Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 466 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
- [Korean]
- Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
- Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):104-112. Published online March 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00458

- 851 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A hybrid energy harvester that consisted of thermoelectric (TE) composite film and electrospun piezoelectric (PE) polymeric membranes was constructed. TE composites were fabricated by dispersing inorganic TE powders inside polyvinylidene fluoride elastomer using a drop-casting technique. The polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene, which was chosen due to its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical stability, and biocompatibility, was electrospun onto an aluminum foil to fabricate the ultra-flexible PE membranes. To create a hybrid energy harvester that can simultaneously convert heat and mechanical energy resources into electricity, the TE composite films attached to the PE membrane were encapsulated with protective polydimethylsiloxane. The fabricated energy harvester converted the outputs with a maximum voltage of 4 V (PE performance) and current signals of 0.2 μA (TE performance) under periodical heat input and mechanical bending in hybrid modes. This study demonstrates the potential of the hybrid energy harvester for powering flexible and wearable electronics, offering a sustainable and reliable power source.
- [Korean]
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00444
- 837 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
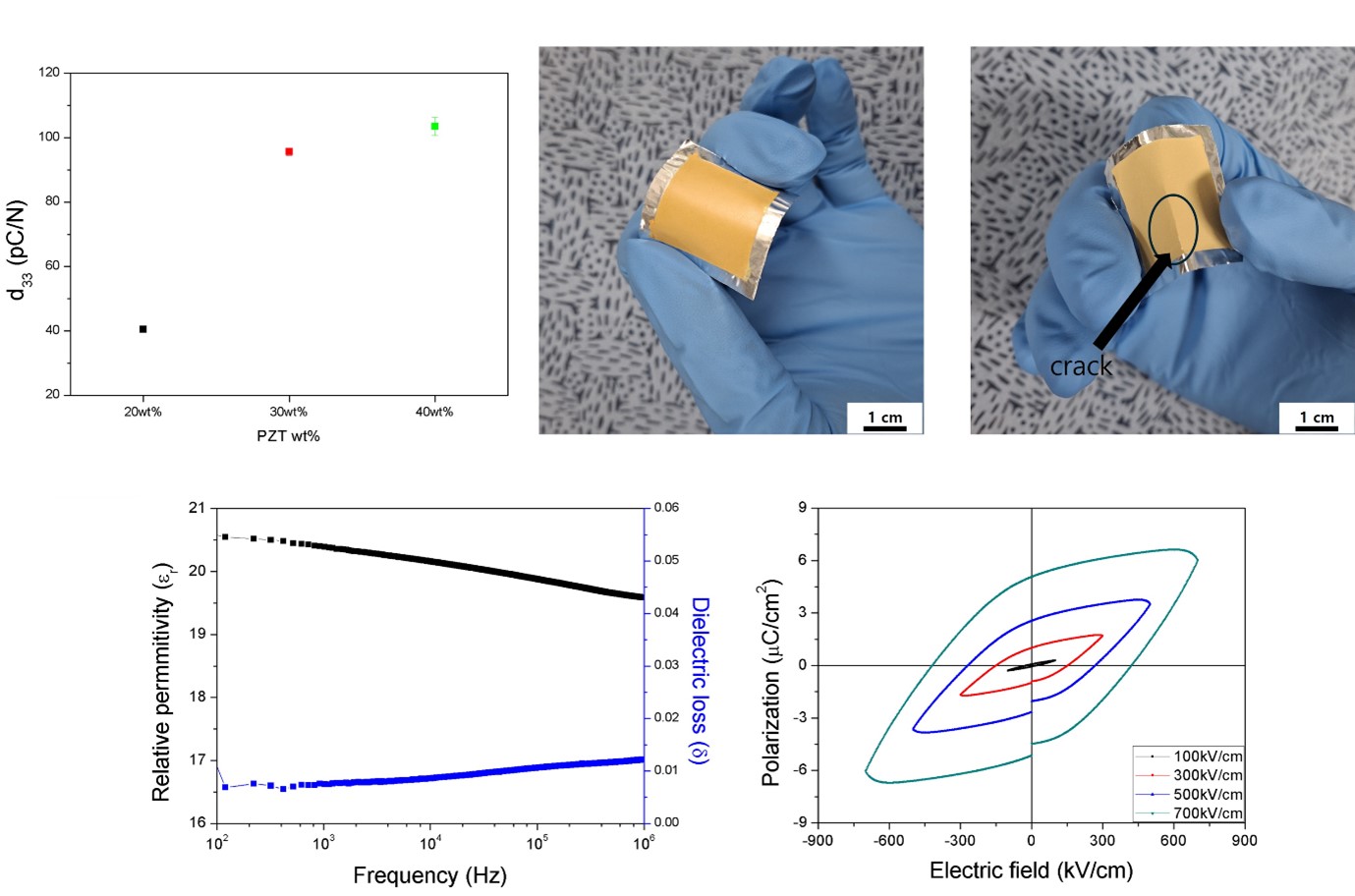
PDF - Piezoelectric composites have attracted significant research interest as sustainable power sources for electronic devices due to their high mechanical stability and electrical output characteristics. This study investigated the optimal processing conditions for fabricating a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester based on Pb(Zr,Ti)O₃ (PZT) powder and a polyimide (PI) matrix composite. Various parameters, including the optimal mixing ratio of PI/PZT, ultrasonic treatment, homogenization, vacuum oven, and UV/O₃ treatment, were optimized to achieve a uniform piezoelectric composite. A PZT content of 30 wt% and 20 minutes of homogenization were identified as the most effective conditions for increasing the uniformity of the composite. The optimized composite exhibited a high piezoelectric coefficient, a typical P-E hysteresis loop, and dielectric properties, exhibiting a voltage output that adjusts in response to variations in the applied touch force. This study provides foundational data for the uniform fabrication of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters and next-generation miniaturized electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Development of Composite-film-based Flexible Energy Harvester using Lead-free BCTZ Piezoelectric Nanomaterials
- Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Haksu Jang, Cheol Min Kim, Donghun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.16
- 1,498 View
- 31 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
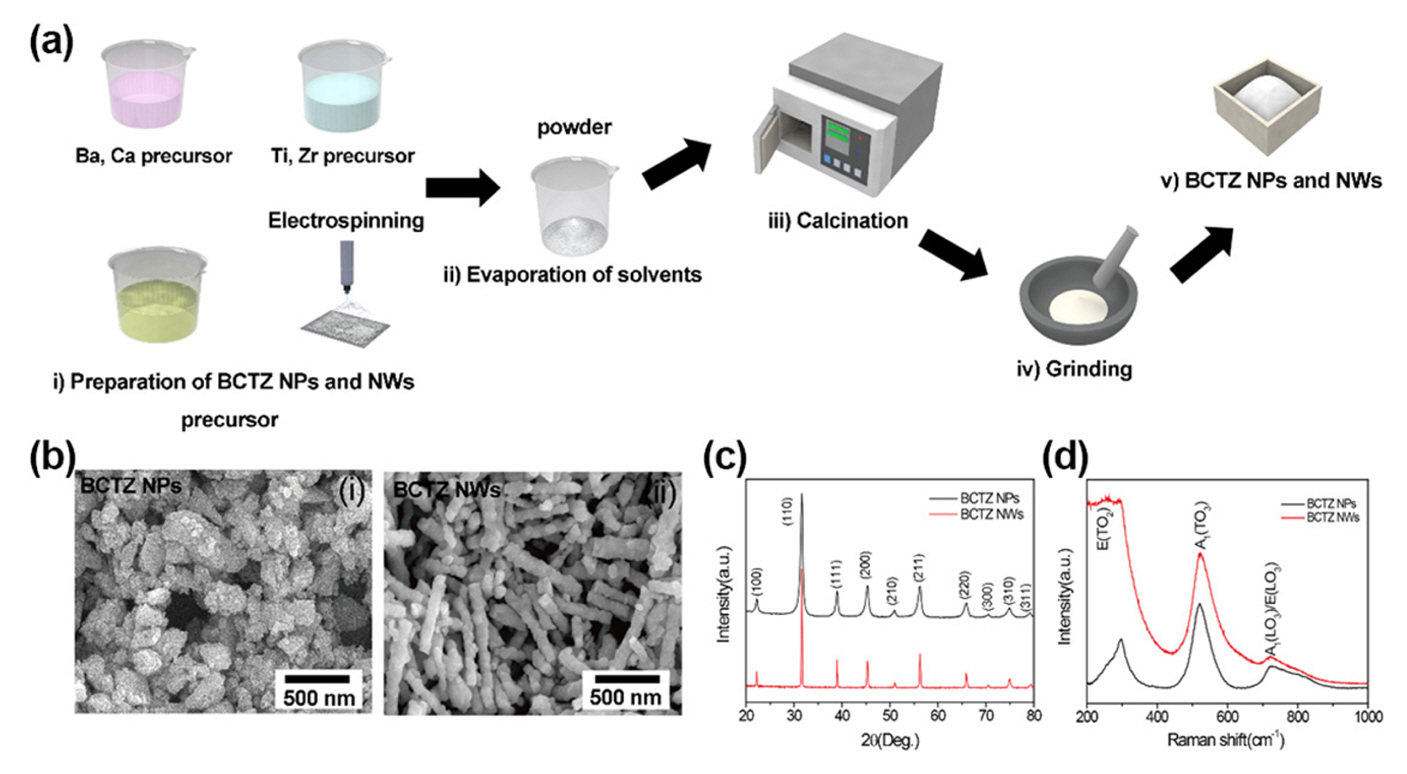
PDF - Composite-based piezoelectric devices are extensively studied to develop sustainable power supply and selfpowered devices owing to their excellent mechanical durability and output performance. In this study, we design a leadfree piezoelectric nanocomposite utilizing (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 (BCTZ) nanomaterials for realizing highly flexible energy harvesters. To improve the output performance of the devices, we incorporate porous BCTZ nanowires (NWs) into the nanoparticle (NP)-based piezoelectric nanocomposite. BCTZ NPs and NWs are synthesized through the solidstate reaction and sol-gel-based electrospinning, respectively; subsequently, they are dispersed inside a polyimide matrix. The output performance of the energy harvesters is measured using an optimized measurement system during repetitive mechanical deformation by varying the composition of the NPs and NWs. A nanocomposite-based