Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290
- 3,516 View
- 91 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
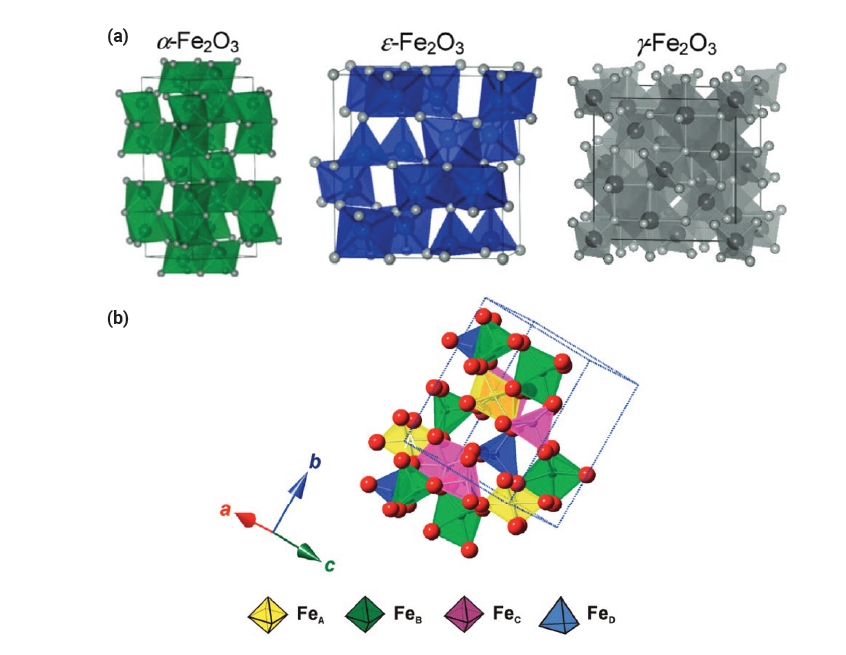
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [English]
- Interaction of Detonation Nanodiamonds with Hispidin
- Changkyu Rhee, Whungwhoe Kim, Andrey E. Burov, Alexey P. Puzyr, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):458-463. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.458
- 720 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Hispidin is a secondary metabolite found in numerous medicinal mushrooms that has attracted significant attention, owing to its distinct biological effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and cytoprotective properties. Experiments are being carried out to study the interaction of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) with synthetic and natural hispidin sourced from extracts of
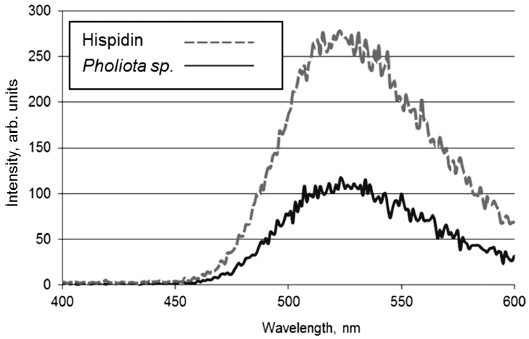
Pholiota sp. fungus. The bioluminescence method is used to determine the adsorption/ desorption properties of DNDs toward hispidin. It is found that hispidin forms strong conjugates with DNDs, and the use of various eluents does not result in a significant release of the adsorbed hispidin molecules. DND-bovine serum albumin (BSA) complex, where DNDs serve as a carrier for the protein and the latter acts as a hispidin sorbent, has been developed and applied in hispidin adsorption/desorption tests. The results support the use of the DNDs as a carrier for hispidin in medical applications. They also advocate the application of the DND-BSA complex for isolating the substance from fungal extracts.
