Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Powder Metall Inst > Volume 23(1); 2016 > Article
-
Article
10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 합성과 광촉매 활성평가 - 김형철, 한재길a,*
- Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders
- Hyeong-Chul Kim, Jae-Kil Hana,*
-
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute 2016;23(1):33-37.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.33
Published online: January 31, 2016
인천대학교 기계시스템공학부
인천테크노파크 융합기술센터
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Incheon, 12-1, Songdo-dong, Yeonsu-gu, Incheon 406-772, Korea
a Technology Convergence Center, Incheon Techno Park, Gaebeo-ro 12, Yeonsu-gu, Incheon 406-130, Korea
- * Corresponding Author: Jae-Kil Han, TEL: +82-32-260-0832, FAX: +82-32-260-0834, E-mail: jkhan@itp.or.kr
• Received: November 26, 2016 • Revised: December 16, 2016 • Accepted: December 21, 2016
© The Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute. All rights reserved.
- 1,017 Views
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
- 10 wt.% and 20 wt.%Li-TiO2 composite powders are synthesized by a sol-gel method using titanium isopropoxide and Li2CO3 as precursors. The as-received amorphous 10 wt.%Li-TiO2 composite powders crystallize into the anatase-type crystal structure upon calcination at 450°C, which then changes to the rutile phase at 750°C. The asreceived 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders, on the other hand, crystallize into the anatase-type structure. As the calcination temperature increases, the anatase TiO2 phase gets transformed to the LiTiO2 phase. The peaks for the samples obtained after calcination at 900°C mainly exhibit the LiTiO2 and Li2TiO3 phases. For a comparison of the photocatalytic activity, 10 wt.% and 20 wt.% Li-TiO2 composite powders calcined at 450°C, 600°C, and 750°C are used. The 20 wt.%Li-TiO2 composite powders calcined at 600°C show excellent efficiency for the removal of methylorange.
- 3.2eV의 밴드갭을 갖는 TiO2는 강한 산화력, 내화학성, 화학적/생물학적 안정성이 우수한 성질을 가지고 있어 가 장 효과적인 대기질 및 수질 정화용 촉매로 알려져 있다. TiO2는 유기물을 흡착하고 UV 빛을 흡수하여 유기물을 광분해하는 촉매이다. TiO2의 광촉매 효율을 향상하기 위 해서 Ag, Cr, Fe, V2O5, ZrO2, WO3, SrO, CeO2 등과 같은 금속 또는 금속 산화물을 첨가하여 TiO2 복합체를 만든다 [1-9]. 또한 질소, 황 또는 탄소와 같은 비금속을 도핑하여 합성된 non-metal doped TiO2는 원자가띠의 밴드갭을 낮 추는 효과가 있어 자외선 영역에서 활성이 있는 이산화티 탄이 가시광선 영역에서도 광촉매 활성을 보인다. 일반적 으로 도핑 이온과 원소들은 원자가띠의 밴드갭을 줄일 뿐 만 아니라 광촉매 물질내의 광전된 전자와 정공의 재결합 을 억제하는 경향이 있다[3]. 최근에 알칼리 화합물인 hydroxyapatite(Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, HAP)를 첨가하여 TiO2- HAP 복합분말을 합성하였고 이 분말은 유기 분자를 흡착 하고 양이온을 잡아주는 효과로 높은 광 분해 효율을 보 였다. TiO2의 낮은 유기물 흡착능력을 개선하여 상대적으 로 높은 광촉매 효율을 보인다[10, 11]. TiO2의 흡착-분해 반응을 증가시켜 광촉매 효율을 향상시키기 위해서 알카 리 금속을 첨가하여 알카리-TiO2 복합분말 합성을 시도하 였다. 알카리 금속 중에서 리튬(Li)은 세상에서 가장 가벼 운 금속으로 CO2 흡착제, 리튬배터리, Al-Li 합금, 의약품 등에 사용된다. 리튬 화합물 중에 수산화 리튬(LiOH)은 실내 호흡기체에 포함되어 있는 이산화탄소(CO2)를 흡착 하는 특성을 가지고 있어 이산화탄소 제거장치(CO2 scrubber)에 사용된다. 원자번호가 3번인 리튬의 반데르 반 스 원자반경은 181 pm로 티타늄의 원자반경 187 pm와 비 슷한 원자반경을 갖는다. 또한 금속이온은 배위수에 의존 하지만 리튬의 이온반경은 59 pm(4배위의 경우) 티타늄의 이온반경은 60 pm(6배위의 경우)로 매우 비슷한 크기를 갖는다. 티타늄 이소프로폭사이드와 탄산리튬을 리튬이 반 응하여 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말을 합성하였다.
