- [English]
- Selective Laser Sintering of Co-Cr Alloy Powders and Sintered Products Properties
-
Dong-Wan Lee, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Metal-additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), are increasingly utilized for new biomaterials, such as cobalt-chrome (Co-Cr). In this study, Co-Cr gas-atomized powders are used as charge materials for the SLS process. The aim is to understand the consolidation of Co-Cr alloy powder and characterization of samples sintered using SLS under various conditions. The results clearly suggest that besides the matrix phase, the second phase, which is attributed to pores and oxidation particles, is observed in the sintered specimens. The as-built samples exhibit completely different microstructural features compared with the casting or wrought products reported in the literature. The microstructure reveals melt pools, which represent the characteristics of the scanning direction, in particular, or of the SLS conditions, in general. It also exposes extremely fine grain sizes inside the melt pools, resulting in an enhancement in the hardness of the as-built products. Thus, the hardness values of the samples prepared by SLS under all parameter conditions used in this study are evidently higher than those of the casting products.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Immiscible Fe-Cu Alloys using Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid
-
Chu Dac Phuc, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):449-457. Published online December 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.449
-
-
1,597
View
-
13
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Iron and copper are practically immiscible in the equilibrium state, even though their atomic radii are similar. As non-equilibrium solid solutions, the metastable Fe-Cu alloys can be synthesized using special methods, such as rapid quenching, vapor deposition, sputtering, ion-beam mixing, and mechanical alloying. The complexity of these methods (multiple steps, low productivity, high cost, and non-eco-friendliness) is a hinderance for their industrial applications. Electrical explosion of wire (EEW) is a well-known and effective method for the synthesis of metallic and alloy nanoparticles, and fabrication using the EEW is a simple and economic process. Therefore, it can be potentially employed to circumvent this problem. In this work, we propose the synthesis of Fe-Cu nanoparticles using EEW in a suitable solution. The powder shape, size distribution, and alloying state are analyzed and discussed according to the conditions of the EEW. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
Hugues Nkomba Museba, BongJu Lee
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1054: 185926. CrossRef - Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
Xuexue Wang, Runqing Lu, Shanhe Gong, Shaokang Yang, Wenbo Wang, Zhongti Sun, Xiaozhen Zhang, Jun Liu, Xiaomeng Lv
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 503: 158488. CrossRef - Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for the removal of p-nitrophenol and its derivatives from wastewater
M. S. Qatan, F. Arshad, M. Miskam, G. A. Naikoo
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.2024; 21(5): 5247. CrossRef - Control of cluster coalescence during formation of bimetallic nanoparticles and nanoalloys obtained via electric explosion of two wires
K.V. Suliz, A.Yu. Kolosov, V.S. Myasnichenko, N.I. Nepsha, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov, A.V. Pervikov
Advanced Powder Technology.2022; 33(3): 103518. CrossRef
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
-
Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14
-
-
989
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- [English]
- Synthesis of Carbonyl Iron-reinforced Polystyrene by High Energy Ball Milling
-
Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Jin-Chun Kim, Young-Soo Kim, Young-Hyuk Kim, Olga B. Nazarenko
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):276-281. Published online August 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.276
-
-
1,261
