Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):288-298. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00213

- 1,104 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective approach to fabricating near β-Ti alloys via in-situ alloying during laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF). A blend of non-spherical pure Ti, 3 wt.% Fe, and 0.1 wt.% SiO2 nanoparticles was used to induce β-phase stabilization and improve flowability. Twenty-five process conditions were evaluated across a volumetric energy density range of 31.75-214.30 J/mm3, achieving a maximum relative density of 99.21% at 89.29 J/mm3. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that the β-Ti phase was partially retained at room temperature, accompanied by lattice contraction in the α’-Ti structure, indicating successful Fe incorporation. Elemental mapping confirmed that the Fe distribution was homogeneous, without significant segregation. Compared to pure Ti, the Ti-3Fe sample exhibited a 49.2% increase in Vickers hardness and notable improvements in yield and ultimate tensile strengths. These results demonstrate the feasibility of in-situ alloying with low-cost elemental powders to produce high-performance near β-Ti alloys using L-PBF.
- [Korean]
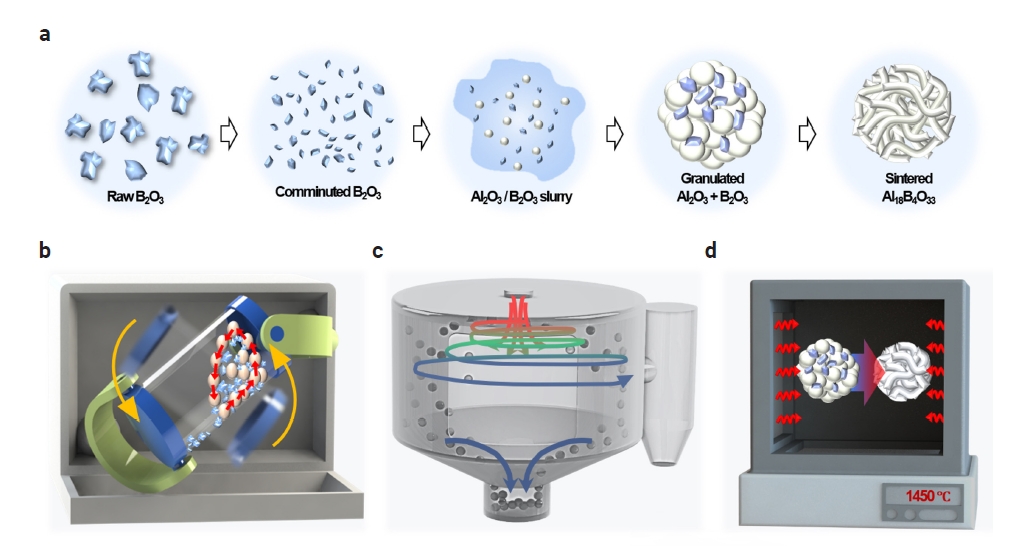
- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
- Kiho Song, Sang in Lee, Hyunseung Song, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):513-520. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00304
- 858 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ceramic materials have become essential due to their high durability, chemical stability, and excellent thermal stability in various advanced industries such as aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor. However, high-performance ceramic materials face limitations in commercialization due to the high cost of raw materials and complex manufacturing processes. Aluminum borate (Al₁₈B₄O₃₃) has emerged as a promising alternative due to its superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, despite its simple manufacturing process and low production cost. In this study, we propose a method for producing Al₁₈B₄O₃₃ spherical powder with increased uniformity and high flowability by controlling the particle size of B₂O₃. The content ratio of the manufactured Al18B4O33 spherical powder was Al2O3: B2O3 = 87:13, and it exhibited a 17% reduction in the Hausner ratio (1.04) and a 29% decrease in the angle of repose (23.9°) compared to pre-milling conditions, demonstrating excellent flowability.
- [English]
- Investigation on Microstructure and Flowability of Gas Atomized Heat-resistant KHR45A Alloy Powders for Additive Manufacturing
- Geonwoo Baek, Mohsen Saboktakin Rizi, Yeeun Lee, SungJae Jo, Joo-Hyun Choi, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):13-21. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.13

- 2,428 View
- 766 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In additive manufacturing, the flowability of feedstock particles determines the quality of the parts that are affected by different parameters, including the chemistry and morphology of the powders and particle size distribution. In this study, the microstructures and flowabilities of gas-atomized heat-resistant alloys for additive manufacturing applications are investigated. A KHR45A alloy powder with a composition of Fe-30Cr-40Mn-1.8Nb (wt.%) is fabricated using gas atomization process. The microstructure and effect of powder chemistry and morphology on the flow behavior are investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and revolution powder analysis. The results reveal the formation of spherical particles composed of single-phase FCC dendritic structures after gas atomization. SEM observations show variations in the microstructures of the powder particles with different size distributions. Elemental distribution maps, line scans, and high-resolution XPS results indicate the presence of a Si-rich oxide accompanied by Fe, Cr, and Nb metal oxides in the outer layer of the powders. The flowability behavior is found to be induced by the particle size distribution, which can be attributed to the interparticle interactions and friction of particles with different sizes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
Min Woo Shin, Sung-Jae Jo, Sourabh Kumar Soni, Ji-Woon Lee, Jongun Moon, Hyoung Seop Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 941: 148599. CrossRef - Al-based amorphous coatings by warm spraying: Numerical simulation and experimental validation
