Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Immiscible Fe-Cu Alloys using Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid
- Chu Dac Phuc, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):449-457. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.449

- 1,587 View
- 12 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron and copper are practically immiscible in the equilibrium state, even though their atomic radii are similar. As non-equilibrium solid solutions, the metastable Fe-Cu alloys can be synthesized using special methods, such as rapid quenching, vapor deposition, sputtering, ion-beam mixing, and mechanical alloying. The complexity of these methods (multiple steps, low productivity, high cost, and non-eco-friendliness) is a hinderance for their industrial applications. Electrical explosion of wire (EEW) is a well-known and effective method for the synthesis of metallic and alloy nanoparticles, and fabrication using the EEW is a simple and economic process. Therefore, it can be potentially employed to circumvent this problem. In this work, we propose the synthesis of Fe-Cu nanoparticles using EEW in a suitable solution. The powder shape, size distribution, and alloying state are analyzed and discussed according to the conditions of the EEW.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
Hugues Nkomba Museba, BongJu Lee
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1054: 185926. CrossRef - Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
Xuexue Wang, Runqing Lu, Shanhe Gong, Shaokang Yang, Wenbo Wang, Zhongti Sun, Xiaozhen Zhang, Jun Liu, Xiaomeng Lv
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 503: 158488. CrossRef - Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for the removal of p-nitrophenol and its derivatives from wastewater
M. S. Qatan, F. Arshad, M. Miskam, G. A. Naikoo
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.2024; 21(5): 5247. CrossRef - Control of cluster coalescence during formation of bimetallic nanoparticles and nanoalloys obtained via electric explosion of two wires
K.V. Suliz, A.Yu. Kolosov, V.S. Myasnichenko, N.I. Nepsha, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov, A.V. Pervikov
Advanced Powder Technology.2022; 33(3): 103518. CrossRef
- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
- Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14

- 983 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
- [English]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Characteristics of Bulk Nickel/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites via the Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- Thuyet-Nguyen Minh, Hai-Nguyen Hong, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):213-220. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.213
- 1,278 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
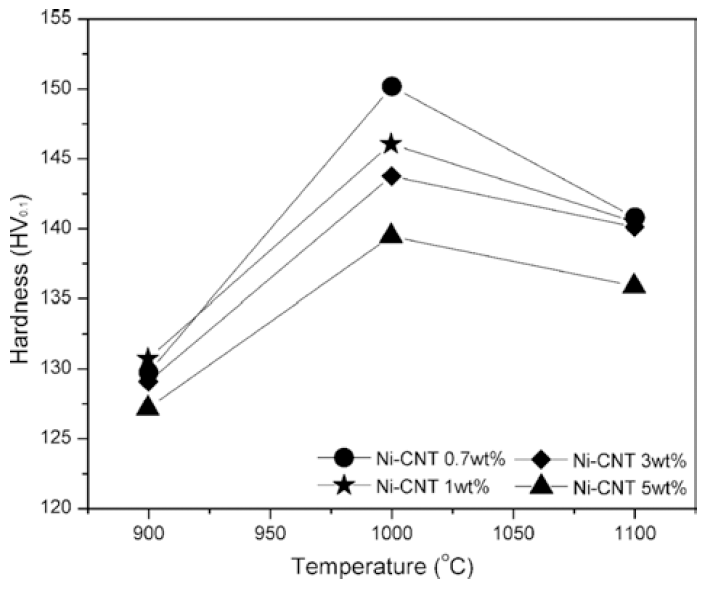
PDF In this study, bulk nickel-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites are synthesized by a novel method which includes a combination of ultrasonication, electrical explosion of wire in liquid and spark plasma sintering. The mechanical characteristics of the bulk Ni-CNT composites synthesized with CNT contents of 0.7, 1, 3 and 5 wt.% are investigated. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy techniques are used to observe the different phases, morphologies and structures of the composite powders as well as the sintered samples. The obtained results reveal that the as-synthesized composite exhibits substantial enhancement in the microhardness and values more than 140 HV are observed. However an empirical reinforcement limit of 3 wt.% is determined for the CNT content, beyond which, there is no significant improvement in the mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
Tao Jiang, Zhongyu Hou
Applied Surface Science.2020; 513: 145824. CrossRef - Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
Jin-Ju Park, Eun-Kwang Park, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Min-Ku Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 143. CrossRef
- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
- [Korean]
- Effect of Oxygen Content in the Tungsten Powder Fabricated by Electrical Explosion of Wire Method on the Behavior of Spark-Plasma Sintering
- Cheol-Hee Kim, Seong Lee, Byung-Kee Kim, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):447-453. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.447
- 651 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
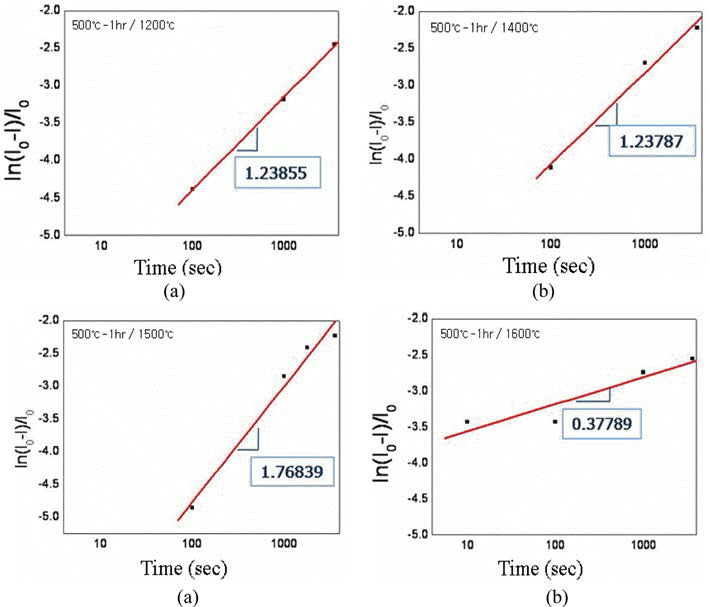
PDF Effect of oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powder fabricated by electrical explosion of wire method on the behvior of spark plasma sintering was investigated. The initial oxygen content of 6.5 wt% of as-fabricated tungsten powder was reduced to 2.3 and 0.7 wt% for the powders which were reduction-treated at 400°C for 2 hour and at 500°C for 1h in hydrogen atmosphere, respectively. The reduction-treated tungsten powders were spark-plasma sintered at 1200-1600°C for 100-3600 sec. with applied pressure of 50 MPa under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Maximun sindered density of 97% relative density was obtained under the condition of 1600°C for 1h from the tungsten powder with 0.7 wt% oxygen. Sintering activation energy of 95.85 kJ/mol−1 was obtained, which is remarkably smaller than the reported ones of 380~460 kJ/mol−1 for pressureless sintering of micron-scale tungsten powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(5): 384. CrossRef
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


