Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
- 1,798 View
- 33 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
- [Korean]
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):415-423. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.415
- 837 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the increasing attention to environmental pollution caused by particulate matter globally, the automotive industry has also become increasingly interested in particulate matter, especially particulate matter generated by automobile brake systems. Here, we designed a coating composition and analyzed its mechanical properties to reduce particulate matter generated by brake systems during braking of vehicles. We designed a composition to check the mechanical properties change by adding Cr3C2 and YSZ to the WC-Ni-Cr composite composition. Based on the designed composition, coating samples were manufactured, and the coating properties were analyzed by Vickers hardness and ball-on-disk tests. As a result of the experiments, we found that the hardness and friction coefficient of the coating increased as the amount of Cr3C2 added decreased. Furthermore, we found that the hardness of the coating layer decreased when YSZ was added at 20vol%, but the friction coefficient was higher than the composition with Cr3C2 addition.
- [Korean]
- Development of Amorphous Iron Based Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
- Jungjoon Kim, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):483-490. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.483
- 614 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A new Fe-Cr-Mo-B-C amorphous alloy is designed, which offers high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance as well as high glass-forming ability and its gas-atomized amorphous powder is deposited on an ASTM A213-T91 steel substrate using the high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. The hybrid coating layer, consisting of nanocrystalline and amorphous phases, exhibits strong bonding features with the substrate, without revealing significant pore formation. By the coating process, it is possible to obtain a dense structure in which pores are hardly observed not only inside the coating layer but also at the interface between the coating layer and the substrate. The coating layer exhibits good adhesive strength as well as good wear resistance, making it suitable for coating layers for biomass applications.
- [Korean]
- Microstructural and Wear Properties of WC-based and Cr3C2-based Cermet Coating Materials Manufactured with High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process
- Yeon-Ji Kang, Gi-Su Ham, Hyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):408-414. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.408
- 740 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the microstructure and wear properties of cermet (ceramic + metal) coating materials manufactured using high velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. Three types of HVOF coating layers are formed by depositing WC-12Co, WC-20Cr-7Ni, and Cr3C2-20NiCr (wt.%) powders on S45C steel substrate. The porosities of the coating layers are 1 ± 0.5% for all three specimens. Microstructural analysis confirms the formation of second carbide phases of W2C, Co6W6C, and Cr7C3 owing to decarburizing of WC phases on WC-based coating layers. In the case of WC-12Co coating, which has a high ratio of W2C phase with high brittleness, the interface property between the carbide and the metal binder slightly decreases. In the Cr3C2-20CrNi coating layer, decarburizing almost does not occur, but fine cavities exist between the splats. The wear loss occurs in the descending order of Cr3C2-20NiCr, WC-12Co, and WC-20Cr-7Ni, where WC-20Cr-7Ni achieves the highest wear resistance property. It can be inferred that the ratio of the carbide and the binding properties between carbide–binder and binder–binder in a cermet coating material manufactured with HVOF as the primary factors determine the wear properties of the cermet coating material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 415. CrossRef - Effects of different HVOF thermal sprayed cermet coatings on tensile and fatigue properties of AISI 1045 steel
Gi-Su Ham, R. Kreethi, Hyung-jun Kim, Sang-hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2021; 15: 6647. CrossRef
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):36-42. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.36
