Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
- Gyuhwi Lee, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):193-197. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.193
- 697 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
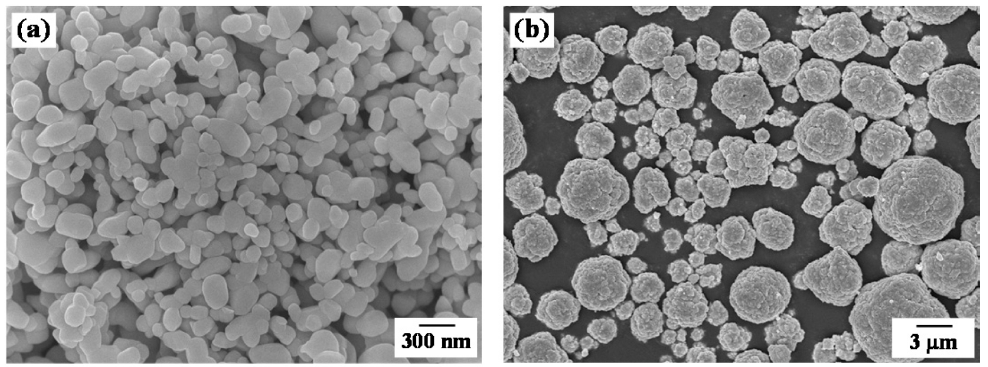
PDF Porous Cu-14 wt% Co with aligned pores is produced by a freeze drying and sintering process. Unidirectional freezing of camphene slurry with CuO-Co3O4 powders is conducted, and pores in the frozen specimens are generated by sublimation of the camphene crystals. The dried bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 500°C and sintered at 800°C for 1 h. The reduction behavior of the CuO-Co3O4 powder mixture is analyzed using a temperature-programmed reduction method in an Ar-10% H2 atmosphere. The sintered bodies show large and aligned parallel pores in the camphene growth direction. In addition, small pores are distributed around the internal walls of the large pores. The size and fraction of the pores decrease as the amount of solid powder added to the slurry increases. The change in pore characteristics according to the amount of the mixed powder is interpreted to be due to the rearrangement and accumulation behavior of the solid particles in the freezing process of the slurry.
- [Korean]
- Freeze Drying Process and Pore Structure Characteristics of Porous Cu with Various Sublimable Vehicles
- Gyuhwi Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Myung-Jin Suk, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):198-202. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.198
- 693 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
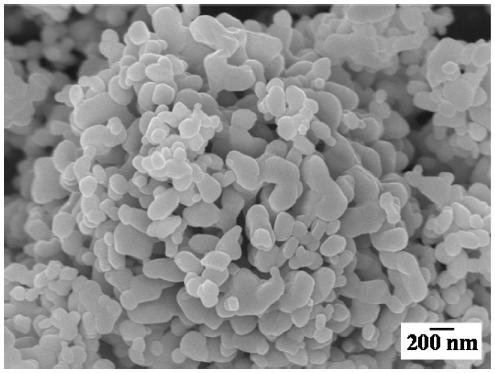
PDF The effect of sublimable vehicles on the pore structure of Cu fabricated by freeze drying is investigated. The 5 vol% CuO-dispersed slurries with camphene and various camphor-naphthalene compositions are frozen in a Teflon mold at -25°C, followed by sublimation at room temperature. After hydrogen reduction at 300°C and sintering at 600 °C, the green bodies of CuO are completely converted to Cu with various pore structures. The sintered samples prepared using CuO/camphene slurries show large pores that are aligned parallel to the sublimable vehicle growth direction. In addition, a dense microstructure is observed in the bottom section of the specimen where the solidification heat was released, owing to the difference in the solidification behavior of the camphene crystals. The porous Cu shows different pore structures, such as dendritic, rod-like, and plate shaped, depending on the composition of the camphornaphthalene system. The change in pore structure is explained by the crystal growth behavior of primary camphor and eutectic and primary naphthalene.
