- [English]
- The Effect of a CNT/MnO2 Nanoparticle Composite–Based Multi-Shell Typed Electrode for a Fiber Supercapacitor (FSC)
-
Yeonggwon Kim, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00416
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
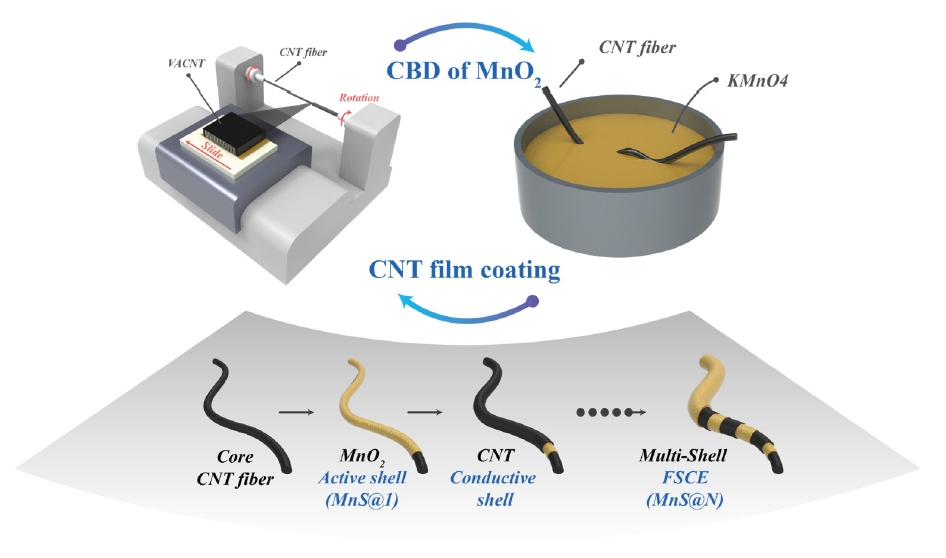
- Fiber supercapacitors have attracted significant interest as potential textile energy storage devices due to their remarkable flexibility and rapid charge/discharge capabilities. This study describes the fabrication of a composite fiber supercapacitor (FSC) electrode through a multi-shell architecture, featuring layers of carbon nanotube (CNT) conductive shells and MnO₂ nanoparticle active shells. The number of layers was adjusted to assess their impact on FSC energy storage performance. Increasing the number of shells reduced electrode resistance and enhanced pseudocapacitive characteristics. Compared to the MnS@1 electrode, the MnS@5 electrode exhibited a high areal capacitance of 301.2 mF/cm², a 411% increase, but showed a higher charge transfer resistance (RCT) of 701.6 Ω. This is attributed to reduced ion diffusion and charge transfer ability resulting from the thicker multi-shell configuration. These results indicate that fine-tuning the quantity of shells is crucial for achieving an optimal balance between energy storage efficiency and stability.
- [Korean]
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
-
Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
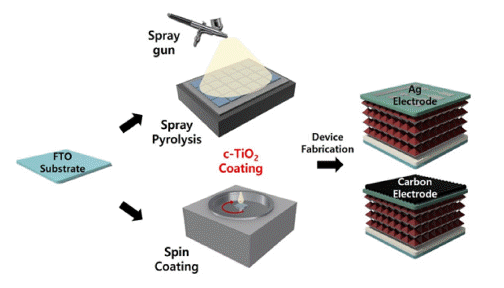
This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
-
Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
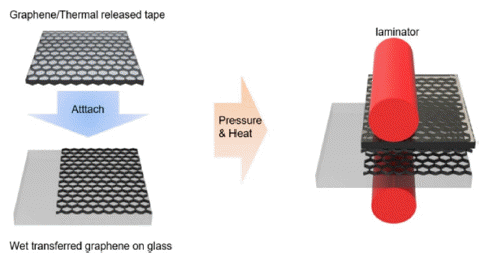
In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
-
Chae-young Woo, Yeongsu Jo, Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):11-15. Published online February 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.11
-
-
1,096
View
-
13
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
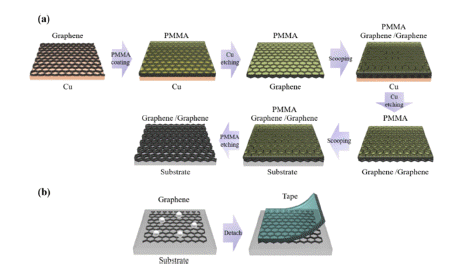
In this study, a method to remove residual powder on a multi-layered graphene and a new approach to transfer multi-layered graphene at once are studied. A graphene one-step transfer (GOST) method is conducted to minimize the residual powder comparison with a layer-by-layer transfer. Furthermore, a residual powder removing process is investigated to remove residual powder at the top of a multi-layered graphene. After residual powder is removed, the sheet resistance of graphene is decreased from 393 to 340 Ohm/sq in a four-layered graphene. In addition, transmittance slightly increases after residual powder is removed from the top of the multi-layered graphene. Optical and atomic-force microscopy images are used to analyze the graphene surface, and the Ra value is reduced from 5.2 to 3.7 nm following residual powder removal. Therefore, GOST and residual powder removal resolve the limited application of graphene electrodes due to residual powder. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 305. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Diffusion Barrier and thin Film Deposition Temperature on Change of Carbon Nanotubes Length
-
Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):248-253. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.248
-
-
335
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, we investigate the effect of the diffusion barrier and substrate temperature on the length of carbon nanotubes. For synthesizing vertically aligned carbon nanotubes, thermal chemical vapor deposition is used and a substrate with a catalytic layer and a buffer layer is prepared using an e-beam evaporator. The length of the carbon nanotubes synthesized on the catalytic layer/diffusion barrier on the silicon substrate is longer than that without a diffusion barrier because the diffusion barrier prevents generation of silicon carbide from the diffusion of carbon atoms into the silicon substrate. The deposition temperature of the catalyst and alumina are varied from room temperature to 150°C, 200°C, and 250°C. On increasing the substrate temperature on depositing the buffer layer on the silicon substrate, shorter carbon nanotubes are obtained owing to the increased bonding force between the buffer layer and silicon substrate. The reason why different lengths of carbon nanotubes are obtained is that the higher bonding force between the buffer layer and the substrate layer prevents uniformity of catalytic islands for synthesizing carbon nanotubes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
Chae-young Woo, Yeongsu Jo, Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 11. CrossRef - Fabrication of robust, ultrathin and light weight, hydrophilic, PVDF-CNT membrane composite for salt rejection
Vivek Dhand, Soon Kyu Hong, Luhe Li, Jong-Man Kim, Soo Hyung Kim, Kyong Yop Rhee, Hyung Woo Lee
Composites Part B: Engineering.2019; 160: 632. CrossRef
|