- [Korean]
- Formation of Phases and Mechanical Properties of YSZ-Based Thermal Barrier Coating Materials Doped with Rare Earth Oxides
-
Yong Seok Choi, Gye Won Lee, Sahn Nahm, Yoon suk Oh
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):402-408. Published online October 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.402
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
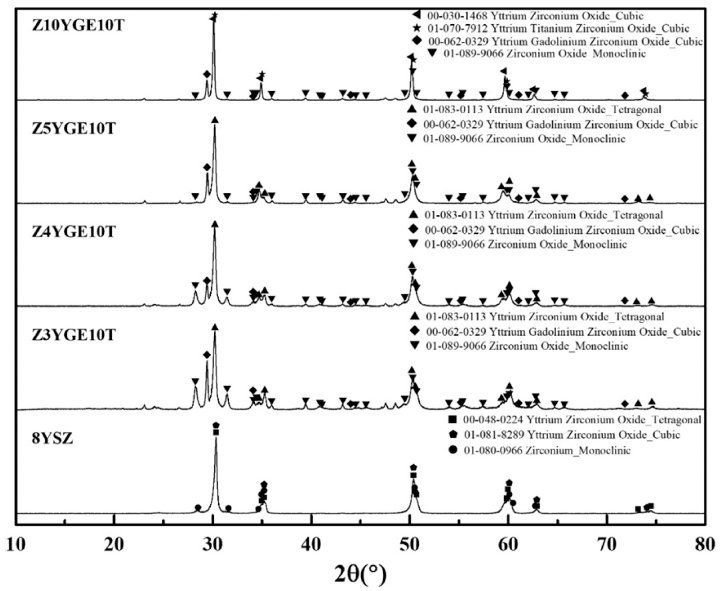
This study focused on improving the phase stability and mechanical properties of yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), commonly utilized in gas turbine engine thermal barrier coatings, by incorporating Gd2O3, Er2O3, and TiO2. The addition of 3-valent rare earth elements to YSZ can reduce thermal conductivity and enhance phase stability while adding the 4-valent element TiO2 can improve phase stability and mechanical properties. Sintered specimens were prepared with hot-press equipment. Phase analysis was conducted with X-ray diffraction (XRD), and mechanical properties were assessed with Vickers hardness equipment. The research results revealed that, except for Z10YGE10T, most compositions predominantly exhibited the t-phase. Increasing the content of 3-valent rare earth oxides resulted in a decrease in the monoclinic phase and an increase in the tetragonal phase. In addition, the t(400) angle decreased while the t(004) angle increased. The addition of 10 mol% of 3-valent rare-earth oxides discarded the t-phase and led to the complete development of the c-phase. Adding 10 mol% TiO2 increased hardness than YSZ.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Light-weight Ceramic Insulation Materials by Using Oxide Ceramic Fibers for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
-
Seongwon Kim, Min-Soo Nam, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sahn Nahm, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):477-484. Published online December 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.477
-
-
1,545
View
-
28
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
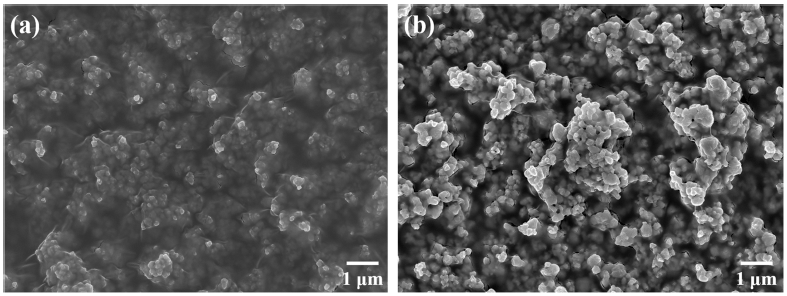
Thermal protection systems (TPS) are a group of materials that are indispensable for protecting spacecraft from the aerodynamic heating occurring during entry into an atmosphere. Among candidate materials for TPS, ceramic insulation materials are usually considered for reusable TPS. In this study, ceramic insulation materials, such as alumina enhanced thermal barrier (AETB), are fabricated via typical ceramic processing from ceramic fiber and additives. Mixtures of silica and alumina fibers are used as raw materials, with the addition of B4C to bind fibers together. Reaction-cured glass is also added on top of AETB to induce water-proof functionality or high emissivity. Some issues, such as the elimination of clumps in the AETB, and processing difficulties in the production of reusable surface insulation are reported as well. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 521. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Comparison of Properties with Different Sintering Process of 3Y-TZP/WC Composites
-
Min-Soo Nam, Jae-Hyung Choi, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):424-431. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.424
-
-
889
View
-
3
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
3Y-TZP ceramics obtained by doping 3 mol.% of Y2O3 to ZrO2 to stabilize the phase transition are widely used in the engineering ceramic industry due to their excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, fracture toughness, and wear resistance. An additional increase in mechanical properties is possible by manufacturing a composite in which a high-hardness material such as oxide or carbide is added to the 3Y-TZP matrix. In this study, composite powder was prepared by dispersing a designated percentage of WC in the 3Y-TZP matrix, and the results were compared after manufacturing the composite using the different processes of spark plasma sintering and HP. The difference between the densification behavior and porosity with the process mechanism was investigated. The correlation between the process conditions and phase formation was examined based on the crystalline phase formation behavior. Changes to the microstructure according to the process conditions were compared using field-emission scanning electron microscopy. The toughness-strengthening mechanism of the composite with densification and phase formation was also investigated. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 409. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Additive and Composition on Cutting Performance of SiAlON
-
Jae-Hyeong Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):415-420. Published online October 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.415
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
SiAlON ceramics are used as ceramic cutting tools for heat-resistant super alloys (HRSAs) due to their excellent fracture toughness and thermal properties. They are manufactured from nitride and oxide raw materials. Mixtures of nitrides and oxides are densified via liquid phase sintering by using gas pressure sintering. Rare earth oxides, when used as sintering additives, affect the color and mechanical properties of SiAlON. Moreover, these sintering additives influence the cutting performance. In this study, we have prepared Ybm/3Si12-(m+n)Alm+nOnN16-n (m = 0.5; n = 0.5, 1.0) ceramics and manufactured SiAlON ceramics, which resulted in different colors. In addition, the characteristics of the sintered SiAlON ceramics such as fracture toughness and microstructure have been investigated and results of the cutting test have been analyzed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Li2O-Bi2O3 Addition on the Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 Ceramics