energy harvester with 4:1 weight ratio generates the maximum open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of 0.83 V and 0.28 A, respectively. In this study, self-powered devices are constructed with enhanced output performance by using piezoelectric energy harvesting for application in flexible and wearable devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long‐Lasting, Steady and Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Inserting a Conductive Layer into the Piezoelectric Polymer
HakSu Jang, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Dong Won Jeon, Hyeon Jun Park, BitNa Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Changyeon Baek, Min‐Ku Lee, Sung Beom Cho, Gyoung‐Ja Lee, Kwi‐Il Park
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Dual-controlled piezoelectric composite film with enhanced crystallinity and defect-free via solvent vapor treatment
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, BitNa Bae, HyoMin Jeon, DongHun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2025; 136: 110705. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 104. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Long‐Lasting, Steady and Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Inserting a Conductive Layer into the Piezoelectric Polymer
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Flexible Energy Harvester Based on BaTiO3 Piezoelectric Nanotube Arrays
- Seo Young Yoon, Cheol Min Kim, Bitna Bae, Yujin Na, Haksu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):521-527. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.521
- 860 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
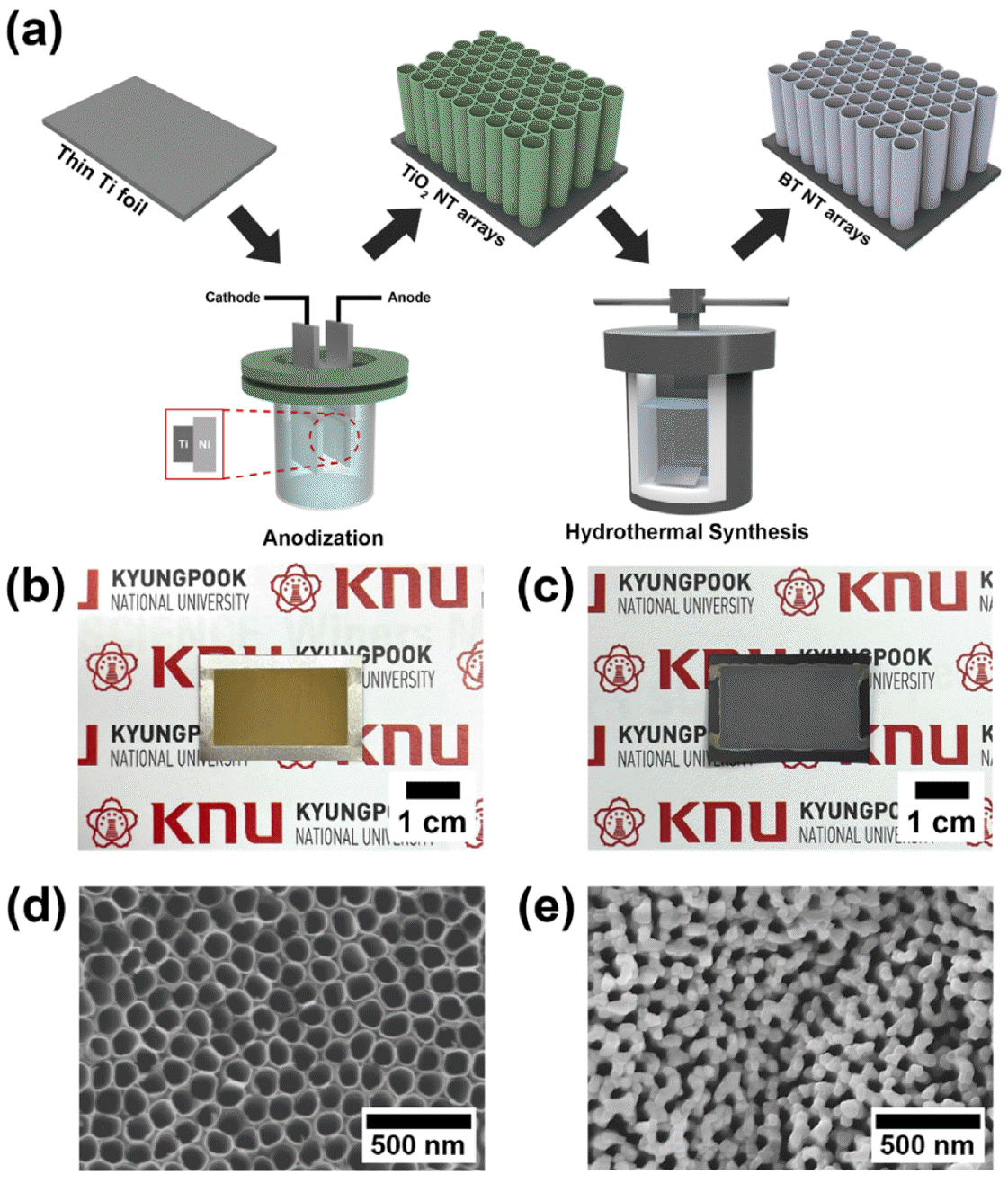
PDF Piezoelectric technology, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, has recently attracted drawn considerable attention in the industry. Among the many kinds of piezoelectric materials, BaTiO3 nanotube arrays, which have outstanding uniformity and anisotropic orientation compared to nanowire-based arrays, can be fabricated using a simple synthesis process. In this study, we