Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- A Study on Morphology Control of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) Nanofibers according to the Composition and Crystallinity of Oxide Nanofibers Synthesized by Electrospinning
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Sung-Tag Oh, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):259-266. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.259
- 651 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
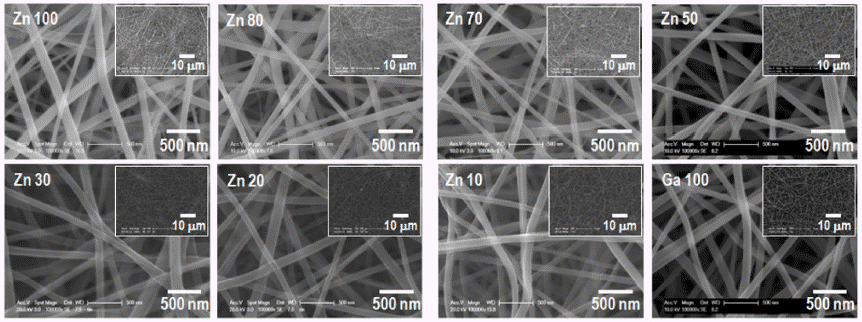
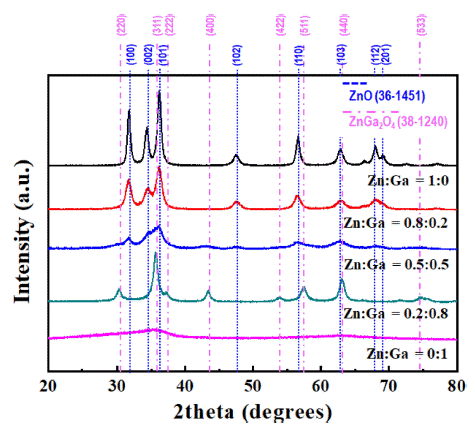
PDF The (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) solid solution is attracting extensive attention for photocatalytic water splitting and wastewater treatment owing to its narrow and controllable band gap. To optimize the photocatalytic performance of the solid solution, the key points are to decrease its band gap and recombination rate. In this study, (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) nanofibers with various Zn fractions are prepared by electrospinning followed by calcination and nitridation. The effect of the composition and crystallinity of electrospun oxide nanofibers on the morphology and optical properties of the obtained solid-solution nanofibers are systematically investigated. The results show that the final shape of the (Ga1-xZnx) (N1-xOx) material is greatly affected by the crystallinity of the oxide nanofibers before nitridation. The photocatalytic properties of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) with different Ga:Zn atomic ratios are investigated by studying the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light irradiation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
Haein Shin, Jongwon Bae, Minsu Kang, Kun-Jae Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 502. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x Nanoparticles Using an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process and Subsequent Chemical Transformation
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Myungjun Ji, Yomin Choi, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):143-149. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.143
- 784 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x solid solution nanoparticles with a high zinc content are prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and subsequent nitridation. The structure and morphology of the samples are investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The characterization results show a phase transition from the Zn and Ga-based oxides (ZnO or ZnGa2O4) to a (GaN)1-x (ZnO)x solid solution under an NH3 atmosphere. The effect of the precursor solution concentration and nitridation temperature on the final products are systematically investigated to obtain (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x nanoparticles with a high Zn concentration. It is confirmed that the powder synthesized from the solution in which the ratio of Zn and Ga was set to 0.8:0.2, as the initial precursor composition was composed of about 0.8-mole fraction of Zn, similar to the initially set one, through nitriding treatment at 700°C. Besides, the synthesized nanoparticles exhibited the typical XRD pattern of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x, and a strong absorption of visible light with a bandgap energy of approximately 2.78 eV, confirming their potential use as a hydrogen production photocatalyst.
- [Korean]
- Research trend in Fabrication of Metastable-phase Iron Nitrides for Hard Magnetic Applications
- Kyung Min Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):146-155. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.146

- 1,710 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets and are integral to the high tech industry, particularly in clean energies, such as electric vehicle motors and wind turbine generators. However, the cost of rare earth materials and the imbalance in supply and demand still remain big problems to solve for permanent magnet related industries. Thus, a magnet with abundant elements and moderate magnetic performance is required to replace rare-earth magnets. Recently, a”-Fe16N2 has attracted considerable attention as a promising candidate for next-generation non-rare-earth permanent magnets due to its gigantic magnetization (3.23 T). Also, metastable a”-Fe16N2 exhibits high tetragonality (c/a = 1.1) by interstitial introduction of N atoms, leading to a high magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (K1 = 1.0MJ/m3). In addition, Fe has a large amount of reserves on the Earth compared to other magnetic materials, leading to low cost of raw materials and manufacturing for industrial production. In this paper, we review the synthetic methods of metastable a”-Fe16N2 with film, powder and bulk form and discuss the approaches to enhance magnetocrystalline anisotropy of a”-Fe16N2. Future research prospects are also offered with patent trends observed thus far.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
So-Young Ko, Shin-Il Go, Kyoung-Jun Jang, Sang-Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(10): 457. CrossRef
- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of GaN Powder Using an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process and Subsequent Nitridation Treatment
- Myeong-Jun Ji, Jae-Hyun Yoo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):482-486. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.482

- 755 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Despite numerous advances in the preparation and use of GaN, and many leading-edge applications in lighting technologies, the preparation of high-quality GaN powder remains a challenge. Ammonolytic preparations of polycrystalline GaN have been studied using various precursors, but all were time-consuming and required high temperatures. In this study, an efficient and low-temperature method to synthesize high-purity hexagonal GaN powder is developed using sub-micron Ga2O3 powder as a starting material. The sub-micron Ga2O3 powder was prepared by an ultrasonic spray pyrolysis process. The GaN powder is synthesized from the sub-micron Ga2O3 powder through a nitridation treatment in an NH3 flow at 800°C. The characteristics of the synthesized powder are systematically examined by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and UV-vis spectrophotometer.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


