Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):375-382. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00248
- 1,107 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
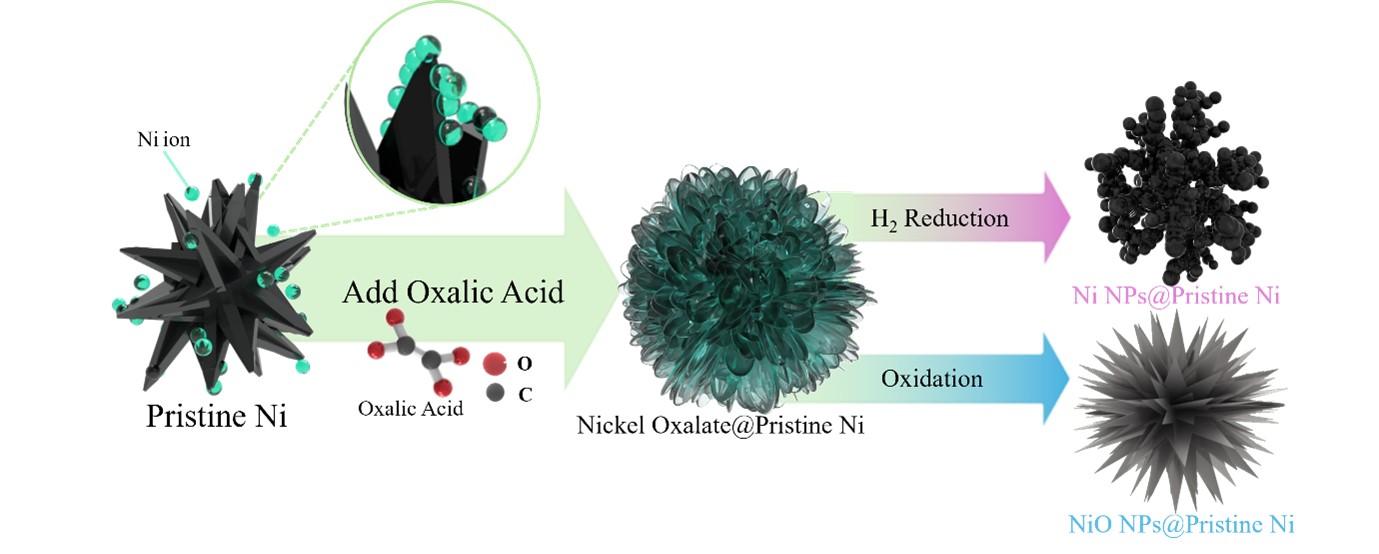
PDF - Nickel is widely used in industrial fields such as electrocatalysis and energy storage devices. Although micron-sized nickel particles exhibit excellent mechanical durability, their low specific surface area limits their reactivity. We modified the surface of micron-sized nickel particles with nanostructured nickel oxalate and investigated the effects of the solvent dielectric constant, surfactant, and thermal treatment atmosphere on the resulting particle morphology and phase transformation. Rietveld refinement analysis confirmed that changes in the solvent dielectric constant led to increased or diminished crystallinity of specific planes in nickel oxalate, resulting in diffraction patterns distinct from standard JCPDS data. These structural changes were also found to influence the morphology of the synthesized nickel oxalate. The results demonstrate that nickel oxalate serves as an effective precursor for producing Ni and NiO phases, and shape control of the final product can increase the surface reactivity of micron-sized nickel materials.
