- [Korean]
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
-
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):244-253. Published online June 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00087
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
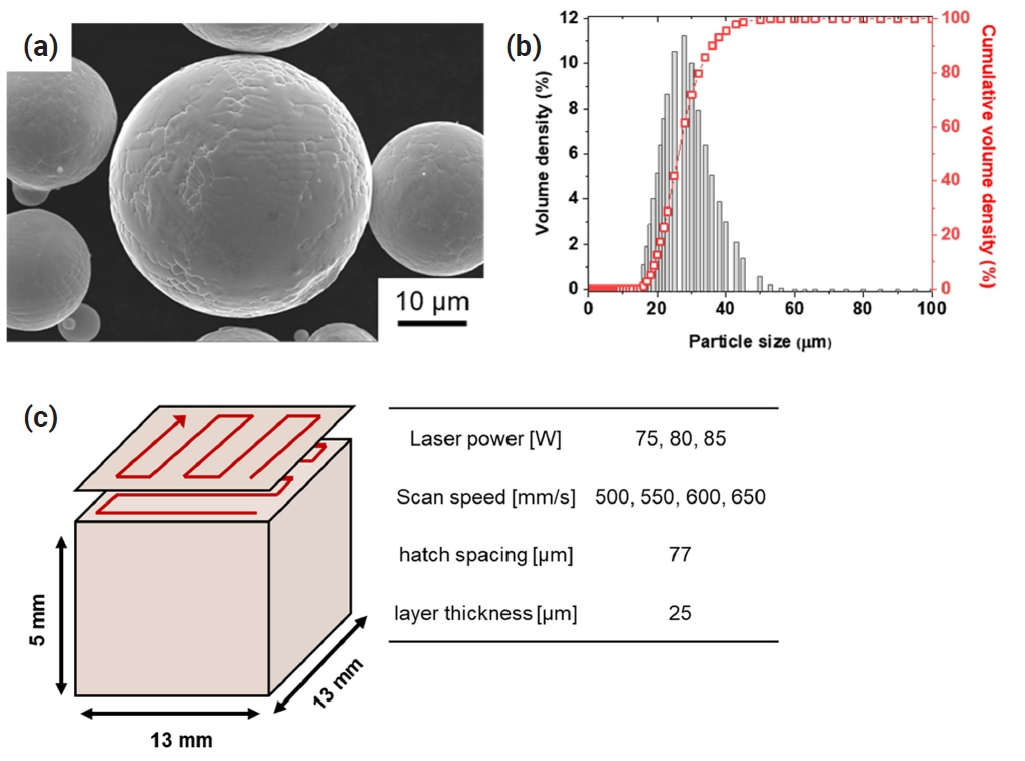
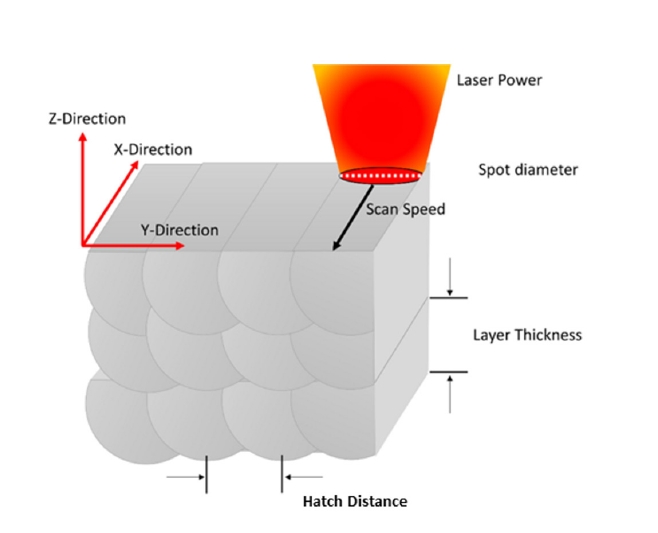
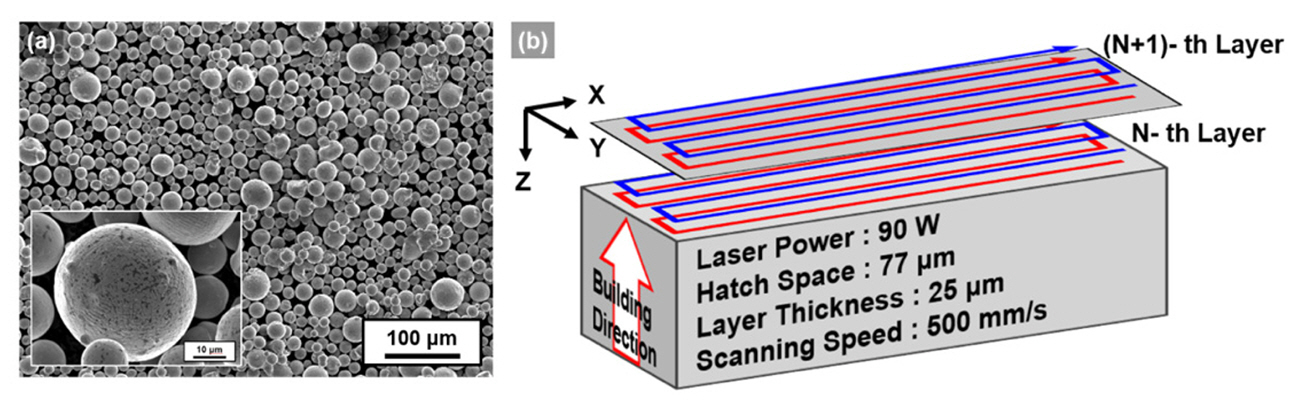
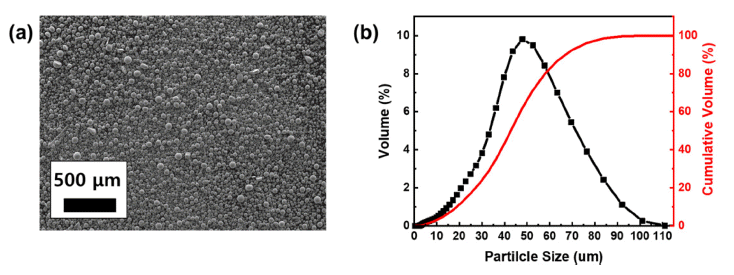
- Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely utilized in aerospace and medical sectors due to its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its low machinability makes it difficult to manufacture complex-shaped products. Advancements in additive manufacturing have focused on producing high-performance, complex components using the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process, which is a specialized technique for customized geometries. The LPBF process exposes materials to extreme thermal conditions and rapid cooling rates, leading to residual stresses within the parts. These stresses are intensified by variations in the thermal history across regions of the component. These variations result in differences in microstructure and mechanical properties, causing distortion. Although support structure design has been researched to minimize residual stress, few studies have conducted quantitative analyses of stress variations due to different support designs. This study investigated changes in the residual stress and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated using LPBF, focusing on support structure design.
