Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Features of Nickel Nanoparticles Structure Synthesized by the Spark Discharge Method
- C. K. Rhee, A. D. Maksimov, I. V. Beketov, A. I. Medvedev, A. M. Murzakaev
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):464-467. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.464
- 1,337 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
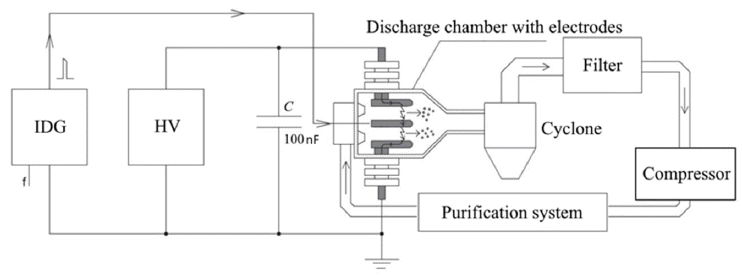
PDF Nickel nanopowders are obtained by the spark discharge method, which is based on the evaporation of the electrode surface under the action of the discharge current, followed by vapor condensation and the formation of nanoparticles. Nickel electrodes with a purity of 99.99% are used to synthesize the nickel nanoparticles in the setup. Nitrogen is used as the carrier gas with a purity of 99.998%. XRD, TEM, and EDX analyses of the nanopowders are performed. Moreover, HRTEM images with measured interplanar spacings are obtained. In the nickel nanopowder samples, a phase of approximately 90 wt% with an expanded crystal lattice of 6.5% on average is found. The results indicate an unusual process of nickel nanoparticle formation when the spark discharge method is employed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2025; 89(10): 1941. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Craters Formed on Cathode and Anode Spots of a Spark Discharge in Air on Iron Electrodes
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2023; 87(S2): S274. CrossRef
- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterisitics of Al2O3-SiC Ceramic Composites for Electrostatic Discharge Safe Components
- Ha-Neul Kim, Hyun-Myung Oh, Young-Jo Park, Jae-Woong Ko, Hyun-Kwuon Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):144-150. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.144
- 543 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Al2O3-SiC ceramic composites are produced using pressureless sintering, and their plasma resistance, electrical resistance, and mechanical properties are evaluated to confirm their applicability as electrostatic-discharge-safe components for semiconductor devices. Through the addition of Mg and Y nitrate sintering aids, it is confirmed that even if SiC content exceeded 10%, complete densification is possible by pressureless sintering. By the uniform distribution of SiC, the total grain growth is suppressed to about 1 μm; thus an Al2O3-SiC sintered body with a high strength over 600 MPa is obtained. The optimum amount of SiC to satisfy all the desired properties of electrostaticdischarge-safe ceramic components is obtained by finding the correlation between the plasma resistance and the electrical resistivity as a function of SiC amount.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Precursor Co-Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Powders
- Woonghee Choi, Chan Hyoung Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):287-296. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.287
- 1,906 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 powders have been synthesized in a continuously stirred tank reactor via a co-precipitation reaction between aqueous metal sulfates and NaOH using NH4OH as a chelating agent. The co-precipitation temperature is varied in the range of 30-80°C. Calcination of the prepared precursors with Li2CO3 for 8 h at 1000°C in air results in Li Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 powders. Two kinds of obtained powders have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, particle size analyzer, and tap density measurements. The co-precipitation temperature does not differentiate the XRD patterns of precursors as well as their final powders. Precursor powders are spherical and dense, consisting of numerous acicular or flaky primary particles. The precursors obtained at 70 and 80°C possess bigger primary particles having more irregular shapes than those at lower temperatures. This is related to the lower tap density measured for the former. The final powders show a similar tendency in terms of primary particle shape and tap density. Electrochemical characterization shows that the initial charge/discharge capacities and cycle life of final powders from the precursors obtained at 70 and 80°C are inferior to those at 50°C. It is concluded that the optimum co-precipitation temperature is around 50°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A kinetic descriptor to optimize Co-precipitation of Nickel-rich cathode precursors for Lithium-ion batteries
