Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
- Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):384-388. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.384

- 895 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of the mixing method on the characteristics of hybrid-structure W powder with nano and micro sizes is investigated. Fine WO3 powders with sizes of ~0.6 μm, prepared by ball milling for 10 h, are mixed with pure W powder with sizes of 12 μm by various mixing process. In the case of simple mixing with ball-milled WO3 and micro sized W powders, WO3 particles are locally present in the form of agglomerates in the surface of large W powders, but in the case of ball milling, a relatively uniform distribution of WO3 particles is exhibited. The microstructural observation reveals that the ball milled WO3 powder, heat-treated at 750°C for 1 h in a hydrogen atmosphere, is fine W particles of ~200 nm or less. The powder mixture prepared by simple mixing and hydrogen reduction exhibits the formation of coarse W particles with agglomeration of the micro sized W powder on the surface. Conversely, in the powder mixture fabricated by ball milling and hydrogen reduction, a uniform distribution of fine W particles forming nano-micro sized hybrid structure is observed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Efficiency of Radiation Shielding Sheet to Reduce Radiation Exposure during C-arm Fluoroscopy
Hosang Jeon, Won Chul Shin, Hee Yun Seol, Yongkan Ki, Kyeong Baek Kim, Ki Seok Choo, Sang Don Lee, Suk-Woong Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 111. CrossRef - Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef - Facile phosphorus-embedding into SnS2 using a high-energy ball mill to improve the surface kinetics of P-SnS2 anodes for a Li-ion battery
Hongsuk Choi, Seungmin Lee, KwangSup Eom
Applied Surface Science.2019; 466: 578. CrossRef - Hydrogen reduction behavior and microstructural characteristics of WO3 and WO3-NiO powders
Hyunji Kang, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 80: 69. CrossRef - Fabrication of Densified W-Ti by Reaction Treatment and Spark Plasma Sintering of WO3-TiH2 Powder Mixtures
Hyunji Kang, Heun Joo Kim, Ju-Yeon Han, Yunju Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(9): 511. CrossRef
- The Efficiency of Radiation Shielding Sheet to Reduce Radiation Exposure during C-arm Fluoroscopy
- [Korean]
- Effect of Heat Treatment Atmosphere on the Microstructure of TiH2-MoO3 Powder Mixtures
- Ki Cheol Jeon, Sung Hyun Park, Na-Yeon Kwon, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):303-306. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.303
- 915 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
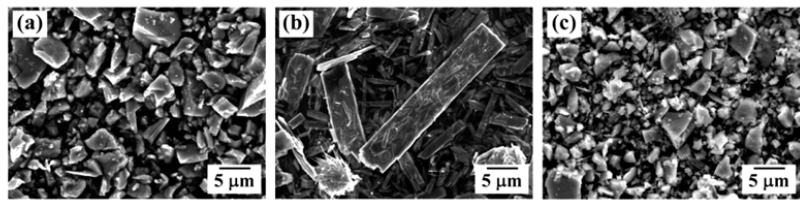
PDF An optimum route to synthesize Ti-Mo system powders is investigated by analyzing the effect of the heat treatment atmosphere on the formation of the reaction phase by dehydrogenation and hydrogen reduction of ball-milled TiH2-MoO3 powder mixtures. Homogeneous powder mixtures with refined particles are prepared by ball milling for 24 h. XRD analysis of the heat-treated powder in a hydrogen atmosphere shows TiH2 and MoO3 peaks in the initial powders as well as the peaks corresponding to the reaction phase species, such as TiH0.7, TiO, MoO2, Mo. In contrast, powder mixtures heated in an argon atmosphere are composed of Ti, TiO, Mo and MoO3 phases. The formation of reaction phases dependent on the atmosphere is explained by the partial pressure of H2 and the reaction temperature, based on thermodynamic considerations for the dehydrogenation reaction of TiH2 and the reduction behavior of MoO3.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of titanium addition on mechanical properties of Mo-Si-B alloys
Won June Choi, Seung Yeong Lee, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Jong Min Byun, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 80: 238. CrossRef
- Effect of titanium addition on mechanical properties of Mo-Si-B alloys
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sublimable Vehicle Compositions in the Camphor-Naphthalene System on the Pore Structure of Porous Cu-Ni
- Na-Yeon Kwon, Myung-Jin Suka, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):362-366. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.362
- 1,096 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
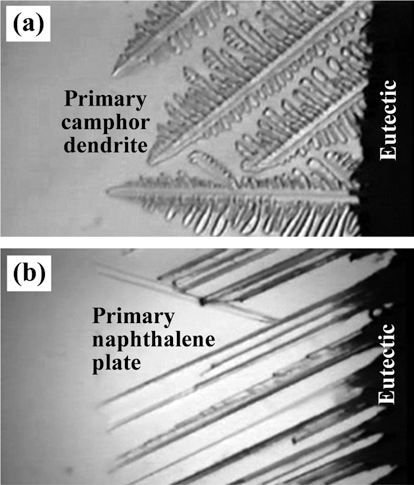
PDF The effect of sublimable vehicle composition in the camphor-naphthalene system on the pore structure of porous Cu-Ni alloy is investigated. The CuO-NiO mixed slurries with hypoeutectic, eutectic and hypereutectic compositions are frozen into a mold at -25°C. Pores are generated by sublimation of the vehicles at room temperature. After hydrogen reduction at 300°C and sintering at 850°C for 1 h, the green body of CuO-NiO is completely converted to porous Cu-Ni alloy with various pore structures. The sintered samples show large pores which are aligned parallel to the sublimable vehicle growth direction. The pore size and porosity decrease with increase in powder content due to the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry. In the hypoeutectic composition slurry, small pores with dendritic morphology are observed in the sintered Cu-Ni, whereas the specimen of hypereutectic composition shows pore structure of plate shape. The change of pore structure is explained by growth behavior of primary camphor and naphthalene crystals during solidification of camphor-naphthalene alloys.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Freeze Drying Process and Pore Structure Characteristics of Porous Cu with Various Sublimable Vehicles