- [Korean]
- Modulation of Microstructure and Energy Storage Performance in (K,Na)NbO3-Bi(Ni,Ta)O3 Ceramics through Zn Doping
- Jueun Kim, Seonhwa Park, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):509-515. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.509
- 904 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
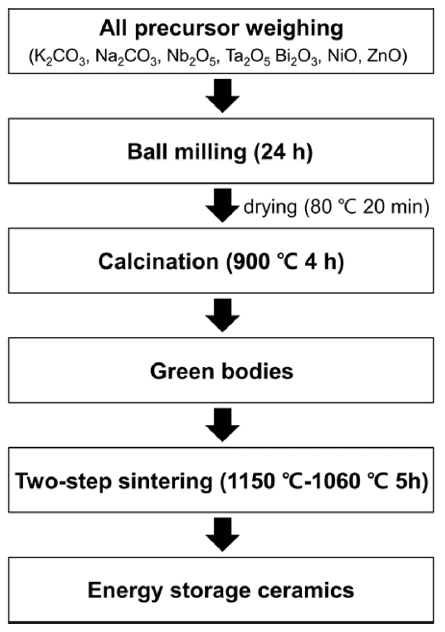
PDF Lead-free perovskite ceramics, which have excellent energy storage capabilities, are attracting attention owing to their high power density and rapid charge-discharge speed. Given that the energy-storage properties of perovskite ceramic capacitors are significantly improved by doping with various elements, modifying their chemical compositions is a fundamental strategy. This study investigated the effect of Zn doping on the microstructure and energy storage performance of potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics. Two types of powders and their corresponding ceramics with compositions of (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3 (KNN-BNT) and (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni1/3Zn1/3Ta1/3) O3 (KNN-BNZT) were prepared via solid-state reactions. The results indicate that Zn doping retards grain growth, resulting in smaller grain sizes in Zn-doped KNN-BNZT than in KNN-BNT ceramics. Moreover, the Zn-doped KNNBNZT ceramics exhibited superior energy storage density and efficiency across all x values. Notably, 0.9KNN-0.1BNZT ceramics demonstrate an energy storage density and efficiency of 0.24 J/cm3 and 96%, respectively. These ceramics also exhibited excellent temperature and frequency stability. This study provides valuable insights into the design of KNNbased ceramic capacitors with enhanced energy storage capabilities through doping strategies.
- [Korean]
- Recent progress on Performance Improvements of Thermoelectric Materials using Atomic Layer Deposition
- Seunghyeok Lee, Tae Joo Park, Seong Keun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):56-62. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.56
- 1,632 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
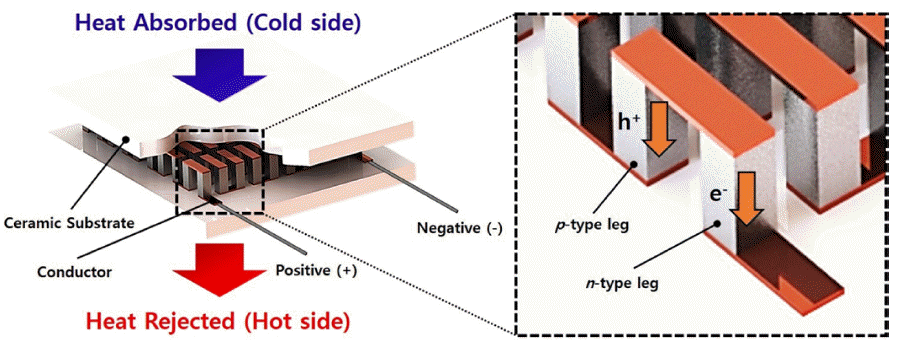
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a promising technology for the uniform deposition of thin films. ALD is based on a self-limiting mechanism, which can effectively deposit thin films on the surfaces of powders of various sizes. Numerous studies are underway to improve the performance of thermoelectric materials by forming core-shell structures in which various materials are deposited on the powder surface using ALD. Thermoelectric materials are especially relevant as clean energy storage materials due to their ability to interconvert between thermal and electrical energy by the Seebeck and Peltier effects. Herein, we introduce a surface and interface modification strategy based on ALD to control the performance of thermoelectric materials. We also discuss the properties of the interface between various deposition materials and thermoelectric materials.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Graphene Coated Aluminum Powders by Self-assemble Reaction
- Jin Uk Hwang, Woo Seong Tak, Sang Yong Nam, Woo Sik Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):383-388. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.383

- 950 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To improve the mechanical properties of aluminum, graphene has been used as a reinforcing material, yielding graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites (GRAMCs). Dispersion of graphene materials is an important factor that affects the properties of GRAMCs, which are mainly manufactured by mechanical mixing methods such as ball milling. However, the use of only mechanical mixing process is limited to achieve homogeneous dispersion of graphene. To overcome this problem, in this study, we have prepared composite materials by coating aluminum particles with graphene by a self-assembly reaction using poly vinylalcohol and ethylene diamine as coupling agents. The scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy results confirm the coating of graphene on the Al surface. Bulk density of the sintered composites by spark plasma sintering achieved a relative density of over 99% up to 0.5 wt.% graphene oxide content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- Atomic Layer Deposition for Powder Coating
