Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison and Characterization of Silodosin-loaded Solid Dispersions Prepared by Various Solid Dispersion Preparation Methods
- Su Man Lee, Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):263-271. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00143
- 1,581 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study focused on improving the solubility of silodosin, a drug poorly soluble in water, by utilizing solid dispersions. Three types of dispersions were examined and compared against the drug powder: surface-attached (SA), solvent-wetted (SW), and solvent-evaporated (SE). Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was identified as the most effective polymer in enhancing solubility. These dispersions were prepared using spray-drying techniques with silodosin and PVA as the polymer, employing solvents such as water, ethanol, and a water-acetone mix. The physicochemical properties and solubility of the dispersions were evaluated. The surface-attached dispersions featured the polymer on a crystalline drug surface, the solvent-wetted dispersions had the amorphous drug on the polymer, and the solvent-evaporated dispersions produced nearly round particles with both components amorphous. Testing revealed that the order of improved solubility was: solvent-evaporated, solvent-wetted, and surface-attached. The results demonstrated that the preparation method of the solid dispersions significantly impacted their physicochemical properties and solubility enhancement.
- [Korean]
- Recent Research Progress on the Atomic Layer Deposition of Noble Metal Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
- Jeong Hwan Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):63-71. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.63
- 604 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
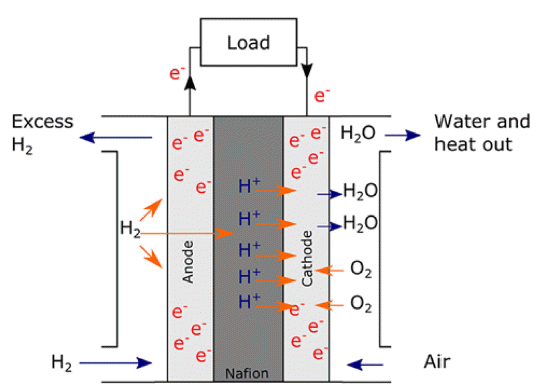
PDF It is necessary to fabricate uniformly dispersed nanoscale catalyst materials with high activity and long-term stability for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent electrochemical characteristics of the oxygen reduction reaction and hydrogen oxidation reaction. Platinum is known as the best noble metal catalyst for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells because of its excellent catalytic activity. However, given that Pt is expensive, considerable efforts have been made to reduce the amount of Pt loading for both anode and cathode catalysts. Meanwhile, the atomic layer deposition (ALD) method shows excellent uniformity and precise particle size controllability over the three-dimensional structure. The research progress on noble metal ALD, such as Pt, Ru, Pd, and various metal alloys, is presented in this review. ALD technology enables the development of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent reactivity and durability.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Sintering Aid for Li7La3Zr2O12 Solid Electrolyte by Heat-treatment of Polymeric Precursors Containing Li and B
- Ran-Hee Shin, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):151-157. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.151

- 988 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the compound Li3BO3 (LBO) is intended to be prepared by a polymeric complex method as a sintering aid for the densification of Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZ) solid electrolyte. A polymeric precursor containing Li and B is heat-treated in an air atmosphere at a temperature range between 600°C and 800°C. Instead of LBO, the compound Li2+xC1-xBxO3 (LCBO) is unexpectedly synthesized after a heat-treatment of 700°C. The effect of LCBO addition on sintering behavior and ion conductivity of LLZ is studied. It is found that the LCBO compound could lead to significant improvements in the densification and ionic conductivity of LLZ compared to pure LLZ. After sintering at 1100°C, the density of the LLZ-12wt%LBO composite is 3.72 g/cm3, with a high Li-ion conductivity of 1.18 × 10−4 Scm-1 at 28°C, while the pure LLZ specimen had a densify of 2.98 g/cm3 and Li-ion conductivity of 5.98 × 10−6 Scm-1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 Solid Electrolyte with an Added Sintering Aid
