Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283
- 1,694 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
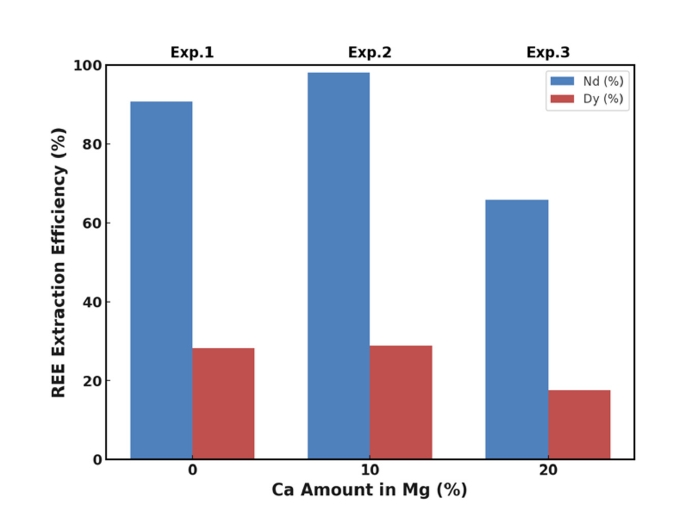
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
- Inorganic Compound and Cycloserine Composite Particles for Improved Stability
- Dongwon Kim, Heeseo Kim, Hongjun Yoon, Hyuk Jun Cho, Sung Giu Jin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):126-131. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00002
- 1,825 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study was to improve the chemical stability of cycloserine containing organic and inorganic compounds. Composite particles were manufactured with a 1:1 weight ratio of organic/inorganic compounds and cycloserine. The influence of organic/inorganic compounds on the stability of cycloserine was investigated under accelerated stress conditions at 60°C/75% RH for 24 hours. In addition, the properties of the composite particles were evaluated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the dissolution of the drug was assessed by preparing it as a hard capsule. Among the organic and inorganic compounds investigated, calcium hydroxide most improved the stability of cycloserine under accelerated stress conditions (53.3 ± 2.2% vs 1.7 ± 0.2%). DSC results confirmed the compatibility between calcium hydroxide and the cycloserine, and SEM results confirmed that it was evenly distributed around the cycloserine. Calcium hydroxide also showed more than 90% cycloserine dissolution within 15 minutes. Therefore, the calcium hydroxide and cycloserine composite particles may be candidates for cycloserine oral pharmaceuticals with enhanced drug stability.
- [Korean]
- Research on the Manufacturing Technology for a PDMS Structure-Based Transpiration Generator Using Biomimetic Capillary Phenomenon
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Jeungjai Yun, So Hyun Baek, Yongbum Kwon, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):268-275. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.268
- 1,168 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The demand for energy is steadily rising because of rapid population growth and improvements in living standards. Consequently, extensive research is being conducted worldwide to enhance the energy supply. Transpiration power generation technology utilizes the vast availability of water, which encompasses more than 70% of the Earth's surface, offering the unique advantage of minimal temporal and spatial constraints over other forms of power generation. Various principles are involved in water-based energy harvesting. In this study, we focused on explaining the generation of energy through the streaming potential within the generator component. The generator was fabricated using sugar cubes, PDMS, carbon black, CTAB, and DI water. In addition, a straightforward and rapid manufacturing method for the generator was proposed. The PDMS generator developed in this study exhibits high performance with a voltage of 29.6 mV and a current of 8.29 μA and can generate power for over 40h. This study contributes to the future development of generators that can achieve high performance and long-term power generation.
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Oxygen Reduction and Surface Chemical State of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb Powder by Ca Vapor
- Taeheon Kim, Hanjung Kwon, Jae-Won Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):31-37. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.31

- 1,110 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study explores reducing the oxygen content of a commercial Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder to less than 400 ppm by deoxidation in the solid state (DOSS) using Ca vapor, and investigates the effect of Ca vapor on the surface chemical state. As the deoxidation temperature increases, the oxygen concentration of the Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder decreases, achieving a low value of 745 ppm at 1100°C. When the deoxidation time is increased to 2 h, the oxygen concentration decreases to 320pp m at 1100°C, and the oxygen reduction rate is approximately 78% compared to that of the raw material. The deoxidized Ti-48Al-2Cr-2nb powder maintains a spherical shape, but the surface shape changes slightly owing to the reaction of Ca and Al. The oxidation state of Ti and Al on the surface of the Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder corresponds to a mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3. As a result, the peaks of metallic Ti and Ti suboxide intensify as TiO2 and Al2O3 in the surface oxide layer are reduced by Ca vapor deposition
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Production of spherical TiAl alloy powder by copper-assisted spheroidization
Jin Qian, Bo Yin, Dashun Dong, Geng Wei, Ming Shi, Shaolong Tang
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 25: 1860. CrossRef - Ca-Mg Multiple Deoxidation of Ti-50Al-2Cr-2Nb Intermetallic Compound Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Seongjae Cho, Taeheon Kim, Jae-Won Lim
ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology.2022; 11(4): 045008. CrossRef
- Production of spherical TiAl alloy powder by copper-assisted spheroidization
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of C3S, C2S, C3A Powders using Ultra-fine Calcium Oxide Powder Synthesized from Eggshell and Effect of C3A Content on Hardened Mixed Aggregates
- Heon Kong, Ki-Beom Kwon, Sang-Jin Park, Whyo-Sub Noh, Sang-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.493
- 1,030 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, ultra-fine calcium oxide (CaO) powder derived from eggshells is used as the starting material to synthesize mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The prepared CaO powder is confirmed to have an average particle size of 500 nm. MTAs are synthesized with three types of fine CaO-based powders, namely, tricalcium silicate (C3S), dicalcium silicate (C2S), and tricalcium aluminate (C3A). The synthesis behavior of C3S, C2S and C3A with ultra-fine CaO powder and the effects of C3A content and curing time on the properties of MTA are investigated. The characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and a universal testing machine (UTM). The microstructure and compressive strength characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are strongly dependent on the C3A wt.% and curing time. Furthermore, MTA with 5 wt.% C3A is found to increase the compressive strength and shorten the curing time.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


