Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Comparative Study of Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels and Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- Sunghee Choi, Seulgi Kim, Seojin Woo, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00472
- 1,627 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
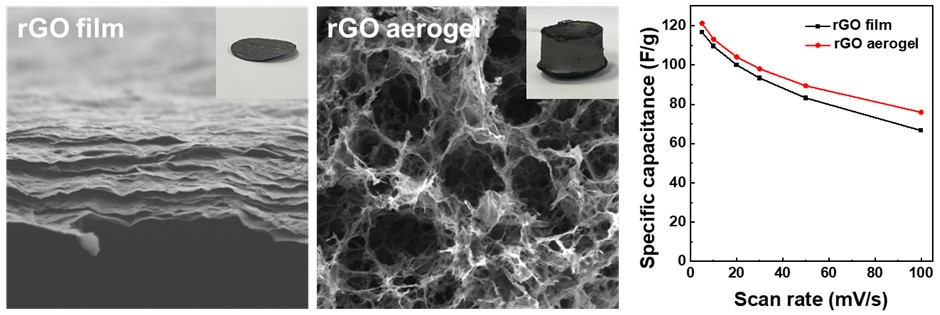
PDF - Supercapacitors, renowned for their high power density and rapid charge-discharge rates, are limited by their low energy density. This limitation has prompted the need for advanced electrode materials. The present study investigated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in two distinct structures, as a film and as an aerogel, for use as supercapacitor electrodes. The rGO film, prepared by vacuum filtration and thermal reduction, exhibited a compact, lamellar structure, while the aerogel, synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, was a highly porous three-dimensional network. Electrochemical analyses demonstrated the aerogel’s superior performance, as shown by a specific capacitance of 121.2 F/g at 5 mV/s, with 94% capacitance retention after 10,000 cycles. These findings emphasize the importance of structural design in optimizing ion accessibility and charge transfer. They also demonstrate the potential of rGO aerogels for increasing the energy storage efficiency of advanced supercapacitor systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Sintering Behavior Analysis of Molybdenum-tungsten Nanopowders by Pechini Process
- Suyeon Kim, Taehyun Kwon, Seulgi Kim, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):436-441. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.436
- 877 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
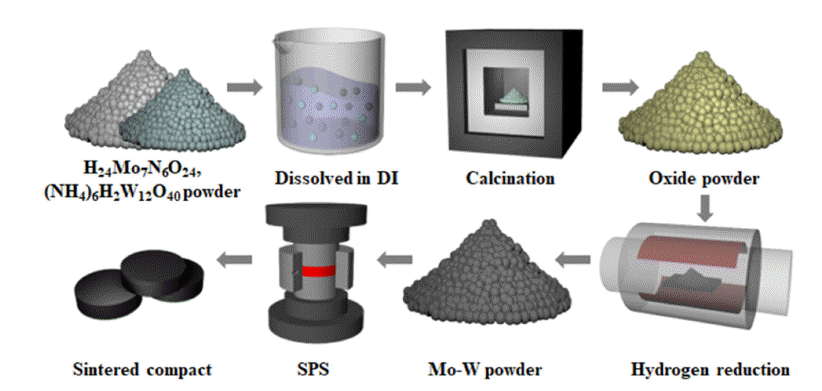
PDF Molybdenum-tungsten (Mo-W) alloy sputtering targets are widely utilized in fields like electronics, nanotechnology, sensors, and as gate electrodes for TFT-LCDs, owing to their superior properties such as hightemperature stability, low thermal expansion coefficient, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. To achieve optimal performance in application, these targets’ purity, relative density, and grain size of these targets must be carefully controlled. We utilized nanopowders, prepared via the Pechini method, to obtain uniform and fine powders, then carried out spark plasma sintering (SPS) to densify these powders. Our studies revealed that the sintered compacts made from these nanopowders exhibited outstanding features, such as a high relative density of more than 99%, consistent grain size of 3.43 μm, and shape, absence of preferred orientation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 509. CrossRef
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
- Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
- 1,092 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
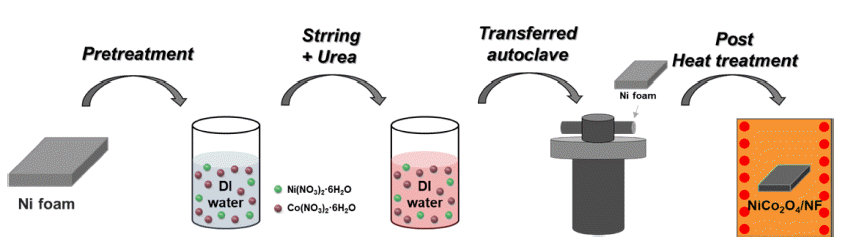
PDF Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Mechano-chemical Ball Milling Process for Fabricating Tungsten Disulfide Nanosheets
- Seulgi Kim, Yunhee Ahn, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):376-381. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.376