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Carbonyl iron (CI) is successfully incorporated as an additive into a polystyrene (PS) matrix via a highenergy ball milling method, under an n-hexane medium with volume fractions between 1% and 5% for electromagnetic interference shielding applications by the combination of magnetic CI and an insulating PS matrix. The morphology and the dispersion of CI are investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, which indicates a uniform distribution of CI in the PS matrix after 2 h of milling. The thermal behavior results indicate no significant degradation of the PS when there is a slight increase in the onset temperature with the addition of CI powder, when compared to the as-received PS pellet. After milling, there are no interactions between the CI and the PS matrix, as confirmed by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. In this study, the milled CI-PS powder is extruded to make filaments, and can have potential applications in the 3-D printing industry. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
Antonio Rizzo, Gregory I. Peterson
Progress in Polymer Science.2024; 159: 101900. CrossRef
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of Fe-Ni-Cu-Mo-C Low Alloy Steel Powder
-
Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Sung Gye Park, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):207-212. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.207
-
-
1,383
View
-
10
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, Fe-Cu-Ni-Mo-C low alloy steel powder is consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The internal structure and the surface fracture behavior are studied using field-emission scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy techniques. The bulk samples are polished and etched in order to observe the internal structure. The sample sintered at 900°C with holding time of 10 minutes achieves nearly full density of 98.9% while the density of the as-received conventionally sintered product is 90.3%. The fracture microstructures indicate that the sample prepared at 900°C by the SPS process is hard to break out because of the presence of both grain boundaries and internal particle fractures. Moreover, the lamellar pearlite structure is also observed in this sample. The samples sintered at 1000 and 1100°C exhibit a large number of tiny particles and pores due to the melting of Cu and aggregation of the alloy elements during the SPS process. The highest hardness value of 296.52 HV is observed for the sample sintered at 900°C with holding time of 10 minutes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of Fe-Si-B Based Amorphous Powder Cores by Spark Plasma Sintered and Their Magnetic Properties
Liang Yan, Biao Yan, Yin Jian
Materials.2022; 15(4): 1603. CrossRef - Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Sintering and Microstructures of SUS 316L Powder Produced by 3D Printing Process
W.J. Kim, H.-H. Nguyen, H.Y. Kim, M.-T. Nguyen, H.S. Park, J.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1215. CrossRef - Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
- [English]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Characteristics of Bulk Nickel/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites via the Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Spark Plasma Sintering Method
-
Thuyet-Nguyen Minh, Hai-Nguyen Hong, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):213-220. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.213
-
-
1,284
View
-
5
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
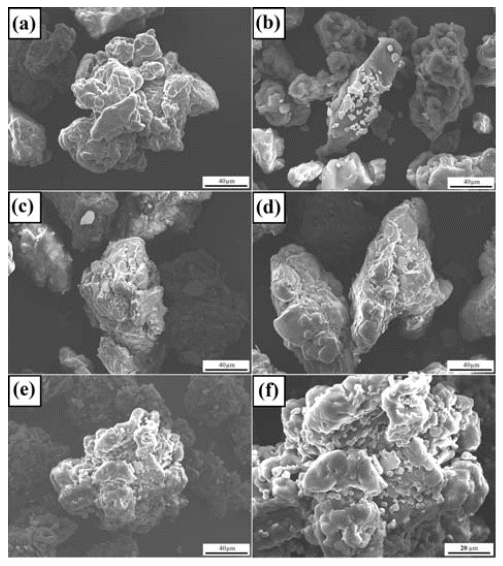
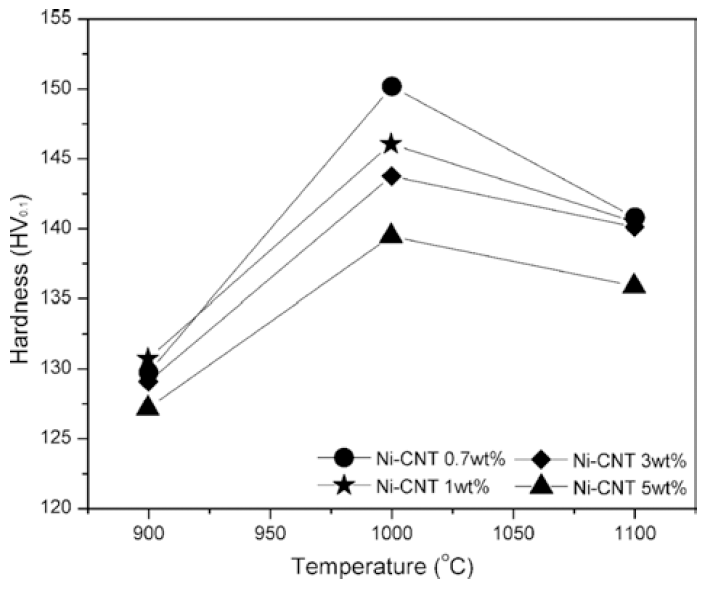
In this study, bulk nickel-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites are synthesized by a novel method which includes a combination of ultrasonication, electrical explosion of wire in liquid and spark plasma sintering. The mechanical characteristics of the bulk Ni-CNT composites synthesized with CNT contents of 0.7, 1, 3 and 5 wt.% are investigated. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy techniques are used to observe the different phases, morphologies and structures of the composite powders as well as the sintered samples. The obtained results reveal that the as-synthesized composite exhibits substantial enhancement in the microhardness and values more than 140 HV are observed. However an empirical reinforcement limit of 3 wt.% is determined for the CNT content, beyond which, there is no significant improvement in the mechanical properties. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
Tao Jiang, Zhongyu Hou
Applied Surface Science.2020; 513: 145824. CrossRef - Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