-
Jae Hyuk Kim, Shi Yeon Kim, Jeoung Sik Choi, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):405-409. Published online October 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.405
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Piezoelectric ceramic specimens with the Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 (PMN-PT) composition are prepared by the solid state reaction method known as the “columbite precursor” method. Moreover, the effects of the Li2O-Bi2O3 additive on the microstructure, crystal structure, and piezoelectric properties of sintered PMN-PT ceramic samples are investigated. The addition of Li2O-Bi2O3 lowers the sintering temperature from 1,200°C to 950°C. Moreover, with the addition of >5 wt.% additive, the crystal structure changes from tetragonal to rhombohedral. Notably, the sample with 3 wt.% additive exhibits excellent piezoelectric properties (d33 = 596 pC/N and Kp = 57%) and a sintered density of 7.92 g/cm3 after sintering at 950°C. In addition, the sample exhibits a curie temperature of 138.6°C at 1 kHz. Finally, the compatibility of the sample with a Cu electrode is examined, because the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data indicate the absence of interdiffusion between Cu and the ceramic material.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameter and Mixing Process of Raw Materials on the Phase and Structure of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spray Method
-
Ho-lim Ryu, Seon-A Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyun Choi, Sahn Nahm, Yoon-Suk Oh
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):437-443. Published online December 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.437
-
-
832
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
SiC-based composite materials with light weight, high durability, and high-temperature stability have been actively studied for use in aerospace and defense applications. Moreover, environmental barrier coating (EBC) technologies using oxide-based ceramic materials have been studied to prevent chemical deterioration at a high temperature of 1300°C or higher. In this study, an ytterbium silicate material, which has recently been actively studied as an environmental barrier coating because of its high-temperature chemical stability, is fabricated on a sintered SiC substrate. Yb2O3 and SiO2 are used as the raw starting materials to form ytterbium disilicate (Yb2Si2O7). Suspension plasma spraying is applied as the coating method. The effect of the mixing method on the particle size and distribution, which affect the coating formation behavior, is investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. It is found that the originally designed compounds are not effectively formed because of the refinement and vaporization of the raw material particles, i.e., SiO2, and the formation of a porous coating structure. By changing the coating parameters such as the deposition distance, it is found that a denser coating structure can be formed at a closer deposition distance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
-
Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):420-425. Published online December 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.420
-
-
1,101
View
-
4
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
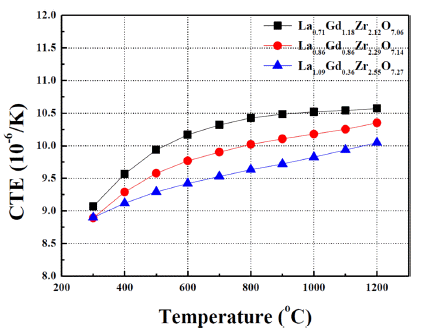
Rare-earth zirconates, such as lanthanum zirconates and gadolinium zirconates, have been intensively investigated due to their excellent properties of low thermal conductivity as well as chemical stability at high temperature, which can make these materials ones of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating applications. In this study, three compositions, lanthanum/gadolinium zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents from stoichiometric RE2Zr2O7 compositions, are fabricated via solid state reaction as well as sintering at 1600°C for 4 hrs. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of three oxide ceramics are examined. In particular, each oxide ceramics exhibits composite structures between pyrochlore and fluorite phases. The potential of lanthanum/ gadolinium zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
Sahar Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Masoud Salavati-Niasari, Azam Sobhani, Zahra Zinatloo-Ajabshir
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 767: 1164. CrossRef - A novel Co-ions complexation method to synthesize pyrochlore La 2 Zr 2 O 7
Chunhui Xu, Hongyun Jin, Qifeng Zhang, Can Huang, Daifeng Zou, Fujian He, Shuen Hou
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2017; 37(8): 2871. CrossRef - Fabrication and Characteristics of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the La2O3-Gd2O3-ZrO2System by Using Suspension Plasma Spray with Different Suspension Preparations
Soyul Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of the Korean institute of surface engineering.2016; 49(6): 595. CrossRef
|