Seon Hwa Lee, Ki Young Kwon, Byeong Kil Choi, Hyun Deog Yoo
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.2022; 924: 116828. CrossRef
- A kinetic descriptor to optimize Co-precipitation of Nickel-rich cathode precursors for Lithium-ion batteries
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 Powders Prepared by Co-Precipitation in Air and Nitrogen Atmospheres
- Woonghee Choi, Se-Ryen Park, Chan Hyoung Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):136-142. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.136
- 2,773 View
- 58 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
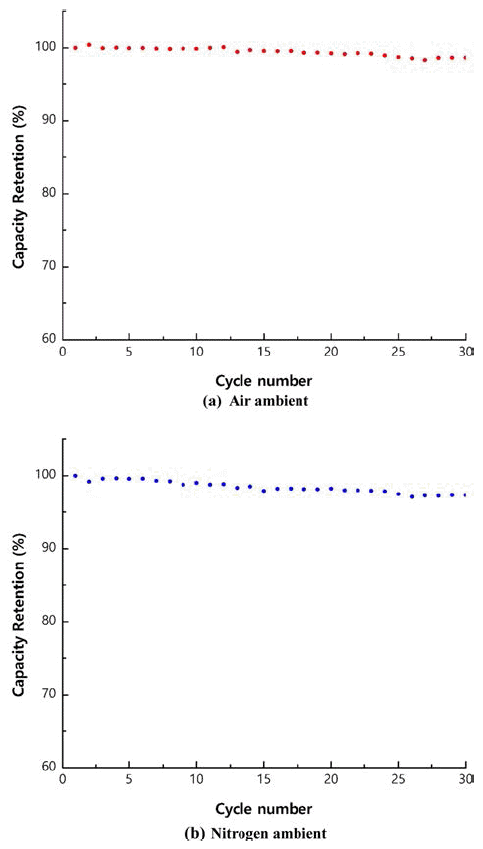
PDF As precursors of cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 powders are prepared in a continuously stirred tank reactor via a co-precipitation reaction between aqueous metal sulfates and NaOH in the presence of NH4OH in air or nitrogen ambient. Calcination of the precursors with Li2CO3 for 8 h at 1,000°C in air produces dense spherical cathode materials. The precursors and final powders are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, particle size analysis, tap density measurement, and thermal gravimetric analysis. The precursor powders obtained in air or nitrogen ambient show XRD patterns identified as Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2. Regardless of the atmosphere, the final powders exhibit the XRD patterns of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM). The precursor powders obtained in air have larger particle size and lower tap density than those obtained in nitrogen ambient. NCM powders show similar tendencies in terms of particle size and tap density. Electrochemical characterization is performed after fabricating a coin cell using NCM as the cathode and Li metal as the anode. The NCM powders from the precursors obtained in air and those from the precursors obtained in nitrogen have similar initial charge/discharge capacities and cycle life. In conclusion, the powders co-precipitated in air can be utilized as precursor materials, replacing those synthesized in the presence of nitrogen injection, which is the usual industrial practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermodynamic modeling and parameters optimization for Ni0.8Co0.1Mn 0.1(OH)2 synthesis via transitional metal coprecipitation
Zanlang Tang, Chen Liu, Xincun Tang, Haonan Liu, Biao Qin
Materials Science and Engineering: B.2026; 326: 119205. CrossRef - Stabilization of High Nickel Cathode Materials with Core-Shell Structure via Co-precipitation Method
Minjeong Kim, Soonhyun Hong, Heongkwon Jeon, Jahun Koo, Heesang Lee, Gyuseok Choi, Chunjoong Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(4): 216. CrossRef - Spherical agglomeration of nickel-manganese-cobalt hydroxide in turbulent Batchelor vortex flow
Xiaotong Sun, Jinsoo Kim, Woo-Sik Kim
Chemical Engineering Journal.2021; 421: 129924. CrossRef - Design strategies for development of nickel-rich ternary lithium-ion battery
Kyu Hwan Choi, Xuyan Liu, Xiaohong Ding, Qiang Li
Ionics.2020; 26(3): 1063. CrossRef - Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 49. CrossRef - Effects of Precursor Co-Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Powders
Woonghee Choi, Chan Hyoung Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(4): 287. CrossRef
- Thermodynamic modeling and parameters optimization for Ni0.8Co0.1Mn 0.1(OH)2 synthesis via transitional metal coprecipitation
- [Korean]
- Dispersion Control and Characterization of the SiO2/PMMA Particles Using Surface Charge
- Yubin Kang, Soojung Son, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):403-407. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.403

- 995 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Poly-methylmetacrylate (PMMA) is mainly applied in the plastic manufacturing industry, but PMMA is weak and gradually got discolor. The strength of PMMA can be improved through organic-inorganic hybrid nano composites with inorganic nano particles such as, SiO2 or ZrO. However, inorganic nano particles are mostly agglomerated spontaneously. In this study, the zeta potential is controlled using different types of organic solvent with different concentrations, dispersibillity of SiO2 nano particles on the PMMA particle are analyzed. When 3 M acetic acid is used, absolute value of the zeta potential is higher, SiO2 nano particle is well attached, and dispersed on the PMMA particle surface. Results indicate that the absolute value of the zeta potential affects the stability of SiO2 dispersion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study of Organic Impurity Removal Efficiency for Waste LCD Touch Panel Glass by Solvents Types