Gyuhwi Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Myung-Jin Suk, Young-Keun Jeong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 198. CrossRef - Interaction of Solid Particles with the Solidifying Front in the Liquid-Particle Mixture
Ho-Suk Lee, Kyu-Hee Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Myung-Jin Suk
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(4): 336. CrossRef
- Freeze Drying Process and Pore Structure Characteristics of Porous Cu with Various Sublimable Vehicles
- [Korean]
- Effect of Powder Characteristic and Freeze Condition on the Pore Characteristics of Porous W
- Na-Yeon Kwon, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(4):259-263.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.4.259

- 911 View
- 1 Download
- 12 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dependence of the freeze-drying process condition on microstructure of porous W and pore formation mechanism were studied. Camphene slurries with WO_3 contents of 10 vol% were prepared by milling at 50°C with a small amount of dispersant. Freezing of a slurry was done in Teflon cylinder attached to a copper bottom plate cooled at -25°C. Pores were generated subsequently by sublimation of the camphene during drying in air for 48 h. The green body was hydrogen-reduced at 800°C for 30 min, and sintered in the furnace at 900°C for 1 h. After heat treatment in hydrogen atmosphere, WO_3 powders were completely converted to metallic W without any reaction phases. The sintered samples showed large pores with the size of about 70µm which were aligned parallel to the camphene growth direction. Also, the internal wall of large pores and near bottom part of specimen had relatively small pores with dendritic structure due to the growth of camphene dendrite depending on the degree of nucleation and powder rearrangement in the slurry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Porous TiO2 with Aligned Pores Using Tert-Butyl Alcohol Based Freeze Casting
Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(12): 929. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous W-Ti by Freeze-Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of WO3-TiH2 Powder Mixtures
Hyunji Kang, Sung Hyun Park, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 472. CrossRef - Synthesis of Aligned Porous Sn by Freeze-Drying of Tin Chloride/camphene Slurry
수룡 방, 승탁 오
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(1): 27~31. CrossRef - Effect of Sublimable Vehicle Compositions in the Camphor-NaphthaleneSystem on the Pore Structure of Porous Cu-Ni
Na-Yeon Kwon, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(5): 362. CrossRef - Porous Mo–30wt.% W alloys synthesized from camphene/MoO3–WO3 slurry by freeze drying and sintering process
Ki Cheol Jeon, Beom Seok Kim, Young Do Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 32. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous Cu-Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of CuO-NiO Powder Mixture
Han Gil Seo, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Synthesis of porous Cu–Sn using freeze-drying process of CuO–SnO2/camphene slurries
Sung-Tag Oh, Wonsuk Lee, Si Young Chang, Myung-Jin Suk
Research on Chemical Intermediates.2014; 40(7): 2495. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous Cu by Freeze-drying Process of Camphene Slurry with CuO-coated Cu Powders
Su-Ryong Bang, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(3): 191. CrossRef - Effect of Solidification Condition of Sublimable Vehicles on the Pore Characteristics in Freeze Drying Process
Myung-Jin Suk, Ji Soon Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 366. CrossRef - Freeze Drying for Porous Mo with Sublimable Vehicles of Eutectic System
Gyu-Tae Lee, Han Gil Seo, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(4): 253. CrossRef - Synthesis of Porous Cu-Sn by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction Treatment of Metal Oxide Composite Powders
Min-Sung Kim, Ho-Suk Yoo, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2013; 23(12): 722. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous Mo by Freeze-Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of MoO3/Camphene Slurry
Wonsuk Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(6): 446. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Porous TiO2 with Aligned Pores Using Tert-Butyl Alcohol Based Freeze Casting
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


