Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Content of MgO Additive and Sintering Temperature on the Densification of Alumina Insulator
- Ri Joo Kim, Han Gyeol Jeong, Ye Ji Son, Sang Ki Ko, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):249-254. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.249

- 1,386 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The influence of MgO addition on the densification and microstructure of alumina (Al2O3) was studied. Compacted alumina specimens were manufactured using ball-milling and one-directional pressing followed by sintering at temperatures below 1700oC. Relative density, shrinkage, hardness, and microstructure were investigated using analytical tools such as FE-SEM, EDS, and XRD. When the MgO was added up to 5.0 wt% and sintered at 1500°C and 1600°C, the relative density exhibited an average value of 97% or more at both temperatures. The maximum density of 99.2% was with the addition of 0.5 wt% MgO at 1500°C. Meanwhile, the specimens showed significantly lower density values when sintered at 1400°C than at 1500°C and 1600°C owing to the relatively low sintering temperature. The hardness and shrinkage data also showed a similar trend in the change in density, implying that the addition of approximately 0.5 wt% MgO can promote the densification of Al2O3. Studying the microstructure confirmed the uniformity of the sintered alumina. These results can be used as basic compositional data for the development of MgOcontaining alumina as high-dielectric insulators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hardness of Ultra-High-Density Alumina Fabricated using the Aerodynamic Levitation Process
Ye-Ji Son, Dong-Wook Kim, Seung-Wook Kim, Hyo-Min Kim, Hui-Woong Kang, Min-Yeong Ha, Dae-Yong Jeong
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2025; 35(9): 436. CrossRef
- Hardness of Ultra-High-Density Alumina Fabricated using the Aerodynamic Levitation Process
- [Korean]
- Aqueous Synthesis and Luminescent Characteristics of Cu:ZnSe Quantum Dots by Internal Doping Method
- Geum Ji Back, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):370-375. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.370
- 830 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
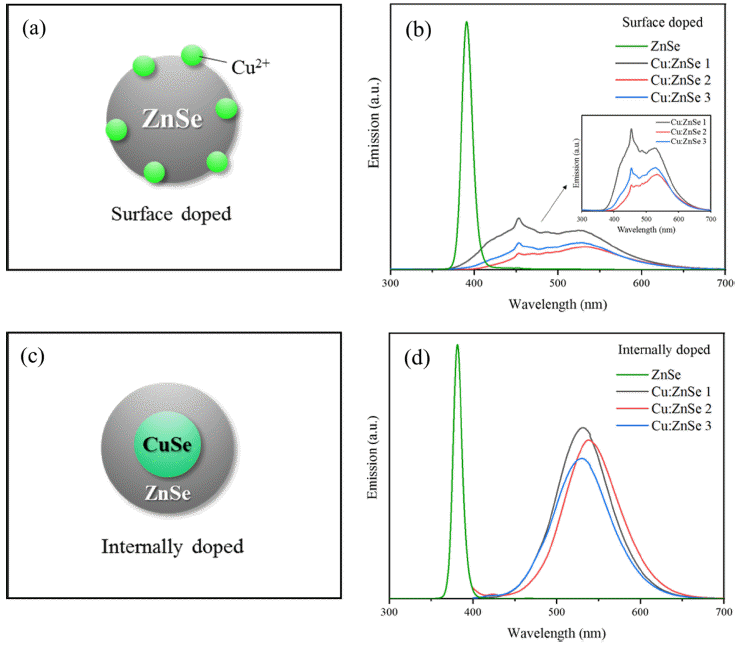
PDF Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots were successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution using an internal doping method. The effects of ligand type, CuSe synthesis temperature, and heating time on Cu-doped ZnSe synthesis were systematically investigated. Of MPA, GSH, TGA, and NAC used as ligands, MPA was the optimal ligand as determined by PL spectrum analysis. In addition, the emission wavelength was found to depend on the synthesis temperature of the internal doping core of CuSe. As the temperature increased, the doping of Cu2+ was enhanced, and the emission wavelength band was redshifted; accordingly, the emission peaks moved from blue to green (up to 550 nm). Thus, the synthesis of Cu:ZnSe using internal doping in aqueous solutions is a potential method for ecomanufacturing of colortuned ZnSe quantum dots for display applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
Hyun Seon Hong, Yerin Kim, Jea Hyung Kim, Hyeon Seon Ryu, Dahye Song
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025; 62(3): 472. CrossRef
- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
- [Korean]
- Effects of Synthesis Conditions on Luminescence Characteristics of Glutathione Capped ZnSe Nano particles
- Geum Ji Back, Ha Yeon Song, Min Seo Lee, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):44-50. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.44
- 1,170 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Zinc selenide (ZnSe) nanoparticles were synthesized in aqueous solution using glutathione (GSH) as a ligand. The influence of the ligand content, reaction temperature, and hydroxyl ion concentration (pH) on the fabrication of the ZnSe particles was investigated. The optical properties of the synthesized ZnSe particles were characterized using various analytical techniques. The nanoparticles absorbed UV-vis light in the range of 350-400 nm, which is shorter than the absorption wavelength of bulk ZnSe particles (460 nm). The lowest ligand concentration for achieving good light absorption and emission properties was 0.6 mmol. The reaction temperature had an impact on the emission properties; photoluminescence spectroscopic analysis showed that the photo-discharge characteristics were greatly enhanced at high temperatures. These discharge characteristics were also affected by the hydroxyl ion concentration in solution; at pH 13, sound emission characteristics were observed, even at a low temperature of 25°C. The manufactured nanoparticles showed excellent light absorption and emission properties, suggesting the possibility of fabricating ZnSe QDs in aqueous solutions at low temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Green synthesis and luminescence characteristics of ZnSe-ZnS core-shell quantum dots
Geum Ji Back, Ha Yeon Song, Min Seo Lee, Jaesik Yoon, Hyun Seon Hong
Journal of Crystal Growth.2024; 626: 127475. CrossRef - Effect of UV Irradiation on Optical Properties of Water-Based Synthetic Zinc Selenide Quantum Dots
Geum Ji Back, Yu Jin Kang, I Ju Kang, Jeong Hyeon Lim, Hyun Seon Hong
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2022; 60(2): 160. CrossRef
- Green synthesis and luminescence characteristics of ZnSe-ZnS core-shell quantum dots
- [Korean]
- Influence of Reducing Agents and Additives on the Synthesis of ZnSe Nanoparticles
- Geum Ji Back, Da Gyeong Lee, Min Seo Lee, Ha Yeon Song, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):233-240. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.233
- 606 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nano-sized ZnSe particles are successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution at room temperature using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and thioglycolic acid (TGA) as the reducing agent and stabilizer, respectively. The effects of the mass ratio of the reducing agent to Se, stabilizer concentration, and stirring time on the synthesis of the ZnSe nanoparticles are evaluated. The light absorption/emission properties of the synthesized nanoparticles are characterized using ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and particle size analyzer (PSA) techniques. At least one mass ratio (NaBH4/Se) of the reducing agent should be added to produce ZnSe nanoparticles finer than 10 nm and to absorb UV–vis light shorter than the ZnSe bulk absorption wavelength of 460 nm. As the ratio of the reducing agent increases, the absorption wavelengths in the UV-vis curves are blue-shifted. Stirring in the atmosphere acts as a deterrent to the reduction reaction and formation of nanoparticles, but if not stirred in the atmosphere, the result is on par with synthesis in a nitrogen atmosphere. The stabilizer, TGA, has an impact on the Zn precursor synthesis. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit excellent photo-absorption/discharge characteristics, suggesting that ZnSe nanoparticles can be alloyed without the need for organic solutions or high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
- Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):278-282. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.278

