Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
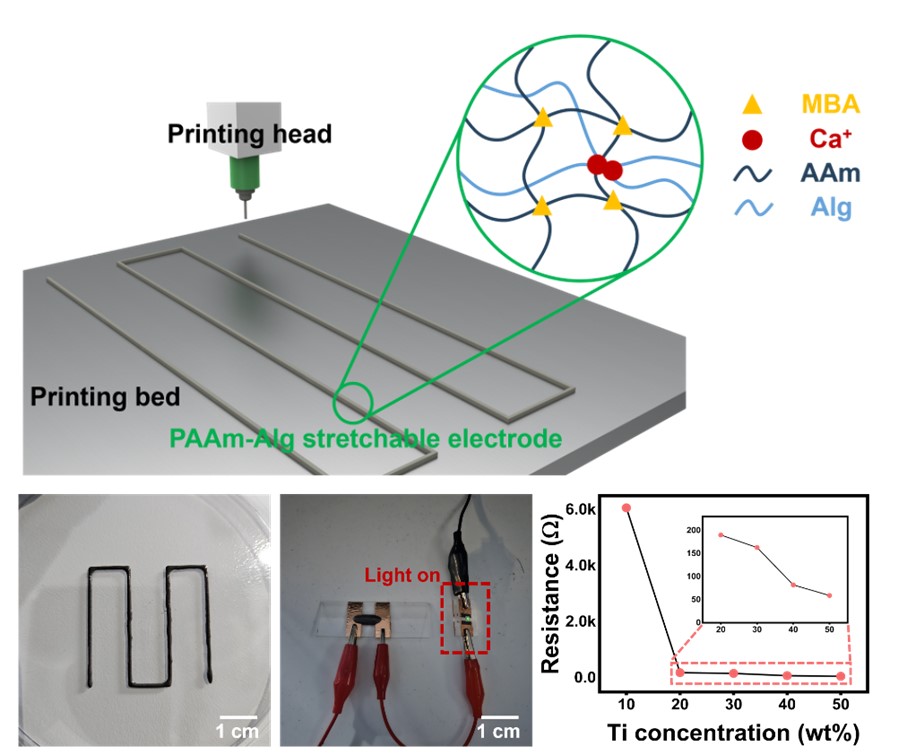
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
- Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
- 837 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
- [Korean]
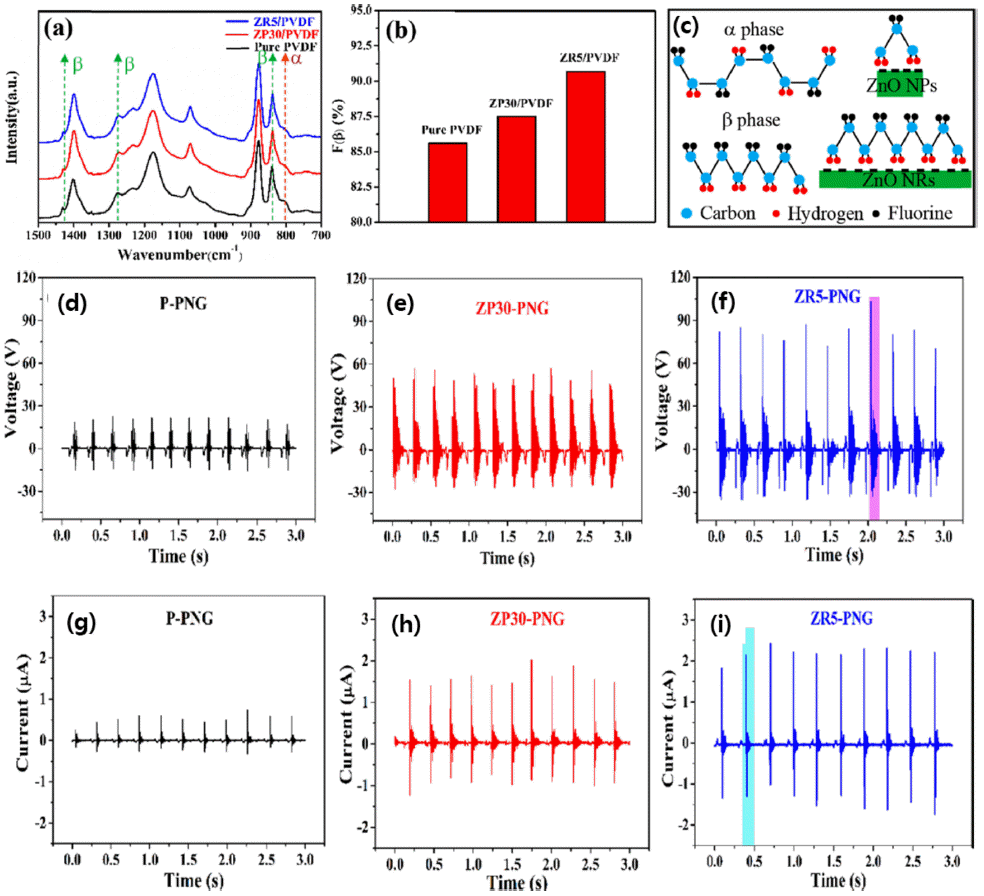
- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
- Geon-Ju Choi, Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):247-255. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.247
- 1,143 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, interest in technology for eco-friendly energy harvesting has been increasing. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is one of the most fascinating materials that has been used in energy harvesting technology as well as micro-filters by utilizing an electrostatic effect. To enhance the performance of the electrostatic effect-based nanogenerator, most studies have focused on enlarging the contact surface area of the pair of materials with different triboelectric series. For this reason, one-dimensional nanofibers have been widely used recently. In order to realize practical energy-harvesting applications, PVDF nanofibers are modified by enlarging their contact surface area, modulating the microstructure of the surface, and maximizing the fraction of the β-phase by incorporating additives or forming composites with inorganic nanoparticles. Among them, nanocomposite structures incorporating various nanoparticles have been widely investigated to increase the β-phase through strong hydrogen bonding or ion-dipole interactions with -CF2/CH2- of PVDF as well as to enhance the mechanical strength. In this study, we report the recent advances in the nanocomposite structure of PVDF nanofibers and inorganic nanopowders.