Hyun-Joon Lee, Liyu-Liu, Won-Jong Jeong, Seoung-Ki Lee, Bong-Ki Ryu
Electronic Materials Letters.2023; 19(1): 55. CrossRef
- Characterization of Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 Solid Electrolyte with an Added Sintering Aid
- [Korean]
- Effect of Organic Additives on Microstructure and Green Density of Zirconia Granules Using Water Solvent
- Ji-Hwan Jung, Sang-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):147-152. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.147
- 1,624 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
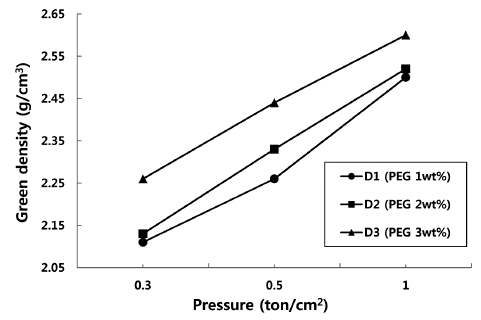
PDF Spherical-type zirconia granules are successfully fabricated by a spray-drying process using a water solvent slurry, and the change in the green density of the granule powder compacts is examined according to the organic polymers used. Two organic binders, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), which are dissolved in a water solvent and have different degrees of polymerization, are applied to the slurry with a plasticizer (polyethylene glycol). The granules employing a binder with a higher degree of polymerization (PVA) are not broken under a uniaxial press; consequently, they exhibit a poor green density of 2.4 g/cm3. In contrast, the granule powder compacts employing a binder with a lower degree of polymerization (HEMA) show a higher density of 2.6 g/cm3 with an increase in plasticizer content. The packing behavior of the granule powders for each organic polymer system is studied by examining the microstructure of the fracture surface at different applied pressures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of TiO2 Addition and Processing Variables on the Properties of Black Aluminum Nitride
Min-Kwon Park, Sin-Il Go, Kwang-Hee Han, Sang-Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2025; 35(8): 345. CrossRef - Uniaxial compaction and sintering of ZrO2−3 mol% Y2O3 using rubber and PEG solutions as binders
M.I. Dvornik, O.O. Shichalin, E.A. Mikhailenko, A.A. Burkov, S.V. Nikolenko, N.M. Vlasova, E.V. Chernyakov, A.A. Gnidenko, P.G. Chigrin, I. Yu Buravlev, N.S. Konovalova
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2024; 328: 129981. CrossRef
- Effects of TiO2 Addition and Processing Variables on the Properties of Black Aluminum Nitride
- [English]
- Synthesis of Carbonyl Iron-reinforced Polystyrene by High Energy Ball Milling
- Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Jin-Chun Kim, Young-Soo Kim, Young-Hyuk Kim, Olga B. Nazarenko
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):276-281. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.276
- 1,245 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
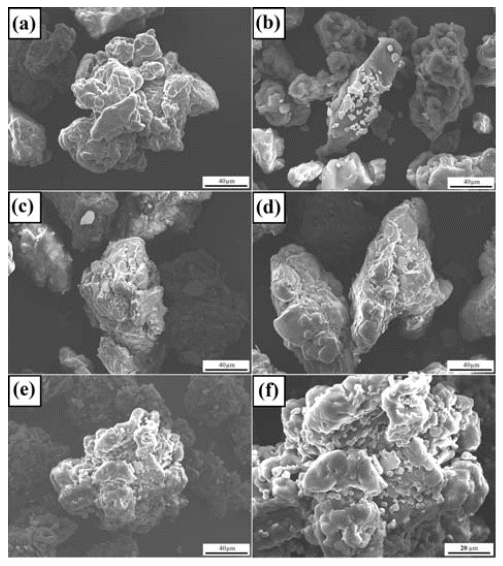
PDF Carbonyl iron (CI) is successfully incorporated as an additive into a polystyrene (PS) matrix via a highenergy ball milling method, under an n-hexane medium with volume fractions between 1% and 5% for electromagnetic interference shielding applications by the combination of magnetic CI and an insulating PS matrix. The morphology and the dispersion of CI are investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, which indicates a uniform distribution of CI in the PS matrix after 2 h of milling. The thermal behavior results indicate no significant degradation of the PS when there is a slight increase in the onset temperature with the addition of CI powder, when compared to the as-received PS pellet. After milling, there are no interactions between the CI and the PS matrix, as confirmed by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. In this study, the milled CI-PS powder is extruded to make filaments, and can have potential applications in the 3-D printing industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
Antonio Rizzo, Gregory I. Peterson
Progress in Polymer Science.2024; 159: 101900. CrossRef
- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Al2O3 Film by Freeze Tape Casting
- Ran-Hee Shin, Jun-Mo Koo, Young-Do Kim, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):438-442. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.438