developed a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester (f-PEH) based on a composite film with PVDF-coated BaTiO3 nanotube arrays through sequential anodization and hydrothermal synthesis processes. The f-PEH fabricated using the piezoelectric composite film exhibited excellent piezoelectric performance and high flexibility compared to the previously reported BaTiO3 nanotube array-based energy harvester. These results demonstrate the possibility for widely application with high performance by our advanced f-PEH technique based on BaTiO3 nanotube arrays.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
- [Korean]
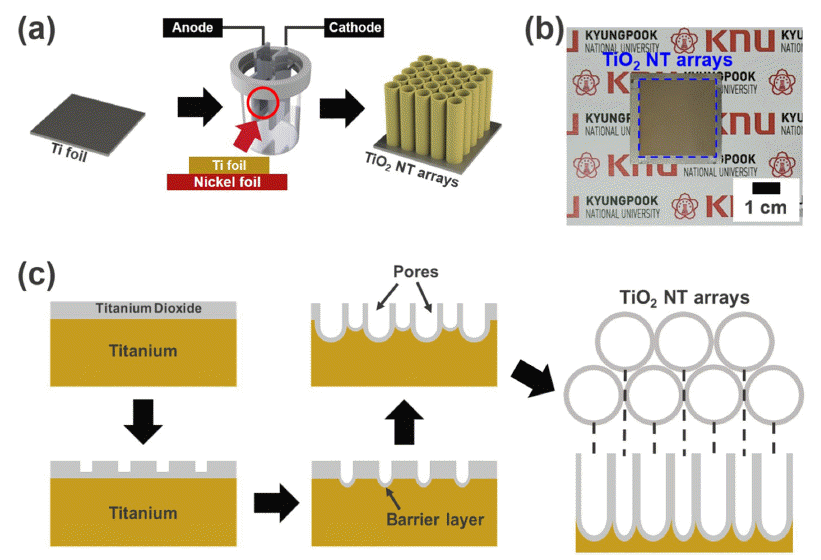
- Effect of Hydrothermal Reaction Conditions on Piezoelectric Output Performance of One Dimensional BaTiO3 Nanotube Arrays
- Jae Hoon Lee, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Heo, Kwi-Il Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):127-133. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.127
- 905 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF One-dimensional (1D) piezoelectric nanostructures are attractive candidates for energy generation because of their excellent piezoelectric properties attributed to their high aspect ratios and large surface areas. Vertically grown BaTiO3 nanotube (NT) arrays on conducting substrates are intensively studied because they can be easily synthesized with excellent uniformity and anisotropic orientation. In this study, we demonstrate the synthesis of 1D BaTiO3 NT arrays on a conductive Ti substrate by electrochemical anodization and sequential hydrothermal reactions. Subsequently, we explore the effect of hydrothermal reaction conditions on the piezoelectric energy conversion efficiency of the BaTiO3 NT arrays. Vertically aligned TiO2 NT arrays, which act as the initial template, are converted into BaTiO3 NT arrays using hydrothermal reaction with various concentrations of the Ba source and reaction times. To validate the electrical output performance of the BaTiO3 NT arrays, we measure the electricity generated from each NT array packaged