Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Powder Metall Inst > Volume 27(4); 2020 > Article
-
ARTICLE
Plasma spray 공정을 이용한 BCuP-5 filler 금속/Ag 기판 복합 소재의 제조, 미세조직 및 접합 특성 - 윤성준, 김영균, 박재성a, 박주현a, 이기안*
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Parka, Joo-Hyun Parka, Kee-Ahn Lee*
-
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute 2020;27(4):333-338.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.333
Published online: July 31, 2020
인하대학교 신소재공학과
메탈㈜
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Inha University, Incheon 22212, Republic of Korea
a LT Metal LTD., 14, Gajaeul-ro, Seo-gu, Incheon, 22828, Republic of Korea
- *Corresponding Author: Kee-Ahn Lee, TEL: +82-32-860-7532, FAX: +82-32-862-5546, E-mail: keeahn@inha.ac.kr
- - 윤성준·김영균: 학생, 박재성: 연구원, 박주현: 상무, 이기안: 교수
• Received: August 20, 2020 • Accepted: August 25, 2020
© The Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute. All rights reserved.
- 733 Views
- 3 Download
Abstract
- In this study, we fabricate a thin- and dense-BCuP-5 coating layer, one of the switching device multilayers, through a plasma spray process. In addition, the microstructure and macroscopic properties of the coating layer, such as hardness and bond strength, are investigated. Both the initial powder feedstock and plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer show the main Cu phase, Cu-Ag-Cu3P ternary phases, and Ag phase. This means that microstructural degradation does not occur during plasma spraying. The Vickers hardness of the coating layer was measured as 117.0 HV, indicating that the fine distribution of the three phases enables the excellent mechanical properties of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer. The pull-off strength of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer is measured as 16.5 kg/cm2. Based on the above findings, the applicability of plasma spray for the fabrication process of low-cost multi-layered electronic contact materials is discussed and suggested.
- 다층 클래딩 전기 접점 소자는 회로의 기계적인 개폐 및 접촉이 발생하는 부분에 이용되는 부품으로서, 자동차, 통 신 기기, 전기-전자 기기 등 다양한 분야에서 각종 스위치, 릴레이, 차단기 및 전기 전자 개폐기로 사용되는 핵심 부 품들 중 하나이다[1]. 전기 접점 재료의 경우 회로의 개폐 및 접촉 시 아크열 발생으로 인해 소재의 열화 및 손상이 발생하기 때문에 이를 최소화하기 위하여 우수한 전기 전 도도, 열전도도 및 내구성이 요구된다[2]. 현재 이러한 특 성을 충족하는 전기 접점 재료에는 귀금속 소재들이 주로 사용되고 있으며 그 중 전류용 접점 재료로는 Ag-M(O)/ Ag 및 Ag-M(O)/Cu계 전기접점 재료가 제시되고 있다[3]. 그러나 상기 소재 및 부품의 경우 제조 단가가 매우 높다 는 단점이 있어 현재 공정 단가를 낮출 수 있는 다양한 방 안들이 검토되고 있다. 그 중 저가의 BCuP-5 삽입 금속 (Cu-15Ag-5P)을 시트(sheet) 형태로 삽입하거나 전기도금 법으로 도금한 후 가공 처리를 통해 접점 재료로 사용하 려는 시도가 진행 중에 있다. 그러나 상기 공정의 경우 얇 고 치밀한 BCuP-5 코팅층을 얻기 위해서는 필요 이상의 두께로 BCuP-5 코팅층을 제조한 후 표면 처리를 수행해 야 하는데, 이는 모재 Ag 손실을 초래하기 때문에 대면적 화에는 적용하기 어렵다. 또한 후 가공 처리 후 소재의 손 실이 매우 크기 때문에 추가적인 경제적 손실이 나타날 수 있다. 따라서 새로운 공정을 이용한 저가 접점 재료 및 소자의 개발이 요구되고 있다.
