Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
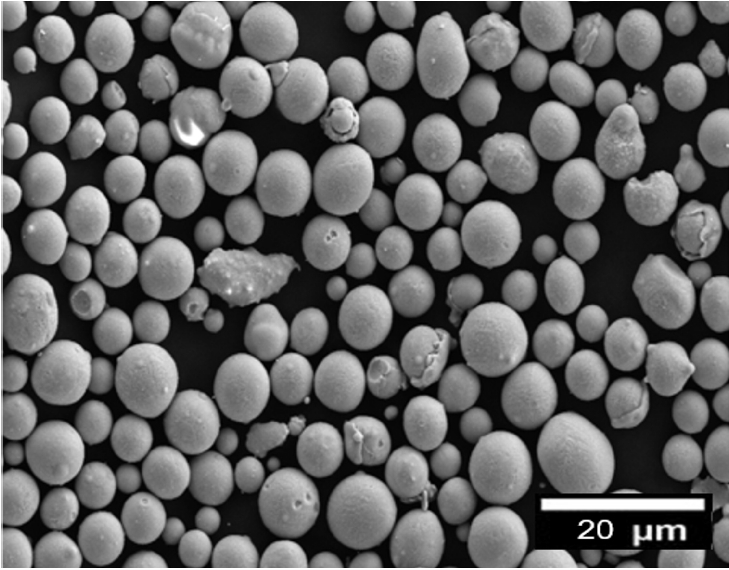
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Powder Bed Fusion 3D-Printed Cu-10Sn Alloy
- Jonggyu Kim, Junghoon Won, Wookjin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):422-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00276
- 1,157 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the optimal process conditions and mechanical properties of Cu-10Sn alloys produced by the powder bed fusion (PBF) method. The optimal PBF conditions were explored by producing samples with various laser scanning speeds and laser power. It was found that under optimized conditions, samples with a density close to the theoretical density could be fabricated using PBF without any serious defects. The microstructure and mechanical properties of samples produced under optimized conditions were investigated and compared with a commercial alloy produced by the conventional method. The hardness, maximum tensile strength, and elongation of the samples were significantly higher than those of the commercially available cast alloy with the same chemical composition. Based on these results, it is expected to be possible to use the PBF technique to manufacture Cu-10Sn products with complex 3D shapes that could not be made using the conventional manufacturing method.
- [Korean]
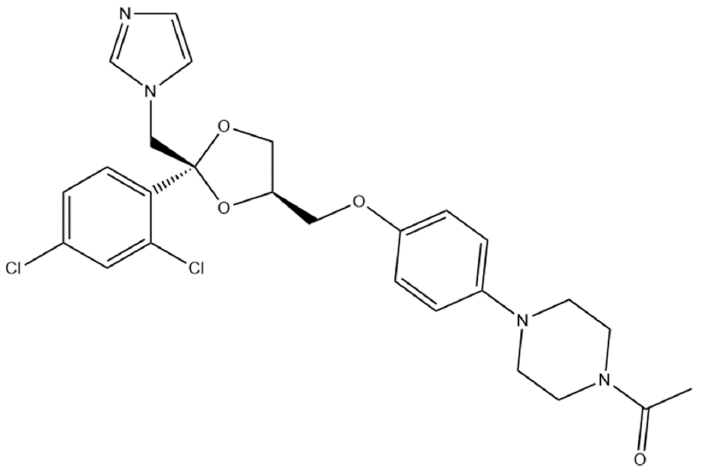
- Preparation and Evaluation of Ketoconazole-loaded Solid-SNEDDS (Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System) using Various Solidification Carriers
- Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.493
- 989 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study aimed to develop a solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (solid-SNEDDS) to enhance the formulation of ketoconazole (KTZ), a BCS Class II drug with poor solubility. Ketoconazole, which is insoluble above pH 3, requires solubilization for effective delivery. This SNEDDS comprises oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant, which spontaneously emulsify in the gastrointestinal tract environment to form nanoemulsions with droplet sizes less than 100 nm. The optimal SNE-vehicle composition of oleic acid, TPGS, and PEG 400 at a 10:80:10 weight ratio was determined based on the smallest droplet size achieved. This composition was used to prepare liquid SNEDDS containing ketoconazole. The droplet size and polydispersity index (PDI) of the resulting liquid SNEDDS were analyzed. Subsequently, solid-SNEDDS was fabricated using a spray-drying method with solidifying carriers such as silicon dioxide, crospovidone, and magnesium alumetasilicate. The physicochemical properties of the solid-SNEDDS were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and powder X-ray diffraction, and its solubility, droplet size, and PDI were evaluated. In particular, the solid-SNEDDS containing ketoconazole and crospovidone in a 2:1 weight ratio exhibited significantly enhanced solubility, highlighting its potential for improved medication adherence and dissolution rates.