with a conductive metal foil and epoxy under mechanical pushings. The generated output voltage signals from the BaTiO3 NT arrays increase with increasing concentration of the Ba source and reaction time. These results provide a new strategy for fabricating advanced 1D piezoelectric nanostructures by demonstrating the correlation between hydrothermal reaction conditions and piezoelectric output performance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Fabrication of Flexible Energy Harvester Based on BaTiO3 Piezoelectric Nanotube Arrays
Seo Young Yoon, Cheol Min Kim, Bitna Bae, Yujin Na, Haksu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 521. CrossRef
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- [Korean]
- Effect of Li2O-Bi2O3 Addition on the Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 Ceramics
- Jae Hyuk Kim, Shi Yeon Kim, Jeoung Sik Choi, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):405-409. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.405

- 681 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Piezoelectric ceramic specimens with the Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 (PMN-PT) composition are prepared by the solid state reaction method known as the “columbite precursor” method. Moreover, the effects of the Li2O-Bi2O3 additive on the microstructure, crystal structure, and piezoelectric properties of sintered PMN-PT ceramic samples are investigated. The addition of Li2O-Bi2O3 lowers the sintering temperature from 1,200°C to 950°C. Moreover, with the addition of >5 wt.% additive, the crystal structure changes from tetragonal to rhombohedral. Notably, the sample with 3 wt.% additive exhibits excellent piezoelectric properties (d33 = 596 pC/N and Kp = 57%) and a sintered density of 7.92 g/cm3 after sintering at 950°C. In addition, the sample exhibits a curie temperature of 138.6°C at 1 kHz. Finally, the compatibility of the sample with a Cu electrode is examined, because the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data indicate the absence of interdiffusion between Cu and the ceramic material.
