Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Powder Metall Inst > Volume 22(3); 2015 > Article
-
ARTICLE
유성볼밀공정으로 제조된 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말 - 이병훈a, 안기봉a, 배상원, 배선우, H. X. Khoab, 김병기, 김지순*
- Fe-TiC Composite Powders Fabricated by Planetary Ball Mill Processing
- B. H. Leea, K. B. Ahna, S. W. Bae, S. W. Bae, H. X. Khoab, B. K. Kim, J. S. Kim*
-
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute 2015;22(3):208-216.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.208
Published online: May 31, 2015
a (주)지아이엘
b 하노이과학기술대학교 재료공학부, 울산대학교 첨단소재공학부
a GIL Co. Ltd., Ulsan, Korea
b School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hanoi University of Science and Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea
- *Corresponding author : Ji Soon Kim, TEL: +82-52-259-2244, FAX: +82-52-259-1688, jskim@ulsan.ac.kr
© The Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute All rights reserved
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 685 Views
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref
Abstract
- Fe-TiC composite powders are fabricated by planetary ball mill processing. Two kinds of powder mixtures are prepared from the starting materials of (a) (Fe, TiC) powders and (b) (Fe, TiH2, Carbon) powders. Milling speed (300, 500 and 700 rpm) and time (1, 2, and 3 h) are varied. For (Fe, TiH2, Carbon) powders, an in situ reaction synthesis of TiC after the planetary ball mill processing is added to obtain a homogeneous distribution of ultrafine TiC particulates in Fe matrix. Powder characteristics such as particle size, size distribution, shape, and mixing homogeneity are investigated. In case of (Fe, TiC) powder many coarse TiC particulates with size of several μm are unevenly distributed in Fe-matrix. The composite powder prepared from (Fe, TiH2, C) powder mixture showed a homogeneous dispersion of ulatrafine TiC particulates.
- 세라믹스 (ceramics) 와 금속 (metal) 의 장점을 조합한 서멧 (cermet) 은 일반적으로 고융점의 산화물이나 탄화물 , 붕화물, 규화물 등을 철족 원소인 Co, Ni, Cr, Fe 등 금 속 기지에 분산시킨 복합재료이다. 세라믹스가 지닌 경도 , 내마모성, 내열성, 내산성 등과 금속의 인성, 연성 등이 더해져 공구강 등 특수 목적으로 사용하는 데 필요한 성 능을 갖도록 할 수 있다. 서멧은 WC-Co계 초경합금의 특 성에 가장 근접하는 소재로 기대되고 있으며, 최근 WCCo계 초경합금의 단점을 보완할 수 있는 방향으로 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다[1-3].
- 대표적인 서멧인 TiC-Ni는 내마모성과 내충격성, 고온 내식성 및 고경도, 고융점, 부식저항성 등의 특징을 가지 고 있어서 전자분야는 물론 절삭 공구재, 내마모성이 요구 되는 금형공구재료로 널리 사용되고 있다[4-5]. Ni의 경우 원소재의 구득성 (availability) 과 가격 면에서 약점이 있 는 것으로 알려져 있다. TiC 세라믹스 강화 Fe계 복합재 료의 경우, 미량의 합금원소를 첨가시켜 내식성, 내마모성, 경화능 등을 개선하여 광산, 절삭, 금형용으로 널리 이용 되고 있다. 저렴한 원재료 가격과 높은 경도, 우수한 가공 성과 함께 초경합금과 유사한 특성을 나타낸다는 장점을 갖고 있다.
- Fe-TiC 복합재료를 제조하기 위한 방법으로는 용해주조 법, 고온자전합성법, 분말야금법 등이 사용되고 있다[6-7]. 용해주조법의 경우, 주조 후 열간 단조 및 압연의 방법으 로 제조되고 있는데, 이 방법으로 제조된 공구강의 경우, 편석이 생겨 조직이 불균일하고, 후가공에 사용되는 열에 의한 결정립 조대화와 변형이 생기고, 방향성이 생기는 특 성 한계가 있다. 분말야금법은 이러한 문제를 해결할 수 있는 방법으로 알려져 있는데, 스크랩 (scrap) 을 분말화하 여 재사용할 수 있어 원료단가를 낮출 수 있을 뿐만 아니 라, 공정이 간단하고, 조성 제어가 비교적 용이하며, 후처 리 가공이 필요 없는 시제품을 바로 만들어 낼 수 있어 대 량 생산의 장점이 있다.
- Fe-TiC 복합재료가 우수한 경도 및 인성을 갖기 위해서 는 Fe 금속 기지상에 TiC 세라믹 입자가 미세하고 균일하 게 분산되어야 하는데, 분말야금법에서는 이를 위한 제조 공정으로 스펙스밀 (spex mill), 아트리터 (attritor), 유성볼 밀 (planetary ball mill) 등의 고에너지 분쇄 공정을 많이 이용하고 있다. 고에너지 분쇄 공정 중에는 원료분말의 분 쇄와 혼합이 이루어지는데, 이 과정에서 원료분말의 분쇄 용이성은 고에너지 분쇄 공정의 효과적 활용을 위해 중요 한 인자가 될 수 있다.
- 이 연구에서는 다음과 같은 서로 다른 두 가지 원료분 말 조합을 선택하여 유성볼밀로 고에너지 분쇄, 혼합하여 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말을 제조하고, 그 특성을 비교하였다: (1) 순수 Fe와 TiC 분말 조합, (2) Fe, TiH2, C 분말 조합. 전자의 경우, 일반적으로 사용되는 단순혼합 공정이며 연 성이 있는 Fe 분말의 경우 밀링과정에서 용기나 볼에 부 착되는 등의 문제가 발생할 수 있을 것으로 예상하였다. 후자의 경우, C분말을 사용함으로써 이런 문제를 해결하 고, 분쇄가 용이한 TiH2 분말을 사용함으로써 분쇄 혼합의 효율성을 높일 뿐 아니라, TiC 강화입자의 크기를 미세화 하고 균일 분산시키기 위한 Fe 기지 내 Ti-C 사이의 in situ 반응 합성을 시도하였다.
서 론
- 사용된 원료분말은 다음과 같다. Fe 분말은 순도가 98.95%이고, 입자크기가 5.3 μm인 분말을 사용하였고, TiC 분말은 순도가 99.5%이고, 입자크기가 2 μm인 분말 을 사용하였다. TiH2 분말은 순도가 99%이고, 입자크기가 45 μm인 분말을 사용하였고, C 분말은 순도가 99.7%이고, 입자크기가 5 μm인 분말을 사용하였다.