- [Korean]
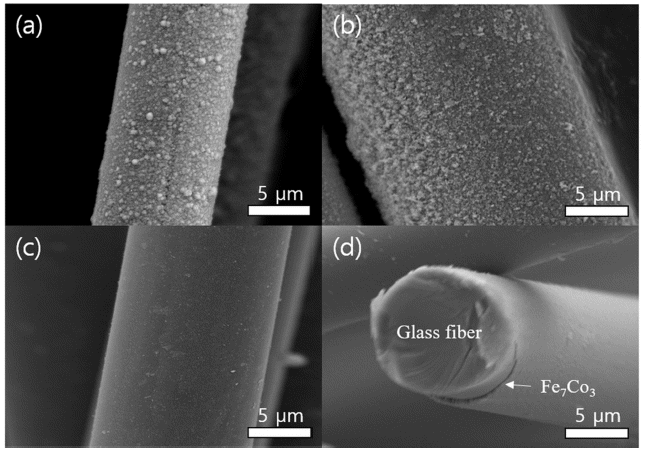
- A Study on Rinsing Effects of Sn Sensitization and Pd Activation Processes for Uniform Electroless Plating
- Seong-Jae Jeong, Mi-Se Chang, Jae-Won Jeong, Sang-Sun Yang, Young-Tae Kwon
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):511-516. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.511
- 1,750 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Electroless plating is widely utilized in engineering for the metallization of insulator substrates, including polymers, glass, and ceramics, without the need for the application of external potential. Homogeneous nucleation of metals requires the presence of Sn-Pd catalysts, which significantly reduce the activation energy of deposition. Therefore, rinsing conducted during Sn sensitization and Pd activation is a key variable for the formation of a uniform seed layer without the lack or excess of catalysts. Herein, we report the optimized rinsing process for the functionalization of Sn-Pd catalysts, which enables the uniform FeCo metallization of the glass fibers. Rinsing enables good deposition of the FeCo alloy because of the removal of excess catalysts from the glass fiber. Concurrently, excessive rinsing results in a complete removal of the Sn–Pd nucleus. Collectively, the comprehensive study of the proposed nanomaterial preparation and surface science show that the metallization of insulators is a promising technology for electronics, solar cells, catalysts, and mechanical parts.
- [Korean]
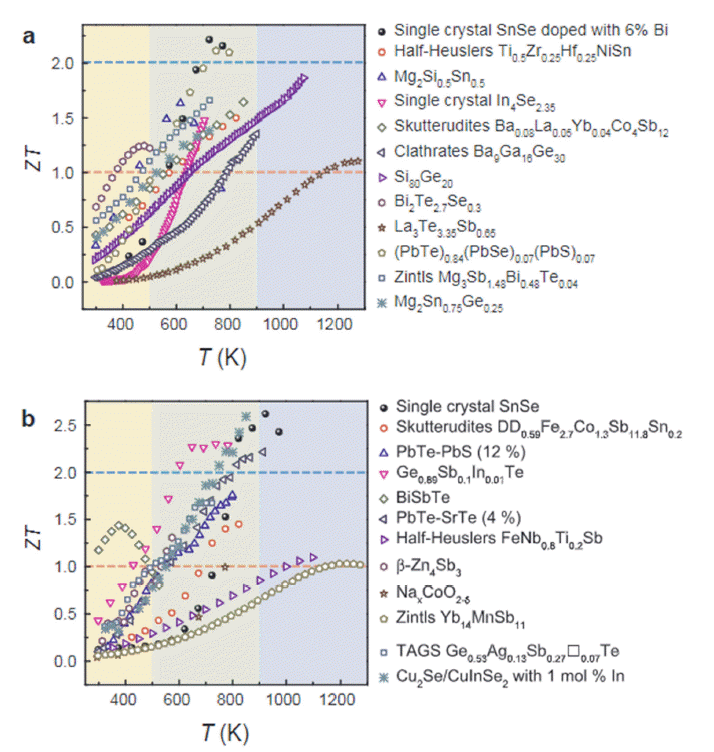
- Recent Studies on Performance Enhancement of Polycrystal SnSe Thermoelectric Materials
- Myeong Jun Jung, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):152-158. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.152
- 1,316 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Thermoelectric materials can reversely convert heat and electricity into each other; therefore, they can be very useful for energy harvesting from heat waste. Among many thermoelectrical materials, SnSe exhibits outstanding thermoelectric performance along the particular direction of a single crystal. However, single-crystal SnSe has poor mechanical properties and thus it is difficult to apply for mass production. Therefore, polycrystalline SnSe materials may be used to replace single-crystal SnSe by overcoming its inferior thermoelectric performance owing to surface oxidation. Considerable efforts are currently focused on enhancing the thermoelectric performance of polycrystalline SnSe. In this study, we briefly review various enhancement methods for SnSe thermoelectric materials, including doping, texturing, and nano-structuring. Finally, we discuss the future prospects of SnSe thermoelectric powder materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mechanism Behind the High zT of SnSe2 Added SnSe at High Temperatures