- 본 연구에서는 티타늄 이소프로폭사이드와 탄산리튬 (Li2CO3)를 전구체로 사용하여 졸-겔법으로 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말을 합성하였다. 합성된 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말의 하소 온도에 따른 상 변화와 미세조직은 XRD와 FE-SEM을 이용하여 수행하였고 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말의 광촉매 활성을 측정 하기 위해서 수용액 상에서 메틸오렌지의 제거 효율을 측 정하였다.
1. 서 론
- 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말은 졸겔법으로 제조 하였다(Fig. 1). 200 mL의 티타늄 이소프로폭사이드 (Ti(O-iPr)4, Aldrich, 99%)를 2,000 mL 반응용기에 넣고 200 mL 이소프로판올 (C3H7OH, 동우화인켐, 98%)과 0.1 mole 아세칠아세톤네이트 (acetylacetonate, Junsei, 99%)를 첨가하여 교반하였다. 혼합용액은 90°C에서 2시간 동안 교반 및 환류 시킨다. 티타늄-졸이 형성된 후, 200 mL 탈 이온수에 6.3 g과 50 g의 Li2CO3를 용해한 용액을 연동펌 프를 이용하여 천천히 첨가하고 혼합용액을 가열하여 겔 을 만든다. 형성된 겔은 80°C에서 24시간 건조한 후 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말을 얻었다. 복합분말은 10°C/min의 승온 속도로 450, 600, 750°C에서 1시간 유지 하여 하소 처리 하였다.
- 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말의 광촉매 활성은 메 틸오렌지(methyl orange)의 제거효율로 측정하였다. Pyrex 로 제작된 용기에 0.2 wt% 비율이 되도록 10 wt%, 20wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말을 반응용액에 넣고 잘 분산 시켰다. 자 외선 광원으로는 250-390 nm의 파장을 갖는 40W 수은 램프 (medium-pressure mercury lamp)를 사용하였고 자외 선 조사에 따른 초기농도 10ppm 메틸오렌지의 농도 변화 를 UV-vis 분광계를 이용하여 측정하였다. 하소 온도에 따 른 10 wt%, 20 wt% Li-TiO2 복합분말 상변화, 미세조직은 XRD(D/MAX2500H, Rigaku, Japan)과 FE-SEM (SU8010, Hitachi, Japan)를 이용하여 관찰하였다.
2. 실험 방법
- Fig. 2은 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 하소 온도에 따른 XRD 측정 결과를 나타내고 있다. As-received 10 wt%Li- TiO2 분말은 결정화가 되지 않은 비정질로 존재하고 하소 온도가 450°C로 증가하면 결정화되어 아나타제-TiO2 상만 출현하고 좀 더 높은 하소온도인 600°C에서는 주상은 아 나타제-TiO2 상이고 소량의 루타일-TiO2 상이 관찰되었다. 하소온도가 750°C 인 경우, 대부분의 피이크는 날카롭고 좁은 띠폭을 보여주고 있어 결정화가 많이 진행된 것으로 판단되며 루타일-TiO2 상과 아나타제-TiO2 상이 혼재하여 관찰되었다.
