- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
-
Youngmoo Kim, Sung Ho Yang, Seong Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):373-380. Published online October 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.373
-
-
1,073
View
-
9
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
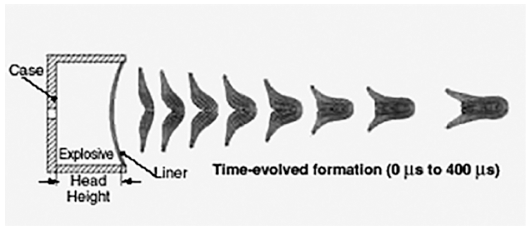
The purpose of this study is to investigate the densification behavior and the corresponding microstructural evolution of tantalum and tantalum-tungsten alloy powders for explosively formed liners. The inherent inhomogeneous microstructures of tantalum manufactured by an ingot metallurgy might degrade the capability of the warhead. Therefore, to overcome such drawbacks, powder metallurgy was incorporated into the near-net shape process in this study. Spark plasma-sintered tantalum and its alloys with finer particle sizes exhibited higher densities and lower grain sizes. However, they were contaminated from the graphite mold during sintering. Higher compaction pressures in die and isostatic compaction techniques also enhanced the sinterability of the tantalum powders; however, a full densification could not be achieved. On the other hand, the powders exhibited full densification after being subjected to hot isostatic pressing over two times. Consequently, it was found that the hot isostatic-pressed tantalum might exhibit a lower grain size and a higher density as compared to those obtained in previous studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Understanding the phase evolution and elemental distribution in MoWTaNbVTix manufactured via powder metallurgical approach
Surya T. Bijjala, Ryan Wilkerson, Chad Beamer, Pankaj Kumar
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 135(11-12): 5925. CrossRef - Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
-
Min-Ho Cho, Sung-Jun Kim, Hyun-Ji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):299-304. Published online August 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.299
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
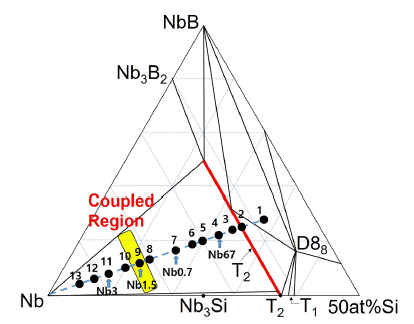