JunSu Kim, Seong-Mee Hwang, Hyunjin Park, Yinglu Tang, Won-Seon Seo, Chae Woo Ryu, Heesun Yang, Weon Ho Shin, Hyun-Sik Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(11): 857. CrossRef
- The Mechanism Behind the High zT of SnSe2 Added SnSe at High Temperatures
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 Contact Materials by Powder Compaction
- Jin Kyu Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):41-46. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.41

- 541 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials using a controlled milling process with a subsequent compaction process. Using magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC), the milled Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 powders have been consolidated into bulk samples. The effects of the compaction conditions on the microstructure and characteristics have been investigated in detail. The nanoscale SnO2 phase and microscale Bi2O3 phase are well-distributed homogeneously in the Ag matrix after the consolidation process. The successful consolidation of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials was achieved by an MPC process with subsequent atmospheric sintering, after which the hardness and electrical conductivity of the Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials were found to be 62–75 HV and 52–63% IACS, respectively, which is related to the interfacial stability between the Ag matrix, the SnO2 phase, and the Bi2O3 phase.
- [Korean]
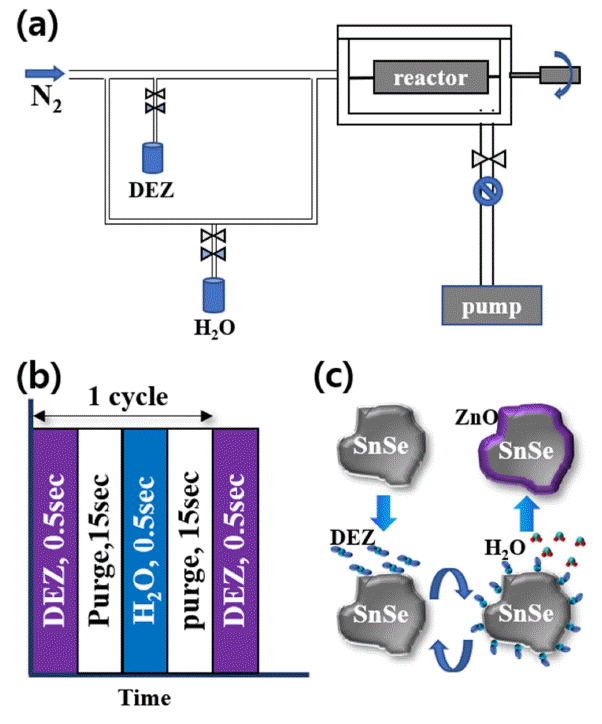
- Rotation Speed Dependence of ZnO Coating Layer on SnSe powders by Rotary Atomic Layer Deposition Reactor
- Myeong Jun Jung, Ye Jun Yun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):239-245. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.239
- 638 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The SnSe single crystal shows an outstanding figure of merit (