- 리튬 원소의 양이 증가된 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 하 소 온도에 따른 XRD 측정 결과를 Fig. 3에 나타내었다. As-received 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말은 아나타제 TiO2상 이 출현하고 하소온도가 450°C인 경우 LiTiO2 상이 검출 되었다. 하소온도가 증가할수록 LiTiO2 피이크가 좁고 강 하게 검출 되었고 750°C에서 LiTiO2 상뿐만 아니라 아나 타제-TiO2 상과 Li2TiO3 상이 함께 검출 되었다. 하소온도 가 상대적으로 낮은 450°C과 600°C에서는 LiTiO2 상과 아 나타제-TiO2 상의 피이크가 인접해 있고 LiTiO2가 피이크 가 폭이 넓어 구분할 수 없지만 하소온도가 높아지면 LiTiO2의 결정화가 많이 진행되어 피이크가 분리되고 강 하고 좁은 폭의 피이크를 보인다.
- 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 하소온도에 따른 미세조직 의 변화를 관찰하기 위해서 FE-SEM을 수행하였다(Fig. 4). As-received 복합분말, 450°C와 600°C에서 하소한 복 합분말은 100 nm 이하의 구형의 미세한 입자들이 응집 되어 있으며 하소 온도가 높은 750°C에서는 결정화와 입 성장 되어 약 150 nm 크기를 갖는 다각형의 입자로 관 찰되었다.
- 하소온도에 따른 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 미세조직 변 화를 관찰하였다(Fig. 5). As-received 복합분말은 10 wt%Li- TiO2 복합분말(Fig. 4(a))의 미세조직과 비슷한 형태로 관 찰되었다. 하소온도가 증가한 450°C에서는 소량의 플레이 크 형태와 다량의 막대기 형태의 입자가 관찰되었다. 하소 온도를 증가시키면 막대기 형태가 증가하고 입자의 크기 도 약간 조대해 지는 경향을 보이고 있다. 750°C에서는 결 정화와 입성장이 증가되어 약 250 nm의 입자 크기를 갖 는 다각형의 입자가 관찰 되었다. 이와 같은 결과는 Fig. 3의 XRD 실험결과와 잘 일치한다.
- 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 하소온도에 따른 광촉매 활 성을 측정하기 위해서 자외선 광원을 이용하여 메틸오렌 지(MO) 용액의 잔류농도를 측정하였다(Fig. 6). 6시간 동 안 UV 광원을 조사한 후에 잔류된 메틸오렌지의 농도를 측정한 결과, as-received와 750°C 하소한 복합분말에서 각 각 6.3 ppm, 5.8 ppm의 메틸오렌지가 측정되었으며 450°C와 600°C에서 하소한 복합분말은 각각 1.7 ppm과 1.4 ppm으 로 측정 되었다. 아나타제-TiO2상이 주상으로 관찰된 450°C와 600°C에서 하소한 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 광촉매 효율이 루타일-TiO2상이 많이 검출된 경우와 결정 화 거의 되지 않은 as-received 복합분말보다 높게 측정되 었다.
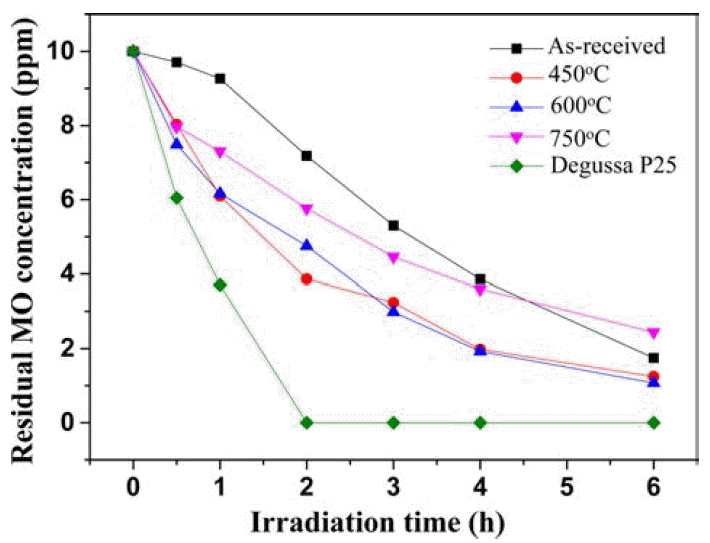
- 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 메틸오렌지 분해능을 측정한 결과를 Fig. 7에 나타내었다. 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말에 6시간 동안 UV 광원을 조사해서 메틸오렌지의 농도를 측 정한 결과. 20 wt%Li-TiO2 as-received, 450°C, 600°C과 750°C 복합분말의 경우 각각 2.4 ppm, 1.8 ppm, 1.2 ppm 와 1.1 ppm로 측정되었다. 같은 하소 조건상에서 20 wt%Li- TiO2 복합분말과 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말를 비교해 보면 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말이 상대적으로 높은 광촉매 효율 을 보이고 있다. 따라서 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 주상 이 LiTiO2이고 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 주상은 아나타 제-TiO2이므로 LiTiO2가 아나타제-TiO2보다 상대적으로 약간 높은 광촉매효율을 보였다.