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
- Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14

- 970 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
- [English]
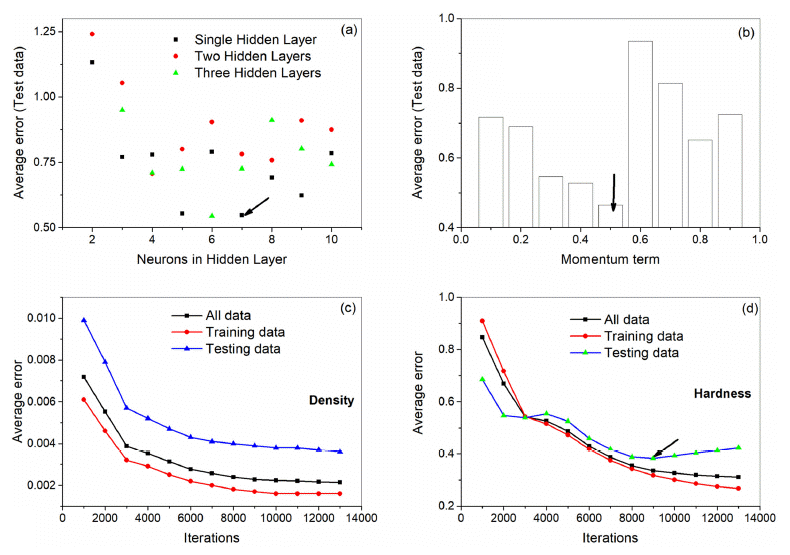
- Modeling the Density and Hardness of AA2024-SiC Nanocomposites
- A-Hyun Jeon, Hong In Kim, Hyokyung Sung, N. S. Reddy
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):275-281. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.275
- 996 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF An artificial neural network (ANN) model is developed for the analysis and simulation of correlation between flake powder metallurgy parameters and properties of AA2024-SiC nanocomposites. The input parameters of the model are AA 2024 matrix size, ball milling time, and weight percentage of SiC nanoparticles and the output parameters are density and hardness. The model can predict the density and hardness of the unseen test data with a correlation of 0.986 beyond the experimental data. A user interface is designed to predict properties at new instances. We have used the model to simulate the individual as well as the combined influence of parameters on the properties. Moreover, we have analyzed the calculated results from the powder metallurgical point of view. The developed model can be used as a guide for further composite development.
