Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of TiO2 Coated Si Nano Particle using Silicon Sawing Sludge
- Dong Hyeok Seo, Hyeon Min Yim, Ho Yoon Na, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):423-428. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.423

- 656 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Here, we report the development of a new and low-cost core-shell structure for lithium-ion battery anodes using silicon waste sludge and the Ti-ion complex. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the raw waste silicon sludge powder to be pure silicon without other metal impurities and the particle size distribution is measured to be from 200 nm to 3 μm by dynamic light scattering (DLS). As a result of pulverization by a planetary mill, the size of the single crystal according to the Scherrer formula is calculated to be 12.1 nm, but the average particle size of the agglomerate is measured to be 123.6 nm. A Si/TiO2 core-shell structure is formed using simple Ti complex ions, and the ratio of TiO2 peaks increased with an increase in the amount of Ti ions. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations revealed that TiO2 coating on Si nanoparticles results in a Si-TiO2 core-shell structure. This result is expected to improve the stability and cycle of lithium-ion batteries as anodes.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
- Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):395-401. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.395
- 2,071 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
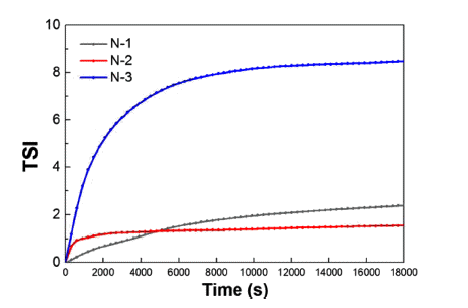
PDF The improvement of dispersion stability for the primary polishing slurry in a CMP process is achieved to prevent defects produced by agglomeration of the slurry. The dispersion properties are analyzed according to the physical characteristics of each silica sol sample. Further, the difference in the dispersion stability is confirmed as the surfactant content. The dispersibility results measured by Zeta potential suggest that the dispersion properties depend on the content and size of the abrasive in the primary polishing slurry. Moreover, the optimum ratio for high dispersion stability is confirmed as the addition content of the surfactant. Based on the aforementioned results, the long-term stability of each slurry is analyzed. Turbiscan analysis demonstrates that the agglomeration occurs depending on the increasing amount of surfactant. As a result, we demonstrate that the increased particle size and the decreased content of silica improve the dispersion stability and long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
Seung-Hwan Oh, Hyeonmin Yim, Donghee Lee, Dong Hyeok Seo, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(9): 396. CrossRef
- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
- Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):489-493. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.489
- 1,559 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
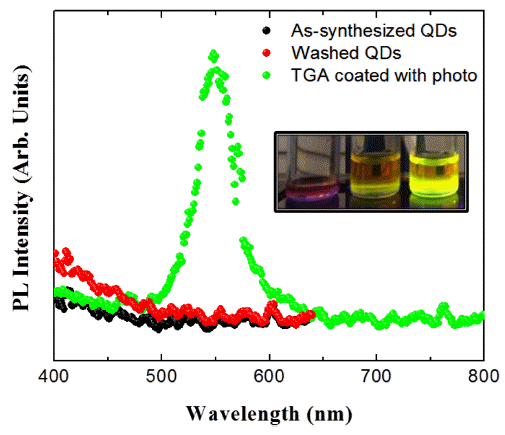
