Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Study on the Recovery Silver and Nanoparticles Synthesis from LTCC By-products of Lowly Concentrated Silver
- Soyeong Joo, Nak-Kyoon Ahn, Chan Gi Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):232-239. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.232
- 875 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
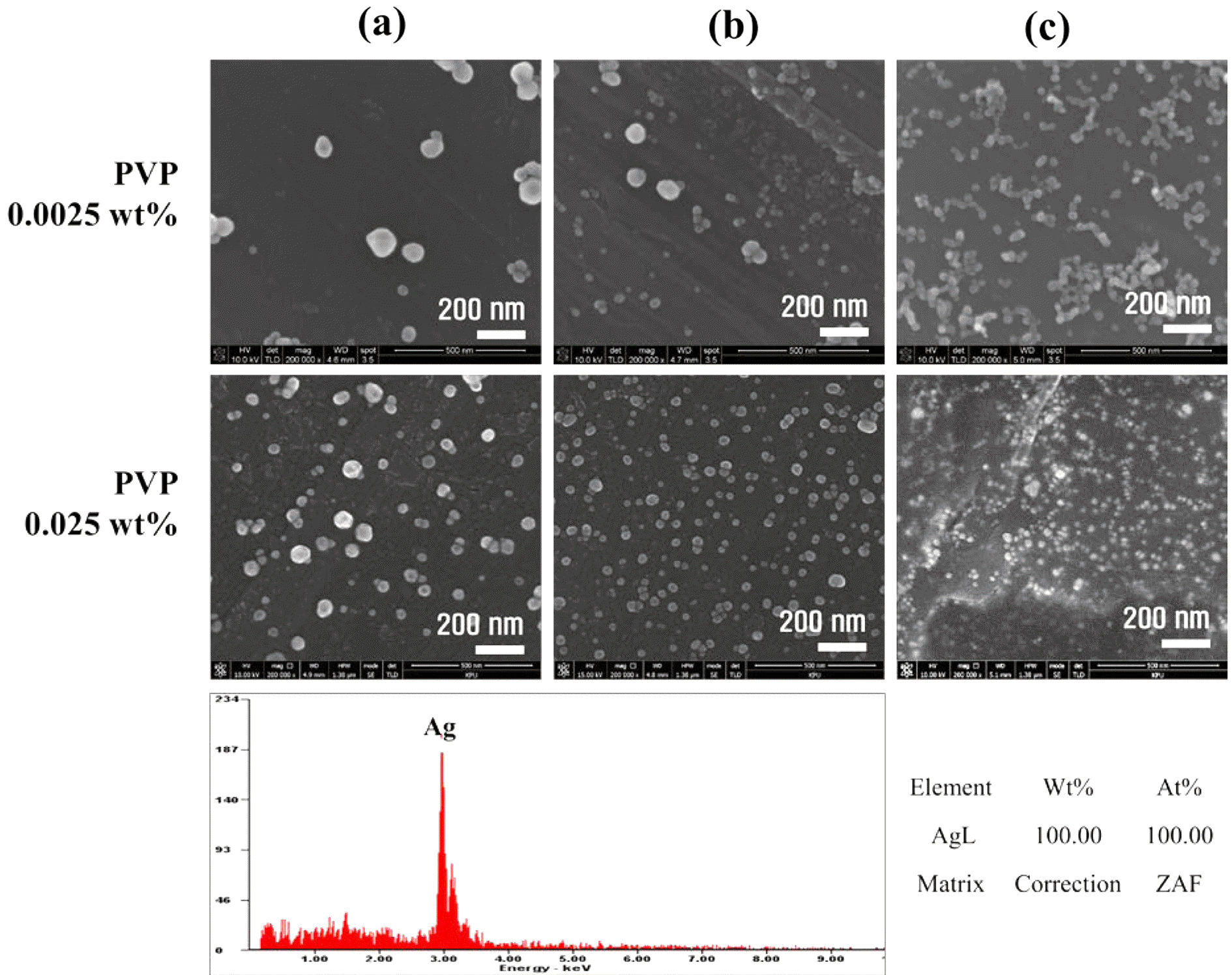
PDF In this paper, the recovery and nanoparticle synthesis of Ag from low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) by-products are studied. The effect of reaction behavior on Ag leaching conditions from the LTCC by-products is confirmed. The optimum leaching conditions are determined to be: 5 M HNO3, a reaction temperature of 75°C, and a pulp density of 50 g/L at 60 min. For the selective recovery of Ag, the [Cl]/[Ag] equivalence ratio experiment is performed using added HCl; most of the Ag (more than 99%) is recovered. The XRD and MP-AES results confirm that the powder is AgCl and that impurities are at less than 1%. Ag nanoparticles are synthesized using a chemical reduction process for recycling, NaBH4 and PVP are used as reducing agents and dispersion stabilizers. UV-vis and FE-SEM results show that AgCl powder is precipitated and that Ag nanoparticles are synthesized. Ag nanoparticles of 100% Ag are obtained under the chemical reaction conditions.