- [Korean]
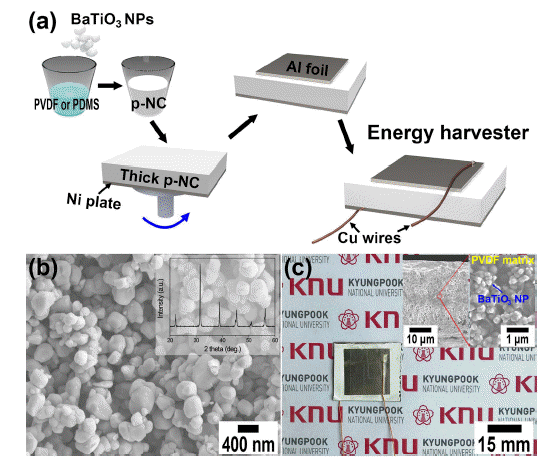
- A Comparison Study of Output Performance of Organic-Inorganic Piezoelectric Nanocomposite Made of Piezoelectric/Non-piezoelectric Polymers and BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
- Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):119-125. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.119
- 944 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Piezoelectric energy harvesting technology is attracting attention, as it can be used to convert more accessible mechanical energy resources to periodic electricity. Recent developments in the field of piezoelectric energy harvesters (PEHs) are associated with nanocomposites made from inorganic piezoelectric nanomaterials and organic elastomers. Here, we used the BaTiO3 nanoparticles and piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) polymeric matrix to fabricate the nanocomposites-based PEH to improve the output performance of PEHs. The piezoelectric nanocomposite is produced by dispersing the inorganic piezo-ceramic nanoparticles inside an organic piezo-polymer and subsequently spin-coat it onto a metal plate. The fabricated organic-inorganic piezoelectric nanocomposite-based PEH harvested the output voltage of ~1.5 V and current signals of ~90 nA under repeated mechanical pushings: these values are compared to those of energy devices made from non-piezoelectric polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomers and supported by a multiphysics simulation software.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Jae-Hoon Ji, Donghun Lee, Young Hwa Jung, Min-Ku Lee, Changyeon Baek, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2024; 33(1): 34. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - Effects of Mixing Ratio and Poling on Output Characteristics of BaTiO3-Poly Vinylidene Fluoride Composite Piezoelectric Generators
Hee-Tae Kim, Sang-Shik Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2023; 33(12): 517. CrossRef - Stretchable Sensor Array Based on Lead-Free Piezoelectric Composites Made of BaTiO3 Nanoparticles and Polymeric Matrix
Jun Ho Bae, Seong Su Ham, Sung Cheol Park, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2022; 31(5): 312. CrossRef - Flexible Energy Harvester Made of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Piezoelectric Nanocomposite
Yu Jeong Kwon, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(6): 371. CrossRef
- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of WO3-CuO Powder Mixture Prepared by High-Energy Ball Milling in a Bead Mill for the Synthesis of W-Cu Nanocomposite Powder
- Hae-Ryong Park, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):406-413. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.406
- 1,034 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
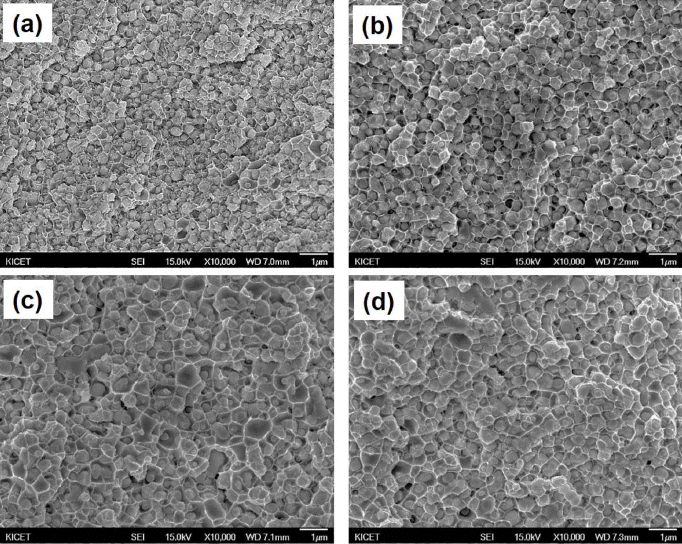
