Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 477 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
- [English]
- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
- Tae-hyung Kim, Jin-Kyeom Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):481-491. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00465
- 503 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
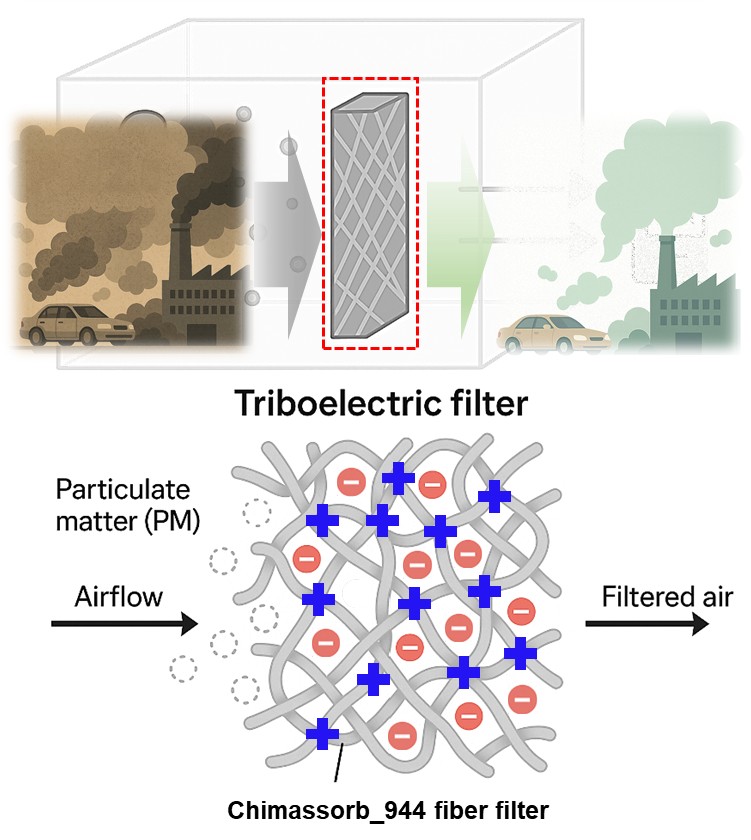
PDF - Particulate matter (PM) pollution demands air filters that combine high efficiency with low pressure drop. Here, we report a self-powered electrostatic filter based on an electrospun cationic microfiber web of Chimassorb 944 (C-fiber). The C-fiber functions as a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), generating a surface charge density of 85.8 85.8 μC/m2 when paired with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which creates a strong electrostatic field for capturing sub-micron particles, including the most penetrating particle size (MPPS). As a result, the triboelectrically charged C-fiber filter maintains >80% filtration efficiency at a high wind speed of 60 cm/s, far exceeding uncharged mechanical filters (<20%) while retaining low air resistance. Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) visualizes the surface-potential change after particle capture, and the gradual decay of TENG output provides a built-in indicator of dust loading. This strategy offers a promising platform for next-generation smart air purification systems.
- [English]
- Eco-Friendly Powder and Particles-Based Triboelectric Energy Harvesters
- Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Jihun Choi, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):528-535. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.528
- 1,795 View
- 36 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
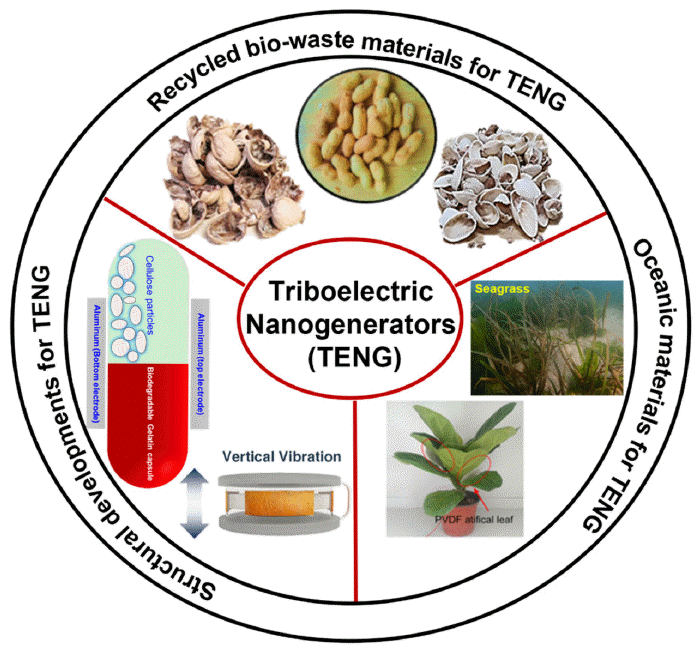
PDF Since their initial development in 2012, triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) have gained popularity worldwide as a desired option for harnessing energy. The urgent demand for TENGs is attributed to their novel structural design, low cost, and use of large-scale materials. The output performance of a TENG depends on the surface charge density of the friction layers. Several recycled and biowaste materials have been explored as friction layers to enhance the output performance of TENGs. Natural and oceanic biomaterials have also been investigated as alternatives for improving the performance of TENG devices. Moreover, structural innovations have been made in TENGs to develop highly efficient devices. This review summarizes the recent developments in recycling and biowaste materials for TENG devices. The potential of natural and oceanic biowaste materials is also discussed. Finally, future outlooks for the structural developments in TENG devices are presented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Maryam Khan, Rui Chang, Carlo Saverio Iorio, Yarjan Abdul Samad, Yijun Shi