- 977 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The GaN-powder scrap generated in the manufacturing process of LED contains significant amounts of gallium. This waste can be an important resource for gallium through recycling of scraps. In the present study, the influence of annealing temperatures on the structural properties of GaN powder was investigated when the waste was recycled through the mechanochemical oxidation process. The annealing temperature varied from 200°C to 1100°C and the changes in crystal structure and microstructure were studied. The annealed powder was characterized using various analytical tools such as TGA, XRD, SEM, and XRF. The results indicate that GaN structure was fully changed to Ga2O3 structure when annealed above 900°C for 2 h. And, as the annealing temperature increased, crystallinity and particle size were enhanced. The increase in particle size of gallium oxide was possibly promoted by powder-sintering which merged particles to larger than 50 nm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
Kang Hyun Choi, Hyun-Su Kim, Chang Hyun Park, Gon-Ho Kim, Kyoung Ho Baik, Sung Ho Lee, Taehyung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(5): 817. CrossRef
- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
- [English]
- Materials Flow Analysis of Metallic Cobalt and Its Powder in Korea
- Hyun Seon Hong, Lee-Seung Kang, Hong-Yoon Kang, Han-Gil Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):235-240. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.235

- 1,602 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The basis of the cobalt demand analysis by use was established via the investigation and analysis of the cobalt materials flow, and the overall cobalt metal material and parts industry structure in Korea was examined to determine the cobalt material flow. The markets of the cobalt material for machinery were studied, including their interrelations, via market and study trends, and relevant plans were examined. The results of the study indicated that the advanced core technology for advanced industry and technology-intensive industry development is required to structurally innovate the parts materials and basic materials industries and to upgrade the catch-up industry structure to the new frontier structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
Xin Sun, Han Hao, Yong Geng, Zongwei Liu, Fuquan Zhao
Fundamental Research.2024; 4(1): 167. CrossRef - Trade structure and risk transmission in the international automotive Li-ion batteries trade
Xiaoqian Hu, Chao Wang, Xiangyu Zhu, Cuiyou Yao, Pezhman Ghadimi
Resources, Conservation and Recycling.2021; 170: 105591. CrossRef
- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
- [Korean]
- Leaching behavior of Ga and In from MOCVD dust
- Kyung-Soo Park, Basudev Swain, Lee Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):202-206. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.202
- 971 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Leaching of MOCVD dust in the LED industry is an essential stage for hydro-metallurgical recovery of pure Ga and In. To recover Ga and In, the leaching behavior of MOCVD scrap of an LED, which contains significant amounts of Ga, In, Al and Fe in various phases, has been investigated. The leaching process must be performed effectively to maximize recovery of Ga and In metals using the most efficient lixiviant. Crystalline structure and metallic composition of the raw MOCVD dust were analyzed prior to digestion. Subsequently, various mineral acids were tested to comprehensively study and optimize the leaching parameters such as acidity, pulp density, temperature and time. The most effective leaching of Ga and In was observed for a boiling 4 M HCl solution vigorously stirred at 400 rpm. Phase transformation of GaN into gallium oxide by heat treatment also improved the leaching efficiency of Ga. Subsequently high purity Ga and In can be recovered by series of hydro processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
Byoungyong Im, Basudev Swain, Chan Gi Lee, Jae Layng Park, Kyung-Soo Park, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(5): 80. CrossRef - Fabrication of High Purity Ga-containing Solution using MOCVD dust
Duk-Hee Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kyung-Soo Park, Myung-Hwan Hong, Chan-Gi Lee, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(4): 50. CrossRef - Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 278. CrossRef
- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