ZT ) of 2.6 at 973 K; thus, it is considered to be a promising thermoelectric material. However, the mass production of SnSe single crystals is difficult, and their mechanical properties are poor. Alternatively, we can use polycrystalline SnSe powder, which has better mechanical properties. In this study, surface modification by atomic layer deposition (ALD) is chosen to increase theZT value of SnSe polycrystalline powder. SnSe powder is ground by a ball mill. An ALD coating process using a rotary-type reactor is adopted. ZnO thin films are grown by 100 ALD cycles using diethylzinc and H2O as precursors at 100°C. ALD is performed at rotation speeds of 30, 40, 50, and 60 rpm to examine the effects of rotation speed on the thin film characteristics. The physical and chemical properties of ALD-coated SnSe powders are characterized by scanning and tunneling electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The results reveal that a smooth oxygenrich ZnO layer is grown on SnSe at a rotation speed of 30 rpm. This result can be applied for the uniform coating of a ZnO layer on various powder materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
Myeong Jun Jung, Su Min Eun, Hogyoung Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 42(14): 3545. CrossRef
- Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
- [Korean]
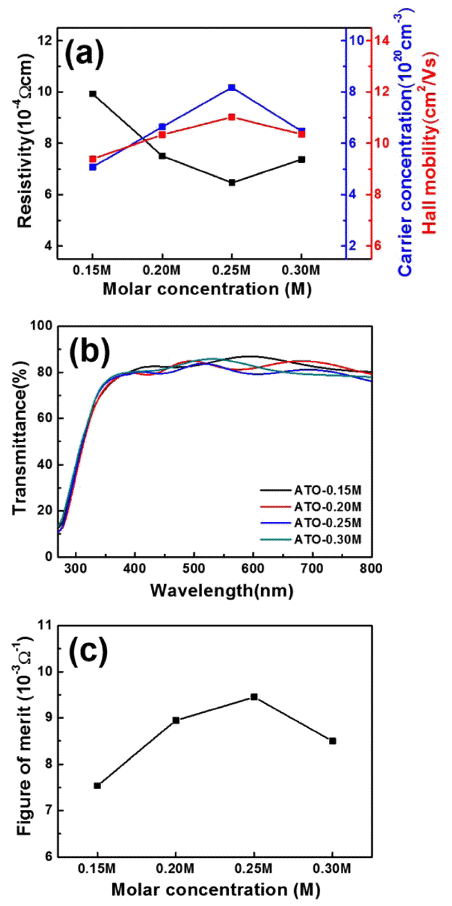
- Fabrication of compact surface structure by molar concentration on Sb-doped SnO2 transparent conducting films
- Ju-Won Bae, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):54-59. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.54
- 735 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Sb-doped SnO2 (ATO) transparent conducting films are fabricated using horizontal ultrasonic spray pyrolysis deposition (HUSPD) to form uniform and compact film structures with homogeneously supplied precursor solution. To optimize the molar concentration and transparent conducting performance of the ATO films using HUSPD, we use precursor solutions of 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, and 0.30 M. As the molar concentration increases, the resultant ATO films exhibit more compact surface structures because of the larger crystallite sizes and higher ATO crystallinity because of the greater thickness from the accelerated growth of ATO. Thus, the ATO films prepared at 0.25 M have the best transparent conducting performance (12.60±0.21 Ω/□ sheet resistance and 80.83% optical transmittance) and the highest figure-of-merit value (9.44±0.17 × 10-3 Ω-1). The improvement in transparent conducting performance is attributed to the enhanced carrier concentration by the improved ATO crystallinity and Hall mobility with the compact surface structure and preferred (211) orientation, ascribed to the accelerated growth of ATO at the optimized molar concentration. Therefore, ATO films fabricated using HUSPD are transparent conducting film candidates for optoelectronic devices.