- 684 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous thick film of alumina which is fabricated by freeze tape casting using a camphene-camphor-acrylate vehicle. Alumina slurry is mixed above the melting point of the camphene-camphor solvent. Upon cooling, the camphene-camphor crystallizes from the solution as particle-free dendrites, with the Al2O3 powder and acrylate liquid in the interdendritic spaces. Subsequently, the acrylate liquid is solidified by photopolymerization to offer mechanical properties for handling. The microstructure of the porous alumina film is characterized for systems with different cooling rate around the melting temperature of camphor-camphene. The structure of the dendritic porosity is compared as a function of ratio of camphene-camphor solvent and acrylate content, and Al2O3 powder volume fraction in acrylate in terms of the dendrite arm width.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Highly Dispersible Metal Nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM Layers and Their Effects on the Performance of Polymer Solar Cells
- Min-Ji Kim, Gyu-Chae Choi, Young-Kuk Kim, Yang-Do Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):179-184. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.179

- 473 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we prepare polymer solar cells incorporating organic ligand-modified Ag nanoparticles (OAgNPs) highly dispersed in the P3HT:PCBM layer. Ag nanoparticles decorated with water-dispersible ligands (WAgNPs) were also utilized as a control sample. The existence of the ligands on the Ag surface was confirmed by FTIR spectra. Metal nanoparticles with different surface chemistries exhibited different dispersion tendencies. O-AgNPs were highly dispersed even at high concentrations, whereas W-AgNPs exhibited significant aggregation in the polymer layer. Both dispersion and blending concentration of the Ag nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM matrix had critical effects on the device performance as well as light absorption. The significant changes in short-circuit current density (JSC) of the solar cells seemed to be related to the change in the polymer morphology according to the concentration of AgNPs introduced. These findings suggested the importance of uniform dispersion of plasmonic metal nanoparticles and their blending concentration conditions in order to boost the solar cell performance.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Flake-like LiCoO2 Nanopowders using Electrospinning
- Bon-Ryul Koo, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):108-113. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.108
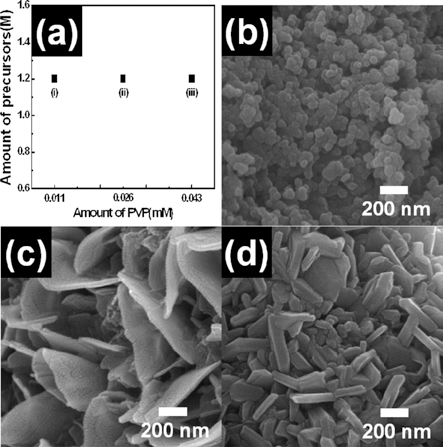
- 807 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Flake-like LiCoO2 nanopowders were fabricated using electrospinning. To investigate their formation mechanism, field-emssion scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were carried out. Among various parameters of electrospinning, we controlled the molar concentration of the precursor and the PVP polymer. When the molar concentration of lithium and cobalt was 0.45 M, the morphology of LiCoO2 nanopowders was irregular and round. For 1.27 M molar concentration, the LiCoO2 nanopowders formed with flake-like morphology. For the PVP polymer, the molar concentration was set to 0.011 mM, 0.026 mM, and 0.043 mM. Irregular LiCoO2 nanopowders were formed at low concentration (0.011 mM), while flake-like LiCoO2 were formed at high concentration (0.026 mM and 0.043 mM). Thus, optimized molar concentration of the precursor and the PVP polymer may be related to the successful formation of flake-like LiCoO2 nanopowders. As a results, the synthesized LiCoO2 nanopowder can be used as the electrode material of Li-ion batteries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 96. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO Core/shell Nanowire Composites
Yu-Jin Lee, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 360. CrossRef
- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