Jin-Ju Park, Eun-Kwang Park, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Min-Ku Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 143. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Reduction and Spark Plasma Sintering of the W(Tungsten) Nanopowder Produced by the Electric Explosion of Wire Process
-
Ji-Soon Kim, Cheol-Hee Kim, Eun-Ju Park, Young-Soon Kwon, Jin-Chun Kim, Sung-Ho Lee, Dong-Ik Jung
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(4):269-277.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.4.269
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- [ beta-W(W_3O) ] oxide layer on the surface of each W(tungsten) nanopowder produced by the electric explosion of wire(EEW) process were formed during the 1vol.% air passivation process. The oxide layer hindered sintering densification of compacts during SPS process. The oxide phase was reduced to the pure W phase during SPS. The W nanopowder's compacts treated by the hydrogen reduction showed high sintered density of 94.5%. after SPS process at 1900°C.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Properties of High Strength Hypereutectic Al-Si Powder by Gas Atomization Process I. Powder Production and Compressibility
-
Yong-Jin Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):296-302.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.296
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- In order to improve mechanical properties, the hypereutectic Al-20 wt%Si based prealloy powder was prepared by gas atomization process. Microstructure and compressibility of the atomized Al-Si powder were investigated. The average powder size was decreased with increasing the atomization gas pressure. Size of primary Si particles of the as-atomized powder was about 5-8;mum. The as-atomized Al-Si powder such as AMB 2712 and AMB 7775 to increase compressibility and sinterability. Relative density of the mixed powder samples sintered at 600°C was reached about 96% of a theoretical density.
- [Korean]
- Formation of CdSe Hollow Sphere by In-Situ-Template-Interface Reaction (ISTIR) Method
-
Moon-Hee Choi, Yoon-Bok Lee, Hyong-Kuk Kim, Young-Mok Rhyim, Jin-Chun Kim, Young-Seok Kim, Yang-Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):291-295.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.291
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- CdSe hollow sphere with average size of about 30-50 nm was synthesized from the mixed solution of cadmium chloride (CdCl_2), sodium selenosulfate (Na_2SeSO_3) and ethylenediamine(EDA, H_2NCH_2CH_2NH_2) at room temperature. The molar ratio of EDA to Cd2+ showed the most significant effect on the morphology of CdSe hollow sphere. This paper will present and discuss the possible formation mechanism of CdSe hollow sphere based on the observation of morphological changes.
- [Korean]
- Production and Application of Nanoparticles by the Chemical Vapor Condensation Process
-
Jin-Chun Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha, Chul-Jin Choi, Byoung-Kee Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):239-248.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.239
-
-
714
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 PDF PDF
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(6): 477. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Microstructure of Fe(C) Nanocapsules by Chemical Vapor Condensation
-
Jung-Han Lee, Sung-Duk Kim, Jin-Chun Kim, Chul-Jin Choi, Chan-Gyu Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2004;11(6):515-521.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2004.11.6.515
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Fe(C) nanocapsules were prepared by the chemical vapor condensation(CVC) process using the pyrolysis of iron pentacarbonyl (Fe(CO)_5). Their characterizations were studied by means of X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectrometer and transmission electron microscopy. The long-chained Fe(C) nanocapsules hav-ing the mean size of under 70 nm could be obtained below 1100°C in different gas flow rates. The particle size of the powders was increased with increasing decomposition temperature, but it was decreased with increasing CO gas flow rate. The Fe powders produced at 500°C consisted of three layers of alpha-Fe/Fe_3C/amorphous phases, but it had two phase core-shell structure which consited of Fe_3C phase of core and graphite of shell at 1100°C.