3. 결과 및 고찰
Fig. 2
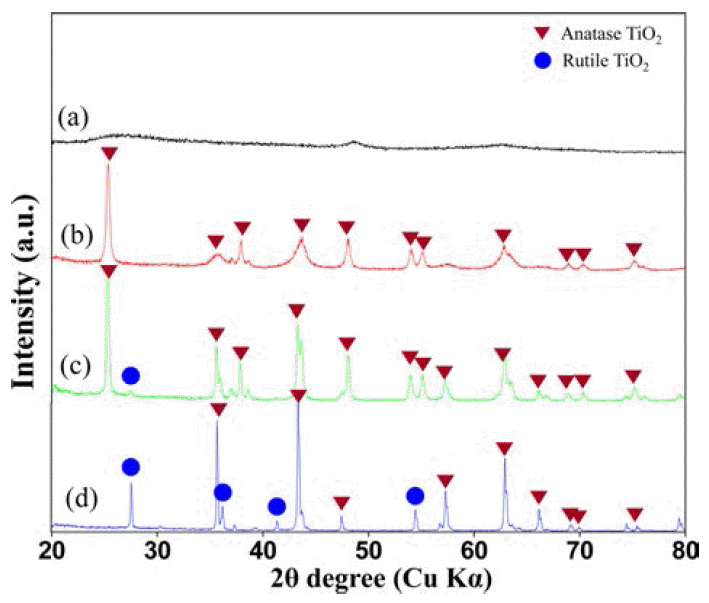
XRD patterns of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders depending on the calcination temperatures; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C, and 750°C.

Fig. 3
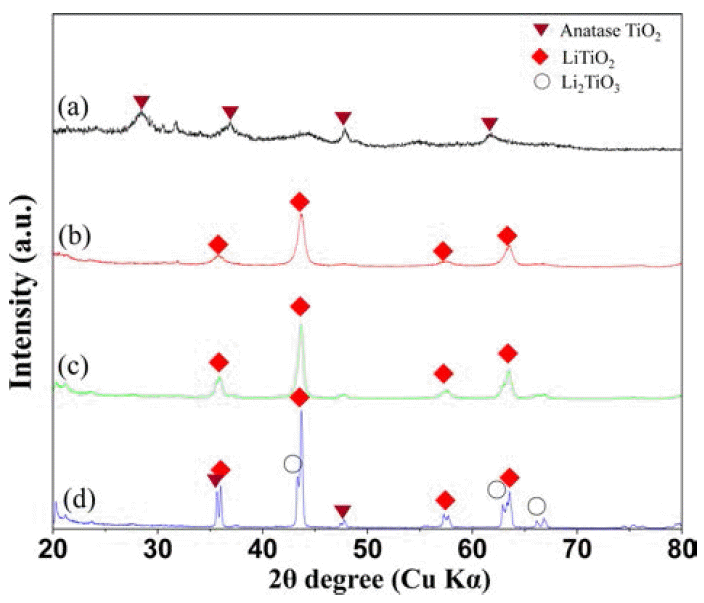
XRD patterns of 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders depending on the calcination temperatures; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C, and 750°C.