- Plasma spray 공정은 고온에서 순간적으로 용융된 분말 을 고압, 고속으로 모재에 분사하여 얇고 건전한 코팅층을 형성시키는 용사 코팅(thermal spray coating) 공정들 중 하 나이다[4]. 이러한 plasma spray 공정은 금속, 세라믹, 복 합소재 등 다양한 분말에 모두 이용될 수 있으며, 코팅층 과 모재 간의 높은 접합성 및 균일성을 유지시킬 수 있다 는 장점을 가진다[5-8]. 즉 plasma spray는 다층 전기 접점 재료의 BCuP-5 삽입 금속을 얇고 균일하게 대면적화 시 킬 수 있는 가능성 있는 대체 공정으로 예상된다. 그러나, 현재까지 plasma spray와 같은 용사 코팅 공정을 이용하여 다층 클래딩 전기 접점재료를 제조하려는 시도는 전혀 수 행된 바 없다.
- 본 연구에서는 plasma spray 공정을 이용하여 접점 소자 의 주 소재로 사용되고 있는 Ag plate 위에 얇고 균일한 BCuP-5 코팅층을 제조하고자 하였다. 그 후 제조된 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층에 대한 미세조직과 기계적 특성을 조사하였다. 상기 결과들을 기반으로 후 처리없이 얇고 균일하며 치밀한 BCuP-5 코팅층의 직접 제조, 그리 고 접점재료로의 적용 가능성을 확인해 보았다.
1. 서 론
- 본 연구에서 사용된 분말은 성광엠파 사의 ‘BCuP-5’ 합 금 분말로 표준 조성(Cu-15Ag-5P(wt.%))와 유사한 Cu- 15.7Ag-4.8P(wt.%)의 화학 조성을 갖는 합금 분말이다. 그 림 1은 BCuP-5 합금 분말의 거시적인 형상과 분말 크기 분포를 보여준다. 그림 1(a)에 나타난 것과 같이 본 연구 에서 사용된 BCuP-5 합금 분말은 대체적으로 구형을 보 였으며, 평균 입도(average particle size)는 21.5 μm로 측정 되었다(그림 1(b)). 상기 분말 원료와 plasma spray 공정을 이용하여 Ag 기판 위에 코팅층을 제조하였다. 이 때 사용 된 plasma spray 공정 조건을 표 1에 정리하였다.
- Plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 초기 미세조직 및 단 면 관찰을 위해 silicon carbide 연마지(#400~#2000)를 사 용하여 연마한 후 최종적으로, 1 μm 수준의 다이아몬드 현탁액(diamond suspension)으로 미세 연마하였다. 초기 미세조직 및 상 분석은 고온 시차 주사 열량계(high temperature differential scanning calorimetry, HT-DSC, DSC 404 F1), 주사 전자 현미경(scanning electron microscope, SEM, VEGA II LMU), 에너지 분산형 분광분석기 (energy dispersive spectroscopy, EDS) 및 X선 회절 분석기(X-ray diffraction, XRD, Rigaku KRD Ultima IV)를 이용하여 수 행하였다.
- Plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 표면 거칠기(roughness) 측정을 위해 표면 거칠기 측정기(SJ-310, Mitutoyo)를 사 용하였으며, 이 때 임의의 영역에 대해 총 3회 측정 후 평 균 값을 이용하였다. Plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 경 도는 마이크로 비커스 경도기(HMV-2, Shimadzu)를 이용 하여 부여 하중 0.5 Kgf 조건으로 12회 측정하였다. 또한 Ag 기판과 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 접합 강도를 측정하기 위해 접합강도 측정기(sebastian 4, Quad group) 를 사용하였으며, 수십 회 반복 실험한 후 평균 값을 구하 였다. 이 때 접합 강도 측정 전 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코 팅층의 표면에 스터드 핀(stud-pin)을 부착한 후 150°C에 서 70분 간 열처리를 수행하여 BCuP-5 코팅층과 스터드 핀을 접합시킨 뒤 실험을 진행하였다.