- [Korean]
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):315-320. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.315

- 502 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There has been much interest in recycling electronic wastes in order to mitigate environmental problems and to recover the large amount of constituent metals. Silver recovery from electronic waste is extensively studied because of environmental and economic benefits and the use of silver in fabricating nanodevices. Hydrometallurgical processing is often used for silver recovery because it has the advantages of low cost and ease of control. Research on synthesis recovered silver into nanoparticles is needed for application to transistors and solar cells. In this study, silver is selectively recovered from the by-product of electrodes. Silver precursors are prepared using the dissolution characteristics of the leaching solution. In the liquid reduction process, silver nanoparticles are synthesized under various surfactant conditions and then analyzed. The purity of the recovered silver is 99.24%, and the average particle size of the silver nanoparticles is 68 nm.
- [Korean]
- The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
- Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):141-146. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.141

- 1,186 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Bi2Te3 powders are recovered by wet chemical reduction for waste n-type thermoelectric chips, and the recovered particles with different morphologies are prepared using various surfactants such as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). When citric acid is added as the surfactant, the shape of the aggregated particles shows no distinctive features. On the other hand, rod-shaped particles are formed in the sample with CTAB, and sheet-like particles are synthesized with the addition of SDBS. Further, particles with a tripod shape are observed when EDTA is added as the surfactant. The growth mechanism of the particle shapes depending on the surfactant is investigated, with a focus on the nucleation and growth phenomena. These results help to elucidate the intrinsic formation mechanism of the rod, plate, and tripod structures of the Bi2Te3 recovered by the wet reduction process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
Haein Shin, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 374. CrossRef
- Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Ag Particles by Polyol Process and Wet Chemical Process
- Juyeon Yoo, Hyosung Jang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.297
- 804 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
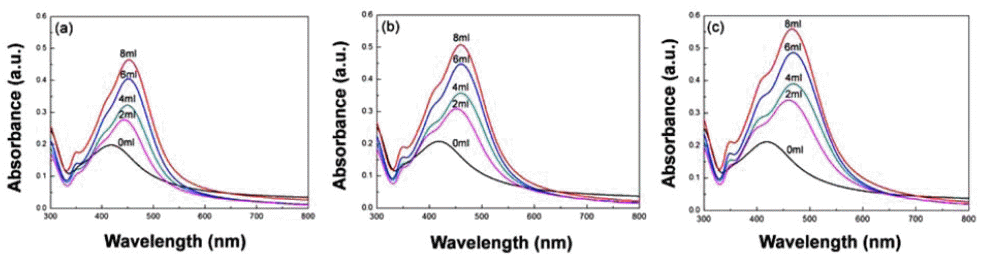
PDF Ag nanoparticles are extensively studied and utilized due to their excellent catalysis, antibiosis and optical properties. They can be easily synthesized by chemical reduction methods and it is possible to prepare particles of uniform size and high purity. These methods are divided into vapor methods and liquid phase reduction methods. In the present study, Ag particles are prepared and analyzed through two chemical reduction methods using solvents containing a silver nitrate precursor. When Ag ions are reduced using a reductant in the aqueous solution, it is possible to control the Ag particle size by controlling the formic acid ratio. In addition, in the Polyol process, Ag nanoparticles prepared at various temperatures and reaction time conditions have multiple twinned and anisotropic structures, and the particle size variation can be confirmed using field emissions scanning electron microscopy and by analyzing the UV-vis spectrum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 315. CrossRef
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- [English]
- Coating of Cobalt Over Tungsten Carbide Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):93-96. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.93
- 1,645 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
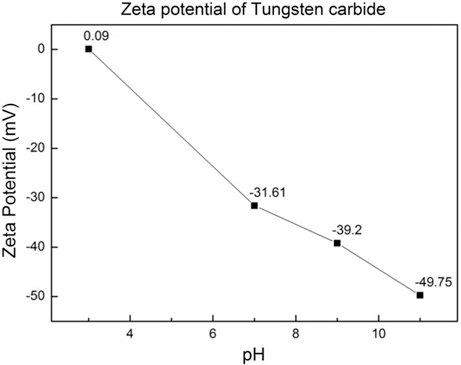
PDF Cobalt coated tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder has been prepared through wet chemical reduction method. The cobalt sulfate solution was converted to the cobalt chloride then the cobalt hydroxide. The tungsten carbide powders were added in to the cobalt hydroxide, the cobalt hydroxide was reduced and coated over tungsten carbide powder using hypo-phosphorous acid. Both the cobalt and the tungsten carbide phase peaks were evident in the tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder by X-ray diffraction. The average particle size measured via scanning electron microscope, particle size analysis was around 380 nm and the thickness of coated cobalt was determined to be 30~40 nm by transmission electron microscopy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
Peng Tang, Shuwen Jiang, Jiawei Yan, Xianquan Li
Next Materials.2025; 6: 100496. CrossRef - Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef - Spark plasma sintering of WC–Co tool materials prepared with emphasis on WC core–Co shell structure development
Sungkyu Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 41. CrossRef
- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


