- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nanopowders by Hydrothermal Method and their Application to Dye-sentisized Solar Cell Materials
-
JinYoung Lim, Jeongseok Ahn, Jung-Ho Ahn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):309-315. Published online August 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.309
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
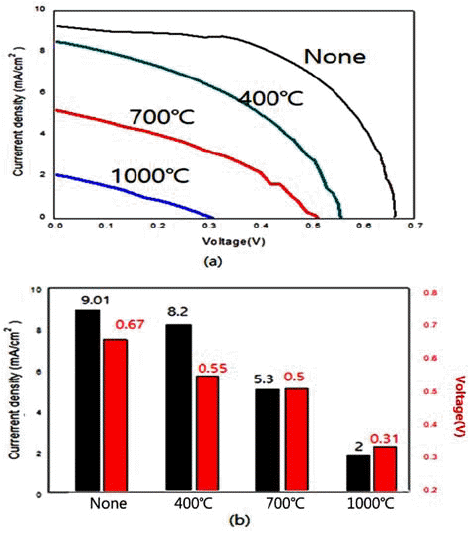
In the present work, we synthesize nano-sized ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 powders by hydrothermal reaction using metal chlorides. We also examine the energy-storage characteristics of the resulting materials to evaluate the potential application of these powders to dye-sensitized solar cells. The control of processing parameters such as pressure, temperature, and the concentration of aqueous solution results in the formation of a variety of powder morphologies with different sizes. Nano-rod, nano-flower, and spherical powders are easily formed with the present method. Heat treatment after the hydrothermal reaction usually increases the size of the powder. At temperatures above 1000°C, a complete collapse of the shape occurs. With regard to the capacity of DSSC materials, the hydrothermally synthesized TiO2 results in the highest current density of 9.1 mA/cm2 among the examined oxides. This is attributed to the fine particle size and morphology with large specific surface area.
- [Korean]
- The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Y2O3-Dispersed Fe-C and Fe-CNT Sintered Steels
-
Jin Young Lim, Jung-Ho Ahn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):298-301. Published online August 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.298
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
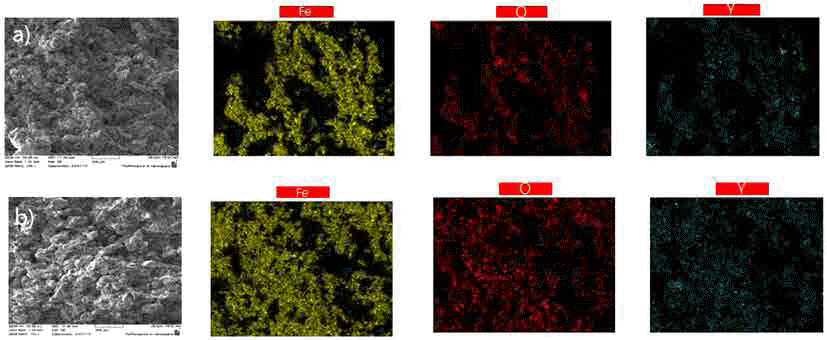
In the present work, we use multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) as the starting material for the fabrication of sintered carbon steel. A comparison is made with conventionally sintered carbon steel, where graphite is used as the starting material. Milling is performed using a horizontal mill sintered in a vacuum furnace. We analyze the grain size, number of pores, X-ray diffraction patterns, and microstructure. Changes in the physical properties are determined by using the Archimedes method and Vickers hardness measurements. The result shows that the use of MWCNTs instead of graphite significantly reduces the size and volume of the pores as well as the grain size after sintering. The addition of Y2O3.to the Fe-MWCNT samples further inhibits the growth of grains.