2. 실험 방법
Fig. 1
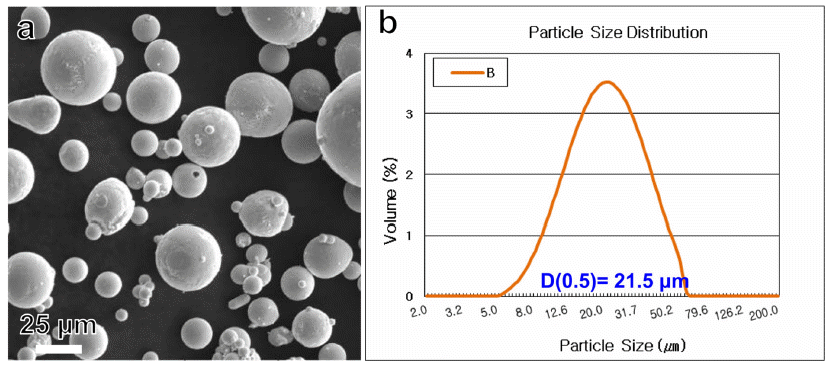
Initial Cu-15.7Ag-4.8P (wt.%) alloy powder characteristics; (a) SEM image showing the morphology of powders and (b) Particle size distribution.

Table 1
Plasma spray process parameters used in this study
| Ar [SCFH] | H2 [SCFH) | Current A] | Gun Distance (mm) | System Voltage (V) | Gun Voltage (V) | Pass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||
| 105 | 35 | 400 | 100 | 53.0 | 49.2 | 2 |
- 그림 2는 초기 BCuP-5 합금 분말의 미세조직을 관찰한 결과이다. 분말의 단면을 저 배율로 관찰한 결과(그림 2(a)), 분말은 상대적으로 밝은 영역과 어두운 영역으로 이 루어진 2 상(dual-phase) 형태를 보였다. 분말의 단면을 고 배율로 관찰한 결과(그림 2(b)), 상대적으로 어두운 영역 내부에서 흰 색 입자들(white particles)이 추가적으로 관찰 되었다. EDS 분석 결과 및 참고 문헌을 통해 상대적으로 밝은 영역은 Cu+Ag+Cu3P 3원 공정(ternary eutectic) 상들 로, 상대적으로 어두운 영역은 Cu 상으로, 그리고 흰색 입 자는 Ag-rich 상으로 분석되었다[9]. 제조된 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 거시적인 이미지를 그림 3에 제 시하였다. 그림에서 알 수 있듯이 제조된 코팅층의 경우 균일하고 건전하게 형성되었음을 알 수 있었다.
- 그림 4는 초기 BCuP-5(Cu-15Ag-5P) 합금 분말 및 제조 된 BCuP-5 코팅층의 XRD 상 분석 결과들이다. XRD 상 분석 결과를 통해 BCuP-5 합금 분말 및 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층은 공통적으로 Cu, Ag 및 Cu3P 상으로 이 루어진 것을 알 수 있었다. 이를 통해 고온 분위기에서 BCuP-5 코팅층을 제조함에도 불구하고 상 변화 혹은 추 가 불순물의 생성이 발생하지 않는 것으로 나타났다.
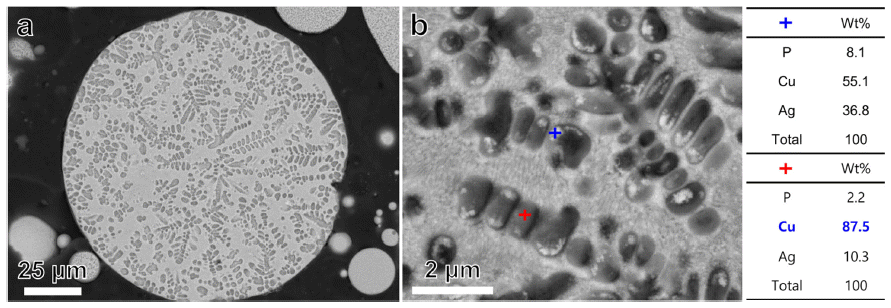
- 그림 5는 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 단면 관찰 결과이다. 그림 5(a)에 나타난 것과 같이 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 두께는 평균 25.2 μm으로 측정되었으며 표면 거칠기 범위는 약 3.3 μm로 확인되었다. 이는 plasma spray 공정이 다층 클래딩 전기 접점 재료용 BCuP-5를 얇 고 균일하게 적층할 수 있는 효과적인 공정 기술임을 의 미한다. Plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 미세조직을 면 밀히 관찰하기 위하여 에칭 후 SEM 이미지를 분석했으며 그 결과를 그림 5(b-c)에 나타냈다. 그림 5(b)를 살펴보면 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층에는 상대적으로 어두운 영 역과 밝은 영역이 함께 존재하는 것을 알 수 있다. 또한 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 고 배율 이미지 관찰 결 과(그림 5(c)), 코팅층 내부에 약 2 μm 수준의 각 형 입자 가 소량 존재하는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 각각의 영역에 대 해 EDS 분석을 수행한 결과, 상대적으로 어두운 영역은 Cu 상이고 상대적으로 밝은 영역은 Cu+Ag+Cu3P 3원 공 정 상들임을, 그리고 약 2 μm 수준의 흰색 입자들은 Agrich 상임을 알 수 있었다(Fig. 5(d)). 즉, plasma spray 공 정으로 BCuP-5를 적층시킬 경우 BCuP-5 코팅층의 미세 조직은 초기 BCuP-5 분말과 같이 Cu 상, Ag-rich 상 및 Cu+Ag+Cu3P 3원 공정 상들로 구성된 것을 XRD와 SEMEDS 분석을 통해 확인할 수 있었다.