- 521 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten disulfide (WS2) nanosheets have attracted considerable attention because of their unique optical and electrical properties. Several methods for fabrication of WS2 nanosheets have been developed. However, methods for mass production of high-quality WS2 nanosheets remain challenging. In this study, WS2 nanosheets were fabricated using mechano-chemical ball milling based on the synergetic effects of chemical intercalation and mechanical exfoliation. The ball-milling time was set as a variable for the optimized fabricating process of WS2 nanosheets. Under the optimized conditions, the WS2 nanosheets had lateral sizes of 500–600 nm with either a monolayer or bilayer. They also exhibited high crystallinity in the 2H semiconducting phase. Thus, the proposed method can be applied to the exfoliation of other transition metal dichalcogenides using suitable chemical intercalants. It can also be used with highperformance WS2-based photodiodes and transistors used in practical semiconductor applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 509. CrossRef
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- [Korean]
- Cobalt Recovery by Oxalic Acid and Hydroxide Precipitation from Waste Cemented Carbide Scrap Cobalt Leaching Solution
- Jaesung Lee, Mingoo Kim, Seulgi Kim, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):497-501. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.497
- 1,272 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
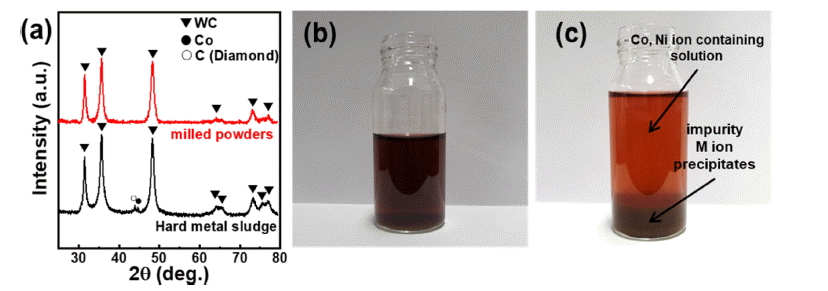
PDF Cobalt (Co) is mainly used to prepare cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and binder metals for WC-Co hard metals. Developing an effective method for recovering Co from WC-Co waste sludge is of immense significance. In this study, Co is extracted from waste cemented carbide soft scrap via mechanochemical milling. The leaching ratio of Co reaches approximately 93%, and the leached solution, from which impurities except nickel are removed by pH titration, exhibits a purity of approximately 97%. The titrated aqueous Co salts are precipitated using oxalic acid and hydroxide precipitation, and the effects of the precipitating agent (oxalic acid and hydroxide) on the cobalt microstructure are investigated. It is confirmed that the type of Co compound and the crystal growth direction change according to the precipitation method, both of which affect the microstructure of the cobalt powders. This novel mechanochemical process is of significant importance for the recovery of Co from waste WC-Co hard metal. The recycled Co can be applied as a cemented carbide binder or a cathode material for lithium secondary batteries.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticle Decorated on Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Composite Electrodes for Supercapacitors
- Hyewon Hwang, Seoyeon Yuk, Minsik Jung, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.470
- 721 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
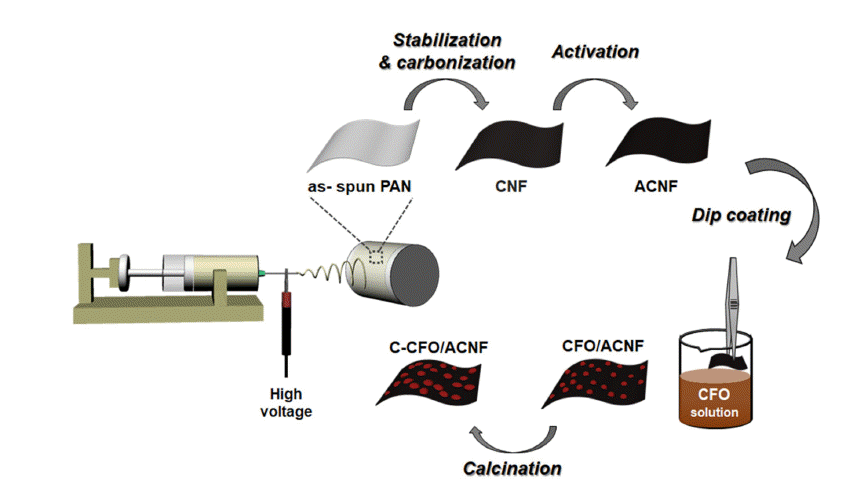