PDF In this study, the surface passivation process for InP-based quantum dots (QDs) is investigated. Surface coating is performed with poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) and thioglycolic acid. The quantum yield (QY) of a PMMA-coated sample slightly increases by approximately 1.3% relative to that of the as-synthesized InP/ZnS QDs. The QYs of the uncoated and PMMA-coated samples drastically decrease after 16 days because of the high defect state density of the InP-based QDs. PMMA does not have a significant effect on the defect passivation. Thioglycolic acid is investigated in this study for the effective surface passivation of InP-based QDs. Surface passivation with thioglycolic acid is more effective than that with the PMMA coating, and the QY increases from 1.7% to 11.3%. ZnS formed on the surface of the InP QDs and S in thioglycolic acid show strong bonding property. Additionally, the QY is further increased up to 21.0% by the photochemical reaction. Electron–hole pairs are formed by light irradiation and lead to strong bonding between the inorganic and thioglycolic acid sulfur. The surface of the InP core QDs, which does not emit light, is passivated by the irradiated light and emits green light after the photochemical reaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef
- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
- [English]
- Lithium-silicate coating on Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2) with a Layered Structure
- Dong-jin Kim, Da-ye Yoon, Woo-byoung Kim, Jae-won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):87-95. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.87
- 1,242 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
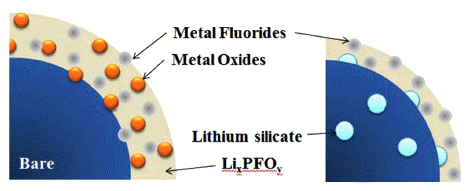
PDF Lithium silicate, a lithium-ion conducting ceramic, is coated on a layer-structured lithium nickel manganese oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2). Residual lithium compounds (Li2CO3 and LiOH) on the surface of the cathode material and SiO2 derived from tetraethylorthosilicate are used as lithium and silicon sources, respectively. Powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy analyses show that lithium silicate is coated uniformly on the cathode particles. Charge and discharge tests of the samples show that the coating can enhance the rate capability and cycle life performance. The improvements are attributed to the reduced interfacial resistance originating from suppression of solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) formation and dissolution of Ni and Mn due to the coating. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the cycled electrodes shows that nickel oxide and manganese oxide particles are formed on the surface of the electrode and that greater decomposition of the electrolyte occurs for the bare sample, which confirms the assumption that SEI formation and Ni and Mn dissolution can be reduced using the coating process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
Hye Ji Song, Seol Heui Jang, Juhyeon Ahn, Si Hyoung Oh, Taeeun Yim
Journal of Power Sources.2019; 416: 1. CrossRef
- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
- [Korean]
- Surface Treatment Method for Long-term Stability of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