- 국내 제작된, 출력 1.5 kW, 최대 1100 rpm의 고에너지 볼밀링이 가능한 유성볼밀 (Planetary Ball Mill, P-100) 을 사용하였다. 장착된 밀링 용기 (vial) 의 수는 2개이었으며, 그 크기는 직경 73.8 mm, 높이 60.7 mm, 재질은 스테인 리스스틸이었다. 분쇄 매체로 사용한 볼과 분말의 비율 (Ball to Powder Ratio, BPR) 은 무게비 20:1로 고정하였 으며, 직경 5 mm의 스테인리스스틸 볼을 사용하였다. 밀 링 공정 중에 발생하는 열과 높은 에너지로 인해 원료 분 말이 산화될 수 있기 때문에 이를 방지하기 위하여 용기 안을 Ar gas로 채워 밀봉한 후 밀링하였다. 유성볼밀링 조 건은, 밀링시간을 1시간으로 고정하고 밀링속도 300, 500, 700 rpm으로 변화를 주었으며, 500 rpm에서 밀링시간을 1, 2, 3시간으로 변화시켜 밀링하였다.
- Fe, TiH2, C 분말 조합을 유성볼밀링한 분말의 경우에는 Fe 기지 내에서 TiH2의 Ti와 C간의 반응 합성을 실시하였 다. 반응 온도를 조사하기 위해 DSC 분석을 실시하였으 며, DSC 분석조건은 온도범위 0~1300 °C, 승온속도 10 °C/min, 분위기는 Ar gas (100 ml/min) 이었다. DSC 결과 를 바탕으로 혼합된 분말을 1000 °C, 1100 °C, 1200 °C에 서 각각 1시간 동안 반응 합성시켜 최종적으로 Fe-TiC 복 합분말을 제조하였다. 반응 합성에 사용한 장치는 내경 40 mm, 외경 50 mm, 길이 1 m의 알루미나 관과 슈퍼칸탈 발열체를 사용한 고온수평관상로이었다. 분쇄 혼합된 (Fe, TiH2, C) 분말을 알루미나 보트에 담아 관상로에 장입하고, 로 내부의 분위기를 Ar gas 분위기로 치환해 주기 위하여 Ar gas를 10분간 Purging 한 후, 반응이 종료될 때까지 180 ml/min의 유량으로 흘려주었다.
- 제조된 Fe-TiC 복합분말의 형상과 미세 조직을 위한 전 계방사주사전자현미경 (FE-SEM) 으로 관찰, 분석하였다. Fe 기지 내 Ti 성분과 성분의 분포를 에너지분산형분광분 석 (EDS) 으로 확인하였다. 분말 입자 크기와 입도분포를 레이저입도분석 (LPSA) 으로 조사하였다. X선회절분석 (XRD) 에 의한 상분석을 실시하여 반응 합성된 TiC를 확 인하였다.
실험방법
- 3.1. 원재료 분말
- 그림 1에 사용된 원료분말들의 FE-SEM 관찰 결과를 요 약하여 나타내었다. 그림에서 보는 바와 같이, Fe 분말은 판상과 다각형 형상이 혼재되어 있으며, TiC 분말은 각진 형상을, TiH2 분말은 불규칙한 각진 형상을, Carbon은 크 기 분포가 불균일하지만 판상 형태를 하고 있다. 그림 2는 이들 분말의 레이저입도분석 (LPSA) 결과를 나타낸 것으 로, 각 원료분말들의 평균입도는 Fe 29.8 μm, TiC 0.5 μm, TiH2 1.8 μm, Carbon 0.8 μm로 확인되었다. 여기서 누적 %로 각각 10%, 90%의 입자크기 (d(0.1), d(0.9)) 로 나타 낸 입도분포를 살펴보면, Fe 분말은 d(0.1)~d(0.9)가 17~110 μm으로 매우 불균일한 분포곡선을 나타내고 있으며, TiC 분말은 d(0.1)~d(0.9)가 0.3~1.0 μm으로 미세하고 균일한 분포곡선을 나타내었다. TiH2 분말은 d(0.1)~d(0.9)가 0.7~5.8 μm으로, Fe 분말에 비해 미세한 입도이긴 하나 bi-modal 형태의 불균일 입도 분포 곡선을 나타내고 있다. Carbon 분말의 경우도 d(0.1)~d(0.9)가 0.5~3.7 μm으로, TiH2 보다 는 조대 입자의 분율이 작기는 하지만, 마찬가지로 bi modal 입도 분포를 보였다.
