Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- The Manufacturing Process of Clean Ni-Cr-Co-Based Superalloy Powder Using a Plasma Rotating Electrode
- Kyu-Sik Kim, Dae Woong Kim, Yeontae Kim, Jung Hyo Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):222-231. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00171

- 784 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ni-based superalloys are widely used for critical components in aerospace, defense, industrial power generation systems, and other applications. Clean superalloy powders and manufacturing processes, such as compaction and hot isostatic pressing, are essential for producing superalloy discs used in turbine engines, which operate under cyclic rotating loads and high-temperature conditions. In this study, the plasma rotating electrode process (PREP), one of the most promising methods for producing clean metallic powders, is employed to fabricate Ni-based superalloy powders. PREP leads to a larger powder size and narrower distribution compared to powders produced by vacuum induction melt gas atomization. An important finding is that highly spheroidized powders almost free of satellites, fractured, and deformed particles can be obtained by PREP, with significantly low oxygen content (approximately 50 ppm). Additionally, large grain size and surface inclusions should be further controlled during the PREP process to produce high-quality powder metallurgy parts.
- [Korean]
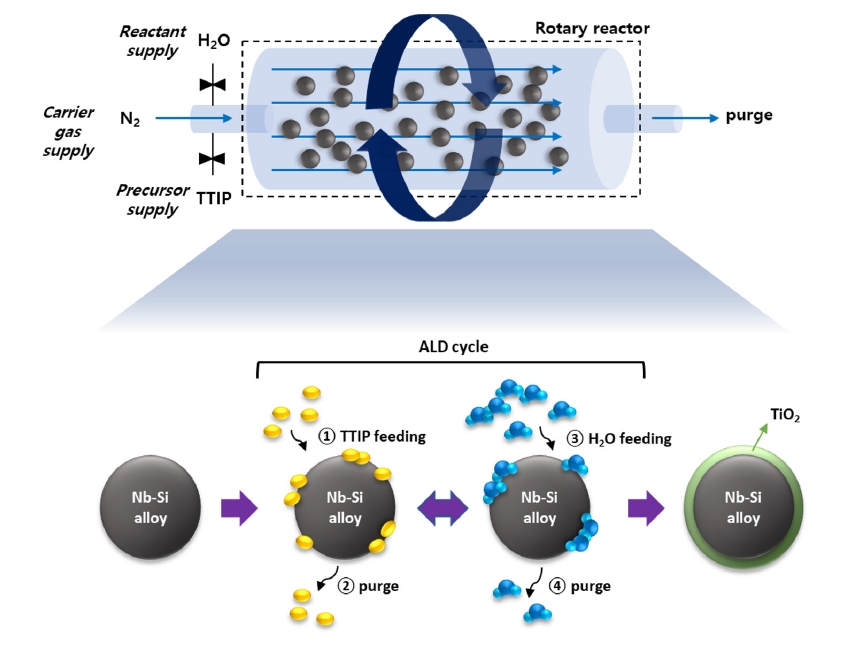
- TiO2 Thin Film Coating on an Nb-Si–Based Superalloy via Atomic Layer Deposition
- Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):255-262. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00052
- 2,054 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nano-oxide dispersion–strengthened (ODS) superalloys have attracted attention because of their outstanding mechanical reinforcement mechanism. Dispersed oxides increase the material’s strength by preventing grain growth and recrystallization, as well as increasing creep resistance. In this research, atomic layer deposition (ALD) was applied to synthesize an ODS alloy. It is useful to coat conformal thin films even on complex matrix shapes, such as nanorods or powders. We coated an Nb-Si–based superalloy with TiO2 thin film by using rotary-reactor type thermal ALD. TiO2 was grown by controlling the deposition recipe, reactor temperature, N2 flow rate, and rotor speed. We could confirm the formation of uniform TiO2 film on the surface of the superalloy. This process was successfully applied to the synthesis of an ODS alloy, which could be a new field of ALD applications.
- [Korean]
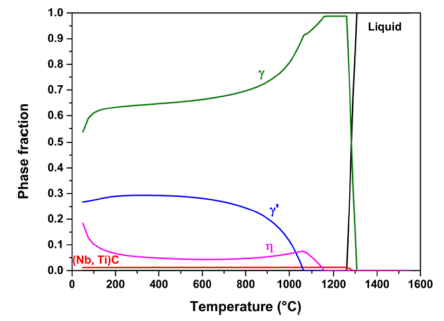
- Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Depending on Sintering Heating Rate of IN 939W Alloy
- Junhyub Jeon, Junho Lee, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):399-410. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.399
- 1,682 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Changes in the mechanical properties and microstructure of an IN 939 W alloy according to the sintering heating rate were evaluated. IN 939 W alloy samples were fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The phase fraction, number density, and mean radius of the IN 939W alloy were calculated using a thermodynamic calculation. A universal testing machine and micro-Vickers hardness tester were employed to confirm the mechanical properties of the IN 939W alloy. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, Cs-corrected-field emission transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry were used to evaluate the microstructure of the alloy. The rapid sintering heating rate resulted in a slightly dispersed γ' phase and chromium oxide. It also suppressed the precipitation of the η phase. These helped to reinforce the mechanical properties.