- [English]
- Expansion of Multi-wall Carbon Nanotubes and its Lithium Storage Property
-
Jung-Ho Ahn, Jeong-Seok Ahn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):275-278. Published online August 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.275
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
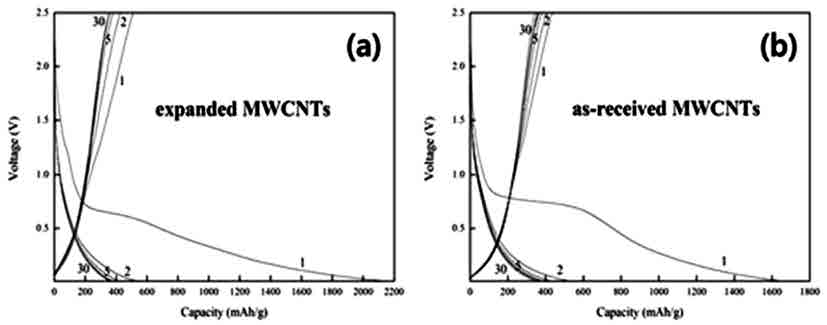
In the present work, we apply a technique that has been used for the expansion of graphite to multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT). The nanotubes are rapidly heated for a short duration, followed by immersion in acid solution, so that they undergo expansion. The diameter of the expanded CNTs is 5-10 times larger than that of the asreceived nanotubes. This results in considerable swelling of the CNTs and opening of the tube tips, which may facilitate the accessibility of lithium ions into the inner holes and the interstices between the nanotube walls. The Li-ion storage capacity of the expanded nanotubes is measured by using the material as an anode in Li-ion cells. The result show that the discharge capacity of the expanded nanotubes in the first cycle is as high as 2,160 mAh/g, which is about 28% higher than that of the un-treated MWCNT anode. However, the charge/discharge capacity quickly drops in subsequent cycles and finally reaches equilibrium values of ~370 mAh/g. This is possibly due to the destruction of the lattice structures by repeated intercalation of Li ions.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles by a Chemical Reduction Method
-
Min Woo Choi, Min Hwan Bae, Jung-Ho Ahn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):228-234. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.228
-
-
1,887
View
-
40
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
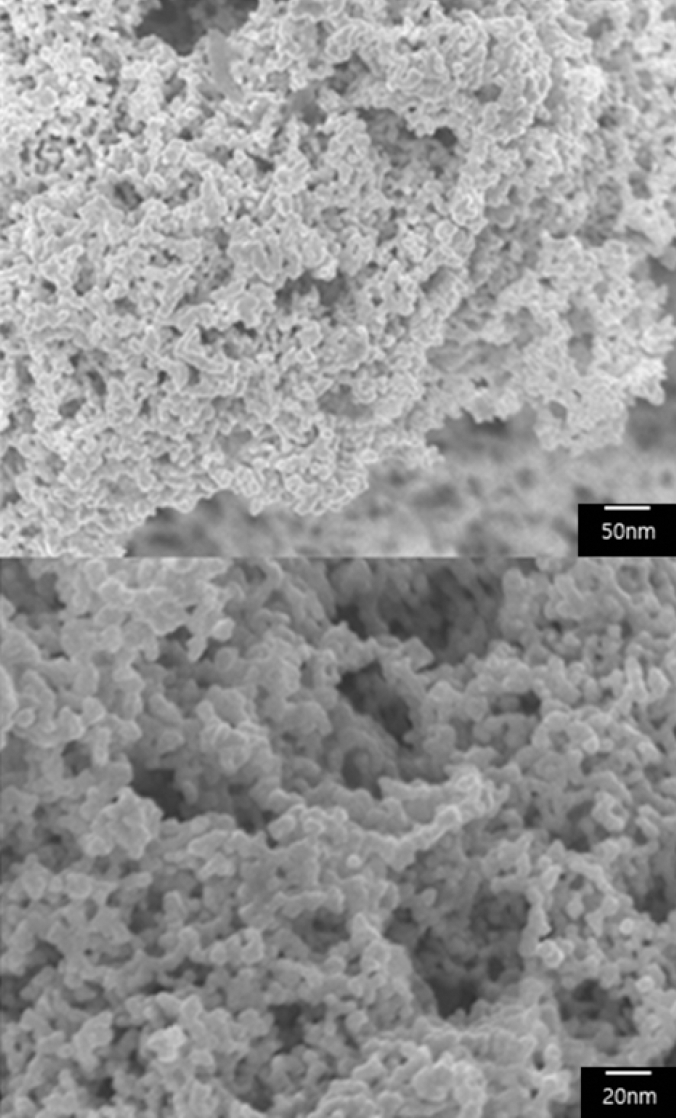
Copper nanoparticles attract much attention as substitutes of noble metals such as silver and can help reduce the manufacturing cost of electronic products due to their lower cost and good conductivity. In the present work, the chemical reduction is examined to optimize the synthesis of nano-sized copper particles from copper sulfate. Sodium borohydride and ascorbic acid are used as reducing and antioxidant agents, respectively. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is used as a size-control and capping agent. An appropriate dose of PEG inhibits the abnormal growth of copper nanoparticles, maintaining chemical stability. The addition of ascorbic acid prevents the oxidation of nanoparticles during synthesis and storage. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) are used to investigate the size of the synthesized nanoparticles and the coordination between copper nanoparticles and PEG. For chemical reduction, copper nanoparticles less than 100 nm in size without oxidized layers are successfully obtained by the present method. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Correlation between electrical conductivity and antibacterial activity of chitosan-stabilized copper and silver nanoparticles
C.Raja Mohan, Ruckmani Kandasamy, J. Kabiriyel
Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications.2024; 7: 100503. CrossRef - Green Synthesis and Characterization of Natural Magnetic Particles/Chitosan Composite Material Impregnated with Copper Nanoparticles
Defia Indah Permatasari, Bambang Rusdiarso, Nuryono Nuryono
Solid State Phenomena.2022; 339: 19. CrossRef - Copper Nanoparticle(CuNP’s)Synthesis: A review of the various ways with Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activity
Israfil Alam Tito, Sahab Uddin, Shafiul Islam, Snahasish Bhowmik
Oriental Journal Of Chemistry.2021; 37(5): 1030. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Alloying of GaSe and GaTe Systems
-
Jung Bo Choi, Jung-Ho Ahn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):338-342. Published online October 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.338
-
-
640
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
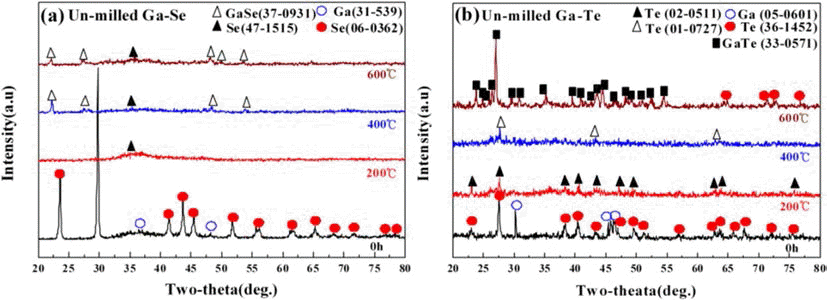
In the present work, we investigated the mechanical alloying of binary Ga-Se(1:1) and Ga-Te(1;1) sysyems. The high-energy ball-milling was performed at 40°C where one of constituents (Ga) is molten state. The purpose of the work was to see whether reactions between constituent elements are accelerated by the presence of a liquid phase. During the ball-milling, the liquid Ga phase completely disappeared and the resulting powders consist of nanocrystalline grain of ~20 nm with partly amorphized phases. However, no intermetallic compounds formed in spite of the presence of the liquid phases which has much higher diffusivity than solid constituents. By subsequent heat-treatments, the inter-metallic compounds such as GaSe and GaTe formed at relatively low temperatures. The formation temperature of theses compound was much lower than those predicted by equilibrium phase diagram. The comparison of the ball-milled powders with un-milled ones indicated that the easy formation of intermetallic compound or allying occurs at low temperatures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
Jung Geun Kim, Yong Ho Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 202. CrossRef
|