- [English]
- Hot-Cracking Behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 Medium-Entropy Alloys Manufactured via Powder Bed Fusion
-
Seungjin Nam, Heechan Jung, Haeum Park, Chahee Jung, Jeong Min Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):537-545. Published online December 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00262
-
-
1,412
View
-
27
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Additive manufacturing makes it possible to improve the mechanical properties of alloys through segregation engineering of specific alloying elements into the dislocation cell structure. In this study, we investigated the mechanical and microstructural characteristics of CoNi-based medium-entropy alloys (MEAs), including the refractory alloying element Mo with a large atomic radius, manufactured via laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF). In an analysis of the printability depending on the processing parameters, we achieved a high compressive yield strength up to 653 MPa in L-PBF for (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs. However, severe residual stress remained at high-angle grain boundaries, and a brittle µ phase was precipitated at Mo-segregated dislocation cells. These resulted in hot-cracking behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs during L-PBF. These findings highlight the need for further research to adjust the Mo content and processing techniques to mitigate cracking behaviors in L-PBF-manufactured (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- [English]
- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
-
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00325
-
-
2,193
View
-
65
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The AlSi10Mg alloy has garnered significant attention for its application in laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF), due to its lightweight properties and good printability using L-PBF. However, the low production speed of the L-PBF process is the main bottleneck in the industrial commercialization of L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy parts. Furthermore, while L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy exhibits excellent mechanical properties, the properties are often over-specified compared to the target properties of parts traditionally fabricated by casting. To accelerate production speed in L-PBF, this study investigated the effects of process parameters on the build rate and mechanical properties of the AlSi10Mg alloy. Guidelines are proposed for high-speed additive manufacturing of the AlSi10Mg alloy for use in automotive parts. The results show a significant increase in the build rate, exceeding the conventional build rate by a factor of 3.6 times or more, while the L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy met the specifications for automotive prototype parts. This strategy can be expected to offer significant cost advantages while maintaining acceptable mechanical properties of topology-optimized parts used in the automobile industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - Lightweight Design of a Connecting Rod Using Lattice-Structure Parameter Optimisation: A Test Case for L-PBF
Michele Amicarelli, Michele Trovato, Paolo Cicconi
Machines.2025; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- [English]
- Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
-
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):137-145. Published online April 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00038
-
-
4,731
View
-
117
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- In order to predict the process window of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) for printing metallic components, the calculation of volumetric energy density (VED) has been widely calculated for controlling process parameters. However, because it is assumed that the process parameters contribute equally to heat input, the VED still has limitation for predicting the process window of LPBF-processed materials. In this study, an explainable machine learning (xML) approach was adopted to predict and understand the contribution of each process parameter to defect evolution in Ti alloys in the LPBF process. Various ML models were trained, and the Shapley additive explanation method was adopted to quantify the importance of each process parameter. This study can offer effective guidelines for fine-tuning process parameters to fabricate high-quality products using LPBF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Automated segmentation and analysis of microscopy images of laser powder bed fusion melt tracks
Aagam Shah, Reimar Weissbach, David A. Griggs, A. John Hart, Elif Ertekin, Sameh Tawfick
