Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Current Status of Titanium Smelting Technology for Powder Metallurgy
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):164-172. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.164
- 773 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
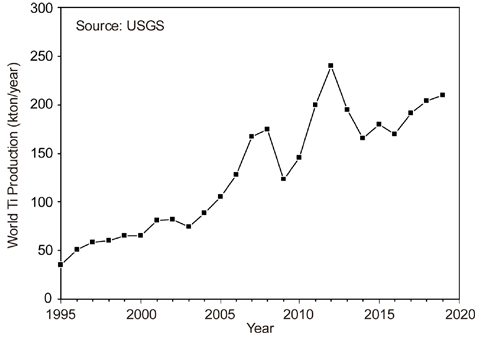
PDF Titanium is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is the fourth most abundant structural metal after aluminum, iron, and magnesium. It exhibits a higher specific strength than steel along with an excellent corrosion resistance, highlighting the promising potential of titanium as a structural metal. However, titanium is difficult to extract from its ore and is classified as a rare metal, despite its abundance. Therefore, the production of titanium is exceedingly low compared to that of common metals. Titanium is conventionally produced as a sponge by the Kroll process. For powder metallurgy (PM), hydrogenation-dehydrogenation (HDH) of the titanium sponge or gas atomization of the titanium bulk is required. Therefore, numerous studies have been conducted on smelting, which replaces the Kroll process and produces powder that can be used directly for PM. In this review, the Kroll process and new smelting technologies of titanium for PM, such as metallothermic, electrolytic, and hydrogen reduction of TiCl4 and TiO2 are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing corrosion resistance of Ti-based amorphous alloy powders via misch metal addition
Yeon Joo Lee, Hyokyung Sung, Jae Bok Seol, Kisub Cho, Hwi Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(3): 230. CrossRef
- Enhancing corrosion resistance of Ti-based amorphous alloy powders via misch metal addition
- [Korean]
- Study on Manufacture of High Purity TiCl4 and Synthesis of High Purity Ti Powders
- Jieun Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon, Chan Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):282-289. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.282
- 1,359 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
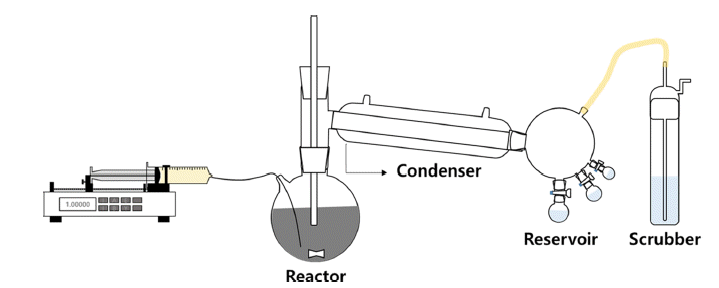
PDF Ti has received considerable attention for aerospace, vehicle, and semiconductor industry applications because of its acid-resistant nature, low density, and high mechanical strength. A common precursor used for preparing Ti materials is TiCl4. To prepare high-purity TiCl4, a process based on the removal of VOCl3 has been widely applied. However, VOCl3 removal by distillation and condensation is difficult because of the similar physical properties of TiCl4 and VOCl3. To circumvent this problem, in this study, we have developed a process for VOCl3 removal using Cu powder and mineral oil as purifying agents. The effects of reaction time and temperature, and ratio of purifying agents on the VOCl3 removal efficiency are investigated by chemical and structural measurements. Clear TiCl4 is obtained after the removal of VOCl3. Notably, complete removal of VOCl3 is achieved with 2.0 wt% of mineral oil. Moreover, the refined TiCl4 is used as a precursor for the synthesis of Ti powder. Ti powder is fabricated by a thermal reduction process at 1,100ºC using an H2-Ar gas mixture. The average size of the Ti powder particles is in the range of 1-3 μm.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