- [English]
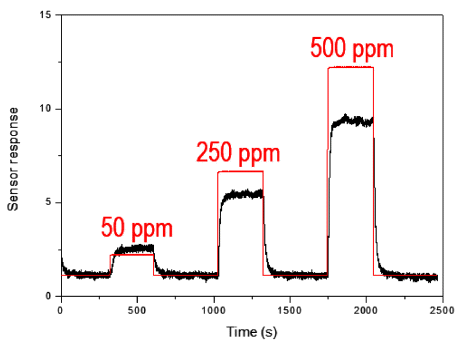
- The Synthesis Method of Tin Dioxide Nanoparticles by Plasma-Assisted Electrolysis Process and Gas Sensing Property
- Tae Hyung Kim, Yoseb Song, Chan-Gi Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):351-356. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.351
- 1,537 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin dioxide nanoparticles are prepared using a newly developed synthesis method of plasma-assisted electrolysis. A high voltage is applied to the tin metal plate to apply a high pressure and temperature to the synthesized oxide layer on the metal surface, producing nanoparticles in a low concentration of sulfuric acid. The particle size, morphology, and size distribution is controlled by the concentration of electrolytes and frequency of the power supply. The as-prepared powder of tin dioxide nanoparticles is used to fabricate a gas sensor to investigate the potential application. The particle-based gas sensor exhibits a short response and recovery time. There is sensitivity to the reduction gas for the gas flowing at rates of 50, 250, and 500 ppm of H2S gas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
Min Ah Han, Hyun-Jong Kim, Hee Chul Lee, Jin-Seong Park, Ho-Nyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 133. CrossRef
- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
- [Korean]
- Effect of Freezing and Sintering Condition of CuO-SnO2/Camphene Slurries on the Pore Structure of Porous Cu-Sn
- Joo-Hyung Kim, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):49-53. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.49

- 707 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The present study demonstrates the effect of freezing conditions on the pore structure of porous Cu-10 wt.% Sn prepared by freeze drying of CuO-SnO2/camphene slurry. Mixtures of CuO and SnO2 powders are prepared by ball milling for 10 h. Camphene slurries with 10 vol.% of CuO-SnO2 are unidirectionally frozen in a mold maintained at a temperature of -30°C for 1 and 24 h, respectively. Pores are generated by the sublimation of camphene at room temperature. After hydrogen reduction and sintering at 650°C for 2 h, the green body of the CuO-SnO2 is completely converted into porous Cu-Sn alloy. Microstructural observation reveals that the sintered samples have large pores which are aligned parallel to the camphene growth direction. The size of the large pores increases from 150 to 300 μm with an increase in the holding time. Also, the internal walls of the large pores contain relatively small pores whose size increases with the holding time. The change in pore structure is explained by the growth behavior of the camphene crystals and rearrangement of the solid particles during the freezing process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Porous Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of NiO/Camphene Slurry
Jae-Hun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 6. CrossRef - Fabrication of Al2O3 Dispersed Porous Cu by Freeze Drying of CuO-Al2O3/Camphene Slurry
Hyunji Kang, Doh-Hyung Riu, Sung-Tag Oh
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 25. CrossRef - Porous W-Ni Alloys Synthesized from Camphene/WO3-NiO Slurry by Freeze Drying and Heat Treatment in Hydrogen Atmosphere
