Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):375-382. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00248
- 1,107 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
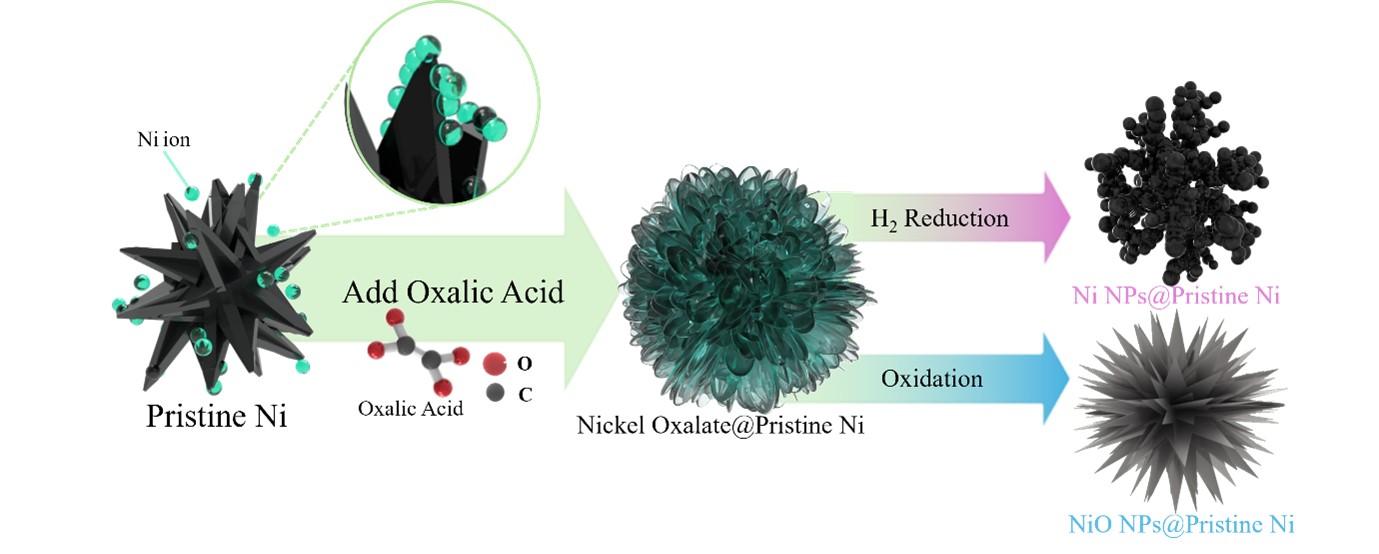
PDF - Nickel is widely used in industrial fields such as electrocatalysis and energy storage devices. Although micron-sized nickel particles exhibit excellent mechanical durability, their low specific surface area limits their reactivity. We modified the surface of micron-sized nickel particles with nanostructured nickel oxalate and investigated the effects of the solvent dielectric constant, surfactant, and thermal treatment atmosphere on the resulting particle morphology and phase transformation. Rietveld refinement analysis confirmed that changes in the solvent dielectric constant led to increased or diminished crystallinity of specific planes in nickel oxalate, resulting in diffraction patterns distinct from standard JCPDS data. These structural changes were also found to influence the morphology of the synthesized nickel oxalate. The results demonstrate that nickel oxalate serves as an effective precursor for producing Ni and NiO phases, and shape control of the final product can increase the surface reactivity of micron-sized nickel materials.