Nano-Micro Letters.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication and Characterization of a Flexible Polyurethane-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for a Harvesting Energy System
Saba Ejaz, Imran Shah, Shahid Aziz, Gul Hassan, Ahmed Shuja, Muhammad Asif Khan, Dong-Won Jung
Micromachines.2025; 16(2): 230. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerator from Abalone Shell Powder for Self-Powered Humidity Sensing
Yunsook Yang, Farhan Akhtar, Shahzad Iqbal, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Woo Young Kim
Sensors.2025; 25(24): 7584. CrossRef
- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Polytetrafluoroethylene thin Film from Powder Dispersion-solution for Energy Nanogenerator Applications
- Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):102-107. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.102
- 977 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
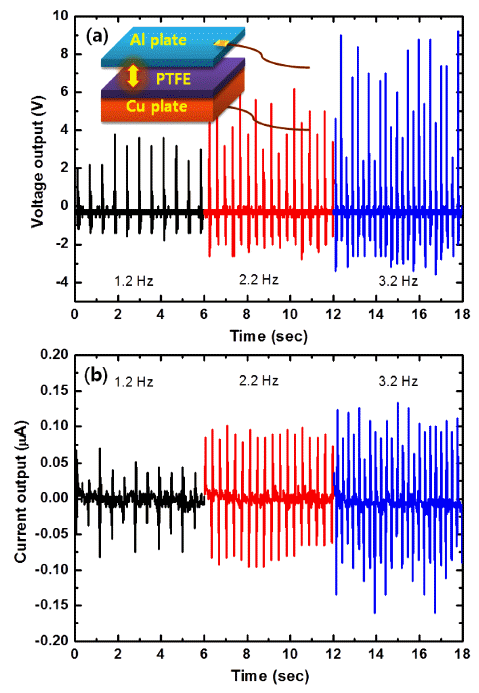
PDF Porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) thin films are fabricated by spin-coating using a dispersion solution containing PTFE powders, and their crystalline properties are investigated after thermal annealing at various temperatures ranging from 300 to 500°C. Before thermal annealing, the film is densely packed and consists of many granular particles 200-300 nm in diameter. However, after thermal annealing, the film contains many voids and fibrous grains on the surface. In addition, the film thickness decreases after thermal annealing owing to evaporation of the surfactant, binder, and solvent composing the PTFE dispersion solution. The film thickness is systematically controlled from 2 to 6.5 μm by decreasing the spin speed from 1,500 to 500 rpm. A triboelectric nanogenerator is fabricated by spin-coating PTFE thin films onto polished Cu foils, where they act as an active layer to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. A triboelectric nanogenerator consisting of a PTFE layer and Al metal foil pair shows typical output characteristics, exhibiting positive and negative peaks during applied strain and relief cycles due to charging and discharging of electrical charge carriers. Further, the voltage and current outputs increase with increasing strain cycle owing to accumulation of electrical charge carriers during charge-discharge.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
Geon-Ju Choi, Il-Kyu Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 247. CrossRef
- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