Journal of Manufacturing Processes.2025; 154: 61. CrossRef - Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of AlSi10Mg, 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloys Made with Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Selami Emanet, Edem Honu, Kekeli Agbewornu, Evelyn Quansah, Congyuan Zeng, Patrick Mensah
Materials.2025; 18(19): 4468. CrossRef - Adaptive slicing for increased productivity of metal laser powder bed fusion
Lars Vanmunster, Louca R. Goossens, Laurent Sergeant, Brecht Van Hooreweder, Bey Vrancken
Additive Manufacturing.2025; 112: 105000. CrossRef
- [English]
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
-
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):8-15. Published online February 28, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.8
-
-
4,529
View
-
139
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The emergence of ferrous-medium entropy alloys (FeMEAs) with excellent tensile properties represents a potential direction for designing alloys based on metastable engineering. In this study, an FeMEA is successfully fabricated using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a metal additive manufacturing technology. Tensile tests are conducted on the LPBF-processed FeMEA at room temperature and cryogenic temperatures (77 K). At 77 K, the LPBF-processed FeMEA exhibits high yield strength and excellent ultimate tensile strength through active deformation-induced martensitic transformation. Furthermore, due to the low stability of the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of the LPBF-processed FeMEA based on nano-scale solute heterogeneity, stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs, accompanied by the appearance of a yield point phenomenon during cryogenic tensile deformation. This study elucidates the origin of the yield point phenomenon and deformation behavior of the FeMEA at 77 K. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
Yoona Lee, Sangwon Park, Dongwon Shin, Marcia Myung Hye Ahn, Wei Xiong, Nokeun Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Je In Lee, Wookjin Lee, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park, Namhyun Kang
Materials Research Letters.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for laser powder bed fusion: Design, processing, microstructure, and performance
Asker Jarlöv, Zhiguang Zhu, Weiming Ji, Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Priyanka Vivegananthan, Yujia Tian, Devesh Raju Kripalani, Haiyang Fan, Hang Li Seet, Changjun Han, Liming Tan, Feng Liu, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, Kun Zhou
Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports.2024; 161: 100834. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Substrate Pre-heating on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnet Manufactured by L-PBF
-
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):116-122. Published online April 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.116
-
-
1,159
View
-
17
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Because magnets fabricated using Nd-Fe-B exhibit excellent magnetic properties, this novel material is used in various high-tech industries. However, because of the brittleness and low formability of Nd-Fe-B magnets, the design freedom of shapes for improving the performance is limited based on conventional tooling and postprocessing. Laserpowder bed fusion (L-PBF), the most famous additive manufacturing (AM) technique, has recently emerged as a novel process for producing geometrically complex shapes of Nd-Fe-B parts owing to its high precision and good spatial resolution. However, because of the repeated thermal shock applied to the materials during L-PBF, it is difficult to fabricate a dense Nd-Fe-B magnet. In this study, a high-density (>96%) Nd-Fe-B magnet is successfully fabricated by minimizing the thermal residual stress caused by substrate heating during L-PBF. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Linkage between process-induced microstructure and magnetic property of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Yeon Woo Kim, Sujin Lee, Yoona Lee, Jae Bok Seol, Namhyun Kang, Yoon Suk Choi, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung-Goo Lee, Tae-Hoon Kim, Jeong Min Park
Materials & Design.2025; 259: 114929. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Bulk Shape on Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
-
Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):140-145. Published online April 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.140
-
-
2,492
View
-
33
Download
-
6
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
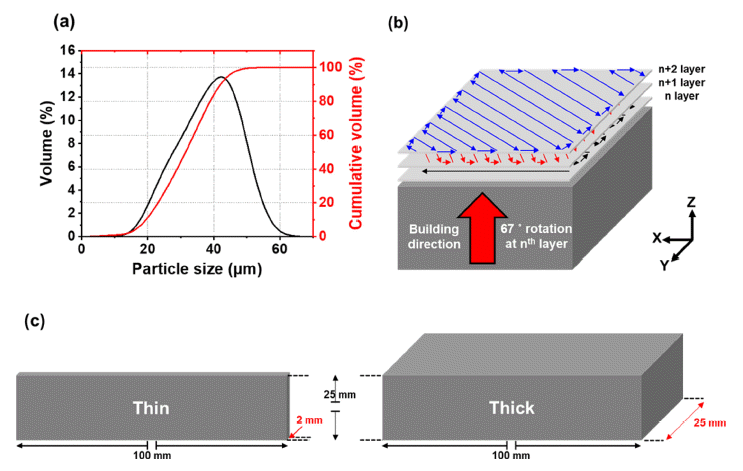