PDF Energy storage systems should address issues such as power fluctuations and rapid charge-discharge; to meet this requirement, CoFe2O4 (CFO) spinel nanoparticles with a suitable electrical conductivity and various redox states are synthesized and used as electrode materials for supercapacitors. In particular, CFO electrodes combined with carbon nanofibers (CNFs) can provide long-term cycling stability by fabricating binder-free three-dimensional electrodes. In this study, CFO-decorated CNFs are prepared by electrospinning and a low-cost hydrothermal method. The effects of heat treatment, such as the activation of CNFs (ACNFs) and calcination of CFO-decorated CNFs (C-CFO/ACNFs), are investigated. The C-CFO/ACNF electrode exhibits a high specific capacitance of 142.9 F/g at a scan rate of 5 mV/s and superior rate capability of 77.6% capacitance retention at a high scan rate of 500 mV/s. This electrode also achieves the lowest charge transfer resistance of 0.0063 Ω and excellent cycling stability (93.5% retention after 5,000 cycles) because of the improved ion conductivity by pathway formation and structural stability. The results of our work are expected to open a new route for manufacturing hybrid capacitor electrodes containing the C-CFO/ACNF electrode that can be easily prepared with a low-cost and simple process with enhanced electrochemical performance.
- [Korean]
- Thermophysical Properties of Copper/graphite Flake Composites by Electroless Plating and Spark Plasma Sintering
- Jaesung Lee, Ji Yeon Kang, Seulgi Kim, Chanhoe Jung, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.25
- 1,259 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
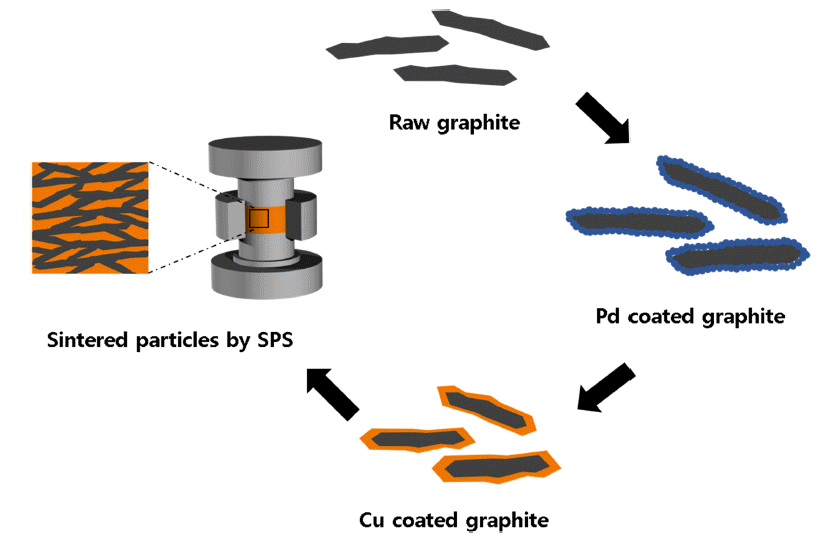
PDF Recently, the amount of heat generated in devices has been increasing due to the miniaturization and high performance of electronic devices. Cu-graphite composites are emerging as a heat sink material, but its capability is limited due to the weak interface bonding between the two materials. To overcome these problems, Cu nanoparticles were deposited on a graphite flake surface by electroless plating to increase the interfacial bonds between Cu and graphite, and then composite materials were consolidated by spark plasma sintering. The Cu content was varied from 20 wt.% to 60 wt.% to investigate the effect of the graphite fraction and microstructure on thermal conductivity of the Cu-graphite composites. The highest thermal conductivity of 692 W m−1K−1 was achieved for the composite with 40 wt.% Cu. The measured coefficients of thermal expansion of the composites ranged from 5.36 × 10−6 to 3.06 × 10−6 K−1. We anticipate that the Cu-graphite composites have remarkable potential for heat dissipation applications in energy storage and electronics owing to their high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion coefficient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experimental and numerical investigation of thermally stable Cu/Mo/Cu spacer with low-CTE and high-k for double side cooling power semiconductor modules
YehRi Kim, Byeongchan Kim, Kue Jin Han, Taeseong Han, Dongjin Kim
Applied Thermal Engineering.2026; 288: 129661. CrossRef
- Experimental and numerical investigation of thermally stable Cu/Mo/Cu spacer with low-CTE and high-k for double side cooling power semiconductor modules
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