- [Korean]
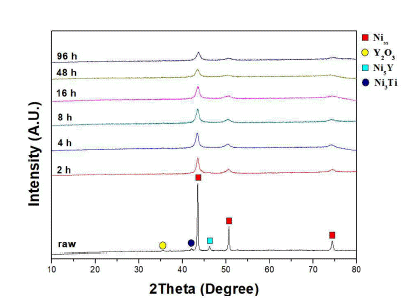
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
- Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101
- 990 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
- [Korean]
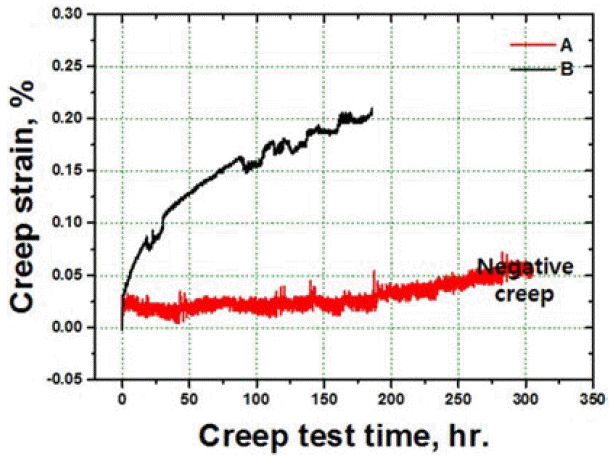
- Analyses of Creep Properties of Ni-base Superalloy Powders as Cooling Rate after Solid Solution Heat Treatment
- Chan Jun, Youngseon Lee, Byeong Beom Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Seong Suk Hong, Donghoon Kim, Jondo Yun, Eun Yoo Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):247-253. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.247
- 956 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, solid solution heat treatment of consolidated nickel-based superalloy powders is carried out by hot isotactic pressing. The effects of the cooling rate of salt quenching, and air cooling on the microstructures and the mechanical properties of the specimens are analyzed . The specimen that is air cooled shows the formation of serrated grain boundaries due to their obstruction by the carbide particles. Moreover, the specimen that is salt quenched shows higher strength than the one that is air cooled due to the presence of fine and close-packed tertiary gamma prime phase. The tensile elongation at high temperatures improves due to the presence of grain boundary serrations in the specimen that is air cooled. On the contrary, the specimen that is salt quenched and consists of unserrated grain boundaries shows better creep properties than the air cooled specimen with the serrated grain boundaries, due to the negative creep phenomenon.
- [English]
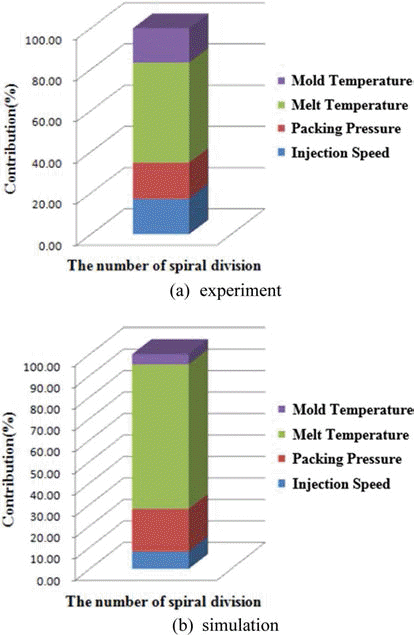
- Simulation and Experiment of Injection Molding Process for Superalloy Feedstock
- Im Doo Jung, Youngmoo Kim, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.1
- 1,311 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder injection molding is an important manufacturing technology to mass produce superalloy components with complex shape. Injection molding step is particularly important for realizing a desired shape, which requires much time and efforts finding the optimum process condition. Therefore computer aided engineering can be very useful to find proper injection molding conditions. In this study, we have conducted a finite element method based simulation for the spiral mold test of superalloy feedstock and compared the results with experimental ones. Sensitivity analysis with both of simulation and experiment reveals that the melt temperature of superalloy feedstock is the most important factor for the full filling of mold cavity. The FEM based simulation matches well the experimental results. This study contributes to the optimization of superalloy powder injection molding process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef - Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 364. CrossRef
- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