- [Korean]
- Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
- Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.203

- 862 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The automotive industry has focused on the development of metallic materials with high specific strength, which can meet both fuel economy and safety goals. Here, a new class of ultrafine-grained high-Mn steels containing nano-scale oxides is developed using powder metallurgy. First, high-energy mechanical milling is performed to dissolve alloying elements in Fe and reduce the grain size to the nanometer regime. Second, the ball-milled powder is consolidated using spark plasma sintering. During spark plasma sintering, nanoscale manganese oxides are generated in Fe-15Mn steels, while other nanoscale oxides (e.g., aluminum, silicon, titanium) are produced in Fe-15Mn-3Al-3Si and Fe-15Mn-3Ti steels. Finally, the phases and resulting hardness of a variety of high-Mn steels are compared. As a result, the sintered pallets exhibit superior hardness when elements with higher oxygen affinity are added; these elements attract oxygen from Mn and form nanoscale oxides that can greatly improve the strength of high-Mn steels.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Liquid Al Erosion Property of Tribaloy T-800 Coating Material Manufactured by Laser Cladding Process
- Kyoung-Wook Kim, Gi-Su Ham, Sun-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):210-218. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.210
- 555 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
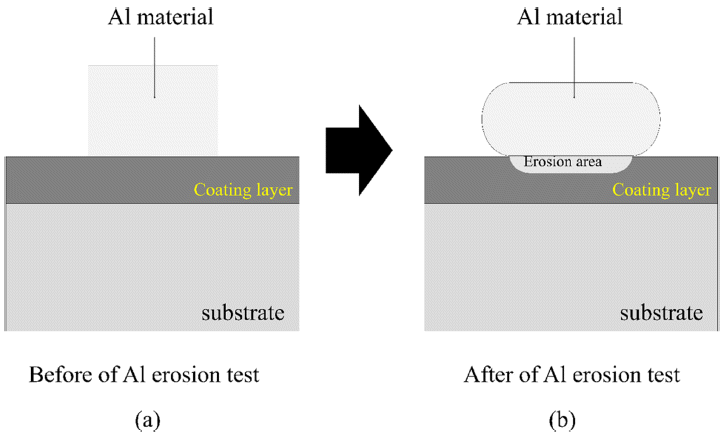
PDF A T-800 (Co-Mo-Cr) coating material is fabricated using Co-Mo-Cr powder feedstock and laser cladding. The microstructure and melted Al erosion properties of the laser-cladded T-800 coating material are investigated. The Al erosion properties of the HVOF-sprayed MoB-CoCr and bulk T-800 material are also examined and compared with the laser-cladded T-800 coating material. Co and lave phases (Co2MoCr and Co3Mo2Si) are detected in both the lasercladded T-800 coating and the bulk T-800 materials. However, the sizes of the lave phases are measured as 7.9 μm and 60.6 μm for the laser-cladded and bulk T-800 materials, respectively. After the Al erosion tests, the erosion layer thicknesses of the three materials are measured as 91.50 μm (HVOF MoB-CoCr coating), 204.83 μm (laser cladded T-800), and 226.33 μm (bulk T-800). In the HVOF MoB-CoCr coating material, coarse cracks and delamination of the coating layer are observed. On the other hand, no cracks or local delamination of the coating layer are detected in the laser T-800 material even after the Al erosion test. Based on the above results, the authors discuss the appropriate material and process that could replace conventional bulk T-800 materials used as molten Al pots.
