Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Stellite 6 Alloy prepared by Directed Energy Deposition
- Joowon Suh, Jae Hyeon Koh, Young-Bum Chun, Young Do Kim, Jinsung Jang, Suk Hoon Kang, Heung Nam Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):152-162. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00066

- 787 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The directed energy deposited (DED) alloys show higher hardness values than the welded alloys due to the finer microstructure following the high cooling rate. However, defects such as microcracks, pores, and the residual stress are remained within the DED alloy. These defects deteriorate the wear behavior so post-processing such as heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are applied to DED alloys to reduce the defects. HIP was chosen in this study because the high pressure and temperature uniformly reduced the defects. The HIP is processed at 1150oC under 100 MPa for 4 hours. After HIP, microcracks are disappeared and porosity is reduced by 86.9%. Carbides are spherodized due to the interdiffusion of Cr and C between the dendrite and interdendrite region. After HIP, the nanohardness (GPa) of carbides increased from 11.1 to 12, and the Co matrix decreased from 8.8 to 7.9. Vickers hardness (HV) decreased by 18.9 % after HIP. The dislocation density (10-2/m2) decreased from 7.34 to 0.34 and the residual stress (MPa) changed from tensile 79 to a compressive -246 by HIP. This study indicates that HIP is effective in reducing defects, and the HIP DED Stellite 6 exhibits a higher HV than welded Stellite 6.
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Content of MgO Additive and Sintering Temperature on the Densification of Alumina Insulator
- Ri Joo Kim, Han Gyeol Jeong, Ye Ji Son, Sang Ki Ko, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):249-254. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.249

- 766 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The influence of MgO addition on the densification and microstructure of alumina (Al2O3) was studied. Compacted alumina specimens were manufactured using ball-milling and one-directional pressing followed by sintering at temperatures below 1700oC. Relative density, shrinkage, hardness, and microstructure were investigated using analytical tools such as FE-SEM, EDS, and XRD. When the MgO was added up to 5.0 wt% and sintered at 1500°C and 1600°C, the relative density exhibited an average value of 97% or more at both temperatures. The maximum density of 99.2% was with the addition of 0.5 wt% MgO at 1500°C. Meanwhile, the specimens showed significantly lower density values when sintered at 1400°C than at 1500°C and 1600°C owing to the relatively low sintering temperature. The hardness and shrinkage data also showed a similar trend in the change in density, implying that the addition of approximately 0.5 wt% MgO can promote the densification of Al2O3. Studying the microstructure confirmed the uniformity of the sintered alumina. These results can be used as basic compositional data for the development of MgOcontaining alumina as high-dielectric insulators.
- [Korean]
- Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Hardness of AlSi10Mg Alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Min-Su Kim, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):210-216. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.210
- 774 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
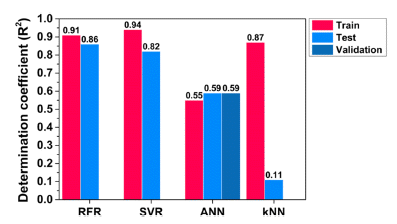
PDF In this study, machine learning models are proposed to predict the Vickers hardness of AlSi10Mg alloys fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). A total of 113 utilizable datasets were collected from the literature. The hyperparameters of the machine-learning models were adjusted to select an accurate predictive model. The random forest regression (RFR) model showed the best performance compared to support vector regression, artificial neural networks, and k-nearest neighbors. The variable importance and prediction mechanisms of the RFR were discussed by Shapley additive explanation (SHAP). Aging time had the greatest influence on the Vickers hardness, followed by solution time, solution temperature, layer thickness, scan speed, power, aging temperature, average particle size, and hatching distance. Detailed prediction mechanisms for RFR are analyzed using SHAP dependence plots.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Powder Size Dependence of Additive Manufactured AlCrFeNi HEA on Its Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
- Jong Woo Choi, Hae Jin Park, Gyeol Chan Kang, Min Seob Jung, Ki Tae Oh, Sung Hwan Hong, Hyun Gil Kim, Ki Buem Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):22-27. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.22
- 429 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
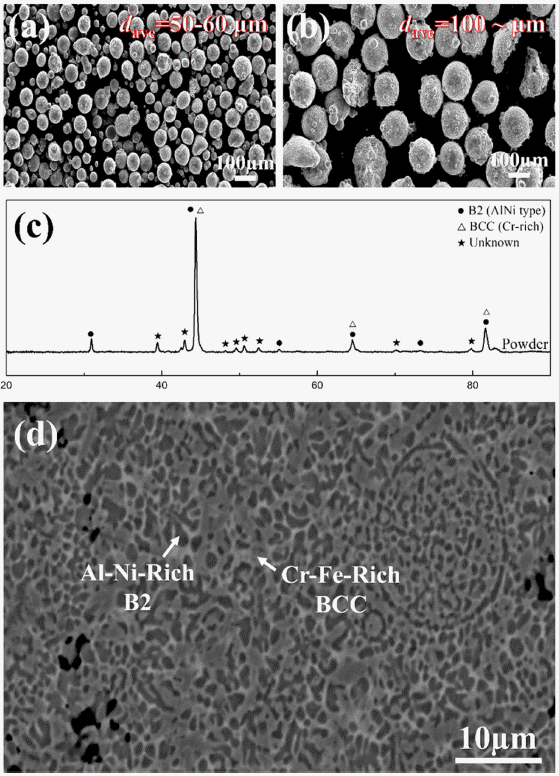
PDF Conventionally, metal materials are produced by subtractive manufacturing followed by melting. However, there has been an increasing interest in additive manufacturing, especially metal 3D printing technology, which is relatively inexpensive because of the absence of complicated processing steps. In this study, we focus on the effect of varying powder size on the synthesis quality, and suggest optimum process conditions for the preparation of AlCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder. The SEM image of the as-fabricated specimens show countless, fine, as-synthesized powders. Furthermore, we have examined the phase and microstructure before and after 3D printing, and found that there are no noticeable changes in the phase or microstructure. However, it was determined that the larger the powder size, the better the Vickers hardness of the material. This study sheds light on the optimization of process conditions in the metal 3D printing field.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of Fe-Ni-Cu-Mo-C Low Alloy Steel Powder
- Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Sung Gye Park, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):207-212. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.207

- 578 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Fe-Cu-Ni-Mo-C low alloy steel powder is consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The internal structure and the surface fracture behavior are studied using field-emission scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy techniques. The bulk samples are polished and etched in order to observe the internal structure. The sample sintered at 900°C with holding time of 10 minutes achieves nearly full density of 98.9% while the density of the as-received conventionally sintered product is 90.3%. The fracture microstructures indicate that the sample prepared at 900°C by the SPS process is hard to break out because of the presence of both grain boundaries and internal particle fractures. Moreover, the lamellar pearlite structure is also observed in this sample. The samples sintered at 1000 and 1100°C exhibit a large number of tiny particles and pores due to the melting of Cu and aggregation of the alloy elements during the SPS process. The highest hardness value of 296.52 HV is observed for the sample sintered at 900°C with holding time of 10 minutes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Fe-Si-B Based Amorphous Powder Cores by Spark Plasma Sintered and Their Magnetic Properties
Liang Yan, Biao Yan, Yin Jian
Materials.2022; 15(4): 1603. CrossRef - Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
W.J. Kim, H.-H. Nguyen, H.Y. Kim, M.-T. Nguyen, H.S. Park, J.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1215. CrossRef - Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Fe-Si-B Based Amorphous Powder Cores by Spark Plasma Sintered and Their Magnetic Properties
TOP
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