- [English]
- Design of Conductive Inks Containing Carbon Black and Silver Nanowires for Patternable Screen-Printing on Fabrics
- Seokhwan Kim, Geumseong Lee, Jinwoo Park, Dahye Shin, Ki-Il Park, Kyoung Jin Jung, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):500-507. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00409
- 1,989 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
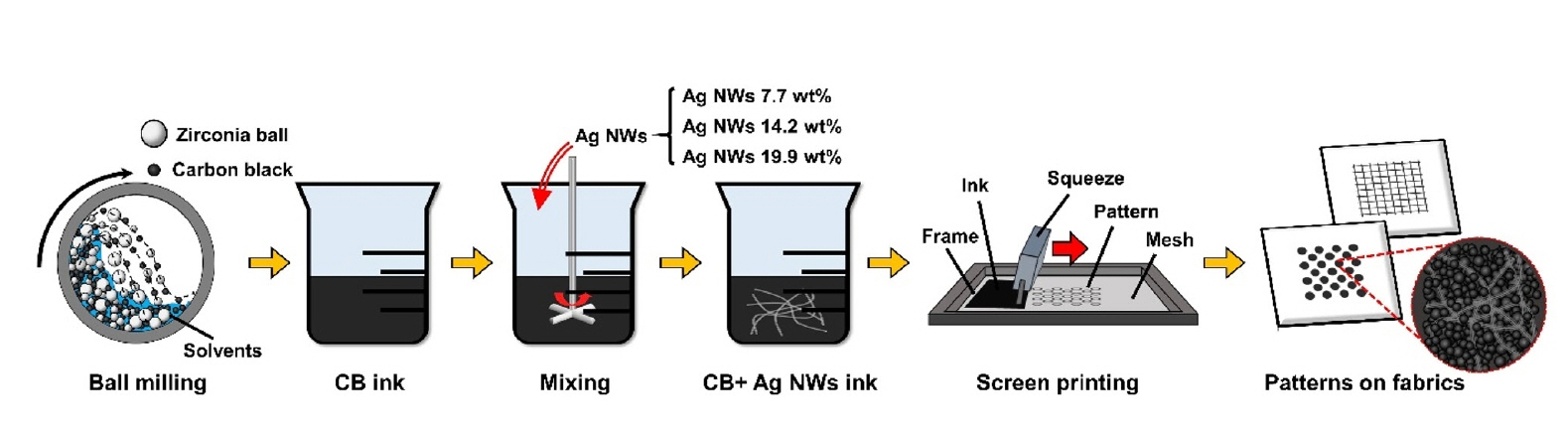
PDF - This study developed conductive inks composed of carbon black (CB) and silver nanowires (Ag NWs) for cost-effective screen-printing on fabrics. The Ag NW density within the CB matrix was precisely controlled, achieving tunable electrical conductivity with minimal Ag NW usage. The resulting inks were successfully patterned into shapes such as square grids and circles on textile surfaces, demonstrating excellent conductivity and fidelity. Adding 19.9 wt% Ag NWs reduced sheet resistance by ~92% compared to CB-only inks, highlighting the effectiveness and potential of this hybrid approach for cost-effective, high-performance textile-based electronics. The one-dimensional morphology of Ag NWs facilitated the formation of conductive percolation networks, creating efficient electron pathways within the CB matrix even at low loadings. This work advances the field of CB-based conductive inks and provides a scalable and practical method for producing functional, patterned electronic textiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
Nahid Islam, Manisha Das, Bashir Ahmed Johan, Syed Shaheen Shah, Atif Saeed Alzahrani, Md. Abdul Aziz
ACS Applied Electronic Materials.2025; 7(16): 7503. CrossRef
- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
- Youngmoo Kim, Sung Ho Yang, Seong Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):373-380. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.373
- 1,073 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to investigate the densification behavior and the corresponding microstructural evolution of tantalum and tantalum-tungsten alloy powders for explosively formed liners. The inherent inhomogeneous microstructures of tantalum manufactured by an ingot metallurgy might degrade the capability of the warhead. Therefore, to overcome such drawbacks, powder metallurgy was incorporated into the near-net shape process in this study. Spark plasma-sintered tantalum and its alloys with finer particle sizes exhibited higher densities and lower grain sizes. However, they were contaminated from the graphite mold during sintering. Higher compaction pressures in die and isostatic compaction techniques also enhanced the sinterability of the tantalum powders; however, a full densification could not be achieved. On the other hand, the powders exhibited full densification after being subjected to hot isostatic pressing over two times. Consequently, it was found that the hot isostatic-pressed tantalum might exhibit a lower grain size and a higher density as compared to those obtained in previous studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the phase evolution and elemental distribution in MoWTaNbVTix manufactured via powder metallurgical approach
Surya T. Bijjala, Ryan Wilkerson, Chad Beamer, Pankaj Kumar
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 135(11-12): 5925. CrossRef - Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef