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
- Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):219-225. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.219

- 1,615 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The directed energy deposition (DED) process of metal 3D printing technologies has been treated as an effective method for welding, repairing, and even 3-dimensional building of machinery parts. In this study, stainless steel 316L (STS316L) and Inconel 625 (IN625) alloy powders are additively manufactured using the DED process, and the microstructure of the fabricated STS316L/IN625 sample is investigated. In particular, there are no secondary phases in the interface between STS316L and the IN625 alloy. The EDS and Vickers hardness results clearly show compositionally and mechanically transient layers a few tens of micrometers in thickness. Interestingly, several cracks are only observed in the STS 316L rather than in the IN625 alloy near the interface. In addition, small-sized voids 200–400 nm in diameter that look like trapped pores are present in both materials. The cracks present near the interface are formed by tensile stress in STS316L caused by the difference in the CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion) between the two materials during the DED process. These results can provide fundamental information for the fabrication of machinery parts that require joining of two materials, such as valves.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructures and mechanical properties of 316LSi/IN625 FGMs manufactured by CMT-WAAM
Jiang Aimin, Ahmad Baharuddin Abdullah, Shahir Mohd Yusuf
Advances in Mechanical Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Microstructures and mechanical properties of 316LSi/IN625 FGMs manufactured by CMT-WAAM
- [Korean]
- Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Microstructure and Photocatalytic Activity of Electrospun BiVO4 Nanofiber
- Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Yun Taek Ko, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.226
- 1,181 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
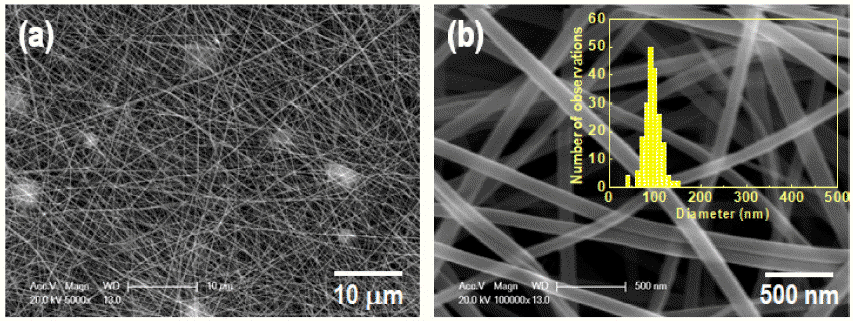
PDF Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is considered a potentially attractive candidate for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. In an effort to enhance their photocatalytic activities, BiVO4 nanofibers with controlled microstructures, grain sizes, and crystallinities are successfully prepared by electrospinning followed by a precisely controlled heat treatment. The structural features, morphologies, and photo-absorption performances of the asprepared samples are systematically investigated and can be readily controlled by varying the calcination temperature. From the physicochemical analysis results of the synthesized nanofiber, it is found that the nanofiber calcines at a lower temperature, shows a smaller crystallite size, and lower crystallinity. The photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B (RhB) reveals that the photocatalytic activity of the BiVO4 nanofibers can be improved by a thermal treatment at a relatively low temperature because of the optimization of the conflicting characteristics, crystallinity, crystallite size, and microstructure. The photocatalytic activity of the nanofiber calcined at 350°C for the degradation of RhB under visible-light irradiation exhibits a greater photocatalytic activity than the nanofibers synthesized at 400°C and 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