Sung Hyun Park, Seong-Min Park, So-Jeong Park, Bo-Yeong Park, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(2): 108. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Porous Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of NiO/Camphene Slurry
- [Korean]
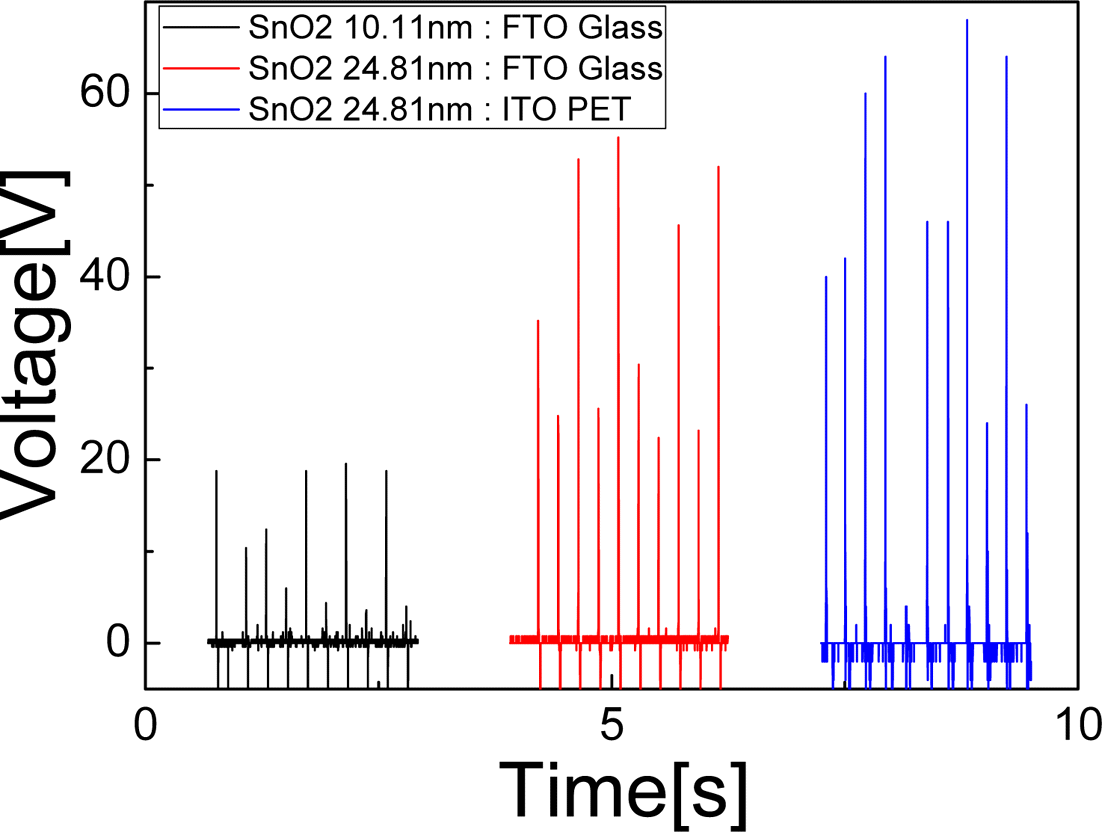
- Improvement of Triboelectric Efficiency using SnO2 Friction Layer for Triboelectric Generator
- No Ho Lee, Jae Rok Shin, Ji Een Yoo, Dong Hun You, Bon-Ryul Koo, Sung Woo Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):321-325. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.321
- 1,019 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The triboelectric property of a material is important to improve an efficiency of triboelectric generator (TEG) in energy harvesting from an ambient energy. In this study, we have studied the TEG property of a semiconducting SnO2 which has yet to be explored so far. As a counter triboelectric material, PET and glass are used. Vertical contact mode is utilized to evaluate the TEG efficiency. SnO2 thin film is deposited by atomic layer deposition on bare Si wafer for various thicknesses from 5.2 nm to 34.6 nm, where the TEG output is increased from 13.9V to 73.5V. Triboelectric series are determined by comparing the polarity of output voltage of 2 samples among SnO2, PET, and glass. In conclusion, SnO2, as an intrinsic n-type material, has the most strong tendency to be positive side to lose the electron and PET has the most strong tendency to be negative side to get the electron, and glass to be between them. Therefore, the SnO2-PET combination shows the highest TEG efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triboelectric charge generation by semiconducting SnO2 film grown by atomic layer deposition
No Ho Lee, Seong Yu Yoon, Dong Ha Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Byung Joon Choi
Electronic Materials Letters.2017; 13(4): 318. CrossRef
- Triboelectric charge generation by semiconducting SnO2 film grown by atomic layer deposition
- [Korean]
- Coloration and Chemical Stability of SiO2 and SnO2 Coated Blue CoAl2O4 Pigment
- JiYeon Yun, Ri Yu, Jae-Hwan Pee, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):377-381. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.377
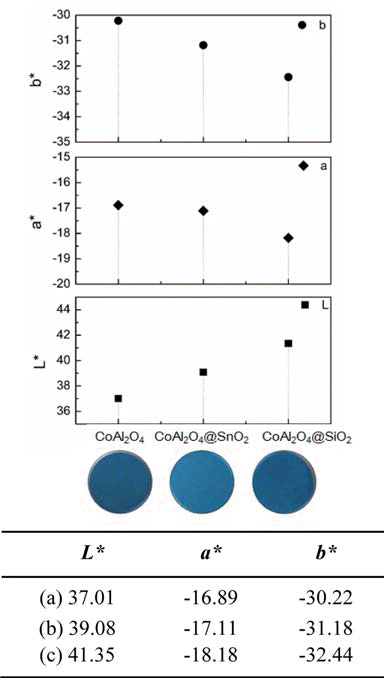
- 654 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This work describes the coloration, chemical stability of SiO2 and SnO2-coated blue CoAl2O4 pigment. The CoAl2O4, raw materials, were synthesized by a co-precipitation method and coated with silica (SiO2) and tin oxide (SnO2) using sol-gel method, respectively. To study phase and coloration of CoAl2O4, we prepared nano sized CoAl2O4 pigments which were coated SiO2 and SnO2 using tetraethylorthosilicate, Na2SiO3 and Na2SnO3 as a coating material. To determine the stability of the coated samples and their colloidal solutions under acidic and basic conditions, colloidal nanoparticle solutions with various pH values were prepared and monitored over time. Blue CoAl2O4 solutions were tuned yellow color under all acidic/basic conditions. On the other hand, the chemical stability of SiO2 and SnO2-coated CoAl2O4 solution were improved when all samples pH values, respectively. Phase stability under acidic/basic condition of the core-shell type CoAl2O4 powders were characterized by transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffraction,
CIE L*a*b* color parameter measurements.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