- [English]
- Microstructure and Properties Comparison of Pure Cu and Cu-5 wt.% Al2O3 Composite Processed by Spark Plasma Sintering
-
Dinh Van Cong, Dong-Wan Lee, Su-Wan Lee, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Nguyen Viet Hoang, Jin-Chun Kim
-
Received December 3, 2025 Accepted February 25, 2026 Published online February 26, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00472
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
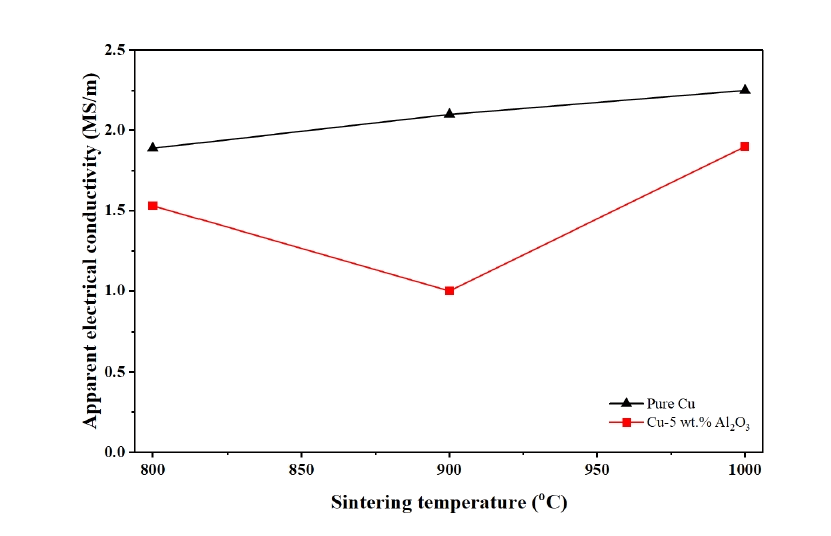
- This study compares the microstructure and properties of pure Cu and Cu-5 wt.% Al2O3 composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering under strictly identical processing conditions at 800-1000 °C. Pure Cu samples achieved near-full densification and exhibited a bimodal grain structure dominated by coarse grains with increasing sintering temperature. In contrast, the composite samples showed lower density and non-monotonic densification behavior, with a minimum relative density at 900 oC and significantly refined equiaxed grains due to strong grain-boundary pinning by nano Al2O3 particles. The higher fractions of high-angle boundaries and pronounced orientation disruption were observed in the composite samples, while high-resolution analysis confirmed the presence of grain-boundary Al2O3-rich regions that restricted Cu grain coalescence and continuity of grain boundary migration. X-ray diffraction results confirmed the absence of reaction phases in both materials. Hardness peaked at 900 °C for both samples, and the composite samples showed consistently lower hardness due to retained porosity. The apparent electrical conductivity of the composite displays a non-linear temperature dependence, reflecting the competing influences of densification, microstructural recovery, and the insulating nature of Al2O3.
- [English]
- Microstruture and Mechanical Properties of Ti.Grade12-Ti/TiN/WC Composite Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering Process
-
Hyun-Su Kim, Su-Gwan Lee, Dinh Van Cong, Jun-Seo Park, Ha-Seung Ryu, Jin-Chun Kim, Seung-Ick Lee
-
Received December 5, 2025 Accepted February 23, 2026 Published online February 26, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00486
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
- Ti.Grade12 is widely used in chemical processing, power generation, and nuclear industries because of its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, enhanced by alloying elements such as Ni and Mo. Ceramic reinforcements such as TiN have been reported to significantly improve the surface hardness and wear resistance of titanium-based materials. Furthermore, nano-sized WC particles can suppress excessive intermetallic compound formation and stabilize the Ti matrix through grain boundary pinning and microstructural control mechanisms. However, strong interfacial bonding between Ti and ceramic reinforcements generally requires high temperatures and prolonged sintering times, which may induce undesirable secondary phase formation. Therefore, optimizing the mixing ratio of Ti, TiN, and WC is essential to achieve a homogeneous interface and a stable composite structure. In this study, a composite layered structure was fabricated on a Ti.Grade12 substrate using mixed Ti, TiN, and nano-sized WC powders via Spark Plasma Sintering. A composition of 60 wt% Ti, 35 wt% TiN, and 5 wt% WC formed a stable coating layer without secondary phases and achieved a micro vickers hardness of approximately 2400 Hv.
|