PDF A Nanosized WO3 and CuO powder mixture is prepared using novel high-energy ball milling in a bead mill to obtain a W-Cu nanocomposite powder, and the effect of milling time on the structural characteristics of WO3-CuO powder mixtures is investigated. The results show that the ball-milled WO3-CuO powder mixture reaches at steady state after 10 h milling, characterized by the uniform and narrow particle size distribution with primary crystalline sizes below 50 nm, a specific surface area of 37 m2/g, and powder mean particle size (D50) of 0.57 μm. The WO3-CuO powder mixtures milled for 10 h are heat-treated at different temperatures in H2 atmosphere to produce W-Cu powder. The XRD results shows that both the WO3 and CuO phases can be reduced to W and Cu phases at temperatures over 700°C. The reduced W-Cu nanocomposite powder exhibits excellent sinterability, and the ultrafine W-Cu composite can be obtained by the Cu liquid phase sintering process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
Chulwoong Han, Song-Yi Kim, Soobin Kim, Ji-Woon Lee
Metals.2024; 14(9): 1070. CrossRef
- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308
- 1,011 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
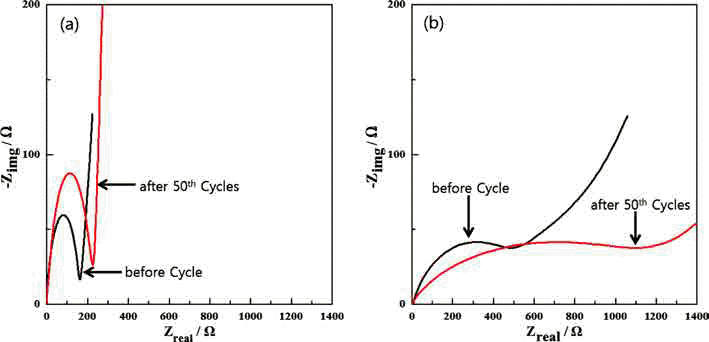
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [English]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Characteristics of Bulk Nickel/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites via the Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- Thuyet-Nguyen Minh, Hai-Nguyen Hong, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):213-220. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.213
- 1,258 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
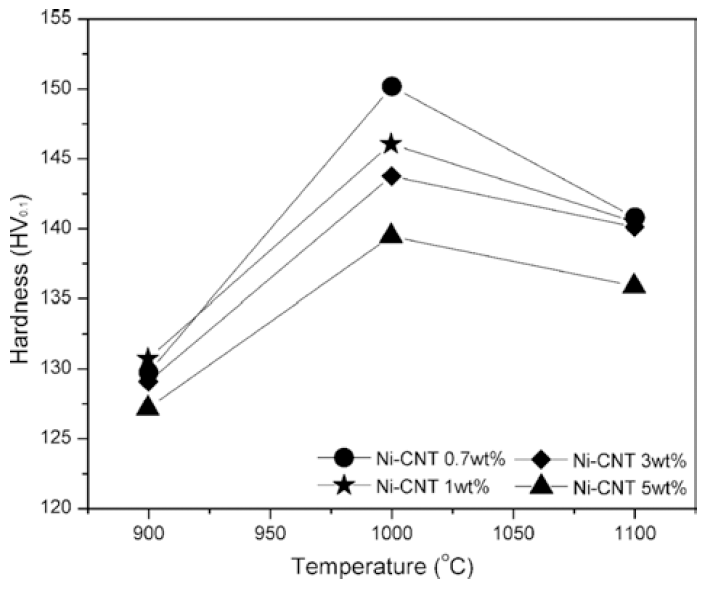
PDF In this study, bulk nickel-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites are synthesized by a novel method which includes a combination of ultrasonication, electrical explosion of wire in liquid and spark plasma sintering. The mechanical characteristics of the bulk Ni-CNT composites synthesized with CNT contents of 0.7, 1, 3 and 5 wt.% are investigated. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy techniques are used to observe the different phases, morphologies and structures of the composite powders as well as the sintered samples. The obtained results reveal that the as-synthesized composite exhibits substantial enhancement in the microhardness and values more than 140 HV are observed. However an empirical reinforcement limit of 3 wt.% is determined for the CNT content, beyond which, there is no significant improvement in the mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
Tao Jiang, Zhongyu Hou
Applied Surface Science.2020; 513: 145824. CrossRef - Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
Jin-Ju Park, Eun-Kwang Park, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Min-Ku Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 143. CrossRef
- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


