Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- A Review of Recent Developments in CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Processed by Powder Metallurgy
- Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, K. Raja Rao, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):145-164. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00430
- 4,331 View
- 111 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
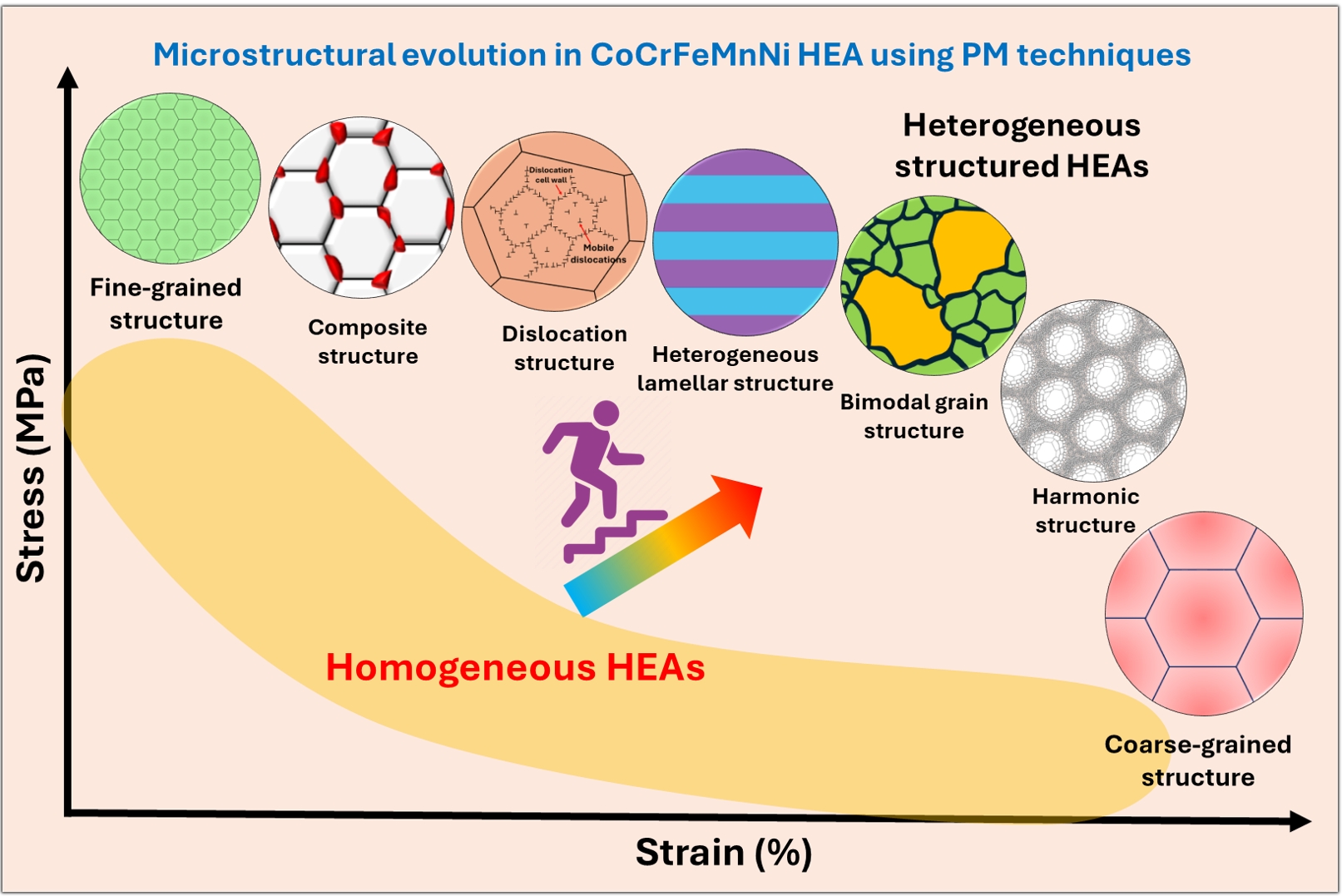
PDF - In recent years, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted considerable attention in materials engineering due to their unique phase stability and mechanical properties compared to conventional alloys. Since the inception of HEAs, CoCrFeMnNi alloys have been widely investigated due to their outstanding strength and fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures. However, their lower yield strength at room temperature limits their structural applications. The mechanical properties of HEAs are greatly influenced by their processing methods and microstructural features. Unlike traditional melting techniques, powder metallurgy (PM) provides a unique opportunity to produce HEAs with nanocrystalline structures and uniform compositions. The current review explores recent advances in optimizing the microstructural characteristics in CoCrFeMnNi HEAs by using PM techniques to improve mechanical performance. The most promising strategies include grain refinement, dispersion strengthening, and the development of heterogeneous microstructures (e.g., harmonic, bimodal, and multi-metal lamellar structures). Thermomechanical treatments along with additive manufacturing techniques are also summarized. Additionally, the review addresses current challenges and suggests future research directions for designing advanced HEAs through PM techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Structural and mechanical characteristics of high-entropy CoCrFeMnNi alloys manufactured by vacuum induction melting
V. K. Drobyshev, I. A. Panchenko, S. V. Konovalov, E. M. Zapolskaya
Russian Physics Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- Advances in Powder Metallurgy for High-Entropy Alloys
- Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Hansung Lee, K. Raja Rao, Man Mohan, Reliance Jain, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):480-492. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00297
- 4,746 View
- 164 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
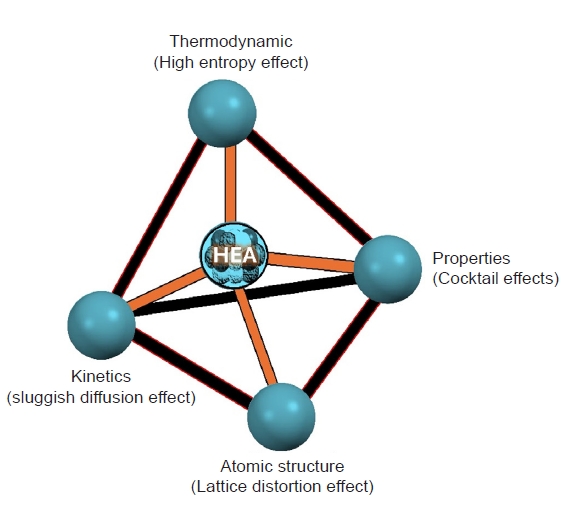