Jimin Lee, Minseob Lim, Tae Sung Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Jong-Sik Lee, Hong-Baek Cho, Joo Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2021; 548: 149198. CrossRef
- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
- [Korean]
- Influence of Reducing Agents and Additives on the Synthesis of ZnSe Nanoparticles
- Geum Ji Back, Da Gyeong Lee, Min Seo Lee, Ha Yeon Song, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):233-240. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.233
- 605 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
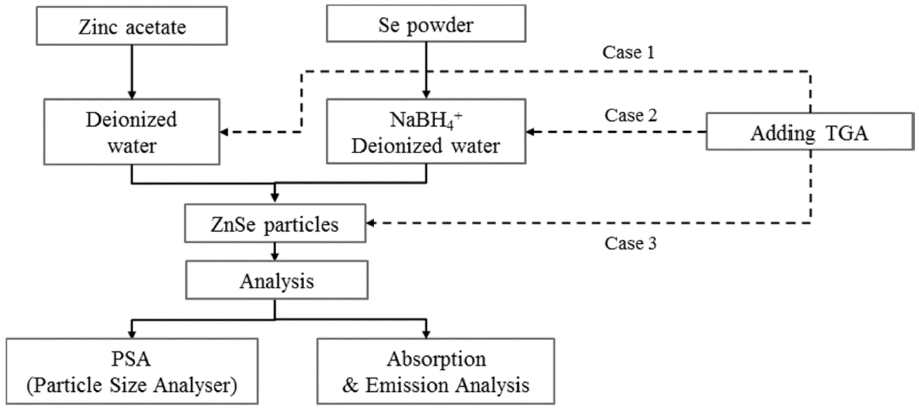
PDF Nano-sized ZnSe particles are successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution at room temperature using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and thioglycolic acid (TGA) as the reducing agent and stabilizer, respectively. The effects of the mass ratio of the reducing agent to Se, stabilizer concentration, and stirring time on the synthesis of the ZnSe nanoparticles are evaluated. The light absorption/emission properties of the synthesized nanoparticles are characterized using ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and particle size analyzer (PSA) techniques. At least one mass ratio (NaBH4/Se) of the reducing agent should be added to produce ZnSe nanoparticles finer than 10 nm and to absorb UV–vis light shorter than the ZnSe bulk absorption wavelength of 460 nm. As the ratio of the reducing agent increases, the absorption wavelengths in the UV-vis curves are blue-shifted. Stirring in the atmosphere acts as a deterrent to the reduction reaction and formation of nanoparticles, but if not stirred in the atmosphere, the result is on par with synthesis in a nitrogen atmosphere. The stabilizer, TGA, has an impact on the Zn precursor synthesis. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit excellent photo-absorption/discharge characteristics, suggesting that ZnSe nanoparticles can be alloyed without the need for organic solutions or high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Gastrodia elata -loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability - Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):241-246. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.241
- 809 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
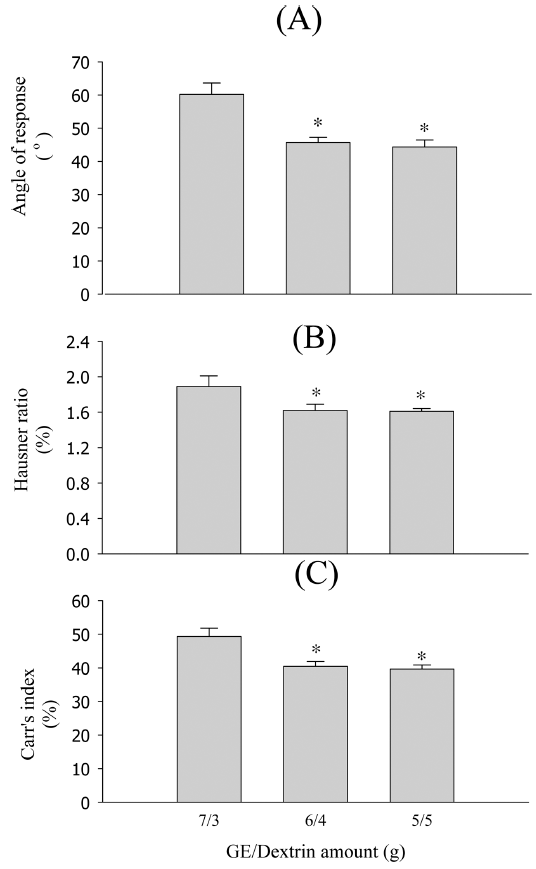
Gastrodia elata (GE)-loaded particles for herbal extract dosage forms, various GE-loaded particles containing dextrin, isomalt, maltodextrin, and silicon dioxide as solidifying carriers in the GE water extract are prepared using the spray drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using the repose angle, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, weight increase rate at 40°C/75% RH condition, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Particles made of dextrin improve the fluidity, compressibility, and water stability. In addition, 2% silicon dioxide increases the fluidity and moisture stability. The best flowability and compressibility of GE-loaded particles are observed with TP, dextrin, and silicon dioxide amounts in the ratio of 6/4/0.2 (34.29 ± 2.86°, 1.48 ± 0.03, and 38.29 ± 2.39%, repose angle, Hausner Ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively) and moisture stability with a 2% weight increase rate for 14 h at 40°C/75% RH condition. Therefore, our results suggest that the particles prepared by the spray drying method with dextrin and 2% silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability, compressibility, and moisture stability of GE.