Yubin Kang, Jin-Ju Choi, Jae Layng Park, Chan Gi Lee
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2020; 29(6): 57. CrossRef - Hard Surface-adhesive Properties of TiO2 Nanoparticles-encapsulated Microparticles Prepared by Spray Drying and Surface Coating Method
Su-Kyung Kim, Jong-Duk Kim, Seung-Jun Lee
Fibers and Polymers.2018; 19(6): 1303. CrossRef
- A Study of Organic Impurity Removal Efficiency for Waste LCD Touch Panel Glass by Solvents Types
- [Korean]
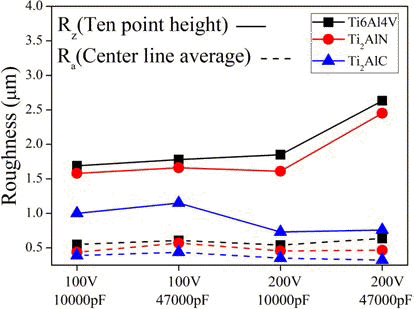
- Characteristics of Material Properties and Machining Surface in Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC Materials
- Eui-Song Choi, Chang-Hoon Lee, Gyung-Rae Baek, KwangHo Kim, Myung Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):163-168. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.163
- 1,012 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ti alloys are extensively used in high-technology application because of their strength, oxidation resistance at high temperature. However, Ti alloys tend to be classified very difficult to cut material. In this paper, The powder synthesis, spark plasma sintering (SPS), bulk material properties such as electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are systematically examined on Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC materials having most light-weight and oxidation resistance among the MAX phases. The bulk samples mainly consisted of Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC materials with density close to theoretical value were synthesized by a SPS method. Machining characteristics such as machining time, surface quality are analyzed with measurement of voltage and current waveform according to machining condition of micro-electrical discharge machining with micro-channel shape.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study on Ablation Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Ti2AlN Bulks Irradiated by Femto-second Laser
Ki Ha Hwang, Hua Feng Wu, Won Suk Choi, Sung Hak Cho, Myungchang Kang
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2019; 18(7): 90. CrossRef
- Comparative Study on Ablation Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Ti2AlN Bulks Irradiated by Femto-second Laser
- [Korean]
- Micro-EDM Feasibility and Material Properties of Hybrid Ti2AlC Ceramic Bulk Materials
- Guk-Hyun Jeong, Kwang-Ho Kim, Myung-Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):301-306. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.301
- 647 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Titanium alloys are extensively used in high-temperature applications due to their excellent high strength and corrosion resistance properties. However, titanium alloys are problematic because they tend to be extremely difficult-tocut material. In this paper, the powder synthesis, spark plasma sintering (SPS), bulk material characteristics and machinability test of hybrid Ti2AlC ceramic bulk materials were systematically examined. The bulk samples mainly consisted of Ti2AlC materials with density close to theoretical value were synthesized by a SPS method. Random orientation and good crystallization of the Ti2AlC was observed at 1100°C for 10 min under SPS sintering conditions. Scanning electron microscopy results indicated a homogeneous distribution and nano-laminated structure of Ti2AlC MAX phase. The hardness and electrical conductivity of Ti2AlC were higher than that of Ti 6242 alloy at sintering temperature of 1000°C~1100°C. Consequently, the machinability of the hybrid Ti2AlC bulk materials is better than that of the Ti 6242 alloy for micro-EDM process of micro-hole shape workpiece.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
Chang-Hun Lee, Gyung Rae Baek, Hee Sang Jung, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 175. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