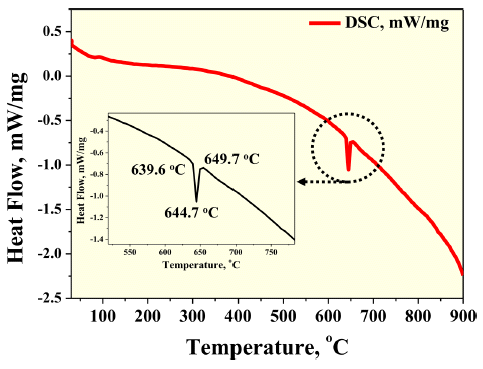
- 그림 6은 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 열적 안정성 을 분석하기위해 수행한 DSC 분석 결과이다. 그림 6을 통 해 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층은 약 640°C 부근에서 흡열 반응을 통한 상 변화가 나타나는 것을 확인할 수 있 다. 일반적으로 BCuP-5 합금은 상온에서부터 약 640°C까 지 Cu 상, Ag-rich 상 그리고 Cu3P 상으로 이루어져 있으 며 그 이상의 온도에서는 Cu3P 이 용융됨에 따라 액상 (liquid phase), Ag-rich 상 및 Cu 상으로 상 변화가 나타난 다고 보고되고 있다[9]. 상기 DSC 결과에서 나타난 640°C 에서의 흡열 반응은 Cu3P 상이 용융되면서 나타난 반응으 로 사료된다. 여기서, BCuP-5 소재의 브레이징을 위한 작 동 온도는 약 710°C로 보고되고 있다[10].
- Plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 건전성을 확인하기 위 하여 분말 및 코팅층에 대한 경도 측정을 수행하였다. 경 도 측정 결과, 분말의 경도 값은 평균 102.1 HV로, 코팅층 의 경도 값은 평균 117.0 HV로 얻어졌다. 일반적인 brazed BCuP-5 코팅층의 경도 값인 71.0 HV와 비교해 볼 때, 분 말 및 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층이 상대적으로 높은 경도 특성을 보였다[10]. 일반적인 브레이징 공정의 경우 공정 중 용융 온도가 낮은 원소의 기화 현상 및 플럭스에 서 생성된 가스에 의해 기공을 발생시키는 것으로 보고되 고 있다[11]. 즉, plasma sprayed BCuP-5의 경우 분말에 존재하는 각각의 상들이 미세하게 분포할 뿐만 아니라 plasma spray의 특징인 고속 고압으로 인해 치밀한 코팅층 을 갖기 때문에 brazed BCuP-5와 비교하여 높은 경도 특 성을 갖는 것으로 사료된다.