- Seok Choi, Jeong Hwan Han, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):243-250. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.243
- 2,064 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
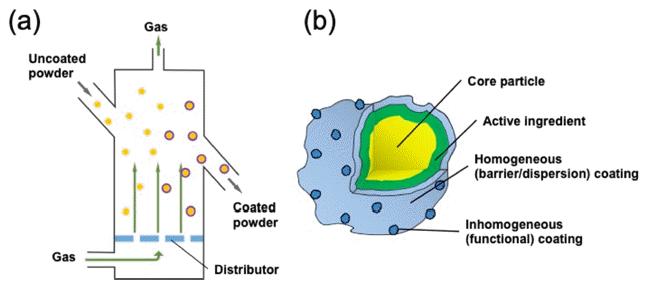
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is widely used as a tool for the formation of near-atomically flat and uniform thin films in the semiconductor and display industries because of its excellent uniformity. Nowadays, ALD is being extensively used in diverse fields, such as energy and biology. By controlling the reactivity of the surface, either homogeneous or inhomogeneous coating on the shell of nanostructured powder can be accomplished by the ALD process. However, the ALD process on the powder largely depends on the displacement of powder in the reactor. Therefore, the technology for the fluidization of the powder is very important to redistribute its position during the ALD process. Herein, an overview of the three types of ALD reactors to agitate or fluidize the powder to improve the conformality of coating is presented. The principle of fluidization its advantages, examples, and limitations are addressed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-performance of ZnO/TiO2 heterostructured thin-film photocatalyst fabricated via atomic layer deposition
Ji Young Park, Jeong Hwan Han, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - TiO2 Thin Film Coating on an Nb-Si–Based Superalloy via Atomic Layer Deposition
Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 255. CrossRef - Atomic layer deposition of ZnO layers on Bi2Te3 powders: Comparison of gas fluidization and rotary reactors
Myeong Jun Jung, Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hwan Han, Young-In Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Min Hwan Lee, Byung Joon Choi
Ceramics International.2022; 48(24): 36773. CrossRef
- High-performance of ZnO/TiO2 heterostructured thin-film photocatalyst fabricated via atomic layer deposition
- [English]
- Nanodiamonds Conjugated with Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs for Transdermal Delivery
- Changkyu Rhee, Alexey P. Puzyr, Andrey E. Burov, Olga G. Burova, Whungwhoe Kim, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):459-465. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.459
- 806 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
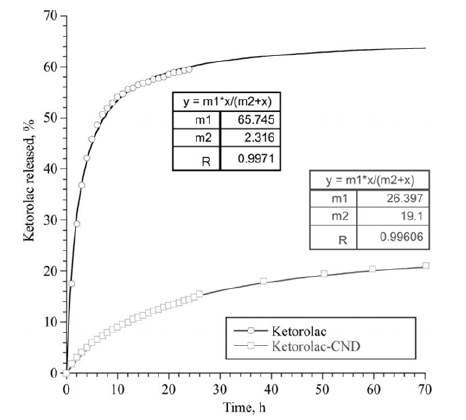
PDF Most commercially available detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) require further processing to qualify for use in biomedical applications, as they often contain many impurities and exhibit poor dispersibility in aqueous media. In this work, DNDs are modified to improve purity and impart a high colloidal stability to the particles. The dispersive and adsorption properties of modified DNDs are evaluated in terms of the suitability of DNDs as carriers for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in transdermal delivery. The study of adsorption on strongly positively and strongly negatively charged DNDs showed their high loading capacity for NSAIDs, and a pronounced relationship between the drugs and the particles’ charges. Experiments on long-term desorption carried out with DND/NSAID complexes indicate that the nanoparticles exert a sustained effect on the drug release process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling the trending paradigms of synthesis and theranostic biomedical potentials of nano-diamonds (NDs) - a state-of-the-art update
Sagnik Nag, Kedlaya Srikrishna H. Damodar, Swayambhik Mukherjee, Dinesh R. Rao, Ipsita Debnath, Sree Haryini, Sourav Mohanto, Mohammed Gulzar Ahmed, Vetriselvan Subramaniyan
Inorganic Chemistry Communications.2025; 177: 114313. CrossRef
- Unveiling the trending paradigms of synthesis and theranostic biomedical potentials of nano-diamonds (NDs) - a state-of-the-art update