Nb-Si-B alloys with Nb-rich compositions are fabricated by spark plasma sintering for high-temperature structural applications. Three compositions are selected: 75 at% Nb (Nb0.7), 82 at% Nb (Nb1.5), and 88 at% Nb (Nb3), the atomic ratio of Si to B being 2. The microstructures of the prepared alloys are composed of Nb and T2 phases. The T2 phase is an intermetallic compound with a stoichiometry of Nb5Si3-xBx (0 ≤ x ≤ 2). In some previous studies, Nb-Si-B alloys have been prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) using Nb and T2 powders (SPS 1). In the present work, the same alloys are prepared by the SPS process (SPS 2) using Nb powders and hypereutectic alloy powders with composition 67at%Nb-22at%Si-11at%B (Nb67). The Nb67 alloy powders comprise T2 and eutectic (T2 + Nb) phases. The microstructures and hardness of the samples prepared in the present work have been compared with those previously reported; the samples prepared in this study exhibit finer and more uniform microstructures and higher hardness.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure Characterization of Nb-Si-B alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering Process
-
Sang-Hwan Kim, Nam-Woo Kim, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):426-431. Published online December 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.426
-
-
961
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
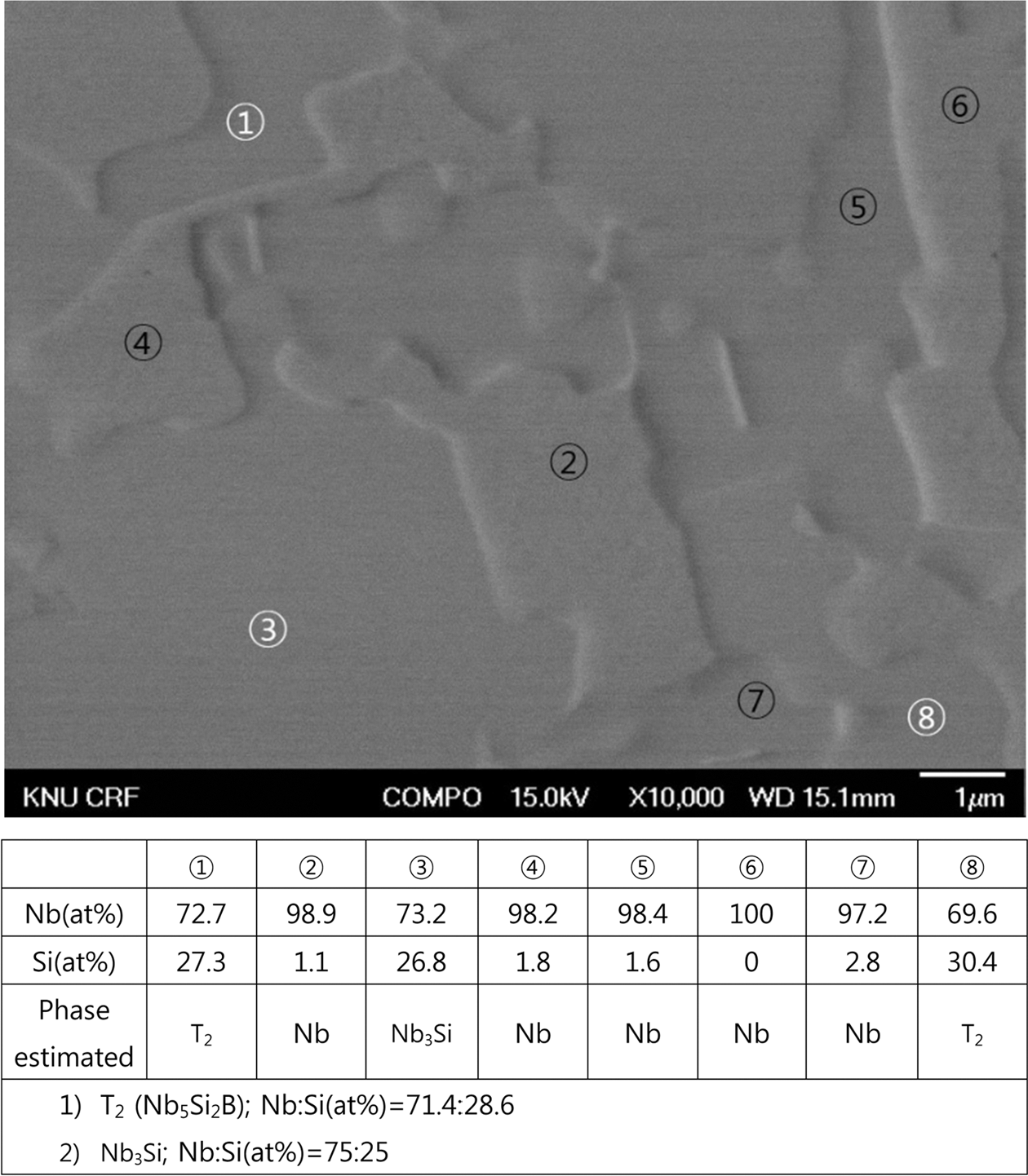
Microstructural examination of the Nb-Si-B alloys at Nb-rich compositions is performed. The Nb-rich corner of the Nb-Si-B system is favorable in that the constituent phases are Nb (ductile and tough phase with high melting temperature) and T2 phase (very hard intermetallic compound with favorable oxidation resistance) which are good combination for high temperature structural materials. The samples containing compositions near Nb-rich corner of the Nb- Si-B ternary system are prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) process using T2 and Nb powders. T2 bulk phase is made in arc furnace by melting the Nb slug and the Si-B powder compact. The T2 bulk phase was subsequently ballmilled to powders. SPS is performed at 1300°C and 1400°C, depending on the composition, under 30 MPa for 600s, to produce disc-shaped specimen with 15 mm in diameter and 3 mm high. Hardness tests (Rockwell A-scale and micro Vickers) are carried out to estimate the mechanical property. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
Min-Ho Cho, Sung-Jun Kim, Hyun-Ji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 299. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Nb-Si-B quaternary alloy fabricated by powder metallurgical method
