Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
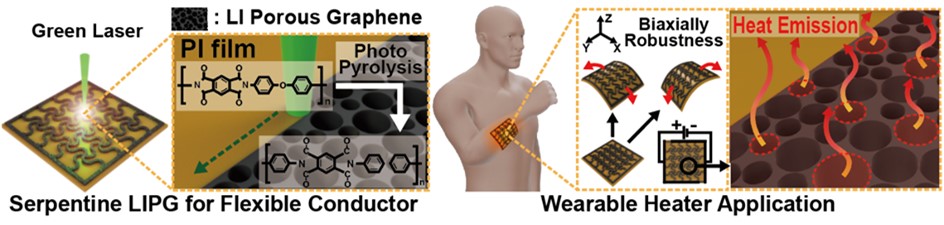
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
- 636 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [English]
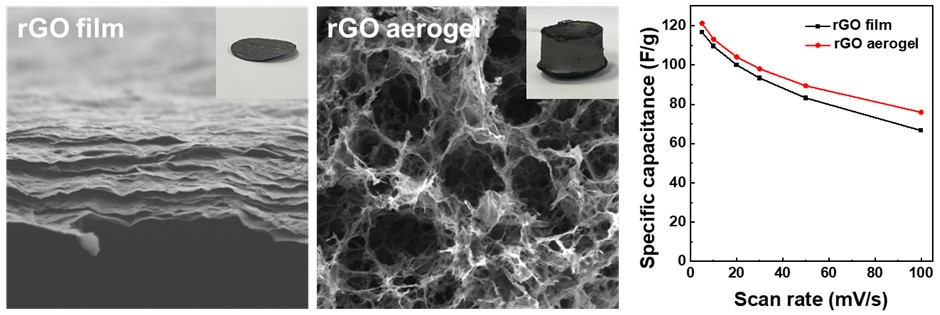
- Comparative Study of Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels and Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- Sunghee Choi, Seulgi Kim, Seojin Woo, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00472
- 1,626 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Supercapacitors, renowned for their high power density and rapid charge-discharge rates, are limited by their low energy density. This limitation has prompted the need for advanced electrode materials. The present study investigated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in two distinct structures, as a film and as an aerogel, for use as supercapacitor electrodes. The rGO film, prepared by vacuum filtration and thermal reduction, exhibited a compact, lamellar structure, while the aerogel, synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, was a highly porous three-dimensional network. Electrochemical analyses demonstrated the aerogel’s superior performance, as shown by a specific capacitance of 121.2 F/g at 5 mV/s, with 94% capacitance retention after 10,000 cycles. These findings emphasize the importance of structural design in optimizing ion accessibility and charge transfer. They also demonstrate the potential of rGO aerogels for increasing the energy storage efficiency of advanced supercapacitor systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [English]
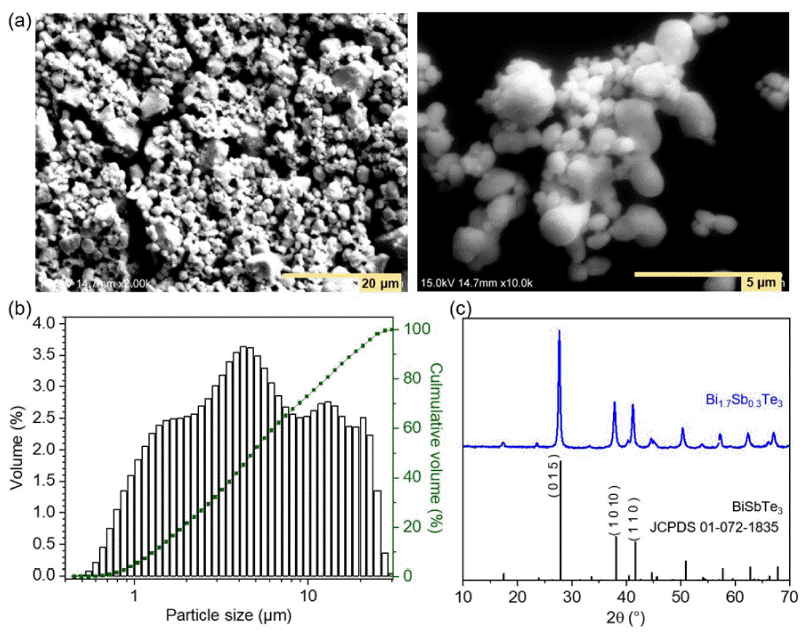
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,684 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- [Korean]
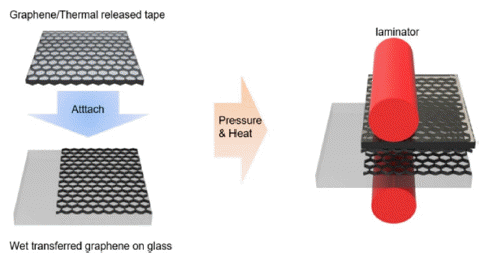
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
- 534 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Graphene Coated Aluminum Powders by Self-assemble Reaction
- Jin Uk Hwang, Woo Seong Tak, Sang Yong Nam, Woo Sik Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):383-388. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.383

- 905 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To improve the mechanical properties of aluminum, graphene has been used as a reinforcing material, yielding graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites (GRAMCs). Dispersion of graphene materials is an important factor that affects the properties of GRAMCs, which are mainly manufactured by mechanical mixing methods such as ball milling. However, the use of only mechanical mixing process is limited to achieve homogeneous dispersion of graphene. To overcome this problem, in this study, we have prepared composite materials by coating aluminum particles with graphene by a self-assembly reaction using poly vinylalcohol and ethylene diamine as coupling agents. The scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy results confirm the coating of graphene on the Al surface. Bulk density of the sintered composites by spark plasma sintering achieved a relative density of over 99% up to 0.5 wt.