- [Korean]
- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
- Geon-Ju Choi, Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):247-255. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.247
- 1,078 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
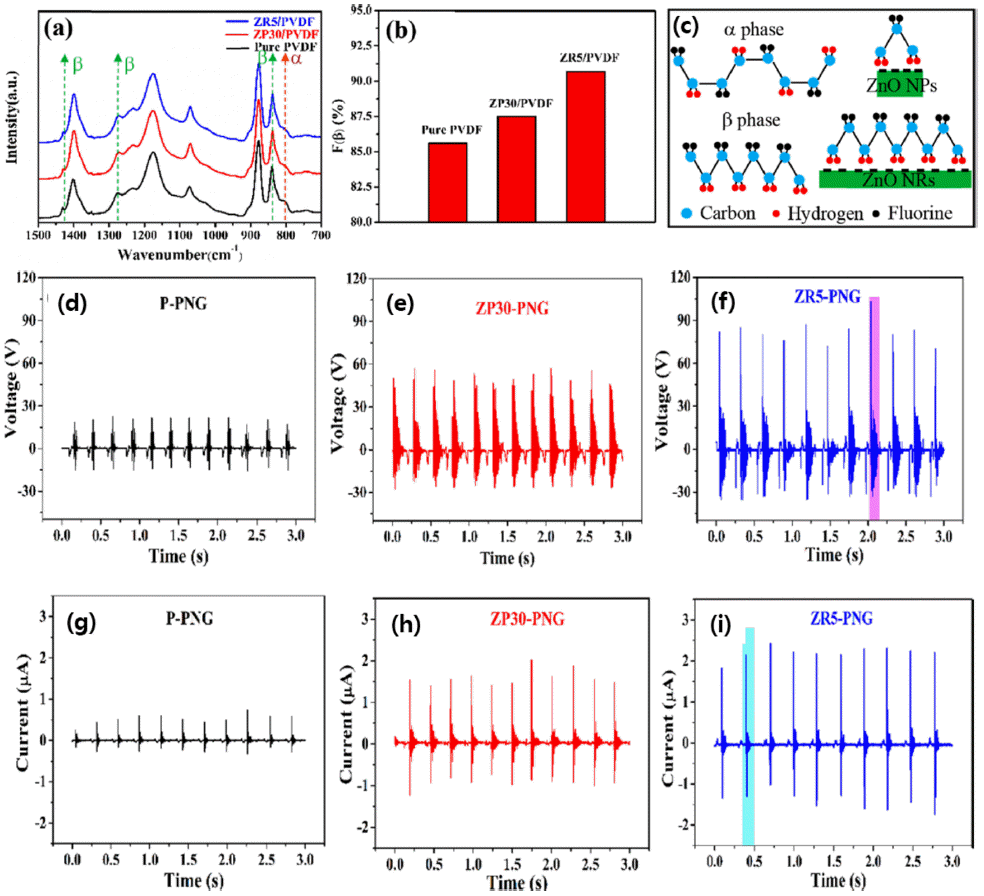
PDF Recently, interest in technology for eco-friendly energy harvesting has been increasing. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is one of the most fascinating materials that has been used in energy harvesting technology as well as micro-filters by utilizing an electrostatic effect. To enhance the performance of the electrostatic effect-based nanogenerator, most studies have focused on enlarging the contact surface area of the pair of materials with different triboelectric series. For this reason, one-dimensional nanofibers have been widely used recently. In order to realize practical energy-harvesting applications, PVDF nanofibers are modified by enlarging their contact surface area, modulating the microstructure of the surface, and maximizing the fraction of the β-phase by incorporating additives or forming composites with inorganic nanoparticles. Among them, nanocomposite structures incorporating various nanoparticles have been widely investigated to increase the β-phase through strong hydrogen bonding or ion-dipole interactions with -CF2/CH2- of PVDF as well as to enhance the mechanical strength. In this study, we report the recent advances in the nanocomposite structure of PVDF nanofibers and inorganic nanopowders.