Deming Wang, Nianchu Wu, Peng Cao
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 1008: 176674. CrossRef
- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
- [Korean]
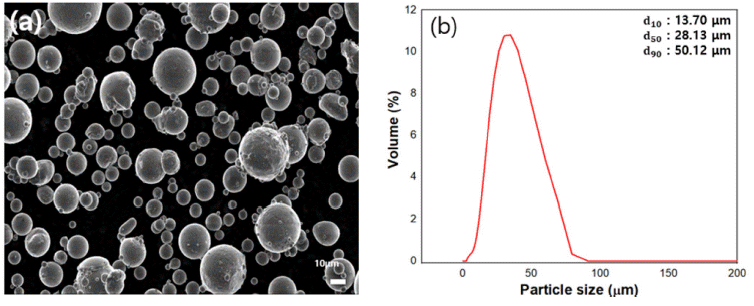
- Improving Flow Property of AlSi10Mg Powder for Additive Manufacturing via Surface Treatment using Methyltrichlorosilane
- Sang Cheol Park, In Yeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Soong Ju Oh, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):363-369. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.363
- 895 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF AlSi10Mg alloys are being actively studied through additive manufacturing for application in the automobile and aerospace industries because of their excellent mechanical properties. To obtain a consistently high quality product through additive manufacturing, studying the flowability and spreadability of the metal powder is necessary. AlSi10Mg powder easily forms an oxide film on the powder surface and has hydrophilic properties, making it vulnerable to moisture. Therefore, in this study, AlSi10Mg powder was hydrophobically modified through silane surface treatment to improve the flowability and spreadability by reducing the effects of moisture. The improved flowability according to the number of silane surface treatments was confirmed using a Carney flowmeter. In addition, to confirm the effects of improved spreadability, the powder prior to surface treatment and that subjected to surface treatment four times were measured and compared using s self-designed recoating tester. The results of this study confirmed the improved flowability and spreadability based on the modified metal powder from hydrophilic to hydrophobic for obtaining a highquality additive manufacturing product.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef
- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
- [Korean]
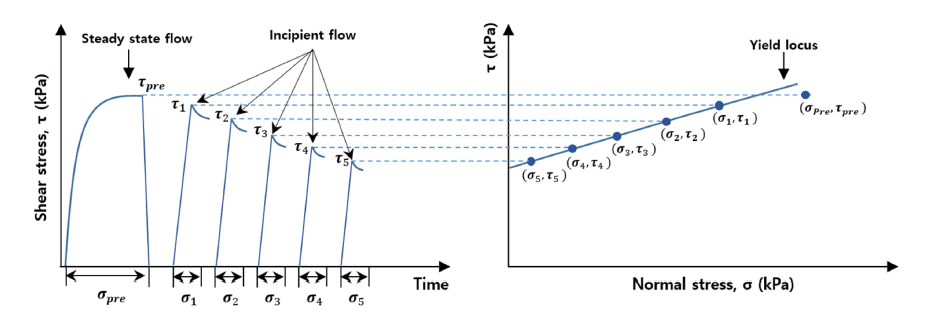
- Effect of Particle Sphericity on the Rheological Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Powders for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- T. Y. Kim, M. H. Kang, J. H. Kim, J.K. Hong, J.H. Yu, J.I. Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):99-109. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.99
- 1,704 View
- 35 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder flowability is critical in additive manufacturing processes, especially for laser powder bed fusion. Many powder features, such as powder size distribution, particle shape, surface roughness, and chemical composition, simultaneously affect the flow properties of a powder; however, the individual effect of each factor on powder flowability has not been comprehensively evaluated. In this study, the impact of particle shape (sphericity) on the rheological properties of Ti-6Al-4V powder is quantified using an FT4 powder rheometer. Dynamic image analysis is conducted on plasma-atomized (PA) and gas-atomized (GA) powders to evaluate their particle sphericity. PA and GA powders exhibit negligible differences in compressibility and permeability tests, but GA powder shows more cohesive behavior, especially in a dynamic state, because lower particle sphericity facilitates interaction between particles during the powder flow. These results provide guidelines for the manufacturing of advanced metal powders with excellent powder flowability for laser powder bed fusion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
Mingyu Chung, Kang-Hyun Lee, Jaeeun Park, Yoon Sun Lee, Gun Jin Yun
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2025; 39(11): 6847. CrossRef - Enhanced Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy with Vanadium Carbide Coating via Directed Energy Deposition
Ui Jun Ko, Ju Hyeong Jung, Jung Hyun Kang, Kyunsuk Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials.2024; 17(3): 733. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef
- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
- [Korean]
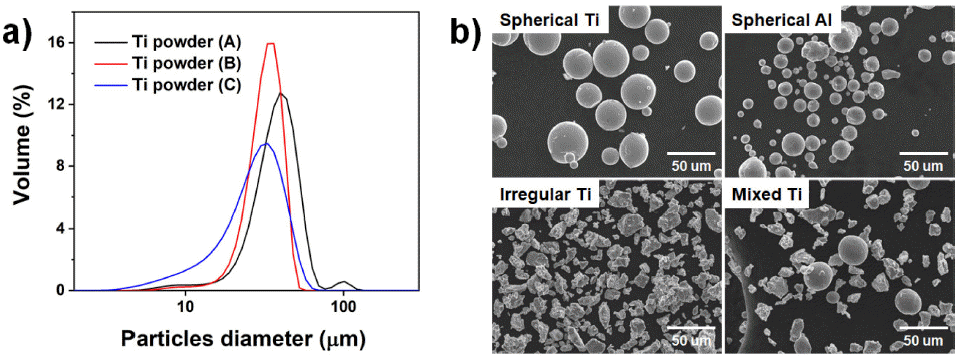
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
- Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
- 1,392 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
Yu Cao, Xiaohui Dong, Yulong Zhu, Tao Huang, Bin Jiang, Chenghang Zhang
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 263: 140. CrossRef -
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