- Understanding the phase evolution and elemental distribution in MoWTaNbVTix manufactured via powder metallurgical approach
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
- Min-Ho Cho, Sung-Jun Kim, Hyun-Ji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):299-304. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.299
- 856 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nb-Si-B alloys with Nb-rich compositions are fabricated by spark plasma sintering for high-temperature structural applications. Three compositions are selected: 75 at% Nb (Nb0.7), 82 at% Nb (Nb1.5), and 88 at% Nb (Nb3), the atomic ratio of Si to B being 2. The microstructures of the prepared alloys are composed of Nb and T2 phases. The T2 phase is an intermetallic compound with a stoichiometry of Nb5Si3-xBx (0 ≤ x ≤ 2). In some previous studies, Nb-Si-B alloys have been prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) using Nb and T2 powders (SPS 1). In the present work, the same alloys are prepared by the SPS process (SPS 2) using Nb powders and hypereutectic alloy powders with composition 67at%Nb-22at%Si-11at%B (Nb67). The Nb67 alloy powders comprise T2 and eutectic (T2 + Nb) phases. The microstructures and hardness of the samples prepared in the present work have been compared with those previously reported; the samples prepared in this study exhibit finer and more uniform microstructures and higher hardness.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure Characterization of Nb-Si-B alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering Process
- Sang-Hwan Kim, Nam-Woo Kim, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):426-431. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.426
- 961 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
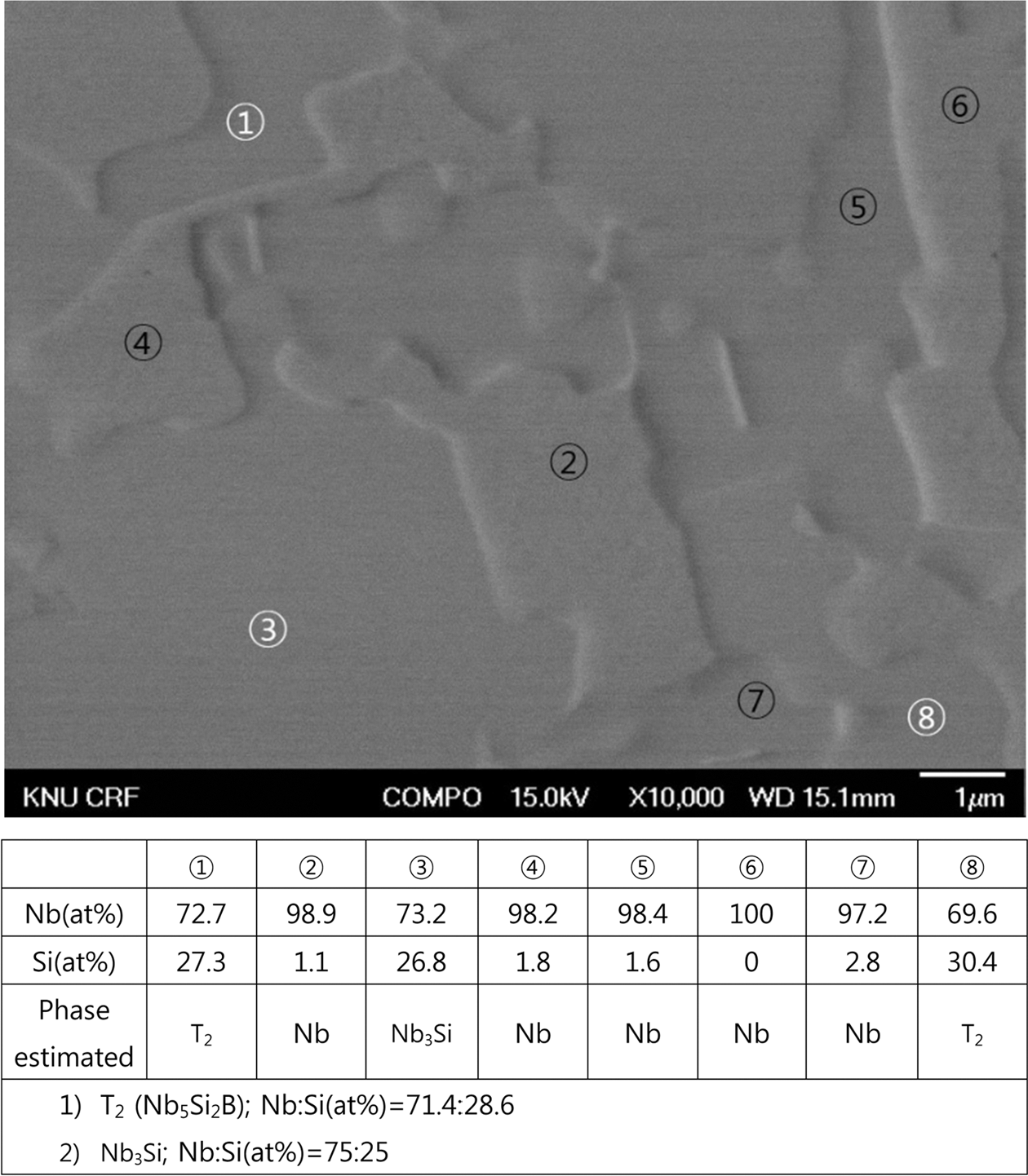
PDF Microstructural examination of the Nb-Si-B alloys at Nb-rich compositions is performed. The Nb-rich corner of the Nb-Si-B system is favorable in that the constituent phases are Nb (ductile and tough phase with high melting temperature) and T2 phase (very hard intermetallic compound with favorable oxidation resistance) which are good combination for high temperature structural materials. The samples containing compositions near Nb-rich corner of the Nb- Si-B ternary system are prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) process using T2 and Nb powders. T2 bulk phase is made in arc furnace by melting the Nb slug and the Si-B powder compact. The T2 bulk phase was subsequently ballmilled to powders. SPS is performed at 1300°C and 1400°C, depending on the composition, under 30 MPa for 600s, to produce disc-shaped specimen with 15 mm in diameter and 3 mm high. Hardness tests (Rockwell A-scale and micro Vickers) are carried out to estimate the mechanical property.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
Min-Ho Cho, Sung-Jun Kim, Hyun-Ji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 299. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Nb-Si-B quaternary alloy fabricated by powder metallurgical method
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Se Hoon Kim, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 14. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Si-B alloys fabricated by using core-shell powder with dispersion of yttria nanoparticles
