 mA/cm2) by efficient electron transfer pathways. Therefore, optimized TiO2 BLs fabricated by USPD may allow performance improvements in DSSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Using Titanium Gel at Low Temperature
Seung Hwan Ji, Hyunsu Park, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Hye Won Yun, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(3): 183. CrossRef - Surface tailoring of zinc electrodes for energy storage devices with high-energy densities and long cycle life
Geon-Hyoung An, SeungNam Cha, Jung Inn Sohn
Applied Surface Science.2019; 467-468: 1157. CrossRef - Crystallinity Control Effects on Vanadium Oxide Films for Enhanced Electrochromic Performances
Kue-Ho Kim, Ju-Won Bae, Tae-Kuen Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(6): 385. CrossRef
- Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Using Titanium Gel at Low Temperature
- [English]
- Coating of Cobalt Over Tungsten Carbide Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):93-96. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.93
- 1,671 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cobalt coated tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder has been prepared through wet chemical reduction method. The cobalt sulfate solution was converted to the cobalt chloride then the cobalt hydroxide. The tungsten carbide powders were added in to the cobalt hydroxide, the cobalt hydroxide was reduced and coated over tungsten carbide powder using hypo-phosphorous acid. Both the cobalt and the tungsten carbide phase peaks were evident in the tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder by X-ray diffraction. The average particle size measured via scanning electron microscope, particle size analysis was around 380 nm and the thickness of coated cobalt was determined to be 30~40 nm by transmission electron microscopy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
Peng Tang, Shuwen Jiang, Jiawei Yan, Xianquan Li
Next Materials.2025; 6: 100496. CrossRef - Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef - Spark plasma sintering of WC–Co tool materials prepared with emphasis on WC core–Co shell structure development
Sungkyu Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 41. CrossRef
- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


