Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
- Youngmoo Kim, Sung Ho Yang, Seong Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):373-380. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.373
- 1,019 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
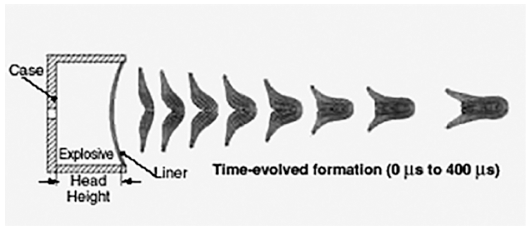
PDF The purpose of this study is to investigate the densification behavior and the corresponding microstructural evolution of tantalum and tantalum-tungsten alloy powders for explosively formed liners. The inherent inhomogeneous microstructures of tantalum manufactured by an ingot metallurgy might degrade the capability of the warhead. Therefore, to overcome such drawbacks, powder metallurgy was incorporated into the near-net shape process in this study. Spark plasma-sintered tantalum and its alloys with finer particle sizes exhibited higher densities and lower grain sizes. However, they were contaminated from the graphite mold during sintering. Higher compaction pressures in die and isostatic compaction techniques also enhanced the sinterability of the tantalum powders; however, a full densification could not be achieved. On the other hand, the powders exhibited full densification after being subjected to hot isostatic pressing over two times. Consequently, it was found that the hot isostatic-pressed tantalum might exhibit a lower grain size and a higher density as compared to those obtained in previous studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the phase evolution and elemental distribution in MoWTaNbVTix manufactured via powder metallurgical approach
Surya T. Bijjala, Ryan Wilkerson, Chad Beamer, Pankaj Kumar
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 135(11-12): 5925. CrossRef - Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef
- Understanding the phase evolution and elemental distribution in MoWTaNbVTix manufactured via powder metallurgical approach
- [Korean]
- Effects of Powder Shape and Densification Mechanism on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Components
- Youngmoo Kim, Young-Sam Kwon, Young-Beom Song, Sung Ho Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):311-318. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.311
- 621 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The objective of this study is to investigate the influence of powder shape and densification mechanism on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V components. BE powders are uniaxially and isostatically pressed, and PA ones are injection molded because of their high strengths. The isostatically compacted samples exhibit a density of 80%, which is higher than those of other samples, because hydrostatic compression can lead to higher strain hardening. Owing to the higher green density, the density of BE-CS (97%) is found to be as high as that of other samples (BE-DS (95%) and P-S (94%)). Furthermore, we have found that BE powders can be consolidated by sintering densification and chemical homogenization, whereas PA ones can be consolidated only by simple densification. After sintering, BE-CS and P-S are hot isostatically pressed and BE-DS is hot forged to remove residual pores in the sintered samples. Apparent microstructural evolution is not observed in BE-CSH and P-SH. Moreover, BE-DSF exhibits significantly fine grains and high density of low-angle grain boundaries. Thus, these microstructures provide Ti-6Al-4V components with enhanced mechanical properties (tensile strength of 1179 MPa).
- [English]
- Solid-state sintering mechanism of blended elemental Ti-6Al-4V powders
- Youngmoo Kim, Young-Beom Song, Sung Ho Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):109-119. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.2.109
- 871 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
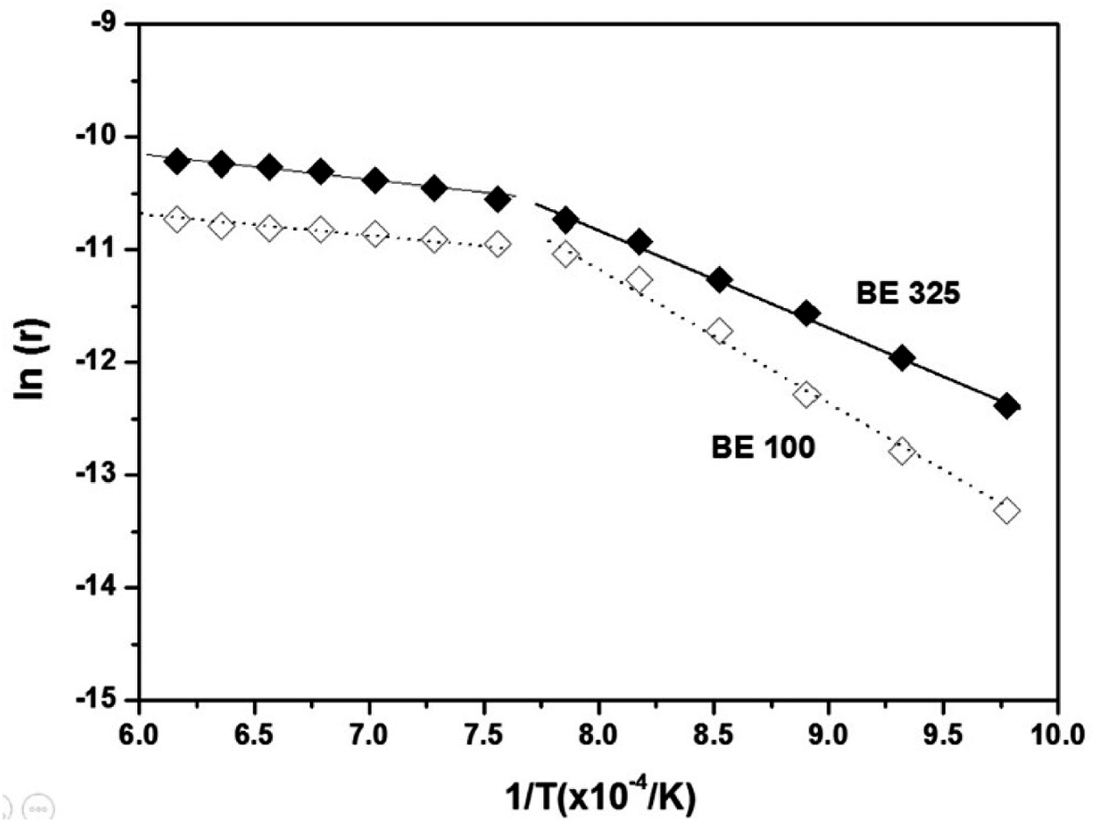
PDF The objective of this study is to reveal the sintering mechanism of mixed Ti-6Al-4V powders considering the densification and the homogenization between Ti and Al/V particles. It is found that the addition of master alloy particles into Ti enhances densification by the migration of Al into the Ti matrix prior to the self-diffusion of Ti. However, as Ti particles become coarser, sintering of the powders appears to be retarded due to slower inter-diffusion of the particles due to the reduced surface energies of Ti. Such phenomena are confirmed by a series of dilatometry tests and microstructural analyses in respect to the sintering temperature. Furthermore, the results are also consistent with the predicted activation energies for sintering. The energies are found to have decreased from 299.35 to 135.48 kJ·mol-1 by adding the Al/V particles because the activation energy for the diffusion of Al in α-Ti (77 kJ·mol-1) is much lower than that of the self-diffusion of α-Ti. The coarser Ti powders increase the energies from 135.48 to 181.16 kJ·mol-1 because the specific surface areas of Ti decrease.