Although the Ti–6Al–4V alloy has been used in the aircraft industry owing to its excellent mechanical properties and low density, the low formability of the alloy hinders broadening its applications. Recently, laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF) has become a novel process for overcoming the limitations of the alloy (i.e., low formability), owing to the high degree of design freedom for the geometry of products having outstanding performance used in hightech applications. In this study, to investigate the effect of bulk shape on the microstructure and mechanical properties of L-PBFed Ti-6Al-4V alloys, two types of samples are fabricated using L-PBF: thick and thin samples. The thick sample exhibits lower strength and higher ductility than the thin sample owing to the larger grain size and lower residual dislocation density of the thick sample because of the heat input during the L-PBF process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 137. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef - High-speed manufacturing-driven strength-ductility improvement of H13 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Young Seong Eom, Dong Gill Ahn, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 582. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi-type High-entropy Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: A Review
-
Jeong Min Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):132-151. Published online April 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.132
-
-
2,617
View
-
37
Download
-
7
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy (HEA), which is the most widely known HEA with a single facecentered cubic structure, has attracted significant academic attention over the past decade owing to its outstanding multifunctional performance. Recent studies have suggested that CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs exhibit excellent printability for selective laser melting (SLM) under a wide range of process conditions. Moreover, it has been suggested that SLM can not only provide great topological freedom of design but also exhibit excellent mechanical properties by overcoming the strength–ductility trade-off via producing a hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure. In this regard, the SLM-processed CoCrFeMnNi HEA has been extensively studied to comprehensively understand the mechanisms of microstructural evolution and resulting changes in mechanical properties. In this review, recent studies on CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs produced using SLM are discussed with respect to process-induced microstructural evolution and the relationship between hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure and mechanical properties. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Investigation of effects of process parameters on microstructure and fracture toughness of SLM CoCrFeMnNi
Joseph Agyapong, Diego Mateos, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye-Yiadom
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 987: 173998. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef - Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 137. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Microstructural evolution and high strain rate deformation response of SLM-printed CoCrFeMnNi after annealing and deep-cryogenic treatment
Joseph Agyapong, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye Yiadom
Materials Characterization.2024; 218: 114506. CrossRef - High-speed manufacturing-driven strength-ductility improvement of H13 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Young Seong Eom, Dong Gill Ahn, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 582. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
-
Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):475-481. Published online December 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.475
-
-
1,342
View
-
12
Download
-
12
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
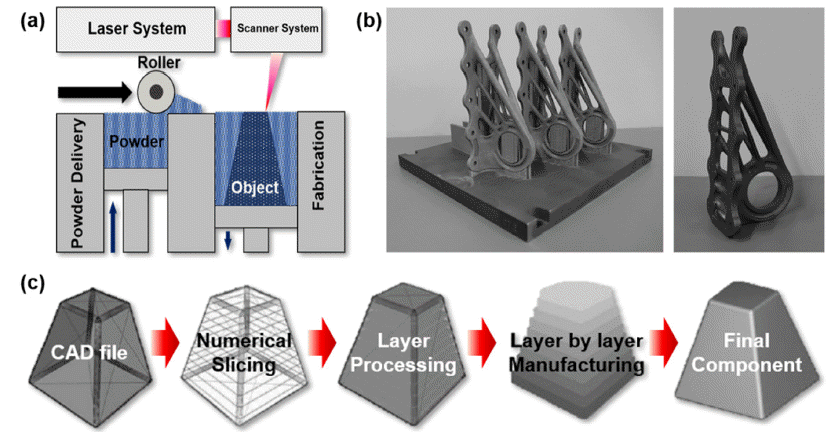
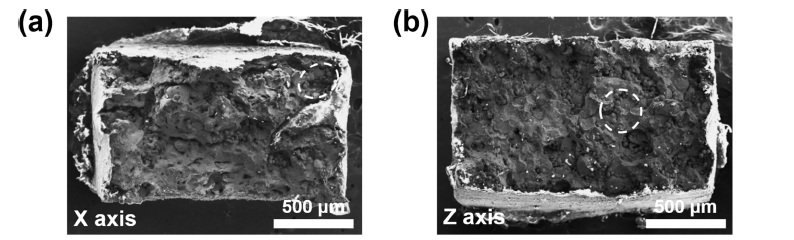
Selective laser melting (SLM), a type of additive manufacturing (AM) technology, leads a global manufacturing trend by enabling the design of geometrically complex products with topology optimization for optimized performance. Using this method, three-dimensional (3D) computer-aided design (CAD) data components can be built up directly in a layer-by-layer fashion using a high-energy laser beam for the selective melting and rapid solidification of thin layers of metallic powders. Although there are considerable expectations that this novel process will overcome many traditional manufacturing process limits, some issues still exist in applying the SLM process to diverse metallic materials, particularly regarding the formation of porosity. This is a major processing-induced phenomenon, and frequently observed in almost all SLM-processed metallic components. In this study, we investigate the mechanical anisotropy of SLM-produced 316L stainless steel based on microstructural factors and highly-oriented porosity. Tensile tests are performed to investigate the microstructure and porosity effects on mechanical anisotropy in terms of both strength and ductility. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of temperature and impact loading condition on deformation behavior in 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Tae Hyeong Kim, Haeum Park, Jun Seok Lee, Jeong Min Park, Jae Wung Bae