- [Korean]
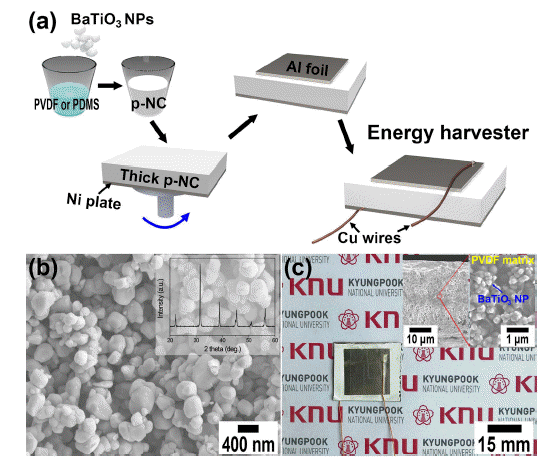
- A Comparison Study of Output Performance of Organic-Inorganic Piezoelectric Nanocomposite Made of Piezoelectric/Non-piezoelectric Polymers and BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
- Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):119-125. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.119
- 831 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Piezoelectric energy harvesting technology is attracting attention, as it can be used to convert more accessible mechanical energy resources to periodic electricity. Recent developments in the field of piezoelectric energy harvesters (PEHs) are associated with nanocomposites made from inorganic piezoelectric nanomaterials and organic elastomers. Here, we used the BaTiO3 nanoparticles and piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) polymeric matrix to fabricate the nanocomposites-based PEH to improve the output performance of PEHs. The piezoelectric nanocomposite is produced by dispersing the inorganic piezo-ceramic nanoparticles inside an organic piezo-polymer and subsequently spin-coat it onto a metal plate. The fabricated organic-inorganic piezoelectric nanocomposite-based PEH harvested the output voltage of ~1.5 V and current signals of ~90 nA under repeated mechanical pushings: these values are compared to those of energy devices made from non-piezoelectric polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomers and supported by a multiphysics simulation software.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Jae-Hoon Ji, Donghun Lee, Young Hwa Jung, Min-Ku Lee, Changyeon Baek, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2024; 33(1): 34. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - Effects of Mixing Ratio and Poling on Output Characteristics of BaTiO3-Poly Vinylidene Fluoride Composite Piezoelectric Generators
Hee-Tae Kim, Sang-Shik Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2023; 33(12): 517. CrossRef - Stretchable Sensor Array Based on Lead-Free Piezoelectric Composites Made of BaTiO3 Nanoparticles and Polymeric Matrix
Jun Ho Bae, Seong Su Ham, Sung Cheol Park, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2022; 31(5): 312. CrossRef - Flexible Energy Harvester Made of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Piezoelectric Nanocomposite
Yu Jeong Kwon, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(6): 371. CrossRef
- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
- [Korean]
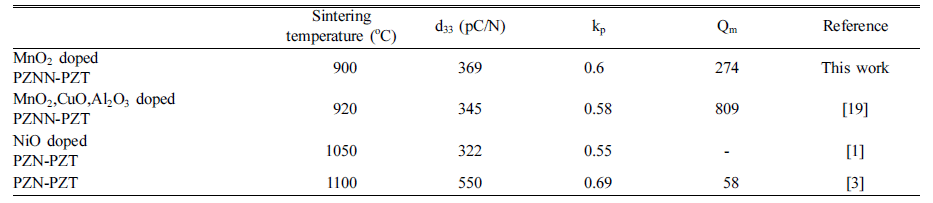
- Effects of the Mixing Method and Sintering Temperature on the Characteristics of PZNN-PZT Piezoelectric Ceramic Materials
- So Won Kim, Yong Jeong Jeong, Hee Chul Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):487-493. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.487
- 855 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The impact of different mixing methods and sintering temperatures on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PZNN-PZT ceramics is investigated. To improve the sinterability and piezoelectric properties of these ceramics, the composition of 0.13Pb((Zn0.8Ni0.2)1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.87Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 (PZNN-PZT) containing a Pb-based relaxor component is selected. Two methods are used to create the powder for the PZNN-PZT ceramics. The first involves blending all source powders at once, followed by calcination. The second involves the preferential