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Won June Choi, Min Sang Kim, Goo Won Noh, Young Do Kim
Metals and Materials International.2017; 23(1): 170. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ta2O5 Dispersion-Strengthened Mo-Si-B Alloy by Powder Metallurgical Method
Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Su-Ryong Bang, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim
JOM.2017; 69(4): 683. CrossRef - Rapid consolidation of nanostuctured WC-FeAl3 by pulsed current activated heating and its mechanical properties
In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 69. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
- [Korean]
- Effect of Oxygen Content in the Tungsten Powder Fabricated by Electrical Explosion of Wire Method on the Behavior of Spark-Plasma Sintering
- Cheol-Hee Kim, Seong Lee, Byung-Kee Kim, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):447-453. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.447
- 652 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
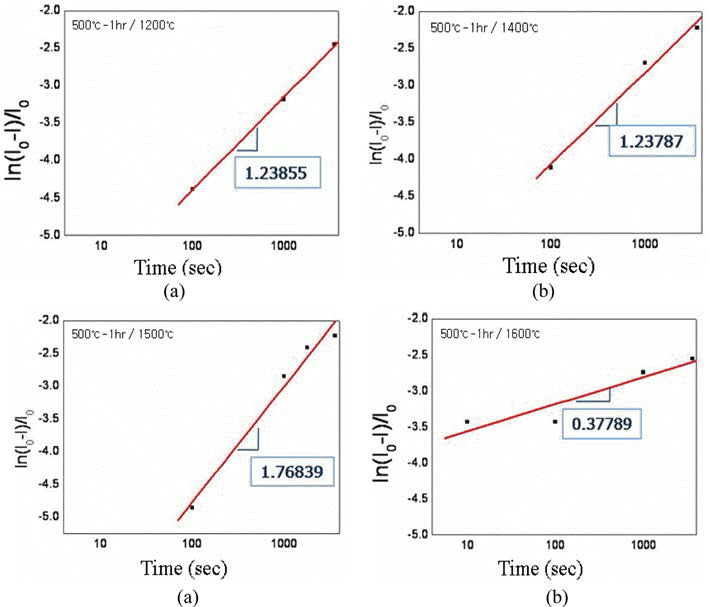
PDF Effect of oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powder fabricated by electrical explosion of wire method on the behvior of spark plasma sintering was investigated. The initial oxygen content of 6.5 wt% of as-fabricated tungsten powder was reduced to 2.3 and 0.7 wt% for the powders which were reduction-treated at 400°C for 2 hour and at 500°C for 1h in hydrogen atmosphere, respectively. The reduction-treated tungsten powders were spark-plasma sintered at 1200-1600°C for 100-3600 sec. with applied pressure of 50 MPa under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Maximun sindered density of 97% relative density was obtained under the condition of 1600°C for 1h from the tungsten powder with 0.7 wt% oxygen. Sintering activation energy of 95.85 kJ/mol−1 was obtained, which is remarkably smaller than the reported ones of 380~460 kJ/mol−1 for pressureless sintering of micron-scale tungsten powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(5): 384. CrossRef
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
- [Korean]
- Research Trend of Mo based Superalloys
- Jong Min Byun, Seok Hyun Hwang, Seong Lee, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(6):487-493.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.6.487

- 813 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of Spherical Mo5Si3 Powder by Inductively Coupled Thermal Plasma Treatment
Jang-Won Kang, Jong Min Park, Byung Hak Choe, Seong Lee, Jung Hyo Park, Ki Beom Park, Hyo Kyu Kim, Tae-Wook Na, Bosung Seo, Hyung-Ki Park
Metals.2018; 8(8): 604. CrossRef
- Preparation of Spherical Mo5Si3 Powder by Inductively Coupled Thermal Plasma Treatment
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Hot Isostatically Pressed Ni-Based Superalloy IN 713C
- Youngmoo Kim, Eun-Pyo Kim, Seong-Taek Chunga, Seong Lee, Joon-Woong Noh, Sung Ho Lee, Young-Sam Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(4):264-268.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.4.264

