Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
- Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):395-401. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.395
- 2,071 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
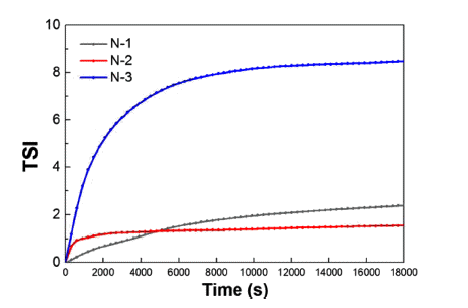
PDF The improvement of dispersion stability for the primary polishing slurry in a CMP process is achieved to prevent defects produced by agglomeration of the slurry. The dispersion properties are analyzed according to the physical characteristics of each silica sol sample. Further, the difference in the dispersion stability is confirmed as the surfactant content. The dispersibility results measured by Zeta potential suggest that the dispersion properties depend on the content and size of the abrasive in the primary polishing slurry. Moreover, the optimum ratio for high dispersion stability is confirmed as the addition content of the surfactant. Based on the aforementioned results, the long-term stability of each slurry is analyzed. Turbiscan analysis demonstrates that the agglomeration occurs depending on the increasing amount of surfactant. As a result, we demonstrate that the increased particle size and the decreased content of silica improve the dispersion stability and long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
Seung-Hwan Oh, Hyeonmin Yim, Donghee Lee, Dong Hyeok Seo, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(9): 396. CrossRef
- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
- [English]
- Coating of Cobalt Over Tungsten Carbide Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):93-96. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.93
- 1,534 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cobalt coated tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder has been prepared through wet chemical reduction method. The cobalt sulfate solution was converted to the cobalt chloride then the cobalt hydroxide. The tungsten carbide powders were added in to the cobalt hydroxide, the cobalt hydroxide was reduced and coated over tungsten carbide powder using hypo-phosphorous acid. Both the cobalt and the tungsten carbide phase peaks were evident in the tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder by X-ray diffraction. The average particle size measured via scanning electron microscope, particle size analysis was around 380 nm and the thickness of coated cobalt was determined to be 30~40 nm by transmission electron microscopy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
Peng Tang, Shuwen Jiang, Jiawei Yan, Xianquan Li
Next Materials.2025; 6: 100496. CrossRef - Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef - Spark plasma sintering of WC–Co tool materials prepared with emphasis on WC core–Co shell structure development
Sungkyu Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 41. CrossRef
- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


