- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Conditions on the Microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo High-Entropy Alloy
-
Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Junho Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):406-413. Published online October 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00185
-
-
1,292
View
-
40
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- We investigated the microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering under different sintering temperatures (1000–1100°C) and times (1–600 s). All sintered alloys consisted of a single face-centered cubic phase. As the sintering time or temperature increased, the grains of the sintered alloys became partially coarse. The formation of Cr7C3 carbide occurred on the surface of the sintered alloys due to carbon diffusion from the graphite crucible. The depth of the layer containing Cr7C3 carbides increased to ~110 μm under severe sintering conditions (1100°C, 60 s). A molten zone was observed on the surface of the alloys sintered at higher temperatures (>1060°C) due to severe carbon diffusion that reduced the melting point of the alloy. The porosity of the sintered alloys decreased with increasing time at 1000°C, but increased at higher temperatures above 1060°C due to melting-induced porosity formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Microstructure and mechanical properties of oxide-dispersion-strengthened CrMnFeCoNiC0.2O0.2 high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering
Sang-Hwa Lee, Seonghyun Park, Ka Ram Lim, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 947: 149284. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si Sintered Alloys with and Without High-energy Ball Milling
-
Junho Lee, Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.470
-
-
2,784
View
-
32
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The effects of annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si alloys fabricated by high-energy ball milling (HEBM) and spark plasma sintering (SPS) were investigated. The HEBM-free sintered alloy primarily contained Mg2Si, Q-AlCuMgSi, and Si phases. Meanwhile, the HEBM-sintered alloy contains Mg-free Si and θ-Al2Cu phases due to the formation of MgO, which causes Mg depletion in the Al matrix. Annealing without and with HEBM at 500°C causes partial dissolution and coarsening of the Q-AlCuMgSi and Mg2Si phases in the alloy and dissolution of the θ-Al2Cu phase in the alloy, respectively. In both alloys, a thermally stable α-AlFeSi phase was formed after long-term heat treatment. The grain size of the sintered alloys with and without HEBM increased from 0.5 to 1.0 μm and from 2.9 to 6.3 μm, respectively. The hardness of the sintered alloy increases after annealing for 1 h but decreases significantly after 24 h of annealing. Extending the annealing time to 168 h improved the hardness of the alloy without HEBM but had little effect on the alloy with HEBM. The relationship between the microstructural factors and the hardness of the sintered and annealed alloys is discussed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microstructural evolution and thermal stability of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si–Zr alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Junho Lee, Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Seung Bae Son, Hanjung Kwon, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 31: 205. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Gradient Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-6%Mn Alloy by Different Sized Powder Stacking
-
Namhyuk Seo, Junho Lee, Woocheol Shin, Junhyub Jeon, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):382-389. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.382
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
A typical trade-off relationship exists between strength and elongation in face-centered cubic metals. Studies have recently been conducted to enhance strength without ductility reduction through surface-treatment-based ultrasonic nanocrystalline surface modification (UNSM), which creates a gradient microstructure in which grains become smaller from the inside to the surface. The transformation-induced plasticity effect in Fe-Mn alloys results in excellent strength and ductility due to their high work-hardening rate. This rate is achieved through strain-induced martensitic transformation when an alloy is plastically deformed. In this study, Fe-6%Mn powders with different sizes were prepared by high-energy ball milling and sintered through spark plasma sintering to produce Fe-6%Mn samples. A gradient microstructure was obtained by stacking the different-sized powders to achieve similar effects as those derived from UNSM. A compressive test was performed to investigate the mechanical properties, including the yielding behavior. The deformed microstructure was observed through electron backscatter diffraction to determine the effects of gradient plastic deformation.