creation of columbite as a precursor, by reacting NiO with Nb2O5 powder. Subsequently, PZNN-PZT powder can be prepared by mixing the columbite powder, PbO, and other components, followed by an additional calcination step. All the PZNNPZT powder samples in this study show a nearly-pure perovskite phase. High-density PZNN-PZT ceramics can be fabricated using powders prepared by a two-step calcination process, with the addition of 0.3 wt% MnO2 at even relatively low sintering temperatures from 800°C to 1000°C. The grain size of the ceramics at sintering temperatures above 900°C is increased to approximately 3 μm. The optimized PZNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics show a piezoelectric constant (d33) of 360 pC/N, an electromechanical coupling factor (kp) of 0.61, and a quality factor (Qm) of 275.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
Haeseong Hwang, Seungho Han, Hyunseop Lee
Lubricants.2023; 11(7): 297. CrossRef - A generalized rule for phase transition generated by additives in piezoelectric ceramics
Jae-Min Cha, Young-Kook Moon, Jung-hwan Kim, Hyun-Ae Cha, Jong-Jin Choi, Byung-Dong Hahn, Seog-Young Yoon, Cheol-Woo Ahn
Materials Today Communications.2023; 37: 107290. CrossRef - Low-Temperature Sintering Properties of Bi2O3 Doped PZT-5H Piezoelectric Ceramics
Wanzi Mao, Qing Xu, Duanping Huang, Huajun Sun, Feng Zhang, Xiaobin Xie
Journal of Electronic Materials.2023; 52(5): 3334. CrossRef - Effect of LiBiO2 on low-temperature sintering of PZT-PZNN ceramics
Sung Cheul Hong, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Zee Hoon Park, Sahn Nahm
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(5): 638. CrossRef - Two-Stage De-binding for Cu Electrode Application to PZT-PZNN Multilayer Actuator
Sung Cheul Hong, Zeehoon Park, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2022; 23(4): 348. CrossRef
- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
- [Korean]
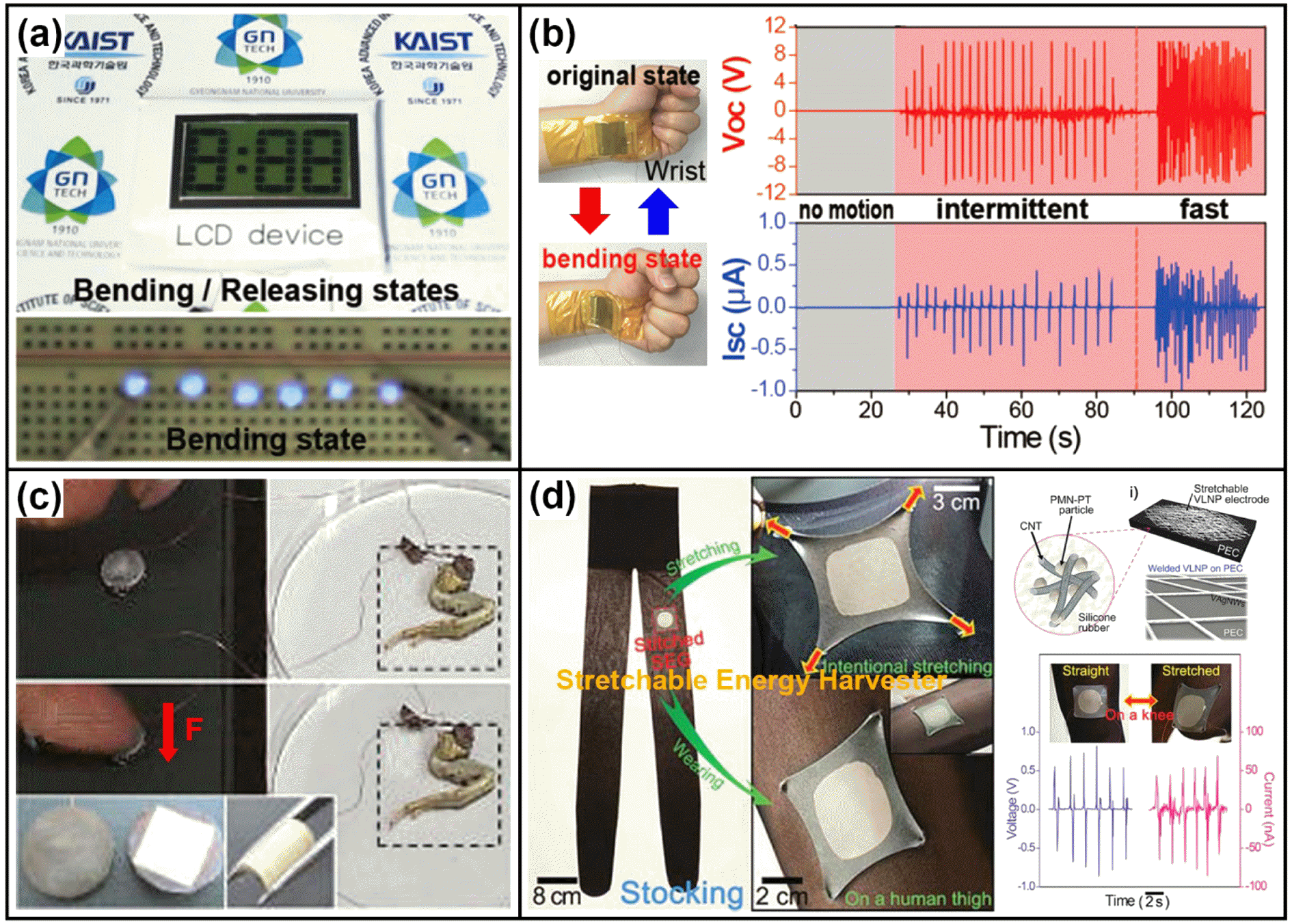
- Recent Progress in Flexible Energy Harvesting Devices based on Piezoelectric Nanomaterials
- Kwi-Il Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):263-272. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.263
- 1,084 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recent developments in the field of energy harvesting technology that convert ambient energy resources into electricity enable the use of self-powered energy systems in wearable and portable electronic devices without the need for additional external power sources. In particular, piezoelectric-effect-based flexible energy harvesters have drawn much attention because they can guarantee power generation from ubiquitous mechanical and vibrational movements. In response to demand for sustainable, permanent, and remote use of real-life personal electronics, many research groups have investigated flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters (f-PEHs) that employ nanoscaled piezoelectric materials such as nanowires, nanoparticles, nanofibers, and nanotubes. In those attempts, they have proven the feasibility of energy harvesting from tiny periodic mechanical deformations and energy utilization of f-PEH in commercial electronic devices. This review paper provides a brief overview of f-PEH devices based on piezoelectric nanomaterials and summarizes the development history, output performance, and applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