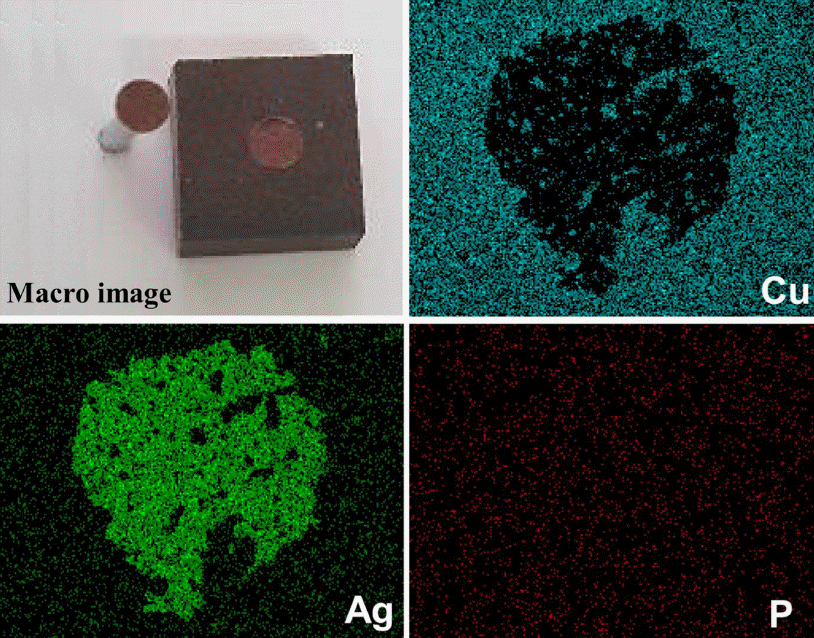
- Plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층을 스위칭 소자용 다층 클래딩 접점재료로 사용하기에 필수적으로 요구되는 Ag 기판과의 접합 강도를 측정하였다. 그 결과, Ag 기판과 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층 사이의 평균 접합 강도는 16.5 kg/cm2으로 얻어져 코팅층으로서 안정적으로 부착되 어 있는 특징을 보였다. 접합 파단 거동을 추가적으로 분 석하기 위하여 접합 강도 시험 후 시편의 표면을 관찰했 으며 그 결과를 그림 7에 나타냈다. EDS 원소 맵핑 분석 결과, 스터드 핀이 존재하던 영역에서 모재인 Ag의 강도 (intensity)가 상대적으로 높게 측정되어 plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층과 모재의 경계(interface)에서 박리가 일어 난 것을 알 수 있었다.
3. 결과 및 고찰
Fig. 2
SEM micrographs of initial Cu-15.7Ag-4.8P (wt.%) alloy powder; (a) low magnification image and (b) high magnification image.

Fig. 4
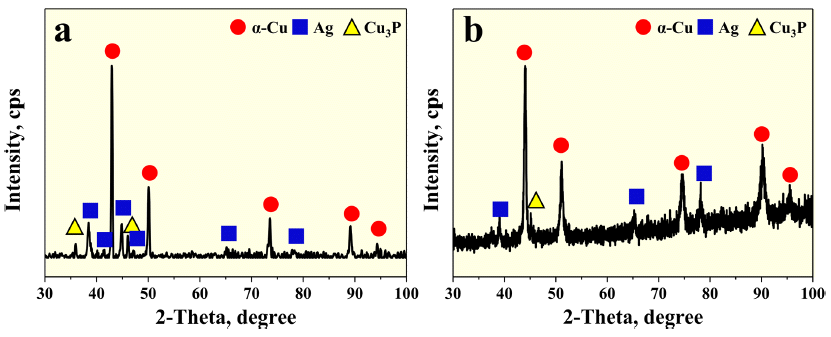
X-ray diffraction analysis results of (a) powder feedstock and (b) plasma sprayed coating layer.