- 719 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In order to expand the application of oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, a composite material is manufactured by adding mechanically alloyed ODS steel powder to conventional steel and investigated in terms of microstructure and wear properties. For comparison, a commercial automobile part material is also tested. Initial microstructural observations confirm that the composite material with added ODS steel contains i) a pearlitic Fe matrix area and ii) an area with Cr-based carbides and ODS steel particles in the form of a Fe-Fe3C structure. In the commercial material, various hard Co-, Fe-Mo-, and Cr-based particles are present in a pearlitic Fe matrix. Wear testing using the VSR engine simulation wear test confirms that the seatface widths of the composite material with added ODS steel and the commercial material are increased by 24% and 47%, respectively, with wear depths of 0.05 mm and 0.1 mm, respectively. The ODS steel-added composite material shows better wear resistance. Post-wear-testing surface and cross-sectional observations show that particles in the commercial material easily fall off, while the ODS steel-added material has an even, smooth wear surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
Ki-Ha Hong, Jae Bok Seol, Jeoung Han Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 69. CrossRef - Thermal Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fe-Co System Valve Seat Alloy by High Densification Process
In-Shup Ahn, Dong-Kyu Park, Kwang-Bok Ahn, Seoung-Mok Shin
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 112. CrossRef
- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing of Ni-Cr-B-Si + WC/12Co Composite Coating Layer Using Laser Cladding Process and its Mechanical Properties
- Gi-Su Ham, Chul-O Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):370-376. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.370

- 623 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study we manufacture a Ni-Cr-B-Si +WC/12Co composite coating layer on a Cu base material using a laser cladding (LC) process, and investigate the microstructural and mechanical properties of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers (reference material). The initial powder used for the LC coating layer is a powder feedstock with an average particle size of 125 μm. To identify the microstructural and mechanical properties, OM, SEM, XRD, room and high temperature hardness, and wear tests are implemented. Microstructural observation of the initial powder and LC coating layer confirm the layer is composed mainly of γ-Ni phases and WC and Cr23C6 carbides. The measured hardness of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers are 653 and 154 Hv, respectively. The hardness measurement from room up to high temperatures of 700°C result in a hardness decrease as the temperature increases, but the hardness of the LC coating layer is higher for all temperature conditions. Room temperature wear results show that the wear loss of the LC coating layer is 1/12 of the wear level of the Ni electroplating layer. The measured bond strength is also greater in the LC coating than the Ni electroplating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2018; 56(6): 423. CrossRef - Microstructural and Wear Properties of WC-based and Cr3C2-based Cermet Coating Materials Manufactured with High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process
Yeon-Ji Kang, Gi-Su Ham, Hyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 408. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
- [Korean]
- Effect of Molding Pressure on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance Property of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
- Ji-Won Kim, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):203-207. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.203
- 759 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
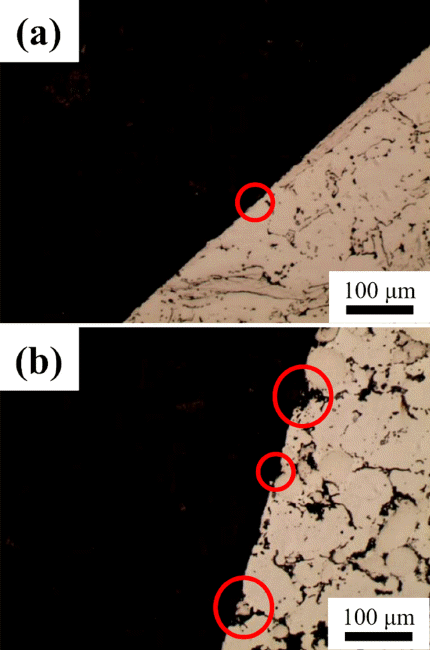
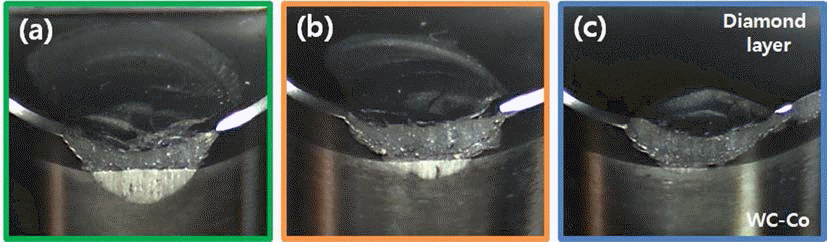
PDF This study investigated the microstructure and wear resistance property of HPHT (high pressure high temperature) sintered PDC (polycrystalline diamond compact) in accordance with initial molding pressure. After quantifying an identical amount of diamond powder, the powder was inserted in top of WC-Co sintered material, and molded under four different pressure conditions (50, 100, 150, 200 kgf/cm2). The obtained diamond compact underwent sintering in high pressure, high temperature conditions. In the case of the 50 kgf/cm2 initial molding pressure condition, cracks were formed on the surface of PDC. On the other hand, PDCs obtained from 100~200 kgf/cm2 initial molding pressure conditions showed a meticulous structure. As molding pressure increased, low Co composition within PDC was detected. A wear resistance test was performed on the PDC, and the 200 kgf/cm2 condition PDC showed the highest wear resistance property.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Co Leaching on the Vertical Turning Lathe Wear Properties of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Manufactured by High Temperature and High Pressure Sintering Process
Min-Seok Baek, Ji-Won Kim, Bae-Gun Park, Hee-Sub Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2020; 58(7): 480. CrossRef - Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Effect of Co Leaching on the Vertical Turning Lathe Wear Properties of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Manufactured by High Temperature and High Pressure Sintering Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