- [English]
- Multi-step Metals Additive Manufacturing Technologies
- Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Hanshin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):256-267. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.256
- 1,543 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
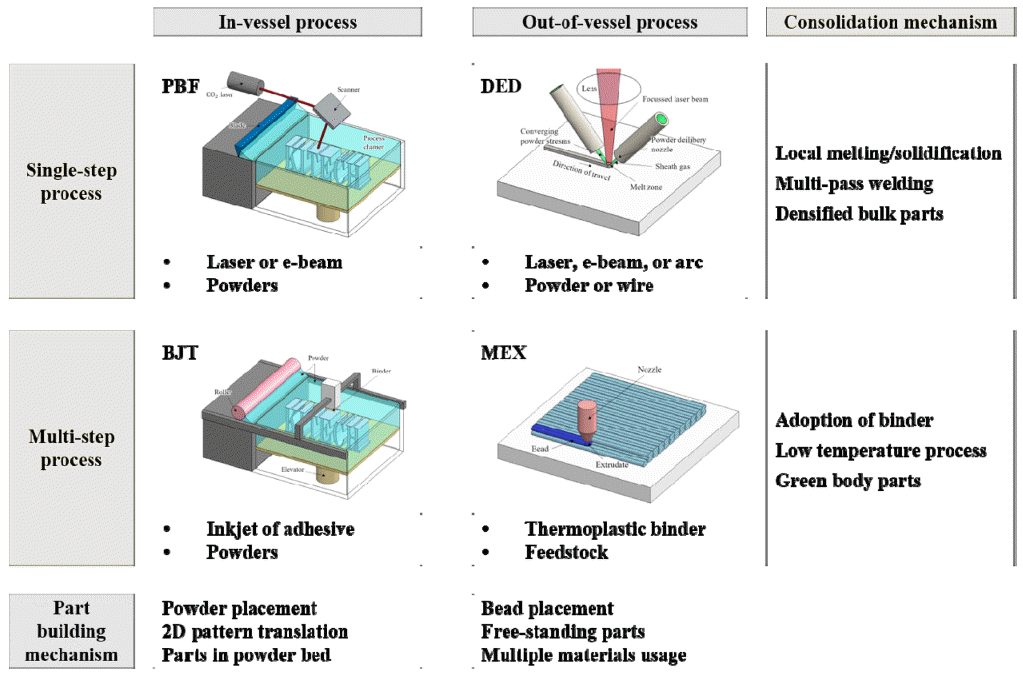
PDF Metal additive manufacturing (AM) technologies are classified into two groups according to the consolidation mechanisms and densification degrees of the as-built parts. Densified parts are obtained via a single-step process such as powder bed fusion, directed energy deposition, and sheet lamination AM technologies. Conversely, green bodies are consolidated with the aid of binder phases in multi-step processes such as binder jetting and material extrusion AM. Green-body part shapes are sustained by binder phases, which are removed for the debinding process. Chemical and/or thermal debinding processes are usually devised to enhance debinding kinetics. The pathways to final densification of the green parts are sintering and/or molten metal infiltration. With respect to innovation types, the multistep metal AM process allows conventional powder metallurgy manufacturing to be innovated continuously. Eliminating cost/time-consuming molds, enlarged 3D design freedom, and wide material selectivity create opportunities for the industrial adoption of multi-step AM technologies. In addition, knowledge of powders and powder metallurgy fuel advances of multi-step AM technologies. In the present study, multi-step AM technologies are briefly introduced from the viewpoint of the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential and challenges for Powder Bed Fusion – Laser Beam (PBF-LB) in industrial ceramic additive manufacturing
Christian Berger, Gabriela Schimo-Aichhorn, Stefan Gronau, Franziska Saft, Sarah Seiringer, Uwe Scheithauer
Open Ceramics.2024; 18: 100614. CrossRef - Fabrication of Cu-Infiltrated Journal Bearing by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing
Jin Man Jang
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 912. CrossRef - SiC-Si composite part fabrication via SiC powder binder jetting additive manufacturing and molten-Si infiltration
Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Sahn Nahm, Hanshin Choi
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2021; 101: 105686. CrossRef
- Potential and challenges for Powder Bed Fusion – Laser Beam (PBF-LB) in industrial ceramic additive manufacturing
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI




 First
First Prev
Prev


