Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Study on the Recovery Silver and Nanoparticles Synthesis from LTCC By-products of Lowly Concentrated Silver
- Soyeong Joo, Nak-Kyoon Ahn, Chan Gi Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):232-239. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.232
- 853 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
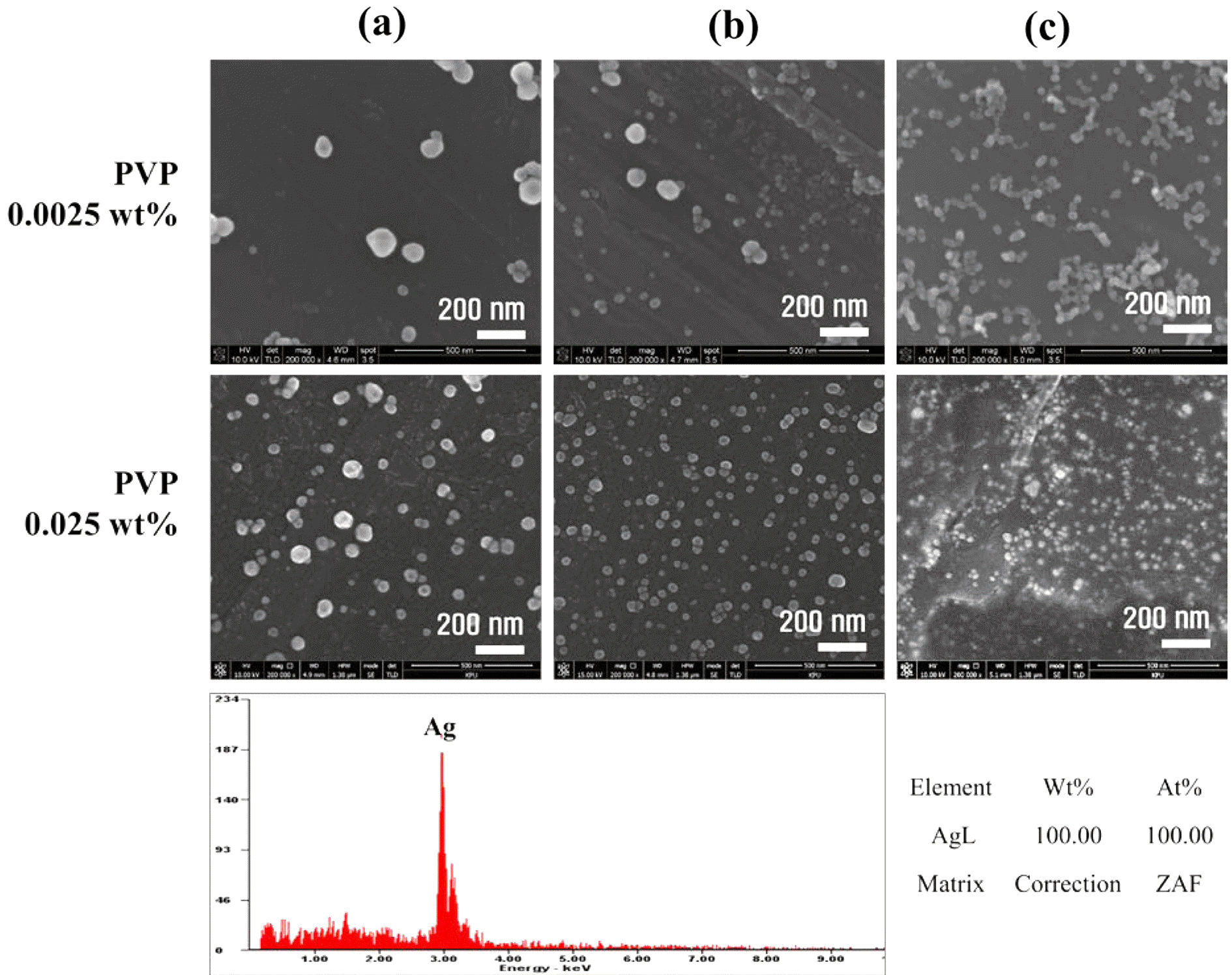
PDF In this paper, the recovery and nanoparticle synthesis of Ag from low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) by-products are studied. The effect of reaction behavior on Ag leaching conditions from the LTCC by-products is confirmed. The optimum leaching conditions are determined to be: 5 M HNO3, a reaction temperature of 75°C, and a pulp density of 50 g/L at 60 min. For the selective recovery of Ag, the [Cl]/[Ag] equivalence ratio experiment is performed using added HCl; most of the Ag (more than 99%) is recovered. The XRD and MP-AES results confirm that the powder is AgCl and that impurities are at less than 1%. Ag nanoparticles are synthesized using a chemical reduction process for recycling, NaBH4 and PVP are used as reducing agents and dispersion stabilizers. UV-vis and FE-SEM results show that AgCl powder is precipitated and that Ag nanoparticles are synthesized. Ag nanoparticles of 100% Ag are obtained under the chemical reaction conditions.
