Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024

- 881 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
- [English]
- The Effect of SnO2 Addition on Sintering Behaviors in a Titanium Oxide-Copper Oxide System
- Ju-Won Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):357-362. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.357
- 589 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
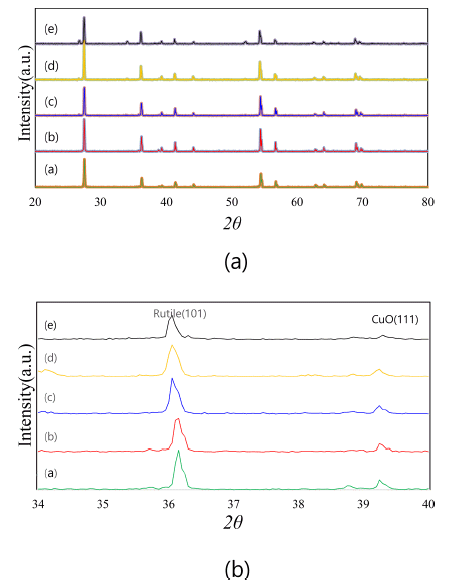
PDF The low-temperature sinterability of TiO2-CuO systems was investigated using a solid solution of SnO2. Sample powders were prepared through conventional ball milling of mixed raw powders. With the SnO2 content, the compositions of the samples were Ti1-xSnxO2-CuO(2 wt.%) in the range of x ≤ 0.08. Compared with the samples without SnO2 addition, the densification was enhanced when the samples were sintered at 900°C. The dominant mass transport mechanism seemed to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 900°C, where active grain-boundary diffusion was responsible for the improved densification. The rapid grain growth featured by activated sintering was also obstructed with the addition of SnO2. This suggested that both CuO as an activator and SnO2 dopant synergistically reduced the sintering temperature of TiO2.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Property Evaluation of Cu-Mn Compacts for Sputtering Target Application by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Method
- Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jae-Won Lim, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):1-7. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.1
- 832 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
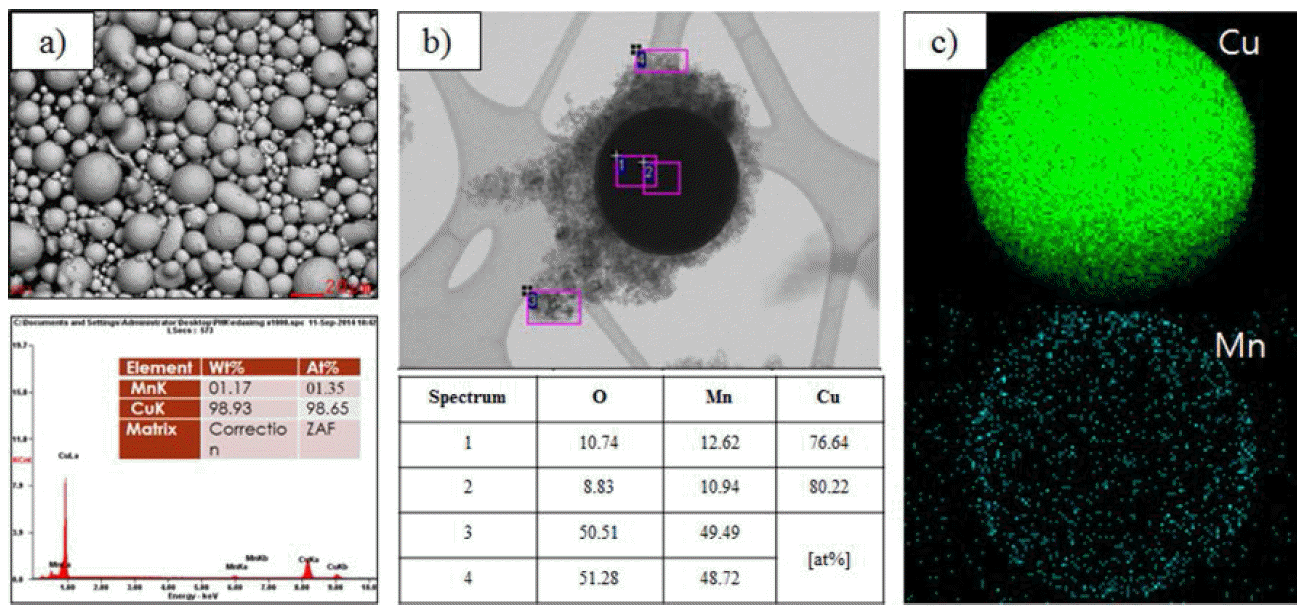
PDF Cu-Mn compacts are fabricated by the pulsed current activated sintering method (PCAS) for sputtering target application. For fabricating the compacts, optimized sintering conditions such as the temperature, pulse ratio, pressure, and heating rate are controlled during the sintering process. The final sintering temperature and heating rate required to fabricate the target materials having high density are 700°C and 80°C/min, respectively. The heating directly progresses up to 700°C with a 3 min holding time. The sputtering target materials having high relative density of 100% are fabricated by employing a uniaxial pressure of 60 MPa and a sintering temperature of 700°C without any significant change in the grain size. Also, the shrinkage displacement of the Cu-Mn target materials considerably increases with an increase in the pressure at sintering temperatures up to 700°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
TOP
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


