Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024

- 980 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
- [English]
- The Effect of SnO2 Addition on Sintering Behaviors in a Titanium Oxide-Copper Oxide System
- Ju-Won Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):357-362. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.357
- 655 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
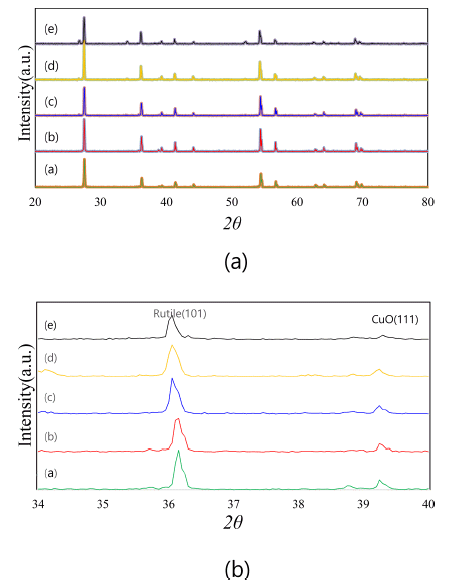
PDF The low-temperature sinterability of TiO2-CuO systems was investigated using a solid solution of SnO2. Sample powders were prepared through conventional ball milling of mixed raw powders. With the SnO2 content, the compositions of the samples were Ti1-xSnxO2-CuO(2 wt.%) in the range of x ≤ 0.08. Compared with the samples without SnO2 addition, the densification was enhanced when the samples were sintered at 900°C. The dominant mass transport mechanism seemed to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 900°C, where active grain-boundary diffusion was responsible for the improved densification. The rapid grain growth featured by activated sintering was also obstructed with the addition of SnO2. This suggested that both CuO as an activator and SnO2 dopant synergistically reduced the sintering temperature of TiO2.
- [Korean]
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):494-500. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.494
- 1,141 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
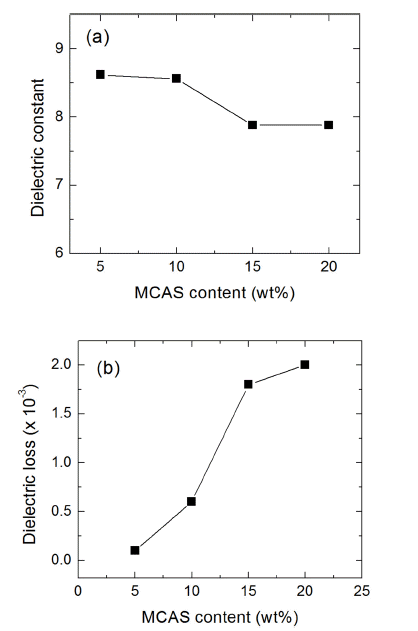
PDF In this study, the effect of the content of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (MCAS) glass additives on the properties of AlN ceramics is investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering for AlN compacts with MCAS contents varying between 5 and 20 wt% are carried out at temperatures ranging up to 1600°C. The results showed that the shrinkage of the AlN specimens increases with increasing MCAS content, and that full densification can be obtained irrespective of the MCAS content. Moreover, properties of the AlN-MCAS specimens such as microhardness, thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss are analyzed. Microhardness and thermal conductivity decrease with increasing MCAS content. An acceptable candidate for AlN application is obtained: an AlN-MCAS composite with a thermal conductivity over 70 W/m·K and a dielectric loss tangent (tan δ) below 0.6 × 10−3, with up to 10 wt% MCAS content.
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Conductivity of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics with MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 Nano-glass Additive
- Su-Hyun Baik, Kyung Min Kim, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):426-434. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.426
- 879 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
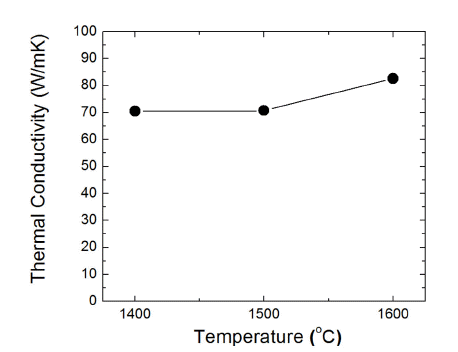
PDF In this study, MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 (MCAS) nanocomposite glass powder having a mean particle size of 50 nm and a specific surface area of 40 m2/g is used as a sintering additive for AlN ceramics. Densification behaviors and thermal properties of AlN with 5 wt% MCAS nano-glass additive are investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering of AlN-5wt% MCAS compact demonstrates that the shrinkage of the AlN specimen increases significantly above 1,300°C via liquid phase sintering of MCAS additive, and complete densification could be achieved after sintering at 1,600°C, which is a reduction in sintering temperature by 200°C compared to conventional AlN-Y2O3 systems. The MCAS glass phase is satisfactorily distributed between AlN particles after sintering at 1,600°C, existing as an amorphous secondary phase. The AlN specimen attained a thermal conductivity of 82.6 W/m·K at 1,600°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 494. CrossRef
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