Tae-hyung Kim, Jin-Kyeom Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 481. CrossRef - Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Jae-Hoon Ji, Donghun Lee, Young Hwa Jung, Min-Ku Lee, Changyeon Baek, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2024; 33(1): 34. CrossRef - Enhanced Piezoelectric Performance of Composite Fibers Based on Lead-Free BCTZ Ceramics and P(VDF-TrFE) Piezopolymer for Self-Powered Wearable Sensors
Sung Cheol Park, Chaeyoung Nam, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.2022; 10(43): 14370. CrossRef - A Comparison Study of Output Performance of Organic-Inorganic Piezoelectric Nanocomposite Made of Piezoelectric/Non-piezoelectric Polymers and BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 119. CrossRef - Piezoelectric Flexible Energy Harvester Based on BaTiO3 Thin Film Enabled by Exfoliating the Mica Substrate
Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
Energy Technology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting from Two-Dimensional Boron Nitride Nanoflakes
Gyoung-Ja Lee, Min-Ku Lee, Jin-Ju Park, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Chang Kyu Jeong, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.2019; 11(41): 37920. CrossRef
- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
- [English]
- Development of Powder Injection Molding Process for a Piezoelectric PAN-PZT Ceramics
- Jun Sae Han, Dong Yong Park, Dongguo Lin, Kwang Hyun Chung, Ravi Bollina, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):112-119. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.112

- 1,339 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A powder injection molding process is developed and optimized for piezoelectric PAN-PZT ceramics. Torque rheometer experiments are conducted to determine the optimal solids loading, and the rheological property of the feedstock is evaluated using a capillary rheometer. Appropriate debinding conditions are chosen using a thermal gravity analyzer, and the debound specimens are sintered using sintering conditions determined in a preliminary investigation. Piezoelectric performance measures, including the piezoelectric charge constant and dielectric constant, are measured to verify the developed process. The average values of the measured piezoelectric charge constant and dielectric constant are 455 pC/N and 1904, respectively. Powder injection molded piezoelectric ceramics produced by the optimized process show adequate piezoelectric performance compared to press-sintered piezoelectric ceramics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on Rheological Behavior and Mechanical Properties of PMN–PZT Ceramic Feedstock
Jae Man Park, Jun Sae Han, Joo Won Oh, Seong Jin Park
Metals and Materials International.2021; 27(5): 1069. CrossRef - Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Sang Soo Han, Jun Sae Han, Dongguo Lin, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(1): 315. CrossRef - Fabrication of pressureless sintered Si3N4 ceramic balls by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Gi Woung Song, Woon Hyung Baek, Hyung Kyu Kim, Dae Keun Lee, Ki Wook Lim, Seong Jin Park
Ceramics International.2019; 45(5): 6418. CrossRef - Experimental analysis for fabrication of high-aspect-ratio piezoelectric ceramic structure by micro-powder injection molding process
Jun Sae Han, Chang Woo Gal, Jae Man Park, Jong Hyun Kim, Seong Jin Park
Materials Research Express.2018; 5(4): 046303. CrossRef
- Study on Rheological Behavior and Mechanical Properties of PMN–PZT Ceramic Feedstock
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