Fig. 4
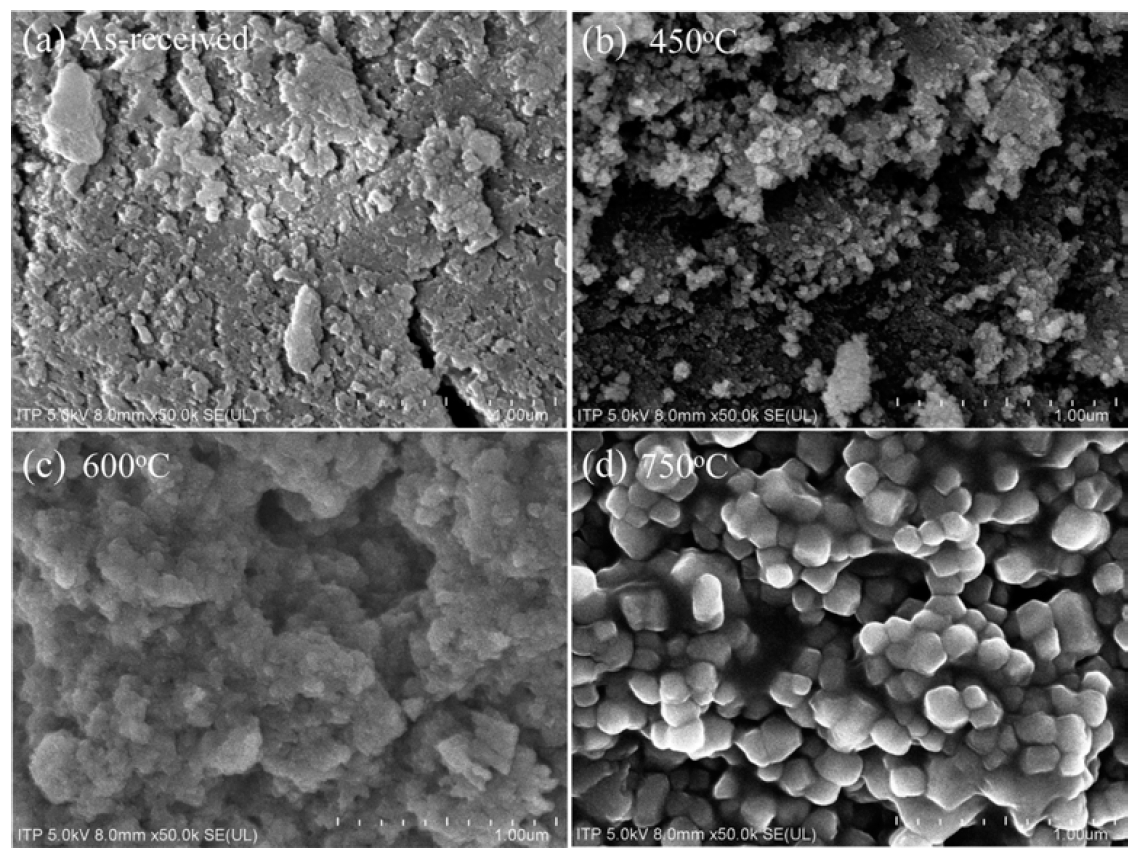
FE-SEM images of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C and 750°C.

Fig. 5

FE-SEM images of 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C and 750°C.

Fig. 6
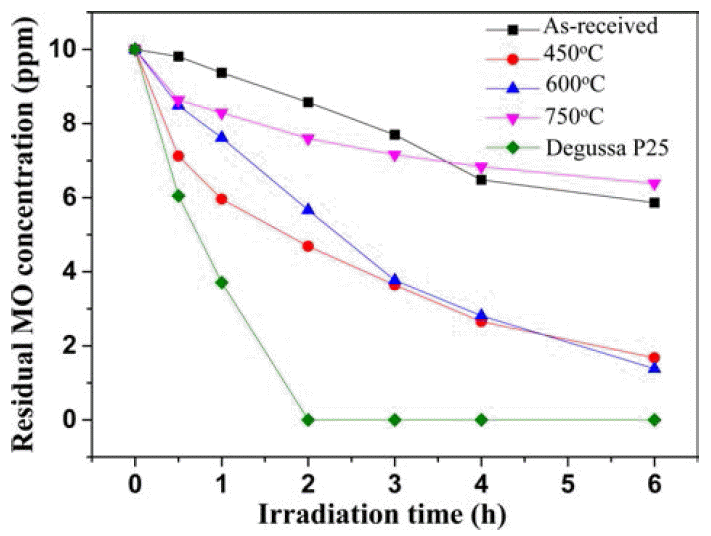
The photodegradation of methyl orange by the of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders with different calcination temperatures.