- [Korean]
- Improved Luminescent Characterization and Synthesis of InP/ZnS Quantum Dot with High-Stability Precursor
- Eun-Jin Lee, Jong-Woo Moon, Yang-Do Kim, Pyung-Woo Shin, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):385-390. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.385
- 1,128 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
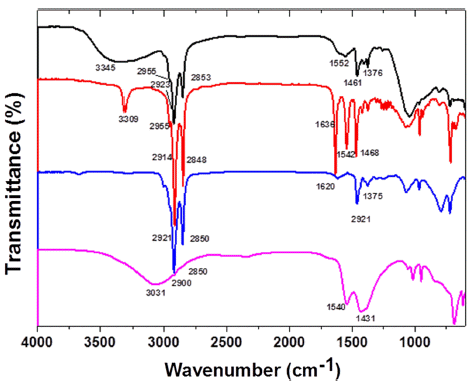
PDF We report a synthesis of non-toxic InP nanocrystals using non-pyrolytic precursors instead of pyrolytic and unstable tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine, a popular precursor for synthesis of InP nanocrystals. In this study, InP nanocrystals are successfully synthesized using hexaethyl phosphorous triamide (HPT) and the synthesized InP nanocrystals showed a broad and weak photoluminescence (PL) spectrum. As synthesized InP nanocrystals are subjected to further surface modification process to enhance their stability and photoluminescence. Surface modification of InP nanocrystals is done at 230°C using 1-dodecanethiol, zinc acetate and fatty acid as sources of ZnS shell. After surface modification, the synthesized InP/ZnS nanocrystals show intense PL spectra centered at the emission wavelength 612 nm through 633 nm. The synthesized InP/ZnS core/shell structure is confirmed with X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Inductively Coupled Plasma - Atomic Emission Spectrometer (ICP-AES). After surface modification, InP/ZnS nanocrystals having narrow particle size distribution are observed by Field Emission Transmission Electron Microscope (FE-TEM). In contrast to uncapped InP nanocrystals, InP/ZnS nanocrystals treated with a newly developed surface modified procedure show highly enhanced PL spectra with quantum yield of 47%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
Hyun Seon Hong, Yerin Kim, Jea Hyung Kim, Hyeon Seon Ryu, Dahye Song
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025; 62(3): 472. CrossRef - Synthesis and Properties of InP/ZnS core/shell Nanoparticles with One-pot process
So Yeong Joo, Myung Hwan Hong, Leeseung Kang, Tae Hyung Kim, Chan Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(1): 11. CrossRef
- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface Modification of Ti Substrate to Improve the Dispersion of Catalytic Metals on Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes
- Seoung Yeol Kwak, Ho Gyu Kim, Jong Min Byun, Ju Hyuk Park, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.28
- 894 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
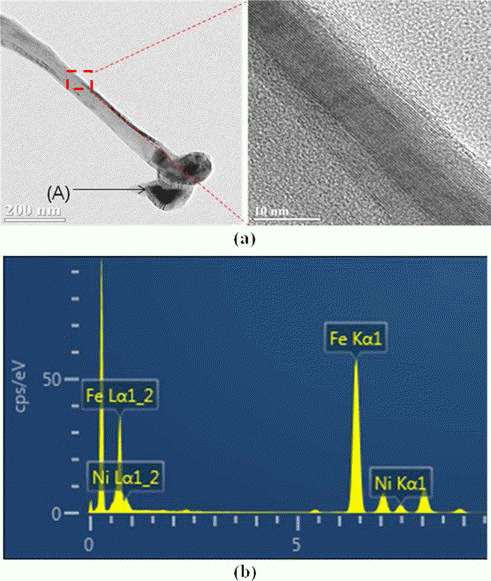
PDF This paper describes the surface modification effect of a Ti substrate for improved dispersibility of the catalytic metal. Etching of a pure titanium substrate was conducted in 50% H2SO4, 50°C for 1 h-12 h to observe the surface roughness as a function of the etching time. At 1 h, the grain boundaries were obvious and the crystal grains were distinguishable. The grain surface showed micro-porosities owing to the formation of micro-pits less than 1 μm in diameter. The depths of the grain boundary and micro-pits appear to increase with etching time. After synthesizing the catalytic metal and growing the carbon nano tube (CNT) on Ti substrate with varying surface roughness, the distribution trends of the catalytic metal and grown CNT on Ti substrate are discussed from a micro-structural perspective.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
Madhavi Konni, Anima S. Dadhich, Saratchandra Babu Mukkamala
Sustainable Energy & Fuels.2018; 2(2): 466. CrossRef - Influence of nickel nanoparticles on hydrogen storage behaviors of MWCNTs
Ye-Ji Han, Soo-Jin Park
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 85. CrossRef - Spontaneous Formation of Titanium Nitride on the Surface of a Ti Rod Induced by Electro-Discharge-Heat-Treatment in an N2 Atmosphere
W.H. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, Y.K. Lee, J.Y. Kim, S.Y. Chang
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1281. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
- Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