- 3.2. 순수 Fe와 TiC 분말의 분쇄, 혼합
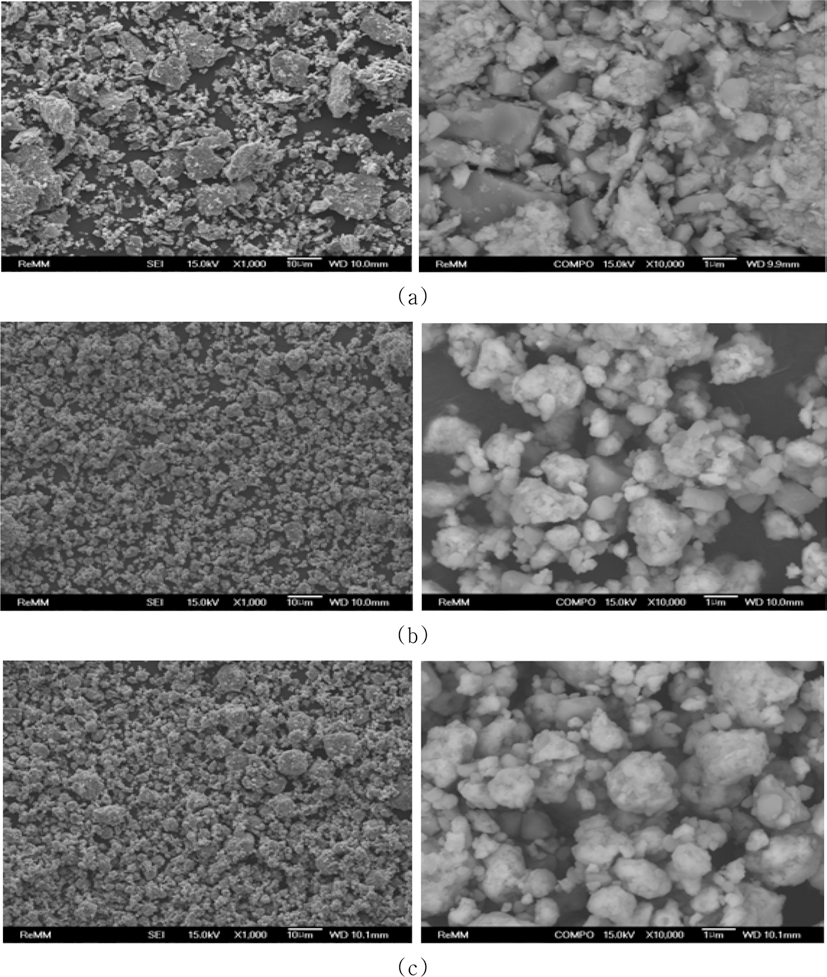
- 그림 3은 순수 Fe와 TiC 원료 분말을 300, 500, 700 rpm으 로 1 h 동안 유성볼밀링한 혼합분말의 이차전자 (secondaryelectron) 이미지 및 후방산란전자 (back-scattered electron) 이미지를 나타낸 것이다. 300 rpm으로 1 h 동안 밀링하였 을 경우 (그림 3(a)), 분쇄가 거의 되지 않고 조대한 각진 형상의 입자들이 다수 관찰 되었으며, 균일한 혼합도 이루 어지지 않았음을 알 수 있다. 500 rpm의 경우 십 μm 대 의 조대 입자들이 사라진 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 분말 형 상 또한 각진 분말 형상은 거의 사라지고, 등축상의 분말 형상으로 변화되었으며, 10,000배로 확대한 후방산란전자 이미지에서 보는 바와 같이, Fe 분말에 TiC 미세 분말들 이 부착되어 있는 형태를 하고 있음을 알 수 있다 (그림 3(b)). 700 rpm으로 밀링속도를 증가시킬 경우에도, 500 rpm의 경우와 유사한 양상을 보이고 있으며, 초미세 분말 들은 다소 감소한 것으로 보인다. 당초 우려하였던 연성 Fe 금속의 밀링 용기나 볼에 대한 부착 현상은 나타나지 않았다.
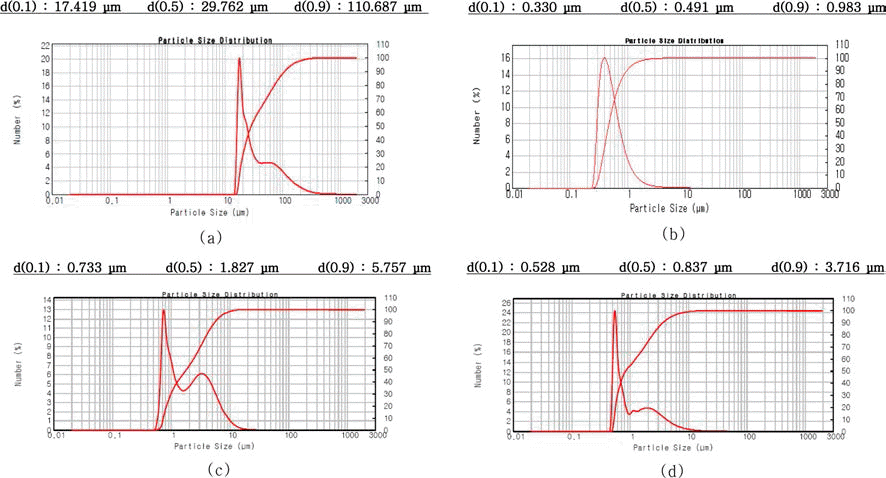
- 위의 혼합분말들에 대한 입도분석 결과를 그림 4에 나 타내었다. 그림 2의 원재료 분말 입도분석 결과에서 평균 입도가 Fe 29.8 μm, TiC 0.5 μm이었으나, 300 rpm으로 1 h 밀링 하였을 경우, 평균입도가 1.0 μm으로 감소하였다. 입도 분포 곡선의 경우 형태의 변화는 없으나 미세 입도 영역으로 위치 이동이 있음을 확인할 수 있다. 500 rpm으 로 밀링 속도를 증가시킬 경우, 평균 입도가 0.7 μm으로 감소함과 동시에 입도 분포의 균일화가 일어남을 알 수 있다. 700 rpm으로 밀링 속도를 올릴 경우 평균 입도의 변 화는 거의 없으며, 조대 입자의 분율이 다소 감소하는 경 향을 보였다. 밀링속도를 500 rpm으로 고정하고 1, 2, 3 h 으로 시간을 변화시켰을 때의 입자 형상과 입도 변화도 조사하였으나 서로 큰 차이를 보이지 않아 그 결과는 제 시하지 않았다.
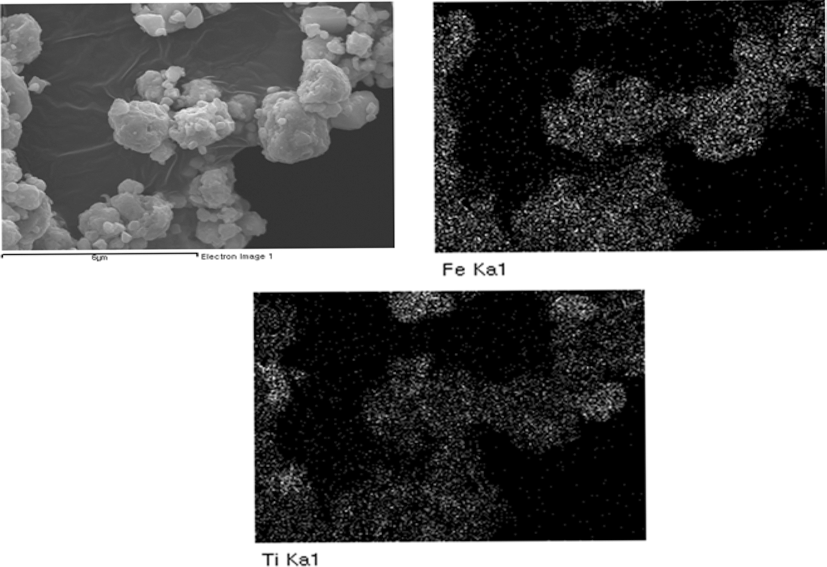
- 그림 5는 500 rpm, 1 h 밀링하여 준비한 Fe-TiC 복합분 말의 혼합 균일성을 확인하기 위해 실시한 Fe, Ti 원소 Xray mapping 결과를 나타낸 것이다. TiC 분말이 독립적으 로 존재하거나, Fe 분말 일부에 편재하는 등 혼합 균일성 이 우수하지 않음을 알 수 있다. 그림 6은 위의 분말을 진 공 마운팅한 후 단면을 연마하여 FE-SEM 후방산란전자 이미지로 관찰한 결과이다. 이미지 내에 어둡게 보이는 부 분이 원자번호가 작은 Ti를 함유하고 있는 TiC이며, 밝은 부분이 Fe 기지이다. 그림에서 보는 바와 같이, 매우 미세 한 TiC 분말 입자들도 Fe 기지 내에 분산되어 있으나, 수 μm 크기의 조대한 TiC 입자가 불균일하게 박혀 있는 형 태로 존재함을 확인할 수 있다.