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a revolutionary class of materials characterized by their multi-principal element compositions and exceptional mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy, a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process, offers significant advantages for the development of HEAs, including precise control over their composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties. This review explores innovative approaches integrating powder metallurgy techniques in the synthesis and optimization of HEAs. Key advances in powder production, sintering methods, and additive manufacturing are examined, highlighting their roles in improving the performance, advancement, and applicability of HEAs. The review also discusses the mechanical properties, potential industrial applications, and future trends in the field, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of HEA development using powder metallurgy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Latest Advancements and Mechanistic Insights into High-Entropy Alloys: Design, Properties and Applications
Anthoula Poulia, Alexander E. Karantzalis
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5616. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Conditions on the Microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo High-Entropy Alloy
- Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Junho Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):406-413. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00185

- 1,216 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
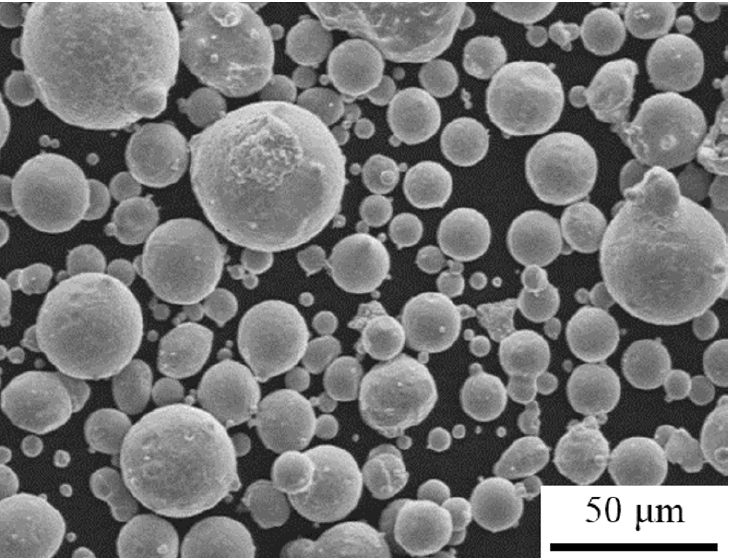
PDF - We investigated the microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering under different sintering temperatures (1000–1100°C) and times (1–600 s). All sintered alloys consisted of a single face-centered cubic phase. As the sintering time or temperature increased, the grains of the sintered alloys became partially coarse. The formation of Cr7C3 carbide occurred on the surface of the sintered alloys due to carbon diffusion from the graphite crucible. The depth of the layer containing Cr7C3 carbides increased to ~110 μm under severe sintering conditions (1100°C, 60 s). A molten zone was observed on the surface of the alloys sintered at higher temperatures (>1060°C) due to severe carbon diffusion that reduced the melting point of the alloy. The porosity of the sintered alloys decreased with increasing time at 1000°C, but increased at higher temperatures above 1060°C due to melting-induced porosity formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Microstructure and mechanical properties of oxide-dispersion-strengthened CrMnFeCoNiC0.2O0.2 high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering
Sang-Hwa Lee, Seonghyun Park, Ka Ram Lim, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 947: 149284. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Interfacial Reaction between Spark Plasma Sintered High-entropy Alloys and Cast Aluminum