- Hyun-Su Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum-Sung Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan-Gi Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.1
- 1,487 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
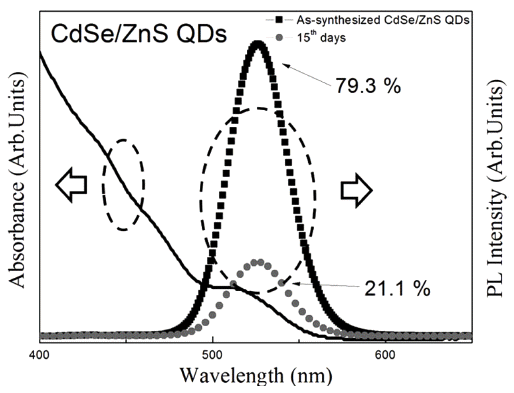
PDF We have investigated the washing method of as-synthesized CdSe/ZnS core/shell structure quantum dots (QDs) and the effective surface passivation method of the washed QDs using PMMA. The quantum yield (QY%) of assynthesized QDs decreases with time, from 79.3% to 21.1%, owing to surface reaction with residual organics. The decreased QY% is restored to the QY% of as-synthesized QDs by washing. However, the QY% of washed QDs also decreases with time, owing to the absence of surface passivation layer. On the other hand, the PMMA-treated QDs maintained a relatively higher QY% after washing than that of the washed QDs that were kept in toluene solution for 30 days. Formation of the PMMA coating layer on CdSe/ZnS QD surface is confirmed by HR-TEM and FT-IR. It is found that the PMMA surface coating, when combined with washing, is useful to be applied in the storage of QDs, owing to its long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
Seung Hwan Ji, Hye Won Yun, Jin Ho Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(1): 16. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 489. CrossRef
- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
- [Korean]
- The Preparation of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Paste Used the Peroxo Titanium Complex and Characteristics by Annealing Temperature
- Hyunsu Park, Soyeong Joo, Joon-Phil Choi, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):396-402. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.396
- 957 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
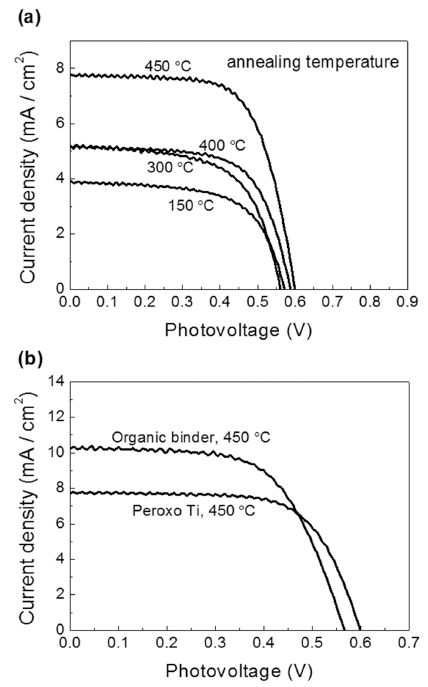
PDF The organic binder-free paste for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) has been investigated using peroxo titanium complex. The crystal structure of TiO2 nanoparticles, morphology of TiO2 film and electrical properties are analyzed by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Electrochemical Impedance Spectra (EIS), and solar simulator. The synthesized TiO2 nanopowders by the peroxo titanium complex at 150, 300, 400°C, and 450°C have anatase phase and average crystal sizes are calculated to be 4.2, 13.7, 16.9, and 20.9 nm, respectively. The DSSC prepared by the peroxo titanium complex binder have higher Voc and lower Jsc values than that of the organic binder. It can be attributed to improvement of sintering properties of TCO/TiO2 and TiO2/TiO2 interface and to formation of agglomerate by the nanoparticles. As a result, we have investigated the organic binder-free paste and 3.178% conversion efficiency of the DSSC at 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
Won Jin Kim, Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Donghee Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(3): 152. CrossRef - Development of eco-friendly thin film manufacturing process using poeroxo titanium complex solution and potential for resistive random access memory
Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 562: 150170. CrossRef - Preparation of ultra-thin TiO2 shell by peroxo titanium complex (PTC) solution-based green surface modification, and photocatalytic activity of homo-core/shell TiO2
Jinho Lee, Jiyong Hwang, Hyunsu Park, Tohru Sekino, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 540: 148399. CrossRef - Effects of Annealing Temperature on the Crystal Structure, Morphology, and Optical Properties of Peroxo-Titanate Nanotubes Prepared by Peroxo-Titanium Complex Ion
Hyunsu Park, Tomoyo Goto, Sunghun Cho, Soo Wohn Lee, Masato Kakihana, Tohru Sekino
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1331. CrossRef - Study on thermal behavior of Ammonium Hexafluofide Titanate for Synthesis of TiO2 Powders
Duk-Hee Lee, Jae-Ryang Park, Chan-Gi Lee, Kyung-Soo Park, Hyeon-Mo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 353. CrossRef
- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
- [Korean]
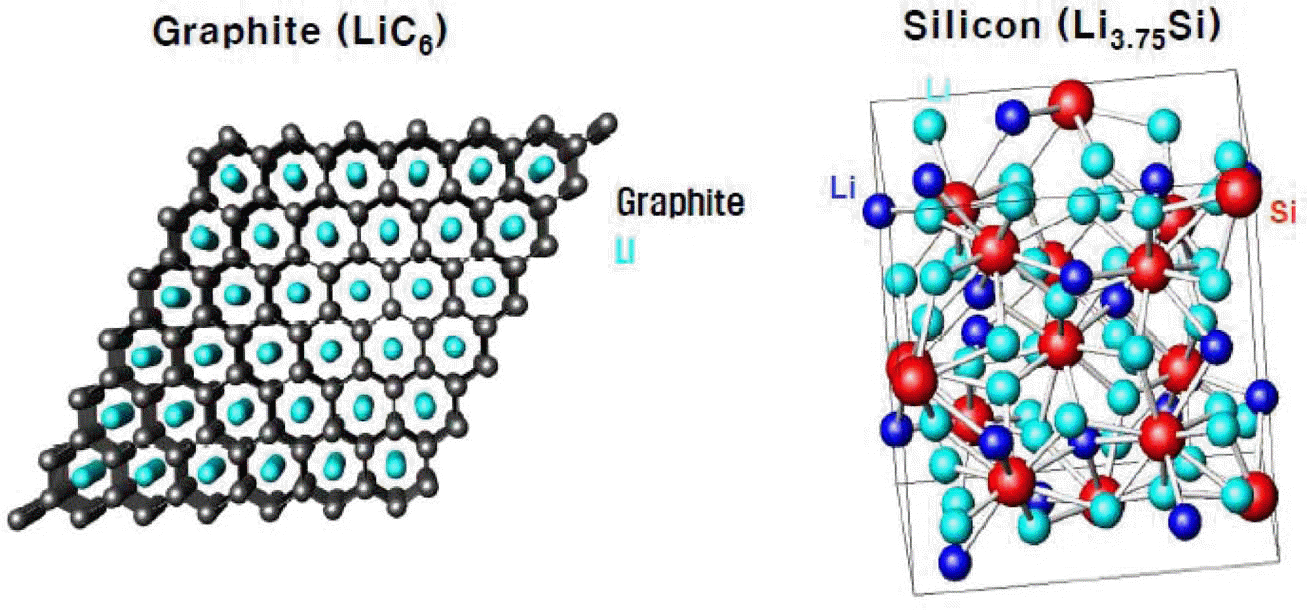
- Research Trend of Electrode Materials for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries
- Jae-won Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):473-479. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.473
- 3,524 View
- 64 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A neuro-fuzzy system to evaluate the remaining useful life of the lithium-ion battery using the impedance spectrum in the overall range of SOCs
Min-Seong Kim, Abdul Shakoor Akram, Woojin Choi
Journal of Power Electronics.2025; 25(1): 103. CrossRef - Highly Stable and Rechargeable Lithium‐Ion Battery Using a Designed Organic PTVE‐Impregnated Porous Graphitic Carbon Composite
Ji-Won Son, Jae Seob Lee, Hyun Ho Choi, Fanglin Wu, Hong-Il Kim, Tae Ju Kang, Hyun Woo Kim, Shan Fang, Ying Liu, Jung Sang Cho, Amar Patil
International Journal of Energy Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydrogen Reduction Behavior of NCM-based Lithium-ion Battery Cathode Materials
So-Yeong Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Dae-Hyeon Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 163. CrossRef - Effect of Calcination Temperature on Ionic Conductivity of All-solid State Battery Electrolytes
Yu Taek Hong, Ji Min Im, Ki Sang Baek, Chan Gyu Kim, Seung Wook Baek, Jung Hyun Kim
New & Renewable Energy.2024; 20(2): 71. CrossRef - FeCO3/rGO Composites Prepared by CO2 Capture and Carbonate Conversion: Anode Material in Lithium-Ion Batteries with Enhanced Performance
Sanglim Lee, Gahwi Gu, Daeung Park, Hwiyun Im, Yongjae Lee, Junseok Moon, Weonho Shin, Hiesang Sohn
Membrane Journal.2024; 34(5): 253. CrossRef - Research Trend in Rock Salt Structured High Entropy Cathode
Minjeong Kim, Jahun Koo, Minjeong Kang, Juah Song, Chunjoong Kim
Ceramist.2022; 25(1): 90. CrossRef - Recovery of Co and Ni from Strong Acidic Solution by Cyanex 301
Yeon-Chul Cho, Ki-Hun Kim, Jae-Woo Ahn
Resources Recycling.2021; 30(6): 28. CrossRef
- A neuro-fuzzy system to evaluate the remaining useful life of the lithium-ion battery using the impedance spectrum in the overall range of SOCs
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