- 위의 결과들을 종합하면, 연성을 갖는 Fe 분말기지 내부 에 경질의 미세한 TiC 분말입자가 침투된 상태로 분쇄되 면서 등축상으로 뭉치는 형상으로 변화하는 것으로 사료 된다. 300 rpm의 밀링속도에서는 충분한 밀링 에너지가 부가되지 못한 것으로 생각되며, 밀링속도 500 rpm 이상 에서는 연성을 갖는 Fe 분말의 가공경화에 따른 파괴 등 으로 분쇄와 혼합이 이루어지지만, Fe 분말 기지 내의 조 대 TiC 분말은 완전히 분쇄되지 않은 것으로 판단된다.
- 3.3. Fe, TiH2, C 분말 조합의 분쇄, 혼합
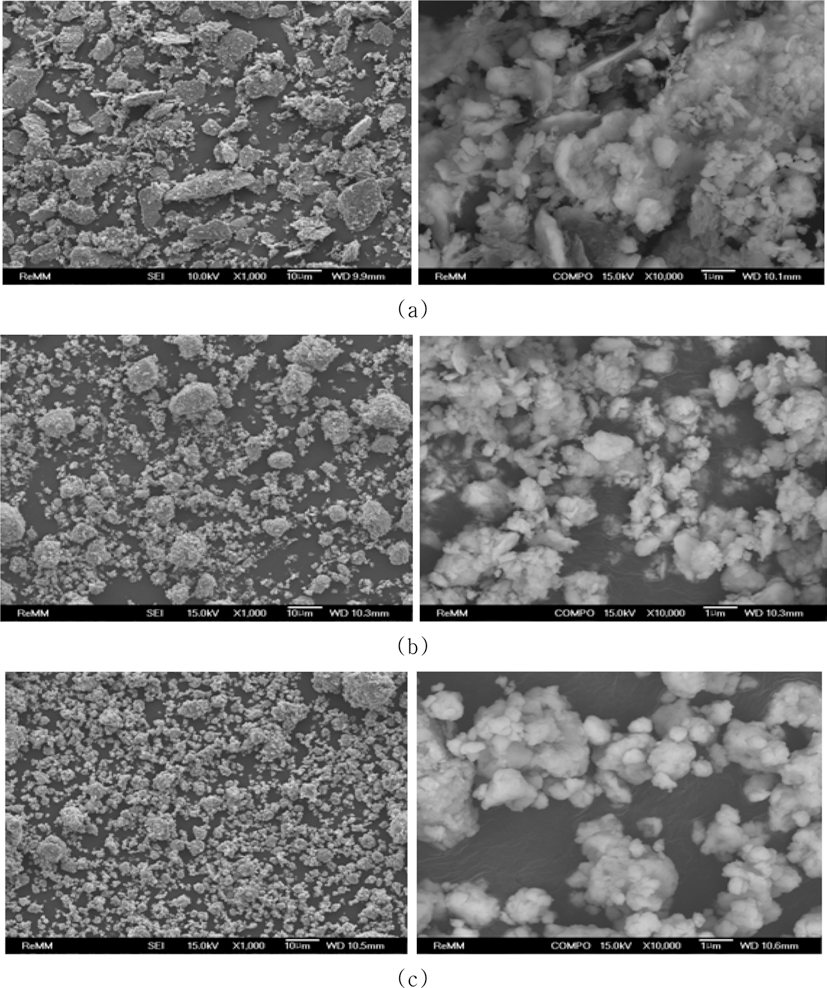
- 그림 7은 Fe와 TiH2, Carbon 원료 분말을 각각 300 rpm, 500 rpm, 700 rpm의 밀링속도로 1 h 동안 유성볼밀링한 혼 합분말의 이차전자 (secondary-electron) 이미지 및 후방산란 전자 (back-scattered electron) 이미지를 나타낸 것이다. 300 rpm으로 1 h 밀링한 경우, 각진 형상의 TiH2 분말입자와 편 상의 Carbon 분말입자가 혼재하고 있으며, 분쇄와 균일 혼 합이 충분히 이루어지지 않았음을 알 수 있다. 500 rpm의 경 우 앞서 관찰되었던 조대한 각진 형상의 분말입자들이 사라 지고, 등축상으로 뭉쳐 있는 형상으로 변화된 것을 알 수 있 다. 700 rpm으로 밀링속도를 증가시킬 경우, 전체적으로 균 일하고 미세한 형상을 보이고 있으며, 등축상으로 뭉쳐 있는 형상을 유지하고 있음을 알 수 있다.
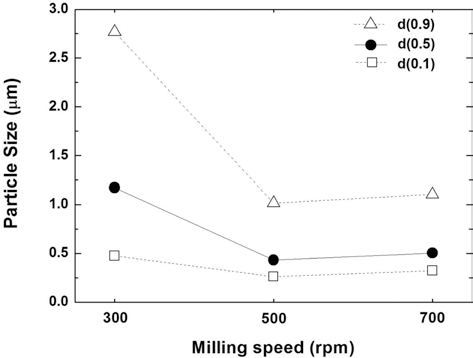
- 그림 8은 위의 분말들에 대한 입도 분석 결과를 정리한 것이다. 300 rpm의 밀링 속도에서는 평균입도가 가장 크고, 넓은 범위의 입도분포를 보여 충분한 분쇄 혼합이 이루어 지지 않았음을 알 수 있다. 500 rpm에서는 평균입도가 급 격히 감소하고 입도분포도 좁은 범위로 변화함을 확인하였 다. 700 rpm으로 밀링 속도를 증가시킨 경우, 입도분석 결 과의 큰 차이는 확인할 수 없었다. 다만 앞에서의 순수 Fe 분말과 TiC 분말의 분쇄, 혼합의 경우에 비해서는 평균입 도가 미세하고 입도분포의 균일성 등에서 모두 상대적으로 우수하였는데, 이는 TiH2가 취성이 강한 재료로서 분쇄가 용이하고, Carbon의 첨가로 밀링 과정의 분쇄기구, 특히 연 성을 갖는 Fe 분말의 변형과 분쇄 과정에 영향을 주었기 때문으로 판단된다.