- 전구체로 티타늄 이소프로폭사이드와 탄산리튬(Li2CO3) 을 졸-겔법에 의해서 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말을 합성하였다. 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 경우, 비정질 형태 의 as-received 복합분말이 하소온도 450°C, 600°C로 증가 함에 따라 아나타제-TiO2 상이 형성되고 750°C에서는 루 타일-TiO2와 아나타제-TiO2 상이 검출되지만 Li의 어떤 상 도 검출되지 않았다. 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 경우, 아 나타제-아나타제-TiO2 상을 갖는 as-receive 복합분말이 검 출되고 하소온도를 450°C, 600°C로 증가하면 LiTiO2 상이 검출되었으며 750°C로 하소온도가 증가하면 LiTiO2, Li2TiO3 와 아나타제-TiO2 상이 검출되었다. 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 자외선 조사에 따른 메틸오렌지 광분해 효과 를 측정한 결과, 10 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말은 450°C, 600°C 에서 하소한 복합분말이 우수한 광촉매 효과를 보였으며 20 wt%Li-TiO2 복합분말의 경우, 전체적으로 우수한 광촉 매 효과를 보여주고 있으며 그중 600°C에서 하소한 복합 분말이 가장 우수한 광촉매 효과를 보였으며 주상은 LiTiO2이었다.
4. 결 론
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by a University of Incheon Research Grant in 2013.
감사의 글
- 1. S. H. Lee, H. C. Cha and Y. C. Nah: J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst., 22 (2015) 326 (Korean). .Article
- 2. J. Y. Kim, J. M. Byum, J. W. Kim and Y. D. Kim: J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst., 21 (2014) 119 (Korean). .Article
- 3. I. C. Kang and I. C. Yeo: J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst., 20 (2015) 474 (Korean). .
- 4. J. Ma, H. He and F. Liu: Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 179 (2015) 21. .Article
- 5. Y. Liu, Z. Wang, W. Wang, X. An, S. Mi, J. Tang and W. Huang: Appl. Surf. Sci., 315 (2014) 314. .Article
- 6. B. T. Lee, J. K. Han and F. Saito: Mater. Lett., 60 (2006) 2101. .Article
- 7. J. K. Han, S. M. Choi and G. H. Lee: Mater. Lett., 61 (2007) 3798. .Article
- 8. D. Das, H. K. Mishra, K. M. Parida and A. K. Dalai: J. Mol. Catal. A-chem., 189 (2002) 271. .Article
- 9. J. K. Han, S. M. Choi, W. S. Hong and B. T. Lee: J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater., 45 (2007) 484 (Korean). .
