Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Thermal Shock Resistance of Cement Composite Incorporating Hollow Glass Microspheres
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):505-510. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.505

- 726 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The thermal shock resistance of cement composites with hollow glass microspheres (HGM) is investigated. Cement composites containing various concentrations of HGM are prepared and their properties studied. The density, thermal conductivity, and coefficient of thermal expansion of the composites decrease with increasing HGM concentration. A thermal shock test is performed by cycling between -60 and 50ºC. After the thermal shock test, the compressive strength of the cement composite without HGM decreases by 28.4%, whereas the compressive strength of the cement composite with 30 wt% HGM decreases by 5.7%. This confirms that the thermal shock resistance of cement is improved by the incorporation of HGM. This effect is attributed to the reduction of the thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the cement composite because of the incorporation of HGM, thereby reducing the occurrence of defects due to external temperature changes.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Hollow Structures using One-pot Wet Chemical Process
- Duk-Hee Lee, Kyung-Soo Park, Jae-Ryang Park, Chan-Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):132-138. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.132

- 512 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A facile one-pot wet chemical process to prepare pure anatase TiO2 hollow structures using ammonium hexafluorotitanate as a precursor is developed. By defining the formic acid ratio, we fabricate TiO2 hollow structures containing fluorine on the surface. The TiO2 hollow sphere is composed of an anatase phase containing fluorine by various analytical techniques. A possible formation mechanism for the obtained hollow samples by self-transformation and Ostwald ripening is proposed. The TiO2 hollow structures containing fluorine exhibits 1.2 - 2.7 times higher performance than their counterparts in photocatalytic activity. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of the TiO2 hollow structures is attributed to the combined effects of high crystallinity, specific surface area (62 m2g-1), and the advantage of surface fluorine ions (at 8%) having strong electron-withdrawing ability of the surface ≡ Ti-F groups reduces the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Ni(OH)2 Hollow Spheres by Solvent Displacement Crystallization Using Micro-Injection Device
- Seiki Kim, Kyungsoo Park, Kwang-Il Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):311-316. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.311
- 998 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
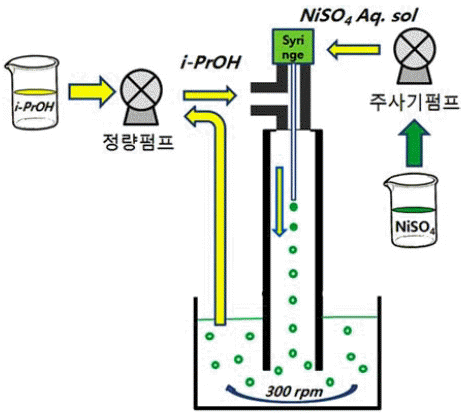
PDF Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres have been prepared by solvent displacement crystallization using a micro-injection device, and the effect of process parameters such as concentration and the relative ratio of the injection speed of the precursor solution, which is an aqueous solution of NiSO4·6H2O, to isopropyl alcohol of displacement solvent have been investigated. The crystal phases after NaOH treatment are in the β-phase for all process parameters. A higher concentration of NiSO4·6H2O aqueous solution is injected by a micro-injection device and bigger Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres with a narrower particle size distribution are formed. The crystallinity and hardness of the as-obtained powder are so poor that hydrothermal treatment of the as-obtained Ni(OH)2 at 120°C for 24 h in distilled water is performed in order to greatly improve the crystallinity. It is thought that a relative ratio of the injection speed of NiSO4·6H2O to that of isopropyl alcohol of at least more than 1 is preferable to synthesize Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres. It is confirmed that this solution- based process is very effective in synthesizing ceramic hollow spheres by simple adjustment of the process parameters such as the concentration and the injection speed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
Dong Yeon Kim, Young-Min Jeong, Seong-Ho Baek, Injoon Son
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(3): 231. CrossRef
- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of KIT-1 Mesoporous Silicates Showing Two Different Macrosporous Strucrtues; Inverse-opal or Hollow Structures
- Youn-Kyoung Baek, Jung-Goo Lee, Young Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):189-194. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.189
- 572 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
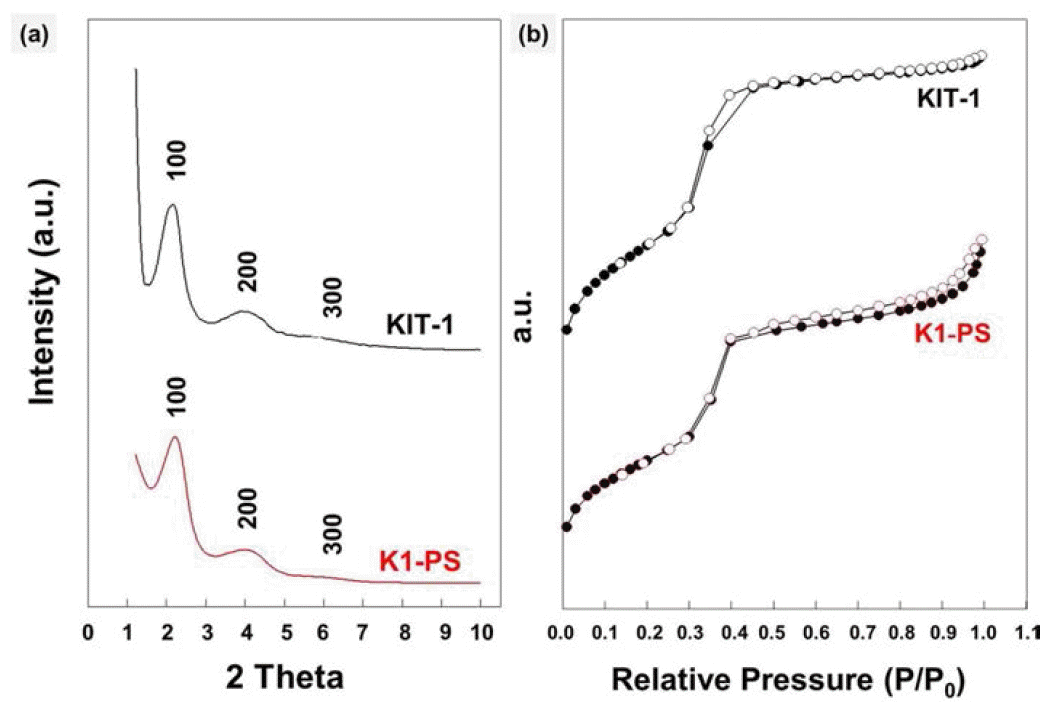
PDF We report a facile method for preparing KIT-1 mesoporous silicates with two different macroporous structures by dual templating. As a template for macropores, polystyrene (PS) beads are assembled into uniform three dimensional arrays by ice templating, i.e., by growing ice crystals during the freezing process of the particle suspension. Then, the polymeric templates are directly introduced into the precursor-gel solution with cationic surfactants for templating the mesopores, which is followed by hydrothermal crystallization and calcination. Later, by burning out the PS beads and the surfactants, KIT-1 mesoporous silicates with macropores are produced in a powder form. The macroporous structures of the silicates can be controlled by changing the amount of EDTANa4 salt under the same templating conditions using the PS beads and inverse-opal or hollow structures can be obtained. This strategy to prepare mesoporous powders with controllable macrostructures is potentially useful for various applications especially those dealing with bulky molecules such as, catalysis, separation, drug carriers and environmental adsorbents.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