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 933: 148286. CrossRef - Selective laser melting additive manufactured H13 tool steel for aluminum extrusion die component construction
Evangelos Giarmas, Vasileios Tsakalos, Emmanuel Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 133(9-10): 4385. CrossRef - Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of Additively Manufactured H13 Steel by Utilizing Selective Laser Melting Technology
Evangelos Giarmas, Emmanouil K. Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
Materials.2024; 17(15): 3756. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef - Development of multi-defect diagnosis algorithm for the directed energy deposition (DED) process with in situ melt-pool monitoring
Hyewon Shin, Jimin Lee, Seung-Kyum Choi, Sang Won Lee
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2023; 125(1-2): 357. CrossRef - Corrosion Resistance of Laser Powder Bed Fused AISI 316L Stainless Steel and Effect of Direct Annealing
Kichang Bae, Dongmin Shin, Jonghun Lee, Seohan Kim, Wookjin Lee, Ilguk Jo, Junghoon Lee
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6336. CrossRef - Experimental investigation on the effect of process parameters in additive/subtractive hybrid manufacturing 316L stainless steel
Chengming Tang, Jibin Zhao, Zhiguo Wang, Yuhui Zhao, Tianran Wang
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2022; 121(3-4): 2461. CrossRef - Interface characteristics and mechanical behavior of additively manufactured multi-material of stainless steel and Inconel
Man Jae Sagong, Eun Seong Kim, Jeong Min Park, Gangaraju Manogna Karthik, Byeong-Joo Lee, Jung-Wook Cho, Chong Soo Lee, Takayoshi Nakano, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2022; 847: 143318. CrossRef - Effect of heat treatment on microstructural heterogeneity and mechanical properties of 1%C-CoCrFeMnNi alloy fabricated by selective laser melting
Jeong Min Park, Eun Seong Kim, Hyeonseok Kwon, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim
Additive Manufacturing.2021; 47: 102283. CrossRef - Manufacturing Aluminum/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Eo Ryeong Lee, Se Eun Shin, Naoki Takata, Makoto Kobashi, Masaki Kato
Materials.2020; 13(18): 3927. CrossRef - Effects of microstructure and internal defects on mechanical anisotropy and asymmetry of selective laser-melted 316L austenitic stainless steel
Jin Myoung Jeon, Jeong Min Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2019; 763: 138152. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Nanosized Gd2O3:Eu3+ Red Phosphor Coated on Mica Flake and Its Luminescent Property
-
Se-Min Ban, Jeong Min Park, Kyeong Youl Jung, Byung-Ki Choi, Kwang-Jung Kang, Myung Chang Kang, Dae-Sung Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):457-463. Published online December 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.457
-
-
985
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Nanosized Gd2O3:Eu3+ red phosphor is prepared using a template method from metal salt impregnated into a crystalline cellulose and is dispersed using a bead mill wet process. The driving force of the surface coating between Gd2O3:Eu3+ and mica is induced by the Coulomb force. The red phosphor nanosol is effectively coated on mica flakes by the electrostatic interaction between positively charged Gd2O3:Eu3+ and negatively charged mica above pH 6. To prepare Gd2O3:Eu3+-coated mica (Gd2O3:Eu/mica), the coating conditions are optimized, including the stirring temperature, pH, calcination temperature, and coating amount (wt%) of Gd2O3:Eu3+. In spite of the low luminescence of the Gd2O3:Eu/mica, the luminescent property is recovered after calcination above 600°C and is enhanced by increasing the Gd2O3:Eu3+ coating amount. The Gd2O3:Eu/mica is characterized using X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, zeta potential measurements, and fluorescence spectrometer analysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Optimization of dispersed LaPO4:Tb nanosol and their photoluminescence properties
Mahboob Ullah, Se-Min Ban, Dae-Sung Kim
Optical Materials.2019; 97: 109366. CrossRef
|