% graphene oxide content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Reactive Al/CuO Nano-composite using Graphene Oxide
- YeSeul Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):220-224. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.220

- 745 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The aluminum (Al)/copper oxide (CuO) complex is known as the most promising material for thermite reactions, releasing a high heat and pressure through ignition or thermal heating. To improve the reaction rate and wettability for handling safety, nanosized primary particles are applied on Al/CuO composite for energetic materials in explosives or propellants. Herein, graphene oxide (GO) is adopted for the Al/CuO composites as the functional supporting materials, preventing a phase-separation between solvent and composites, leading to a significantly enhanced reactivity. The characterizations of Al/CuO decorated on GO(Al/CuO/GO) are performed through scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy mapping analysis. Moreover, the functional bridging between Al/CuO and GO is suggested by identifying the chemical bonding with GO in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. The reactivity of Al/CuO/GO composites is evaluated by comparing the maximum pressure and rate of the pressure increase of Al/CuO and Al/CuO/GO. The composites with a specific concentration of GO (10 wt%) demonstrate a well-dispersed mixture in hexane solution without phase separation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 332. CrossRef
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- [Korean]
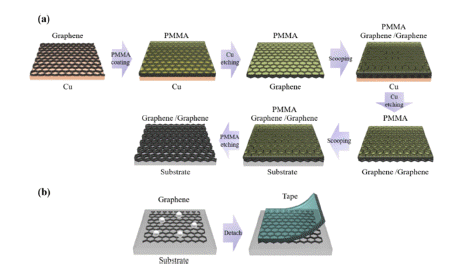
- A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
- Chae-young Woo, Yeongsu Jo, Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):11-15. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.11
- 1,488 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a method to remove residual powder on a multi-layered graphene and a new approach to transfer multi-layered graphene at once are studied. A graphene one-step transfer (GOST) method is conducted to minimize the residual powder comparison with a layer-by-layer transfer. Furthermore, a residual powder removing process is investigated to remove residual powder at the top of a multi-layered graphene. After residual powder is removed, the sheet resistance of graphene is decreased from 393 to 340 Ohm/sq in