- [English]
- A Study on the Removal of Heavy Metal with Mg-Modified Zeolite
- Jei-Pil Wang, Gyu-Cheol Kim, Min-Seok Go
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):287-292. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.287
- 1,840 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
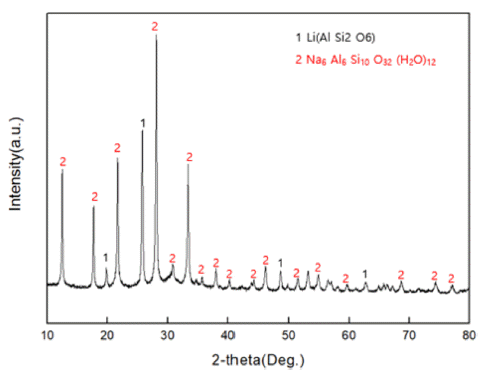
PDF The subject of this study is a zeolite generated as a by-product of recycling LAS (lithium-aluminum-silicate) resources, a kind of glass and ceramic produced by induction. The zeolite by-product is modified into Mg-zeolite using Mg as a cation to absorb Pb, a heavy metal generated from water pollution caused by recent industrial wastewater. An ion-exchange method is used to carry out the modification process, from zeolite byproduct to Mg-zeolite, and simultaneously absorb the Pb in the heavy-metal solution (99.032 mg/L). It is found that the sodium zeolite in the raw material residue can be modified to magnesium zeolite by reacting it with a mixture solution at 1 M concentration for 24 h. As a result, it is found that the residual Pb (0.130 mg/L) in the heavy metal solution is shown to be absorbed by 99.86%, with successful formation of a Mg-modified zeolite.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Penentuan Kualitas Kaolin sebagai Prekursor Sintesis Zeolit pada Kegiatan Praktikum
Rohmat Ismail, Manasye Erlangga, Ari Himawan, Givana Indah Nurul Afiah
Jurnal Pengelolaan Laboratorium Pendidikan.2025; 7(2): 81. CrossRef - Y-Type Zeolite Synthesized from an Illite Applied for Removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution: Box-Behnken Design and Kinetics
Kinjal J. Shah, Jiacheng Yu, Ting Zhang, Zhaoyang You
Water.2023; 15(6): 1171. CrossRef
- Penentuan Kualitas Kaolin sebagai Prekursor Sintesis Zeolit pada Kegiatan Praktikum
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic and Adsorption Properties of WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):483-488. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.483
- 1,157 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
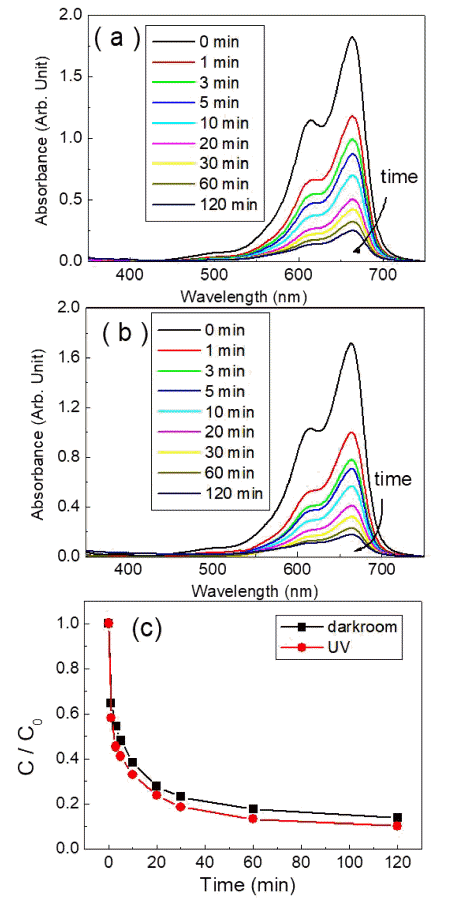
PDF Transition-metal oxide semiconductors have various band gaps. Therefore, many studies have been conducted in various application fields. Among these, methods for the adsorption of organic dyes and utilization of photocatalytic properties have been developed using various metal oxides. In this study, the adsorption and photocatalytic effects of WO3 nanomaterials prepared by hydrothermal synthesis are investigated, with citric acid added in the hydrothermal process as a structure-directing agent. The nanostructures of WO3 are studied using transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy images. The crystal structure is investigated using X-ray diffraction patterns, and the changes in the dye concentrations adsorbed on WO3 nanorods are measured with a UV-visible absorption spectrophotometer based on Beer-Lambert’s law. The methylene blue (MB) dye solution is subjected to acid or base conditions to monitor the change in the maximum adsorption amount in relation to the pH. The maximum adsorption capacity is observed at pH 3. In addition to the dye adsorption, UV irradiation is carried out to investigate the decomposition of the MB dye as a result of photocatalytic effects. Significant photocatalytic properties are observed and compared with the adsorption effects for dye removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
Kwang-Mo Kang, Ji-Hye Jeong, Ga-In Lee, Jae-Min Im, Hyun-Jeong Cheon, Deok-Hyeon Kim, Yoon-Chae Nah
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 40. CrossRef - Photocatalysis of TiO<sub>2</sub>/WO<sub>3</sub> Composites Synthesized by Ball Milling
Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(4): 316. CrossRef
- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