- Min-Sang Kim, Hansol Son, Cha Hee Jung, Juyeon Han, Jung Joon Kim, Young-Do Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):213-218. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.213

- 839 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the interfacial reaction between powder-metallurgy high-entropy alloys (HEAs) and cast aluminum. HEA pellets are produced by the spark plasma sintering of Al0.5CoCrCu0.5FeNi HEA powder. These sintered pellets are then placed in molten Al, and the phases formed at the interface between the HEA pellets and cast Al are analyzed. First, Kirkendall voids are observed due to the difference in the diffusion rates between the liquid Al and solid HEA phases. In addition, although Co, Fe, and Ni atoms, which have low mixing enthalpies with Al, diffuse toward Al, Cu atoms, which have a high mixing enthalpy with Al, tend to form Al–Cu intermetallic compounds. These results provide guidelines for designing Al matrix composites containing high-entropy phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
Chahee Jung, Seungin Nam, Hansol Son, Juyeon Han, Jaewon Jeong, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 33: 1470. CrossRef
- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Condition on Tensile Strength of Fe-based Non-equiatomic High Entropy Alloy
- Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jeon, Gwanghun Kim, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):221-226. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.221

- 939 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We fabricate the non-equiatomic high-entropy alloy (NE-HEA) Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 (at.%) using spark plasma sintering under various sintering conditions. Each elemental pure powder is milled by high-energy ball milling to prepare NE-HEA powder. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the sintered samples are investigated using various methods. We use the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method to investigate the microstructural characteristics. Quantitative phase analysis is performed by direct comparison of the XRD results. A tensile test is used to compare the mechanical properties of small samples. Next, electron backscatter diffraction analysis is performed to analyze the phase fraction, and the results are compared to those of XRD analysis. By combining different sintering durations and temperature conditions, we attempt to identify suitable spark plasma sintering conditions that yield mechanical properties comparable with previously reported values. The samples sintered at 900 and 1000°C with no holding time have a tensile strength of over 1000 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