- 3.4. 분쇄, 혼합된 [Fe, TiH2, C] 분말의 in situ TiC 합성
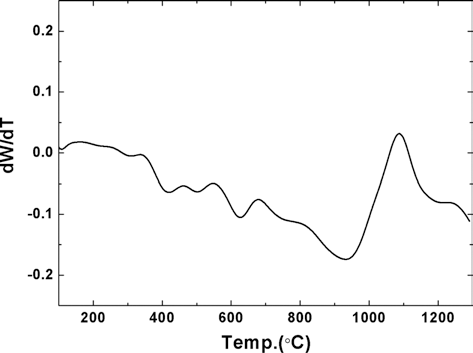
- 준비된 [Fe, TiH2, C] 혼합 분말의 TiH2 내의 Ti와 C 간 의 in situ 반응을 통해 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말을 최종적으로 합성하기 위한 반응 온도 조건을 찾기위해 실시한 시차열분 석 (DSC) 결과를 그림 9에 나타내었다. 열분석 곡선 상의 약 420~630 °C 범위에서 흡열반응을 확인할 수 있으며, 약 930 °C 부근에서 발열반응을 확인할 수 있다. 문헌에 보고된 바 에 의하면, 전자는 TiH2가 Ti와 H2로 분해되는 반응이며, 후 자는 TiC가 합성되는 반응인 것으로 판단된다[7].
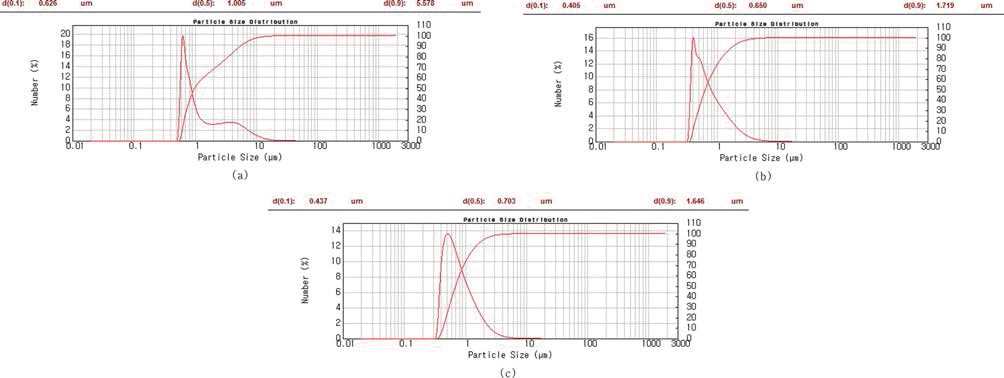
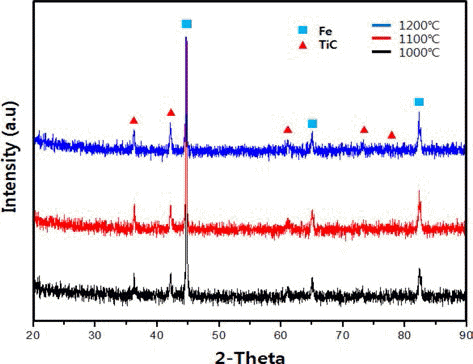
- 위의 결과를 바탕으로 1000, 1100, 1200 °C의 합성온도 에서 각 1 h 동안 유지하여 반응시킨 [Fe, TiH2, C] 혼합 분말의 XRD 분석 결과를 그림 10에 나타내었다. 조사된 모든 반응온도에서 TiC 합성 반응이 완료되어 Fe와 TiC 상만이 공존하는 것을 확인하였다. 반응 합성 후의 혼합분 말에 대한 입도분석 결과, 반응 전 혼합분말의 평균입도가 0.5 μm인데 반해, 반응합성 후 조사된 온도 범위에서 1.0~1.2 μm 정도로 입자 크기가 증가하였다.
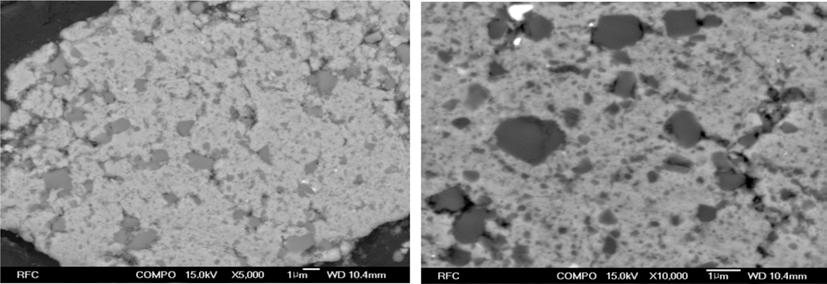
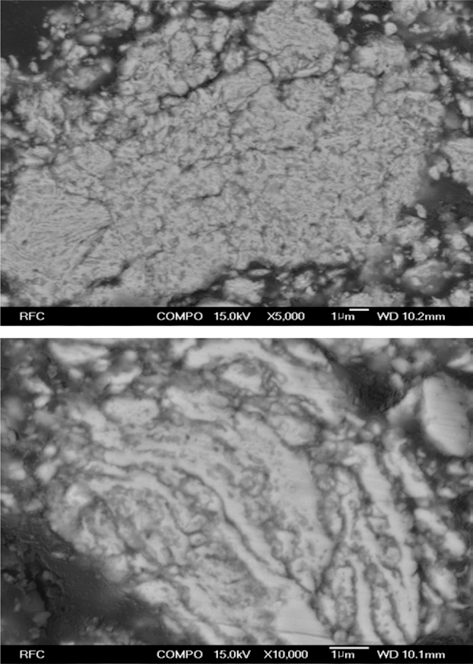
- 그림 11은 반응합성이 완료된 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말을 진공 마운팅한 후 단면을 연마하여 FE-SEM 후방산란전 자 이미지로 관찰한 결과이다. 균일한 크기의 매우 미세한 TiC 입자가 Fe 기지 내에 전체적으로 고르게 분산되어 있 음을 알 수 있다 (x5,000 사진). 10,000배로 관찰한 사진에 서는 길이 방향으로 늘어난 Fe 기지가 형성되어 있고, 기 지 내부 또는 기지층 사이에 TiC 입자가 존재하는 것도 확인할 수 있다. 순수 Fe 분말과 TiC 분말의 분쇄, 혼합에 서와는 달리, [Fe, TiH2, C] 혼합분말의 경우에는 Carbon 이 고체 윤활제 역할을 함으로써 밀링 과정에서 Fe 분말 이 전단 변형 되고, 전단 변형된 flake 형태의 Fe 분말입 자들이 등축상 입자 형상으로 뭉쳐짐에 따라 이러한 형상 이 만들어졌을 것으로 예상된다.
