Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bandgap Tuning and Quenching Effects of In(Zn)P@ZnSe@ZnS Quantum Dots
- Sang Yeon Lee, Su Hyun Park, Gyungsu Byun, Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):226-235. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00003

- 91 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - InP quantum dot (QDs) have attracted researchers’ interest due to their applicability in quantum dot light-emitting displays (QLED) or biomarkers for detecting cancers or viruses. The surface or interface control of InP QD core/shell has substantially increased quantum efficiency, with a quantum yield of 100% reached by introducing HF to inhibit oxide generation. In this study, we focused on the control of bandgap energy of quantum dots by changing the Zn/(In+Zn) ratio in the In(Zn)P core. Zinc incorporation can change the photoluminescent light colors of green, yellow, orange, and red. Diluting a solution of as-synthesized QDs by more than 100 times did not show any quenching effects by the Förster resonance energy transfer phenomenon between neighboring QDs.
- Fabrication of TiO2 Coated Si Nano Particle using Silicon Sawing Sludge
- Dong Hyeok Seo, Hyeon Min Yim, Ho Yoon Na, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):423-428. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.423

- 44 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Here, we report the development of a new and low-cost core-shell structure for lithium-ion battery anodes using silicon waste sludge and the Ti-ion complex. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the raw waste silicon sludge powder to be pure silicon without other metal impurities and the particle size distribution is measured to be from 200 nm to 3 μm by dynamic light scattering (DLS). As a result of pulverization by a planetary mill, the size of the single crystal according to the Scherrer formula is calculated to be 12.1 nm, but the average particle size of the agglomerate is measured to be 123.6 nm. A Si/TiO2 core-shell structure is formed using simple Ti complex ions, and the ratio of TiO2 peaks increased with an increase in the amount of Ti ions. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations revealed that TiO2 coating on Si nanoparticles results in a Si-TiO2 core-shell structure. This result is expected to improve the stability and cycle of lithium-ion batteries as anodes.
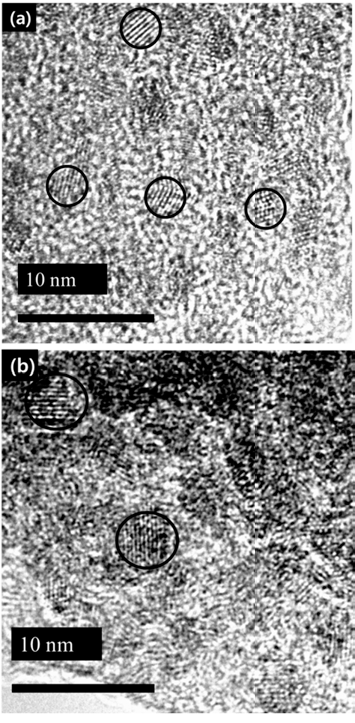
- Luminescence Properties of InP/ZnS Quantum Dots depending on InP Core synthesis Temperature
- Han Wook Seo, Da-Woon Jeong, Min Young Kim, Seoung Kyun Hyun, Ji Sun On, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):321-325. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.321
- 272 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we investigate the optical properties of InP/ZnS core/shell quantum dots (QDs) by controlling the synthesis temperature of InP. The size of InP determined by the empirical formula tends to increase with temperature: the size of InP synthesized at 140oC and 220oC is 2.46 nm and 4.52 nm, respectively. However, the photoluminescence (PL) spectrum of InP is not observed because of the formation of defects on the InP surface. The growth of InP is observed during the deposition of the shell (ZnS) on the synthesized InP, which is ended up with green-red PL spectrum. We can adjust the PL spectrum and absorption spectrum of InP/ZnS by simply adjusting the core temperature. Thus, we conclude that there exists an optimum shell thickness for the QDs according to the size.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 489. CrossRef
- Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
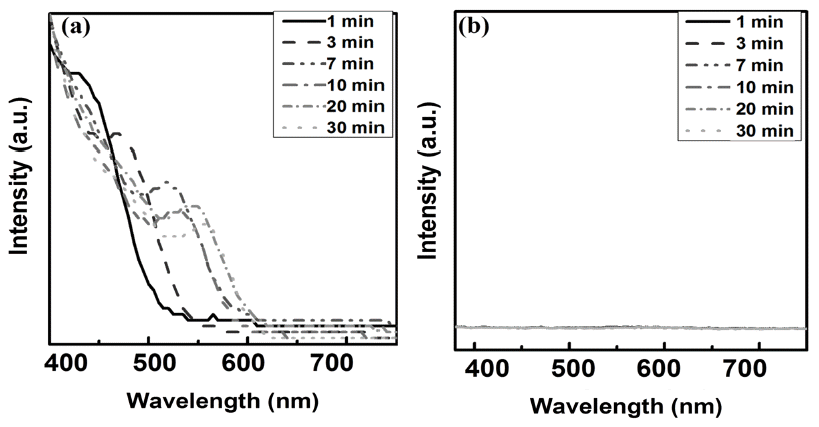
- Growth mechanism of InP and InP/ZnS synthesis using colloidal synthesis
- Han wook Seo, Da-woon Jeong, Bin Lee, Seoung kyun Hyun, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):6-10. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.6
- 294 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the main growth mechanism of InP during InP/ZnS reaction of quantum dots (QDs). The size of the InP core, considering a synthesis time of 1-30 min, increased from the initial 2.56 nm to 3.97 nm. As a result of applying the proposed particle growth model, the migration mechanism, with time index 7, was found to be the main reaction. In addition, after the removal of unreacted In and P precursors from bath, further InP growth (of up to 4.19 nm (5%)), was observed when ZnS was added. The full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the synthesized InP/ZnS quantum dots was found to be relatively uniform, measuring about 59 nm. However, kinetic growth mechanism provides limited information for InP / ZnS core shell QDs, because the surface state of InP changes with reaction time. Further study is necessary, in order to clearly determine the kinetic growth mechanism of InP / ZnS core shell QDs.
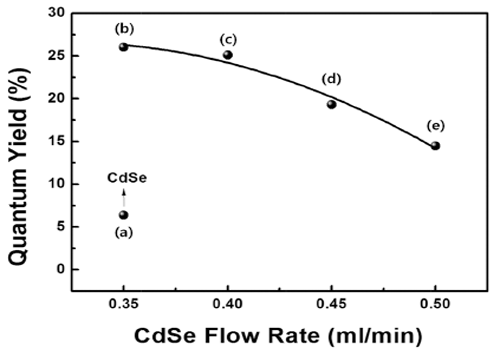
- Optical Characteristics of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot with Precursor Flow Rate Synthesized by using Microreactor
- Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Won Ju, Han Wook Seo, Yong-Ho Choa, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):91-94. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.91
- 287 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-quality colloidal CdSe/ZnS (core/shell) is synthesized using a continuous microreactor. The particle size of the synthesized quantum dots (QDs) is a function of the precursor flow rate; as the precursor flow rate increases, the size of the QDs decreases and the band gap energy increases. The photoluminescence properties are found to depend strongly on the flow rate of the CdSe precursor owing to the change in the core size. In addition, a gradual shift in the maximum luminescent wave (λmax) to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) is found owing to the decrease in the QD size in accordance with the quantum confinement effect. The ZnS shell decreases the surface defect concentration of CdSe. It also lowers the thermal energy dissipation by increasing the concentration of recombination. Thus, a relatively high emission and quantum yield occur because of an increase in the optical energy emitted at equal concentration. In addition, the maximum quantum yield is derived for process conditions of 0.35 ml/min and is related to the optimum thickness of the shell material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantum materials made in microfluidics - critical review and perspective
M. Wojnicki, V. Hessel
Chemical Engineering Journal.2022; 438: 135616. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef
- Quantum materials made in microfluidics - critical review and perspective
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