- [Korean]
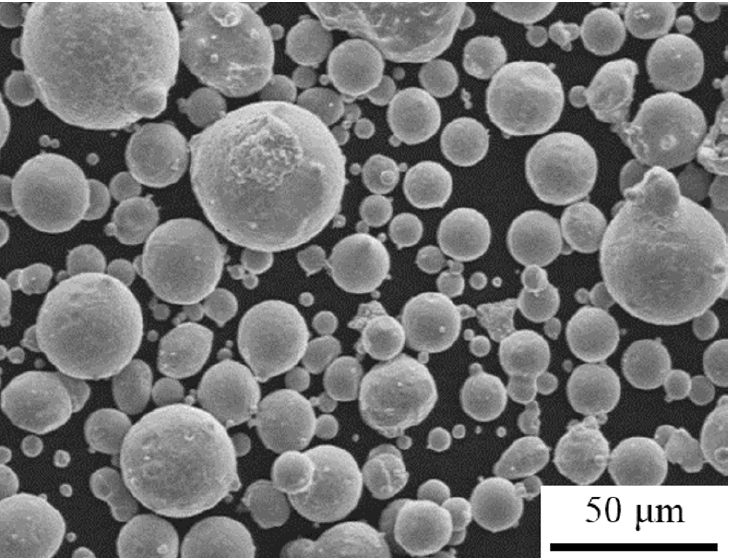
- Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Depending on Sintering Heating Rate of IN 939W Alloy
-
Junhyub Jeon, Junho Lee, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):399-410. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.399
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
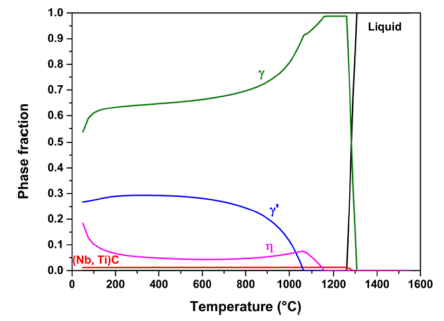
Changes in the mechanical properties and microstructure of an IN 939 W alloy according to the sintering heating rate were evaluated. IN 939 W alloy samples were fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The phase fraction, number density, and mean radius of the IN 939W alloy were calculated using a thermodynamic calculation. A universal testing machine and micro-Vickers hardness tester were employed to confirm the mechanical properties of the IN 939W alloy. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, Cs-corrected-field emission transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry were used to evaluate the microstructure of the alloy. The rapid sintering heating rate resulted in a slightly dispersed γ' phase and chromium oxide. It also suppressed the precipitation of the η phase. These helped to reinforce the mechanical properties.
- [Korean]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Method to Replace Carburizing Process
-
Junhyub Jeon, Junho Lee, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):219-225. Published online June 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.219
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
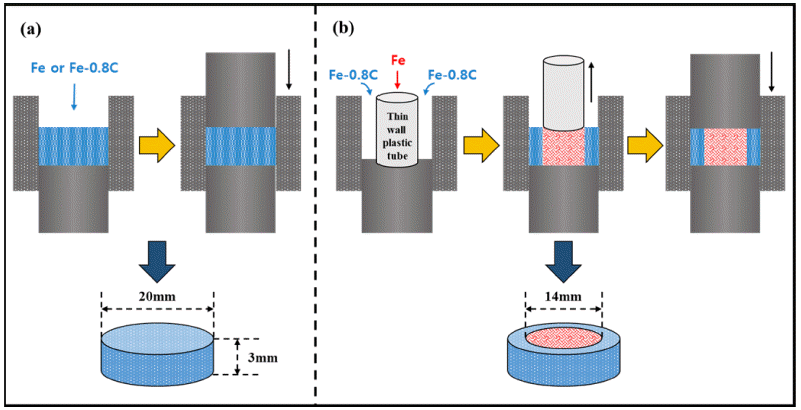
An alternative fabrication method for carburizing steel using spark plasma sintering (SPS) is investigated. The sintered carburized sample, which exhibits surface modification effects such as carburizing, sintered Fe, and sintered Fe–0.8 wt.%C alloys, is fabricated using SPS. X-ray diffraction and micro Vickers tests are employed to confirm the phase and properties. Finite element analysis is performed to evaluate the change in hardness and analyze the carbon content and residual stress of the carburized sample. The change in the hardness of the carburized sample has the same tendency to predict hardness. The difference in hardness between the carburized sample and the predicted value is also discussed. The carburized sample exhibits a compressive residual stress at the surface. These results indicate that the carburized sample experiences a surface modification effect without carburization. Field emission scanning electron microscopy is employed to verify the change in phase. A novel fabrication method for altering the carburization is successfully proposed. We expect this fabrication method to solve the problems associated with carburization.
|