결과 및 고찰
FE-SEM images of starting powders used in this study: (a) Fe, (b) TiC, (c) TiH2, and (d) Carbon.

Results of laser particle size analysis of starting powders used in this study: (a) Fe, (b) TiC, (c) TiH2, and (d) Carbon.
FE-SEM images of (Fe, TiC) powder mixture after planetary ball milling at (a) 300, (b) 500 and (c) 700 rpm for 1 h (Left: Seconary-electron image, Right: Back-scattered electron image).
Results of laser particle size analysis of (Fe, TiC) powder mixture after planetary ball milling at (a) 300, (b) 500 and (c) 700 rpm for 1 h.
Results of X-ray mapping for (a) Fe and (b) Ti elements of (Fe, TiC) powder mixture after planetary ball milling at 500 rpm for 1 h.
FE-SEM images of the polished cross-section of (Fe, TiC) powder mixture after planetary ball milling at 500 rpm for 1 h (Back-scattered electron images. top: x5,000, down: x10,000).
FE-SEM images of (Fe, TiH2, C) powder mixture after planetary ball milling at (a) 300, (b) 500 and (c) 700 rpm for 1 h (Left: Secondary-electron image, Right: Back-scattered electron image).
Change in particle size as a function of milling speed of (Fe, TiH2, C) powder mixture after planetary ball milling for 1 h.
Result of DSC analysis of (Fe, TiH2, C) powder mixture prepared by planetary ball milling at 500 rpm for 1 h.
Result of XRD analysis of (Fe, TiH2, C) powder mixture after in situ reaction synthesis at 1000, 1100 and 1200 °C for 1 h.
- 서로 다른 두 가지 원료분말 조합에 대해 유성볼밀링 공 정을 사용하여 다음과 같이 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말을 제조 하였다. (a) 순수 Fe 분말과 TiC 분말의 단순 분쇄 혼합, (b) 미세 분쇄가 보다 용이한 [Fe, TiH2, C] 원료분말을 유 성볼밀링 공정으로 분쇄, 혼합 후, in situ TiC 반응 합성 공정으로 Fe-TiC 복합분말을 제조하여 각각의 분말 특성 을 비교 분석하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
순수 Fe 분말과 TiC 분말의 단순 분쇄 혼합으로 얻 어진 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말의 경우, Fe 기지 내에서 TiC 강화입자가 미세하게 분쇄되지 않아 조대한 TiC 입자들이 잔류하였으며, 불균일한 분산을 나타내었다.
[Fe, TiH2, C] 원료분말을 유성볼밀링 공정으로 분쇄, 혼 합 후, in situ TiC 반응 합성 공정으로 Fe-TiC 복합분말을 제조한 경우, 취성이 강한 TiH2 분말의 사용으로 분쇄가 매우 용이하였으며, Carbon의 영향으로 연성 Fe 분말이 전단 변형되어 flake 형상을 이루고, 이 flake들이 뭉치는 형태로 분쇄 혼합이 진행되었다.
유성볼밀링으로 준비된 [Fe, TiH2, C] 혼합분말을 in situ TiC 합성반응으로 최종 Fe-TiC 복합재료 분말을 제조 할 경우, 서브마이크로미터 이하의 크기를 갖는 TiC가 Fe 기지 내에 전체적으로 고르게 분산된 분말을 제조할 수 있었다.
결 론
-
Acknowledgements
- 이 논문은 2012년 정부(교육부)의 재원으로 한국연구재단 의 지원을 받아 수행된 연구임(NRF-2012R1A1A2044930).
감사의 글
- 1. P Arato, L Bartha, R Porat, S Berger and A Rosen, Nanostruct. Mat. (1998) 10 245.
- 2. BK Kim, GH Ha and DW Lee, J. Mater. Process. Technology. (1997) 63 317.Article
- 3. Y Zheng, S Wang, M You, H Tan and W Xiong, Met. Chem. Phys. (2005) 92 64.Article
- 4. HS Kalish, Met. Prog. (1983) 124 21.
- 5. JC Lasalvia and MA Meyers, Int. J. Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synth. (1995) 4 43.
- 6. YJ Baik and KY Eun, J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. (1989) 27 823(Korean).