Fig. 5
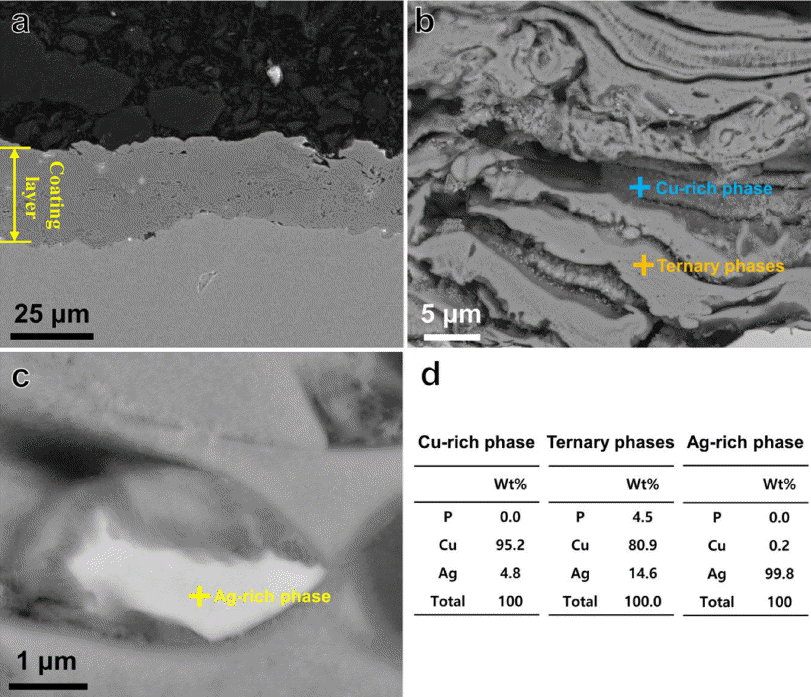
Cross-sectional SEM micrographs (a-c) and corresponding EDS elemental point analysis results (d) of plasma sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer.

- 본 연구에서는 plasma spray 공정을 이용하여 Ag 기판 위에 다층 클래딩 전기 접점재료인 BCuP-5 코팅층 제조 를 시도하였다. 그 결과, plasma spray 공정으로 전기 접점 재료에서 요구되는 균일하고 얇은 BCuP-5 코팅층을 성공 적으로 제조할 수 있었다. 제조된 코팅층의 두께는 평균 25.2 μm로 측정되었으며 표면 거칠기는 3.3 μm로 나타났 다. 미세조직 분석 결과, 초기 분말에서 존재하던 Cu 상, Ag 상 및 Cu-Ag-Cu3P 3원 공정 상들이 코팅층 형성 후에 도 그대로 존재하는 특징을 보였다. Plasma sprayed BCuP-5 코팅층의 경도 및 접합 강도 시험 결과, 평균 117.0 HV의 경도와 평균 16.5 kg/cm2의 접합 강도를 보여 건전한 코팅층이 형성된 것을 알 수 있었다. 상기의 결과 들을 기반으로 plasma spray 공정을 이용한 다층 클래딩 전기 접점 소자용 BCuP-5 코팅층의 제조 가능성을 확인 하였다.
4. 결 론
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0002007, The Competency Development Program for Industry Specialist). It was also supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program (code#: 10070219) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
감사의 글
- 1. F. Findik and H. Uzun: Mater. Des., 24 (2003) 489. .Article
- 2. M. Madej: Arch. Metall. Mater., 57 (2012) 605. .
- 3. A. Ksiazkiewicz: Poznan University of Technology Academic Journals. Electrical Engineering, 82 (2015) 207. .
- 4. H.-Y. Zhang, C.-X. Li, S.-H. Liu, L. Li, G.-J. Yang, C.-J. Li and S.-L. Zhang: Surf. Coat. Tech., 395 (2020) 125939. .Article
- 5. H. L. Ryu, S.-A. Choi, S.-M. Lee, Y.-S. Han, K. Choi, S. Nahm and Y.-S. Oh: J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst., 24 (2017) 437 (Korean). .Article
- 6. C. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Meng, W. Zhang, Y. Wang, D. Li and Z. Wang: Micron., 97 (2017) 1. .ArticlePubMed
- 7. G.-S. Ham, K.-W. Kim, G.-S. Cho, C. P. Kim and K.-A. Lee: Mater. Des., 195 (2020) 109043. .Article
- 8. A. Ranjan, A. Islam, M. Pathak, M. K. Khan and A. K. Keshri: Vacuum, 168 (2019) 108834. .Article
- 9. T. Takemoto, I. Okamoto and J. Matsumura: Trans. JWRI, 16 (1987) 301. .