- [English]
- Simulation and Experiment of Injection Molding Process for Superalloy Feedstock
- Im Doo Jung, Youngmoo Kim, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.1
- 1,237 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
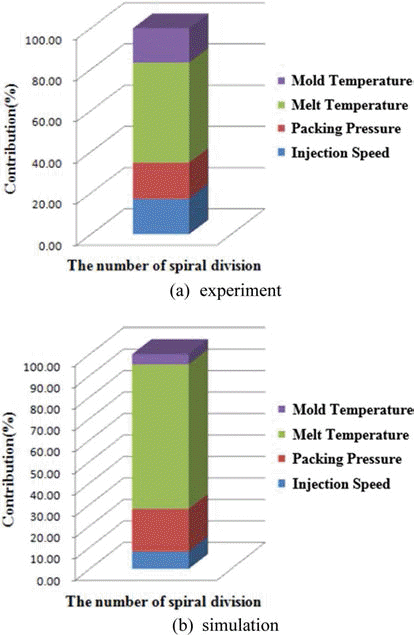
PDF Powder injection molding is an important manufacturing technology to mass produce superalloy components with complex shape. Injection molding step is particularly important for realizing a desired shape, which requires much time and efforts finding the optimum process condition. Therefore computer aided engineering can be very useful to find proper injection molding conditions. In this study, we have conducted a finite element method based simulation for the spiral mold test of superalloy feedstock and compared the results with experimental ones. Sensitivity analysis with both of simulation and experiment reveals that the melt temperature of superalloy feedstock is the most important factor for the full filling of mold cavity. The FEM based simulation matches well the experimental results. This study contributes to the optimization of superalloy powder injection molding process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef - Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 364. CrossRef
- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
- [Korean]
- Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Powder Metallurgy Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Youngmoo Kim, Young-Beom Song, Sung Ho Lee, Young-Sam Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):277-285. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.277
- 948 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effects of processing parameters on the flow behavior and microstructures were investigated in hot compression of powder metallurgy (P/M) Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The alloy was fabricated by a blended elemental (B/E) approach and it exhibited lamellar α+β microstructure. The hot compression tests were performed in the range of temperature 800-1000°C with 50°C intervals, strain rate 10−4-10 s−1, and strain up to 0.5. At 800-950°C, continuous flow softening after a peak stress was observed with strain rates lower than 0.1 s−1. At strain rates higher than 1 s−1, rapid drop in flow stress with strain hardening or broad oscillations was recorded. The processing map of P/M Ti-6Al-4V was designed based on the compression test and revealed the peak efficiency at 850°C and 0.001 s−1. As the processing temperature increased, the volume fraction of β phase was increased. In addition, below 950°C, the globularization of phase at the slower strain rate and kinking microstructures were found. Based on these data, the preferred working condition of the alloy may be in the range of 850-950°C and strain rate of 0.001-0.01 s−1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure control and dynamic recrystallization behavior analysis in hot forging of metastable beta Ti-5Mo-4Fe alloy
In-Kyeong Jin, Jae-Gwan Lee, Yong-Jae Lee, Dong-Geun Lee
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1010: 178125. CrossRef - High Temperature Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of Homogenized AA 2026 Alloy
HyeonWoo Kang, SooBin Kim, ByoungLok Jang, HeeKook Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(5): 338. CrossRef - Effect of Fe Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Al-Mo-V-Cr-Fe Alloys
K.C. Bae, J.J. Oak, Y.H. Kim, Y.H. Park
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1105. CrossRef
- Microstructure control and dynamic recrystallization behavior analysis in hot forging of metastable beta Ti-5Mo-4Fe alloy
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Behaviors of M-type Barium Hexaferrite Nano Powders
- Im Doo Jung, Youngmoo Kim, Yang-Ki Hong, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):256-259. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.256

- 1,040 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A magnetic powder, M-type barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19), was consolidated with the spark plasma sintering process. Three different holding temperatures, 850°C, 875°C and 900°C were applied to the spark plasma sintering process with the same holding times, heating rates and compaction pressure of 30 MPa. The relative density was measured simultaneously with spark plasma sintering and the convergent relative density after cooling was found to be proportional to the holding temperature. The full relative density was obtained at 900°C and the total sintering time was only 33.3 min, which was much less than the conventional furnace sintering method. The higher holding temperature also led to the higher saturation magnetic moment (σs) and the higher coercivity (Hc) in the vibrating sample magnetometer measurement. The saturation magnetic moment (σs) and the coercivity (Hc) obtained at 900°C were 56.3 emu/g and 541.5 Oe for each.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of microwave sintering on density, microstructural and magnetic properties of pure strontium hexaferrite at low temperatures and heating rate
Wail M. Matran, Mazli Mustapha, Mohd Faizairi Nor, Faizal Mustapha, Fahd Saeed Alakbari, Gamal Al-shawesh, Mohammed Bawahab
Heliyon.2024; 10(20): e38766. CrossRef - A study of crystalline – texture and anisotropic properties of hexagonal BaFe12O19 sintered by in-situ magnetic-anisotropy spark plasma sintering (MASPS)
Haetham G. Mohammed, Thar Mohammed Badri Albarody, Husam Kareem Mohsin Al-Jothery, Mazli Mustapha, N.M Sultan
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials.2022; 553: 169268. CrossRef - Process Optimization of In Situ Magnetic-Anisotropy Spark Plasma Sintering of M-Type-Based Barium Hexaferrite BaFe12O19
Haetham Mohammed, Thar Albarody, Susilawati Susilawati, Scott Gohery, Aris Doyan, Saiful Prayogi, Muhammad Bilad, Reza Alebrahim, Anwar Saeed
Materials.2021; 14(10): 2650. CrossRef - Self-Consolidation and Surface Modification of Mechanical Alloyed Ti-25.0 at.% Al Powder Mixture by Using an Electro-Discharge Technique
S.Y. Chang, H.S. Jang, Y.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, J.Y. Kim, Y.K. Lee, W.H. Lee
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1293. CrossRef - Plastic deformation and microstructural evolution during the shock consolidation of ultrafine copper powders
Dong-Hyun Ahn, Wooyeol Kim, Minju Kang, Lee Ju Park, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2015; 625: 230. CrossRef
- Effect of microwave sintering on density, microstructural and magnetic properties of pure strontium hexaferrite at low temperatures and heating rate
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Hot Isostatically Pressed Ni-Based Superalloy IN 713C
- Youngmoo Kim, Eun-Pyo Kim, Seong-Taek Chunga, Seong Lee, Joon-Woong Noh, Sung Ho Lee, Young-Sam Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(4):264-268.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.4.264

- 791 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nickel-based superalloy IN 713C powders have been consolidated by hot isostatic pressing (HIPing). The microstructure and mechanical properties of the superalloys were investigated at the HIPing temperature ranging from 1030°C to 1230°C. When the IN 713C powder was heated above gammaprime solvus temperature (about 1180°C), the microstructure was composed of the austenitic FCC matrix phase gamma plus a variety of secondary phases, such as gammaprime precipitates in gamma matrix and MC carbides at grain boundaries. The yield and tensile strengths of HIPed specimens at room temperature were decreased while the elongation and reduction of area were increased as the processing temperature increased. At 700°C, the strength was similar regardless of HIPing temperature; however, the ductility was drastically increased with increasing the temperature. It is considered that these properties compared to those of cast products are originated from the homogeneity of microstructure obtained from a PM process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
W.J. Kim, H.-H. Nguyen, H.Y. Kim, M.-T. Nguyen, H.S. Park, J.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1215. CrossRef
- Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