- 859 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nickel-based superalloy IN 713C powders have been consolidated by hot isostatic pressing (HIPing). The microstructure and mechanical properties of the superalloys were investigated at the HIPing temperature ranging from 1030°C to 1230°C. When the IN 713C powder was heated above gammaprime solvus temperature (about 1180°C), the microstructure was composed of the austenitic FCC matrix phase gamma plus a variety of secondary phases, such as gammaprime precipitates in gamma matrix and MC carbides at grain boundaries. The yield and tensile strengths of HIPed specimens at room temperature were decreased while the elongation and reduction of area were increased as the processing temperature increased. At 700°C, the strength was similar regardless of HIPing temperature; however, the ductility was drastically increased with increasing the temperature. It is considered that these properties compared to those of cast products are originated from the homogeneity of microstructure obtained from a PM process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
W.J. Kim, H.-H. Nguyen, H.Y. Kim, M.-T. Nguyen, H.S. Park, J.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1215. CrossRef
- Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
- [Korean]
- Microstructural Evolution during Hot Deformation of Molybdenum using Processing Map Approach
- Young-Moo Kim, Sung-Ho Lee, Seong Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(6):458-465.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.6.458

- 785 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The hot deformation characteristics of pure molybdenum was investigated in the temperature range of 600sim1200°C and strain rate range of 0.01sim10.0/s using a Gleeble test machine. The power dissipation map for hot working was developed on the basis of the Dynamic Materials Model. According to the map, dynamic recrystallization (DRX) occurs in the temperature range of 1000sim1100°C and the strain rate range of 0.01sim10.0/s, which are the optimum conditions for hot working of this material. The average grain size after DRX is 5µm. The material undergoes flow instabilities at temperatures of 900sim1200°C and the strain rates of 0.01sim10.0/s, as calculated by the continuum instability criterion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hot Deformation Constitutive Analysis and Processing Maps of Ultrasonic Melt Treated A5052 Alloy
Sun-Ki Kim, Seung-Hyun Koo, Hoon Cho, Seong-Ho Ha
Materials.2024; 17(13): 3182. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution during Hot Deformation of P/M Copper using Processing Map
Soo-Ho Chang, Young-Moo Kim, Kyung-Chae Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(2): 134. CrossRef
- Hot Deformation Constitutive Analysis and Processing Maps of Ultrasonic Melt Treated A5052 Alloy
- [Korean]
- Application of Refractory Metal Powders to Military Material Fields
- Young-Moo Kim, Eun-Pyo Kim, Seong Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(4):221-229.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.4.221

- 650 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and Nucleation Behavior of MoO3 Nano Particles with Concentration of Precursors
Seyoung Lee, Namhun Kwon, Jaeseok Roh, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 394. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ultra Fine Grained Molybdenum and Mechanical Properties
Se-Hoon Kim, Young-Ik Seo, Dae-Gun Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Young-Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(3): 235. CrossRef
- Synthesis and Nucleation Behavior of MoO3 Nano Particles with Concentration of Precursors