- 7. HJ Cho and MS Thesis, The Fabrication and Properties of Fe-TiC Composite for Wear-Resistance Tools using Spark Plasma Sintering. (2007) Gyeongsang National University, Jinju.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Abrasive Wear Performance of Spherical Hierarchical Structured TiC/High-Manganese Steel Composites
Tao He, Shengnian Zhao, Dehong Lu, Yehua Jiang, Mojin Zhou
Materials.2024; 18(1): 130. CrossRef - Effect of TiC particle size on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiC reinforced stainless steel
Yeong-Hwan Lee, Sungmin Ko, Hyeonjae Park, Donghyun Lee, Sangmin Shin, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Yangdo Kim, Seungchan Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 480: 951. CrossRef - Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Heebong Kim, Hyuk-Tae Kwon, Sang-Kwan Lee, Sang-Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 155. CrossRef - Sintering of Fe-30 wt% TiC Composite Powders Fabricated from (Fe, TiH2, C) Powder Mixture
Byunghoon Lee, Ji Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(5): 356. CrossRef - Pressureless Sintering and Spark-Plasma Sintering of Fe-TiC Composite Powders
B. H. Lee, S. W. Bae, S. W. Bae, H. X. Khoa, J. S. Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 283. CrossRef
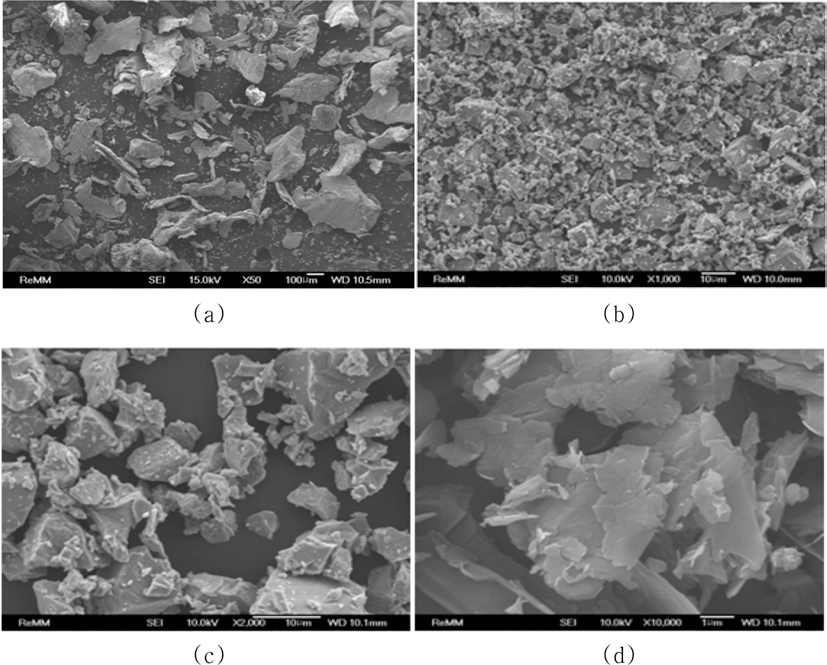
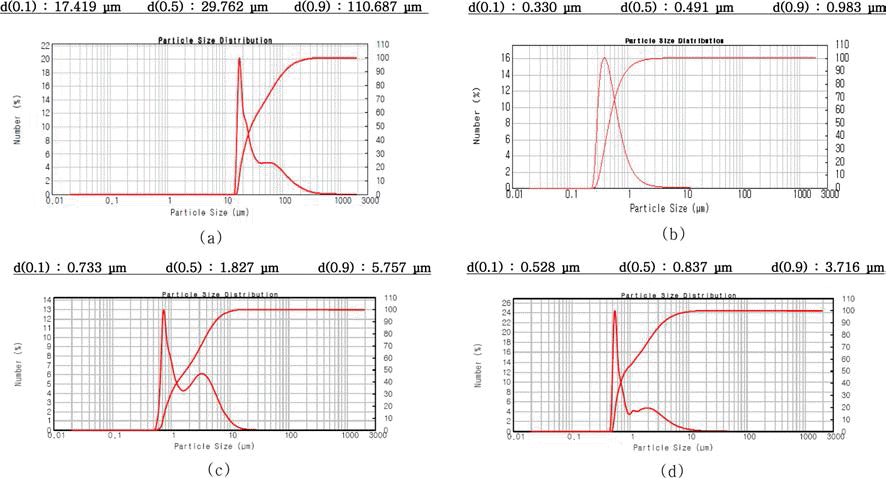
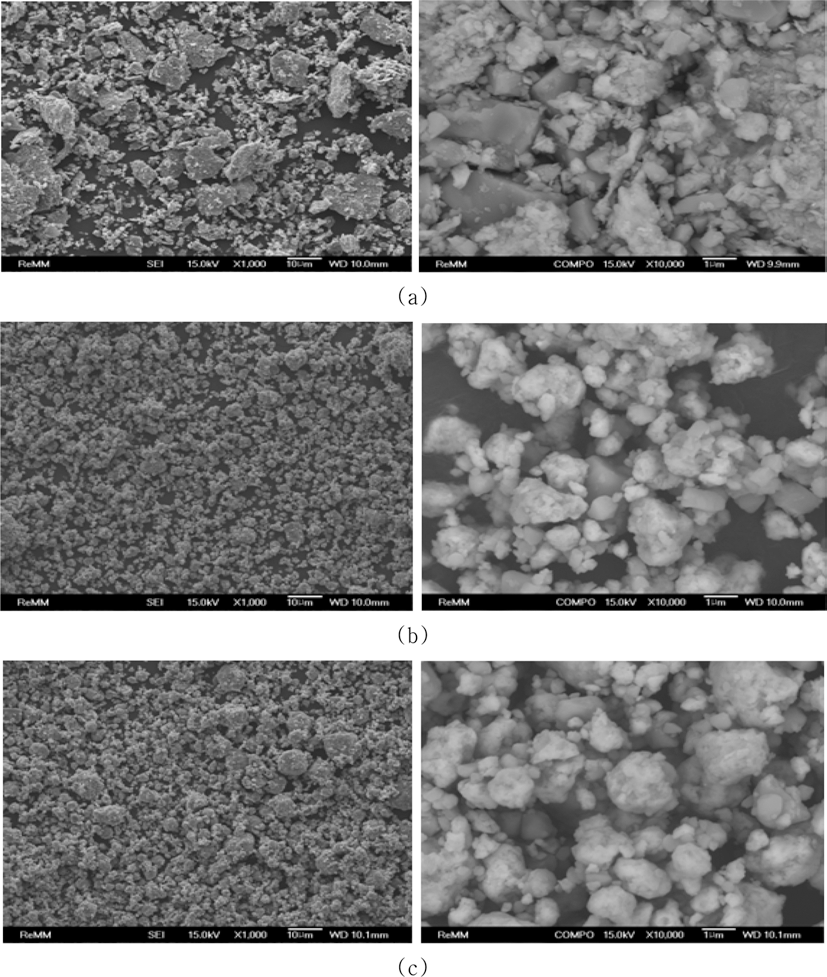
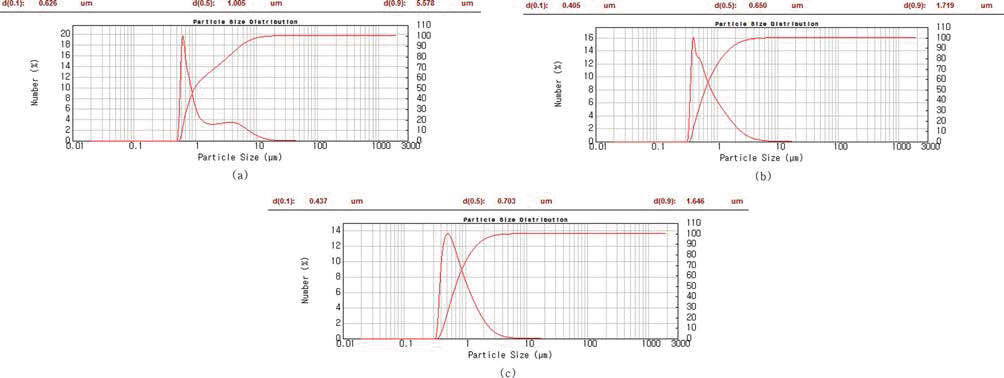
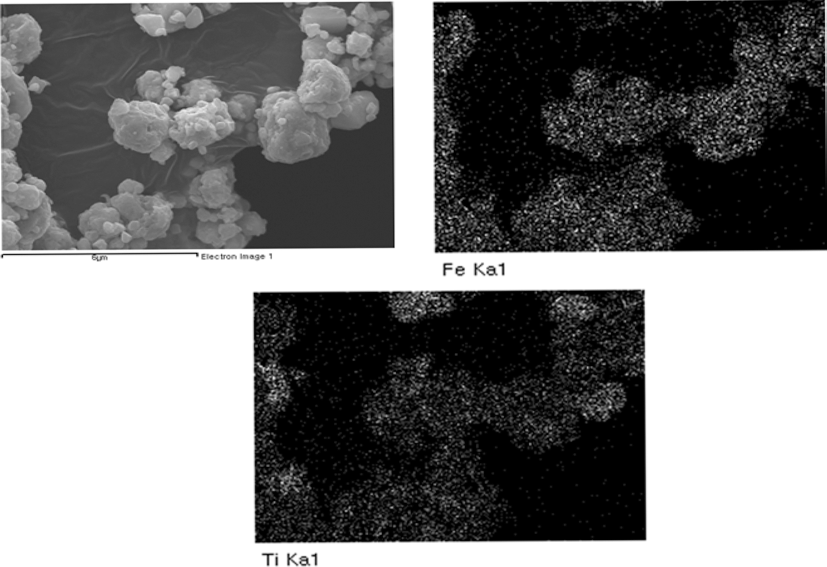

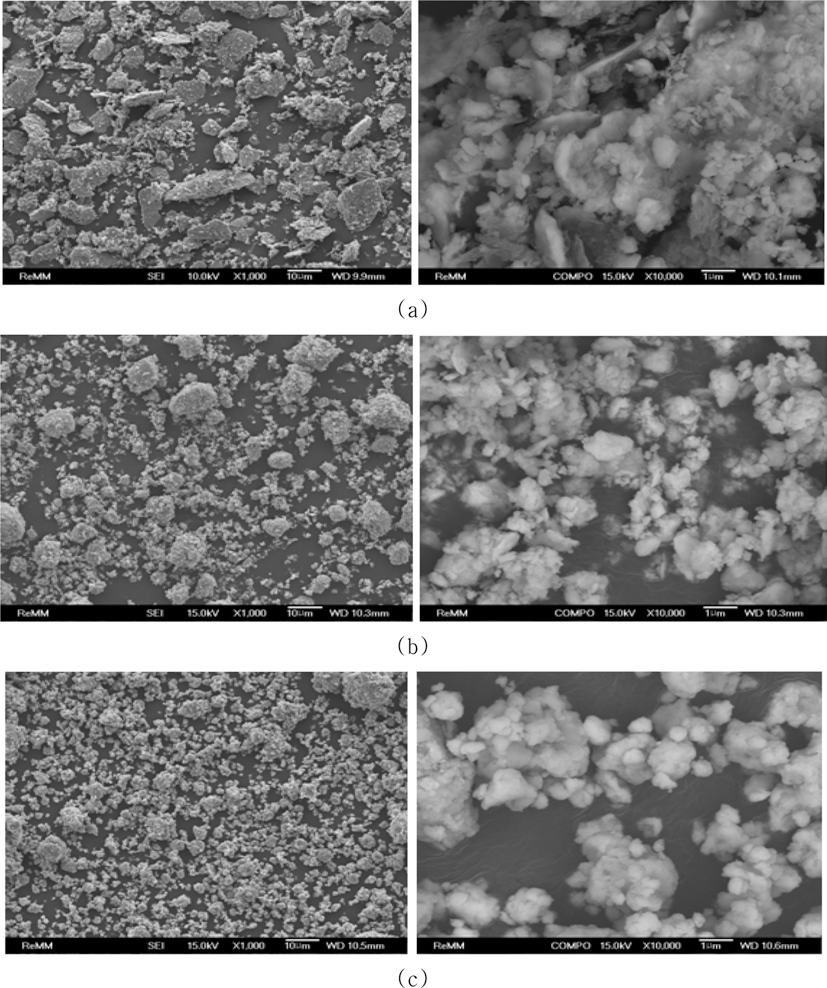
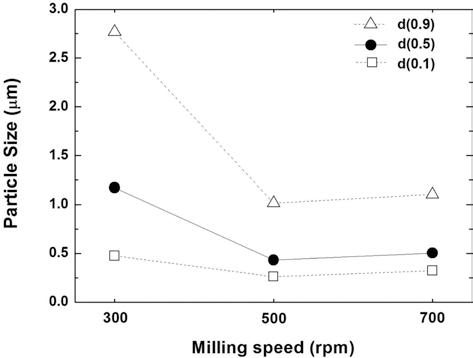
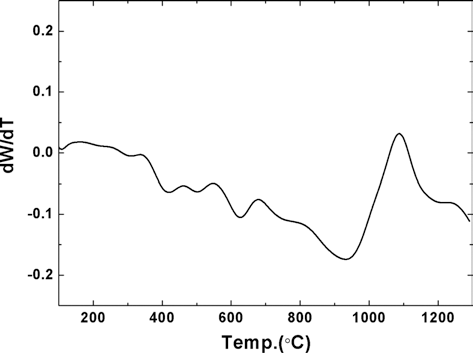

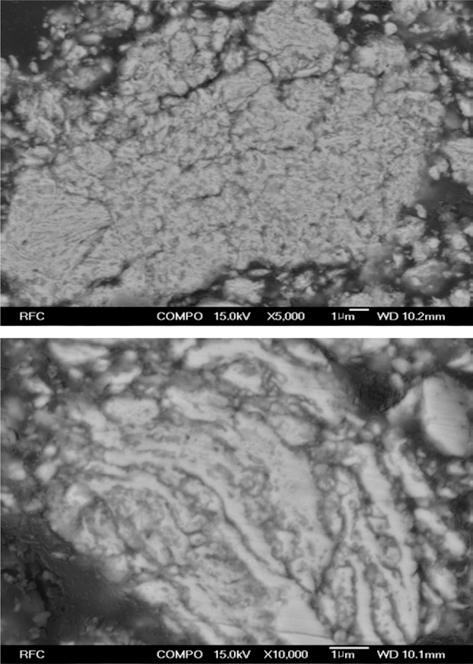
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 6.
Fig. 7.
Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
Fig. 10.
Fig. 11.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 Cite this Article
Cite this Article