- 10. J. Xie, X. Meng, Z. Zhou, P. Li, L. Yao, X. Gao and Y. Wei: Mater. Lett., 110 (2013) 57..Article
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
Min-Sang Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Tohru Sekino, Young-Do Kim, Se-Hoon Kim
Catalysts.2021; 11(8): 987. CrossRef - Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 257. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 coatings on reduced graphene oxide for enhancing the visible light photocatalytic activity
Yifan Zhang, Hye Mee Yang, Soo-Jin Park
Current Applied Physics.2018; 18(2): 163. CrossRef
Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders


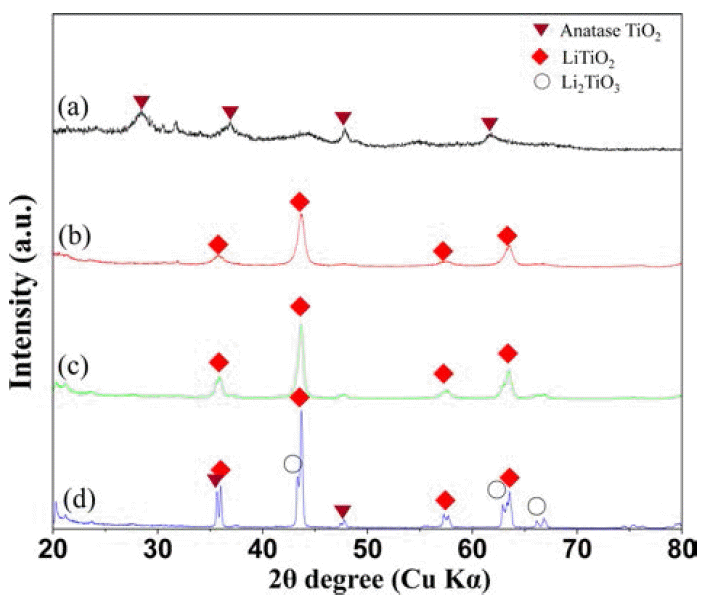


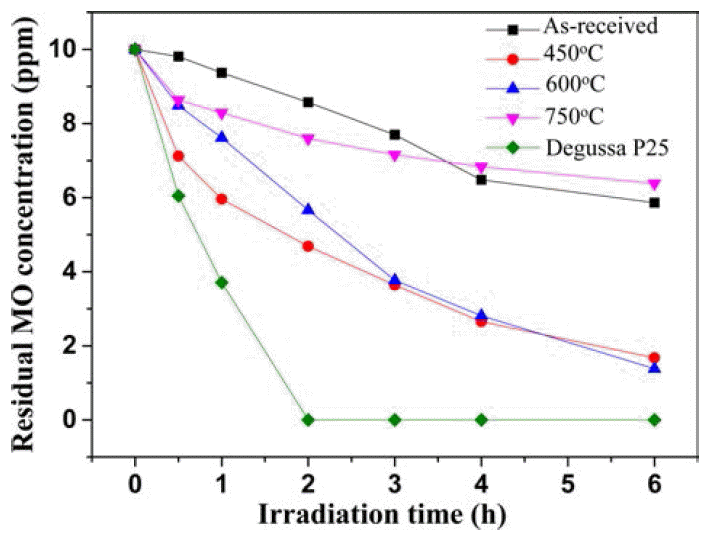
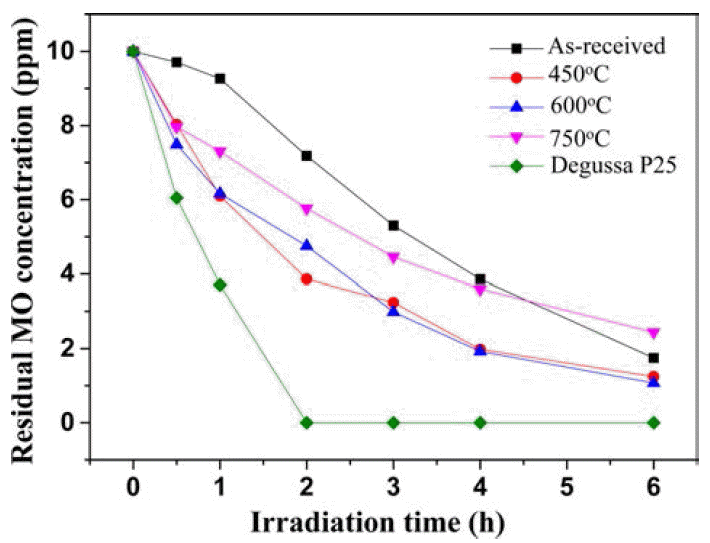
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of experimental procedure.
Fig. 2
XRD patterns of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders depending on the calcination temperatures; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C, and 750°C.
Fig. 3
XRD patterns of 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders depending on the calcination temperatures; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C, and 750°C.
Fig. 4
FE-SEM images of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C and 750°C.
Fig. 5
FE-SEM images of 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders; (a) as-received, (b) 450°C, (c) 600°C and 750°C.
Fig. 6
The photodegradation of methyl orange by the of 10 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders with different calcination temperatures.
Fig. 7
The photodegradation of methyl orange by the of 20 wt%Li-TiO2 composite powders with different calcination temperatures.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 Cite this Article
Cite this Article