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Reduction Mechanism of Tungsten and Copper Oxide Composite Powders
- Seong Lee, Moon-Hee Hong, Eun-Pyo Kim, Sung-Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2003;10(6):422-429.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2003.10.6.422

- 602 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The reduction mechanism of the composite powders mixed with WO_3 and CuO has been studied by using thermogravimetry (TG), X-ray diffraction, and microstructure analyses. The composite powders were made by simple Turbula mixing, spray drying, and ball-milling in a stainless steel jar with the ball to powder ratio of 32 to 1 at 80 rpm for 1 h without process controlling agents. It is observed that all the oxide composite powders are converted to W-coated Cu composite powder after reducing treatment under hydrogen atmosphere. For the formation mechanism of W-coated Cu composite powder, the sequential reduction steps are proposed as follows: CuO contained in the ball-milled composite powder is initially reduced to Cu at the temperature range from 200°C to 300°C. Then, WO_3 powder is reduced to W O_2 via W O_2.9 and W O_2.72 at higher temperature region. Finally, the gaseous phase of WO_3(OH)_2 formed by reaction of WO_2 with water vapour migrates to previously reduced Cu and deposits on it as W reduced by hydrogen. The proposed mechanism has been proved through the model experiment which was performed by using Cu plate and WO_3 powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of W–Cu composite with Cu-network structure via W-coated Cu powder structure optimization
Gang Yao, Xu Shen, Cai-Yan Wang, Xi-Peng Ding, Lai-Ma Luo, Jia-Qin Liu, Xiang Zan, Yu-Cheng Wu
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 36: 4719. CrossRef
- Preparation of W–Cu composite with Cu-network structure via W-coated Cu powder structure optimization
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstryctural Evoulution of the Reagion Aheas of Craters Created by Copper and W-Cu Shaped Charge Jets
- Seong Lee, Moon-Hee Hong, Woon-Hyung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 1999;6(1):69-74.

- 325 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The microstructure of the reagion of carters, created by Cu and W-Cu shaped charge jets, in a 1020 mild steel target has been intestiaged. The region ahead of the crater created by the Cu shaped charge jet, reveals dramatic grain refinement implying the occurrence of a dynamic recrystallization, while that of W-Cu one dose a martensitic transformation indicative of heating up to an austenitic region followed by rapid cooling.The impacting pressure calculated when the W-Cu shaped charge jet encounters the target is higher than that of the Cu one. The micro-hardness of the region ahead of the crater created by the W-Cu shaped charge jet is also higher than that of the Cu one. The microstructure of W-Cu slug remained in the inside of the craters depicts the occurrence of the remarkable elongation of W particles during the liner collaphse. From these results, the microstructural variation of the region ahead of the crater with Cu and W-Cu shaped charge jets is discussed in trems of the pressure dependency of the transformation region of ferrite and austenite phases.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