a four-layered graphene. In addition, transmittance slightly increases after residual powder is removed from the top of the multi-layered graphene. Optical and atomic-force microscopy images are used to analyze the graphene surface, and the Ra value is reduced from 5.2 to 3.7 nm following residual powder removal. Therefore, GOST and residual powder removal resolve the limited application of graphene electrodes due to residual powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 305. CrossRef
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- [Korean]
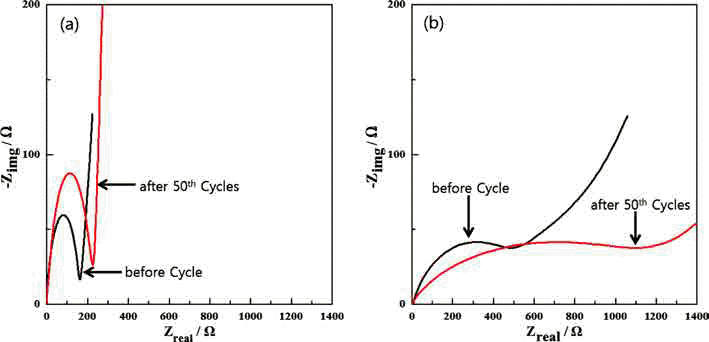
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308
- 972 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [Korean]
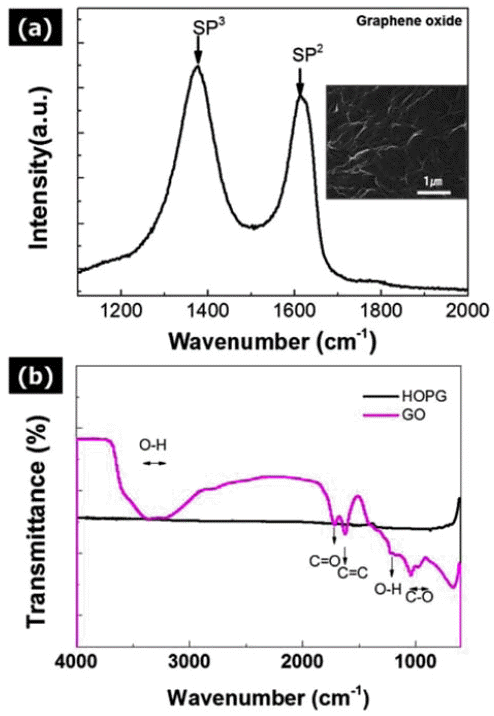
- Investigation on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Telluride Matrix Composites by Addition of Graphene Oxide Powders
- Kyung Tae Kim, Taesik Min, Dong Won Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):263-269. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.263
- 749 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Graphene oxide (GO) powder processed by Hummer's method is mixed with p-type Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by a high-energy ball milling process. The synthesized GO-dispersed p-type Bi2Te3 composite powder has a composition of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 (BSbT), and the powder is consolidated into composites with different contents of GO powder by using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. It is found that the addition of GO powder significantly decreases the thermal conductivity of the pure BSbT material through active phonon scattering at the newly formed interfaces. In addition, the electrical properties of the GO/BSbT composites are degraded by the addition of GO powder except in the case of the 0.1 wt% GO/BSbT composite. It is found that defects on the surface of GO powder hinder the electrical transport properties. As a result, the maximum thermoelectric performance (ZT value of 0.91) is achieved from the 0.1% GO/BSbT composite at 398 K. These results indicate that introducing GO powder into thermoelectric materials is a promising method to achieve enhanced thermoelectric performance due to the reduction in thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
Hua‐Lu Zhuang, Jincheng Yu, Jing‐Feng Li
Small Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - The role of edge-oxidized graphene to improve the thermopower of p-type bismuth telluride-based thick films
Young Min Cho, Kyung Tae Kim, Gi Seung Lee, Soo Hyung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 476: 533. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef
- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