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Se Hoon Kim, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 14. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Si-B alloys fabricated by using core-shell powder with dispersion of yttria nanoparticles
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Won June Choi, Min Sang Kim, Goo Won Noh, Young Do Kim
Metals and Materials International.2017; 23(1): 170. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ta2O5 Dispersion-Strengthened Mo-Si-B Alloy by Powder Metallurgical Method
Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Su-Ryong Bang, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim
JOM.2017; 69(4): 683. CrossRef - Rapid consolidation of nanostuctured WC-FeAl3 by pulsed current activated heating and its mechanical properties
In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 69. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Oxygen Content in the Tungsten Powder Fabricated by Electrical Explosion of Wire Method on the Behavior of Spark-Plasma Sintering
-
Cheol-Hee Kim, Seong Lee, Byung-Kee Kim, Ji Soon Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):447-453. Published online December 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.447
-
-
650
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
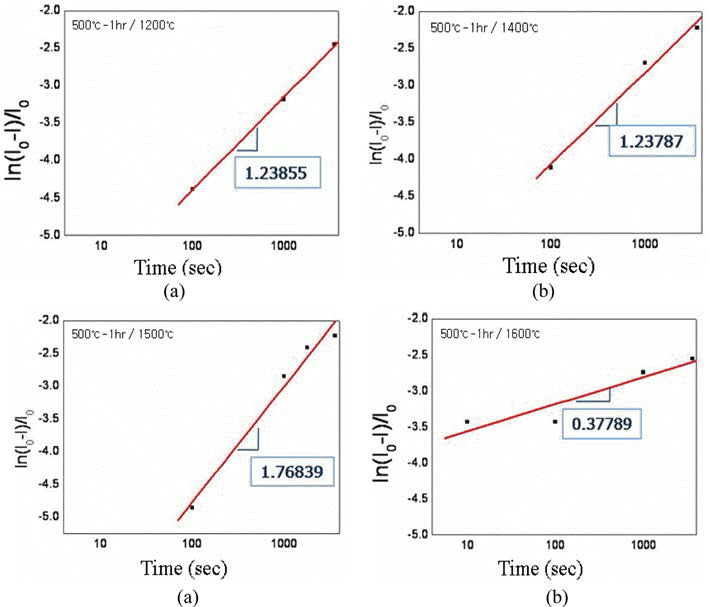
Effect of oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powder fabricated by electrical explosion of wire method on the behvior of spark plasma sintering was investigated. The initial oxygen content of 6.5 wt% of as-fabricated tungsten powder was reduced to 2.3 and 0.7 wt% for the powders which were reduction-treated at 400°C for 2 hour and at 500°C for 1h in hydrogen atmosphere, respectively. The reduction-treated tungsten powders were spark-plasma sintered at 1200-1600°C for 100-3600 sec. with applied pressure of 50 MPa under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Maximun sindered density of 97% relative density was obtained under the condition of 1600°C for 1h from the tungsten powder with 0.7 wt% oxygen. Sintering activation energy of 95.85 kJ/mol−1 was obtained, which is remarkably smaller than the reported ones of 380~460 kJ/mol−1 for pressureless sintering of micron-scale tungsten powders. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(5): 384. CrossRef
|