- [Korean]
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):315-320. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.315

- 492 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There has been much interest in recycling electronic wastes in order to mitigate environmental problems and to recover the large amount of constituent metals. Silver recovery from electronic waste is extensively studied because of environmental and economic benefits and the use of silver in fabricating nanodevices. Hydrometallurgical processing is often used for silver recovery because it has the advantages of low cost and ease of control. Research on synthesis recovered silver into nanoparticles is needed for application to transistors and solar cells. In this study, silver is selectively recovered from the by-product of electrodes. Silver precursors are prepared using the dissolution characteristics of the leaching solution. In the liquid reduction process, silver nanoparticles are synthesized under various surfactant conditions and then analyzed. The purity of the recovered silver is 99.24%, and the average particle size of the silver nanoparticles is 68 nm.
- [Korean]
- Leaching behavior of Ga and In from MOCVD dust
- Kyung-Soo Park, Basudev Swain, Lee Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):202-206. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.202
- 971 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Leaching of MOCVD dust in the LED industry is an essential stage for hydro-metallurgical recovery of pure Ga and In. To recover Ga and In, the leaching behavior of MOCVD scrap of an LED, which contains significant amounts of Ga, In, Al and Fe in various phases, has been investigated. The leaching process must be performed effectively to maximize recovery of Ga and In metals using the most efficient lixiviant. Crystalline structure and metallic composition of the raw MOCVD dust were analyzed prior to digestion. Subsequently, various mineral acids were tested to comprehensively study and optimize the leaching parameters such as acidity, pulp density, temperature and time. The most effective leaching of Ga and In was observed for a boiling 4 M HCl solution vigorously stirred at 400 rpm. Phase transformation of GaN into gallium oxide by heat treatment also improved the leaching efficiency of Ga. Subsequently high purity Ga and In can be recovered by series of hydro processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
Byoungyong Im, Basudev Swain, Chan Gi Lee, Jae Layng Park, Kyung-Soo Park, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(5): 80. CrossRef - Fabrication of High Purity Ga-containing Solution using MOCVD dust
Duk-Hee Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kyung-Soo Park, Myung-Hwan Hong, Chan-Gi Lee, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(4): 50. CrossRef - Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 278. CrossRef
- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
- [Korean]
- Development of Pre-treatment for Tin Recovery from Waste Resources
- Y. H Jin, D. H Jang, H. C Jung, K. W Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):142-146. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.142
- 691 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
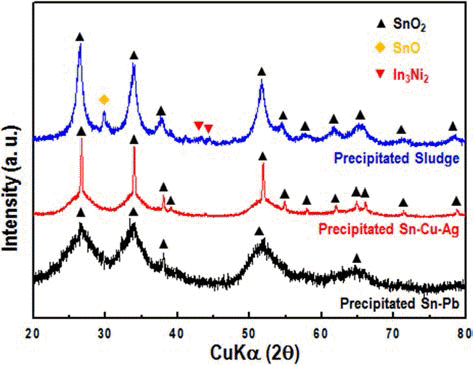
PDF Fundamental experiences have been studied for development of pre-treatment process of Sn by-products such as solders. Dry and wet separation/recovery processes were considered by the differences of physical properties. The by-products, which are analyzed by solder metal and oxides. The metal and oxide were simply separated by dry ball-milling process for 12 hours, after that recovery metal powder might be reusable as lead or lead-free solders. In terms of wet separation process, samples were dissolved in HNO3 + H2O2 and the precipitation were analyzed by SnO2. Overall efficiency of recovery might be increasing via developing simple pre-treatment process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Material Flow Analysis for Stable Supply and Demand Management of Tin
Sang Hyun Oh, Hong-Yoon Kang, Yong Woo Hwang, Doo Hwan Kim, Kayoung Shin, Nam Seok Kim
Resources Recycling.2023; 32(4): 18. CrossRef - The Current Status and Securing Strategies of tin Resources for Future Core Industries
Hoseok Jeon, Dohyun Jeong, Yeoni Chu, Seongmin Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Mineral and Energy Resources Engineers.2022; 59(4): 408. CrossRef
- Material Flow Analysis for Stable Supply and Demand Management of Tin
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