- 10. A.-M. Aminazad, A.-M. Hadian and F. Ghasimakbari: Proc. Mat. Sci., 11 (2015) 672. .Article
- 11. M.-B. Karamis, A. Tasdemirci and F. Nair: J. Mater. Pr ocess.Tech., 141 (2003) 302. .Article
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Al-B4C Composites Fabricated by DED Process
- Evaluation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Functionally Graded Materials (STS 316L and Low Alloy Steel) Produced by DED Processes
- Effect of Post Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal Coating Layers Fabricated by High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Thermal Spray Process on Ag Substrate
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesion Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Clad Material by Using High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Thermal Spray Process
Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
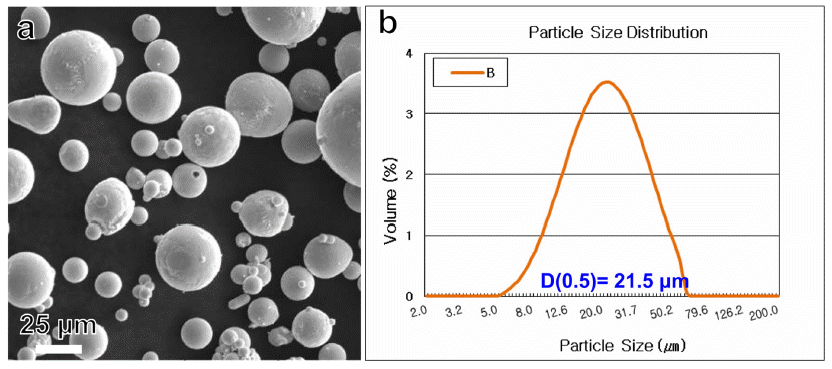
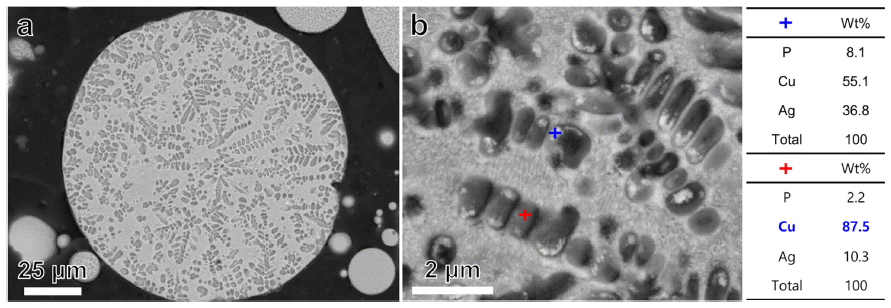

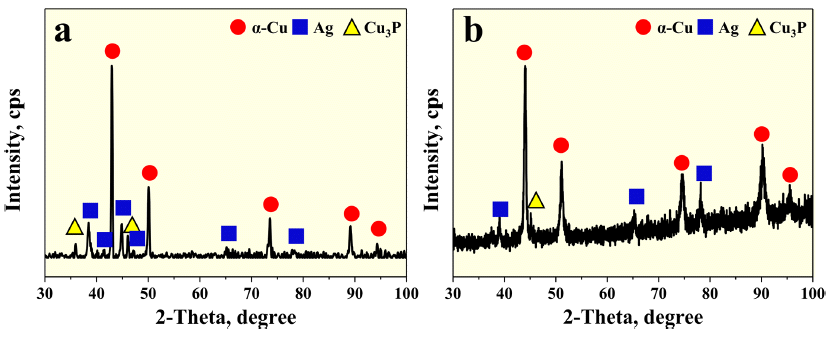
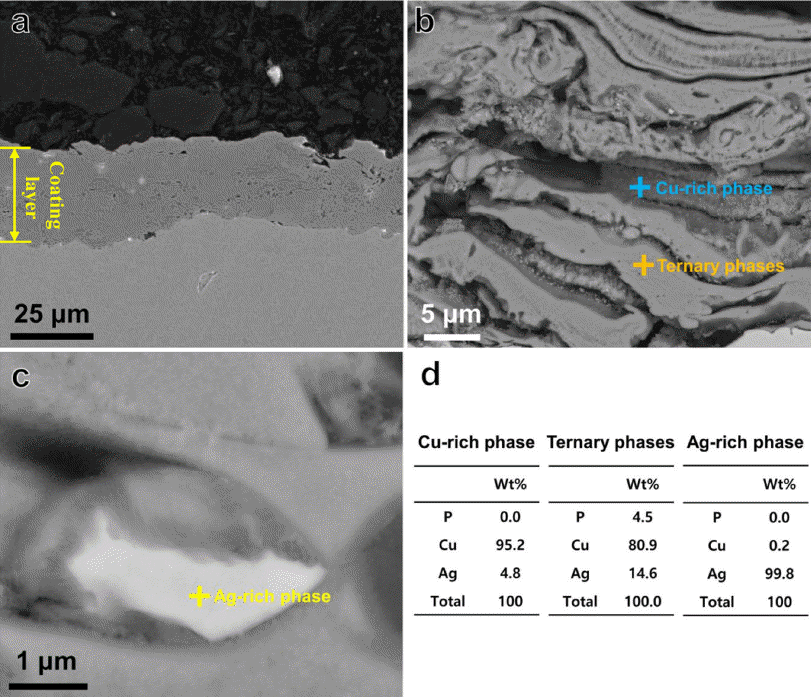
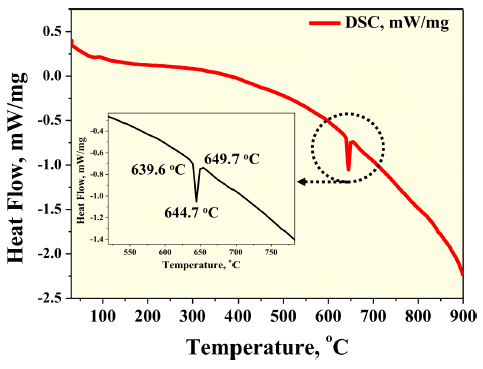
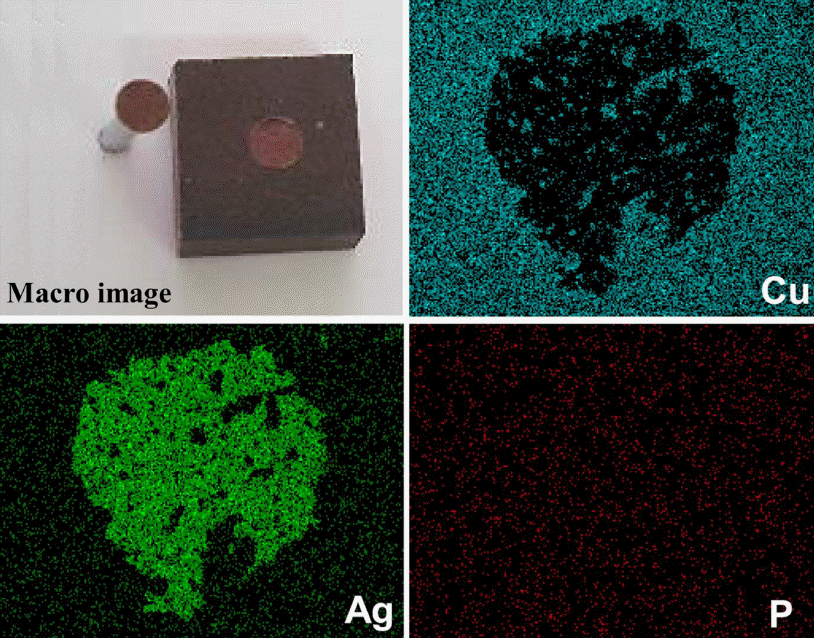
Fig. 1
Initial Cu-15.7Ag-4.8P (wt.%) alloy powder characteristics; (a) SEM image showing the morphology of powders and (b) Particle size distribution.
Fig. 2
SEM micrographs of initial Cu-15.7Ag-4.8P (wt.%) alloy powder; (a) low magnification image and (b) high magnification image.
Fig. 3
Mac rosc opic t op v iew of p lasma sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer on Ag plate.
Fig. 4
X-ray diffraction analysis results of (a) powder feedstock and (b) plasma sprayed coating layer.
Fig. 5
Cross-sectional SEM micrographs (a-c) and corresponding EDS elemental point analysis results (d) of plasma sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer.
Fig. 6
DSC analysis result of plasma sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer.
Fig. 7
Macroscopic image of stud pull tested specimen and corresponding EDS elemental mapping results.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
| Ar [SCFH] | H2 [SCFH) | Current A] | Gun Distance (mm) | System Voltage (V) | Gun Voltage (V) | Pass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||
| 105 | 35 | 400 | 100 | 53.0 | 49.2 | 2 |
Table 1
Plasma spray process parameters used in this study
Table 1
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI