Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
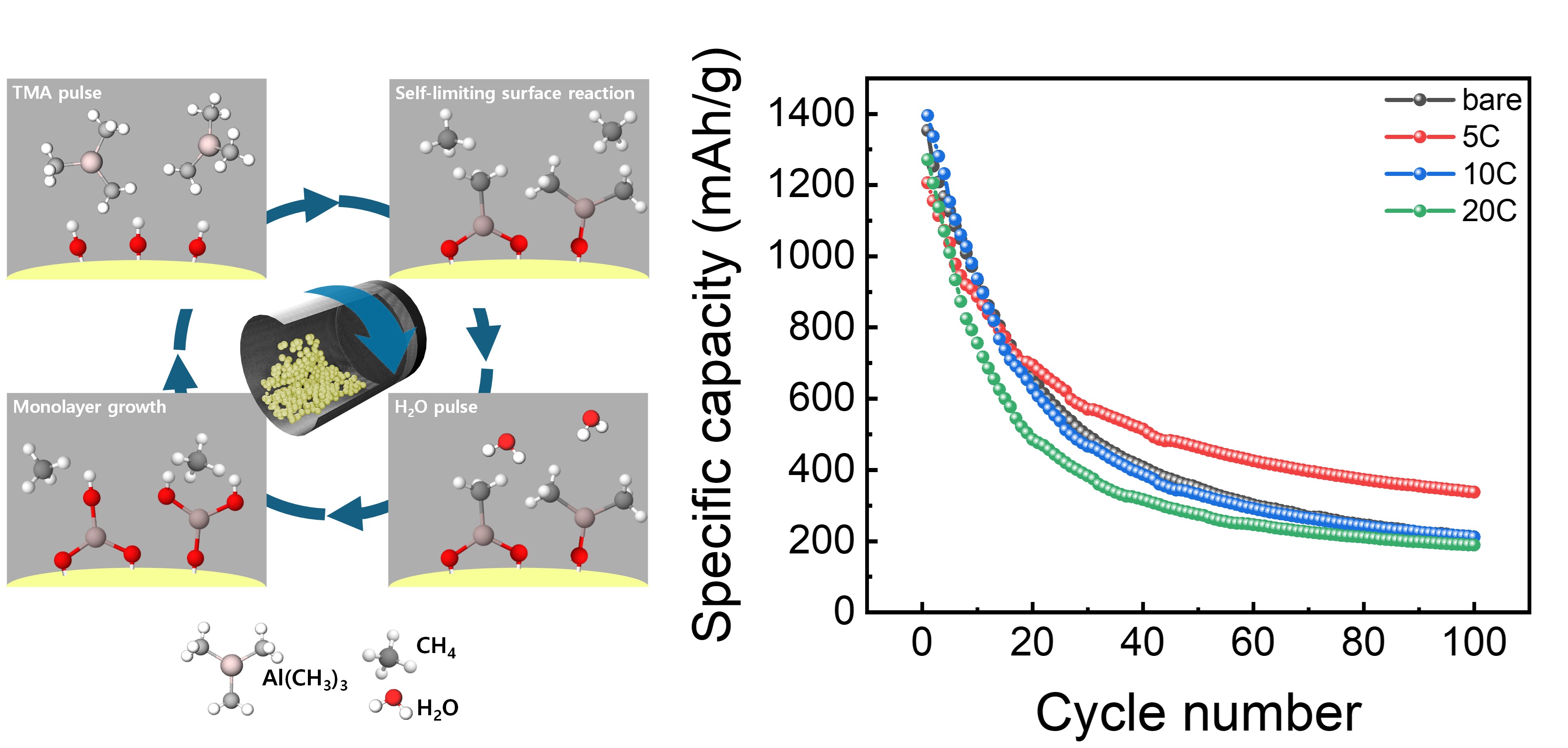
- Enhancement of the Electrochemical Performance of SiOx Anodes by Al2O3 Coating via Powder Atomic Layer Deposition
- Donggeon Shin, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):501-508. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00416
- 693 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Silicon based anode materials offer high theoretical capacity but suffer from severe volume expansion and unstable interfacial properties during repeated lithiation and delithiation, resulting in rapid performance degradation. In this study, a thin aluminum oxide coating layer was deposited on Si/SiOx Carbon anode materials using a powder atomic layer deposition (PALD) process to address these limitations. EDS mapping and XRD analyses confirmed the uniform formation of an amorphous aluminum oxide coating with increasing thickness as the deposition cycles increased. Electrochemical evaluation showed that the electrode coated with 5 PALD cycles exhibited approximately 78% higher capacity retention after 100 cycles at 1 A g-1 and a higher initial Coulombic efficiency compared to the bare electrode. The coated electrode also delivered approximately 22% higher capacity at a high current density of 5 A g-1, indicating enhanced rate capability. Cyclic voltammetry analysis revealed increased surface controlled reaction contributions and improved reaction kinetics. These results demonstrate that PALD derived aluminum oxide coatings effectively stabilize the electrode electrolyte interface and enhance the electrochemical performance of silicon based anodes, highlighting their potential for next generation high capacity lithium ion batteries. generation high capacity lithium ion battery anode materials.
- [English]
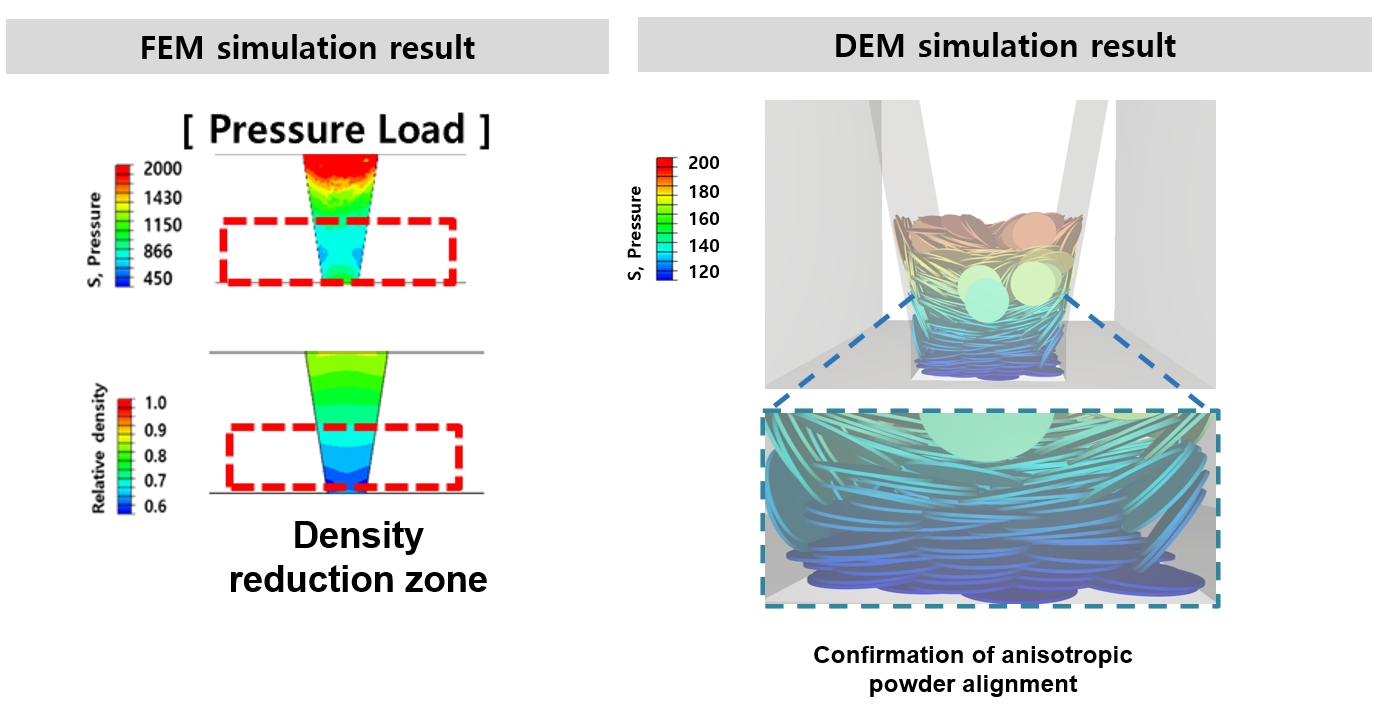
- Finite Element and Discrete Element Analyses of Anisotropic Powder Compaction for Axial Flux Motor Cores
- Jeong Ah Lee, Do Won Lee, , Hyojeong Ha, Ki Hyuk Kwon, Eon Byeong Park, Taeyoung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):451-458. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00409
- 859 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates the compaction behavior of anisotropic, plate-like powders used in axial flux motor cores through a combined FEM–DEM approach. A porous continuum FEM model captures stress and density evolution during die pressing, revealing strong gradients along the compaction direction, with higher stress and densification near the upper punch and reduced compaction in the lower region. Guided by these results, DEM simulations examine particle packing, orientation, and contact pressure in representative zones. The DEM analysis shows that higher local pressure promotes denser packing and in-plane particle alignment near the upper punch, while the lower region exhibits more random orientations and lower contact forces. As a result, the multi-scale FEM–DEM framework clarifies how anisotropic particle behavior governs local densification and offers practical guidance for die design and process optimization to achieve more uniform density and controlled magnetic-property-relevant particle alignment in axial flux motor cores.
- [Korean]
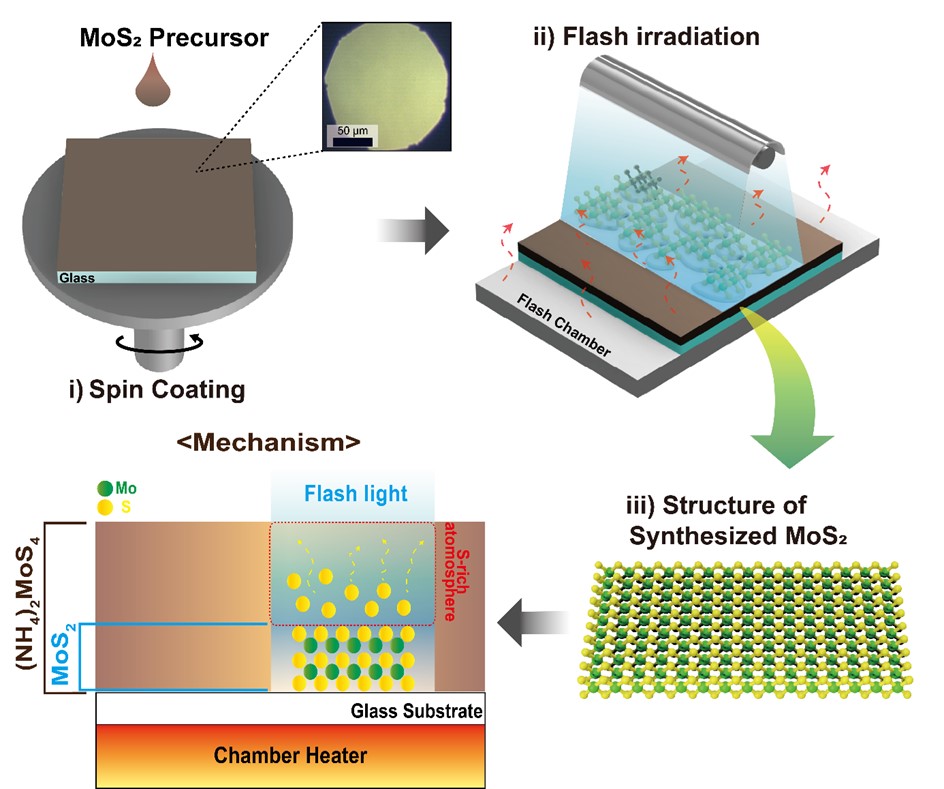
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 684 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
- [Korean]
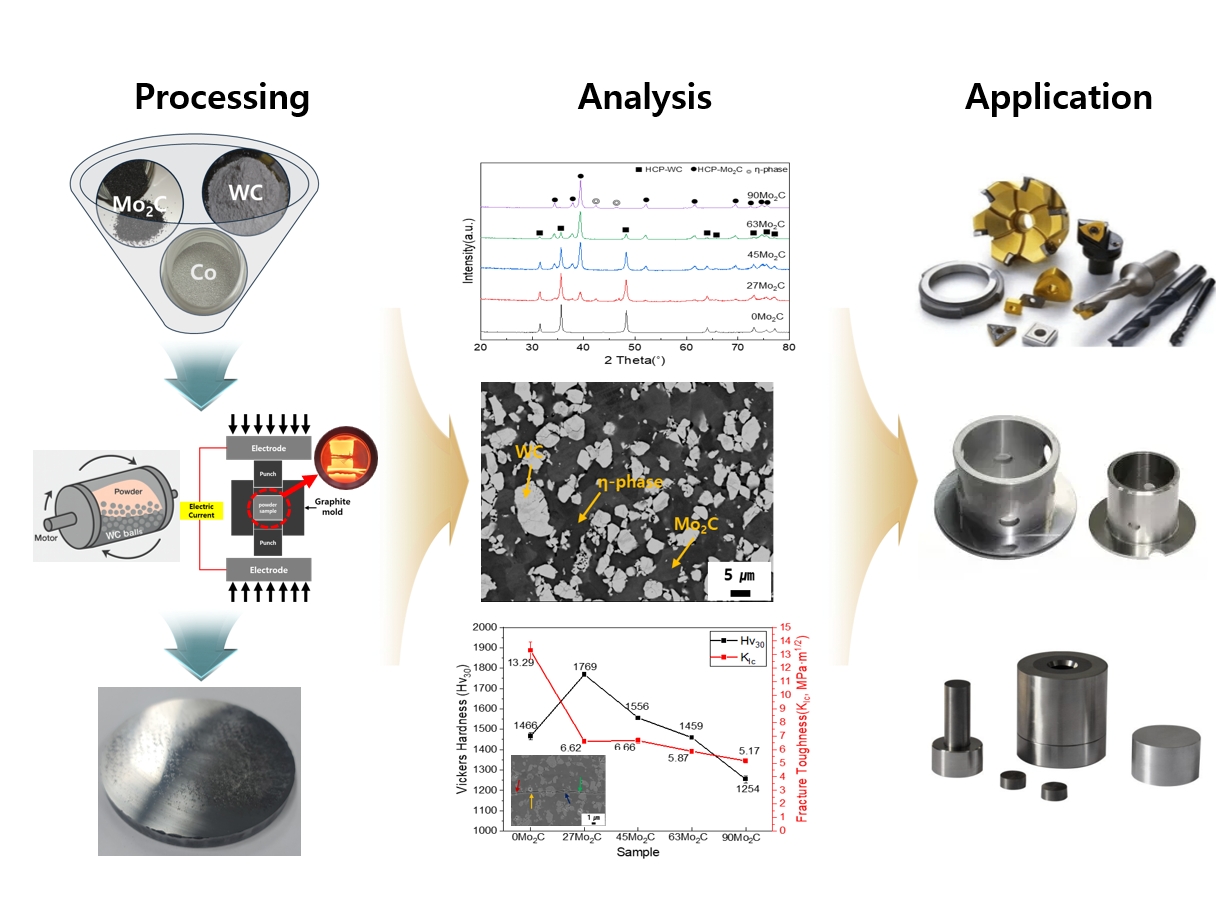
- Optimization of Mechanical Properties in WC–Mo₂C–Co Cemented Carbides via Dual Hard-Phase Based Heterogeneous Microstructure Design
- Jinwoo Seok, Jong Tae Kim, Juree Jung, SongYi Kim, Bin Lee, Junhee Han, Leeseung Kang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):428-436. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00297
- 530 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - WC–Mo₂C–Co cemented carbides were fabricated to investigate the effects of Mo₂C addition on microstructure and mechanical properties. Dual hard-phase design using WC and Mo₂C was employed to optimize the balance between hardness and toughness. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) was conducted at various temperatures after ball milling, and 1300 °C for 5 min was identified as the optimized sintering condition, achieving complete densification and phase stability. The addition of Mo₂C refined the microstructure by suppressing abnormal WC grain growth through preferential dissolution of Mo₂C into the Co binder. Hardness increased up to 1769 Hv30 due to grain refinement and solid-solution strengthening, while promoted η-phase formation and reduced fracture toughness.The 27Mo₂C composition exhibited the most balanced combination of hardness and toughness. These results demonstrate that controlled Mo₂C addition enables dual hard-phase strengthening and microstructure optimization in WC–Mo₂C–Co carbides for advanced cutting and forming applications.
- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
- Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
- 501 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
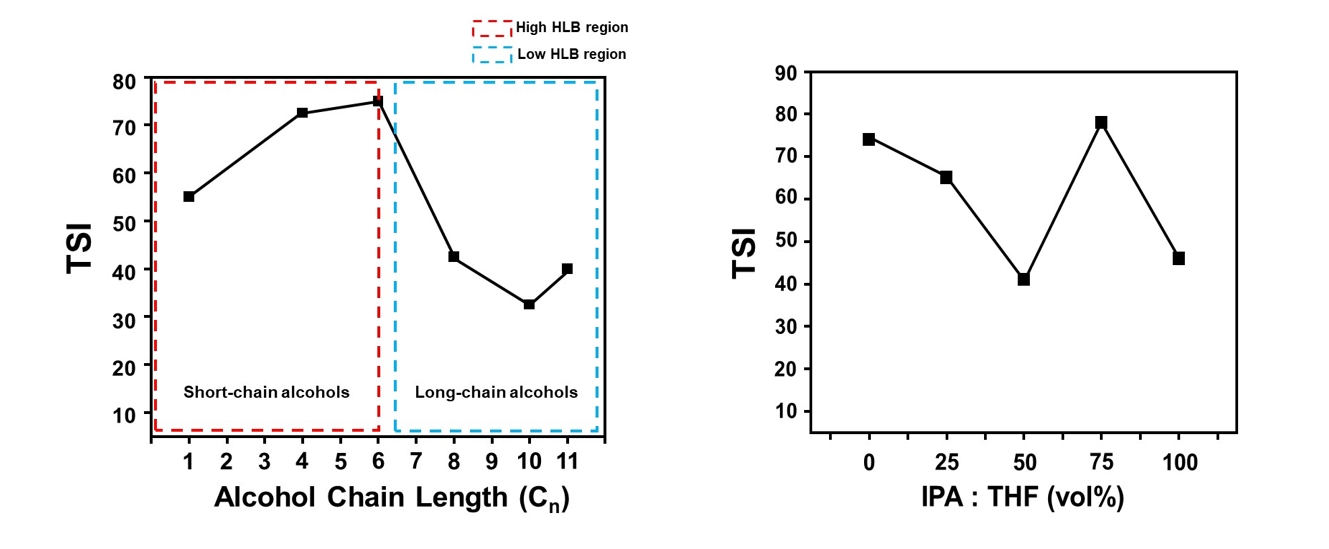
PDF - This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):399-405. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00227
- 433 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
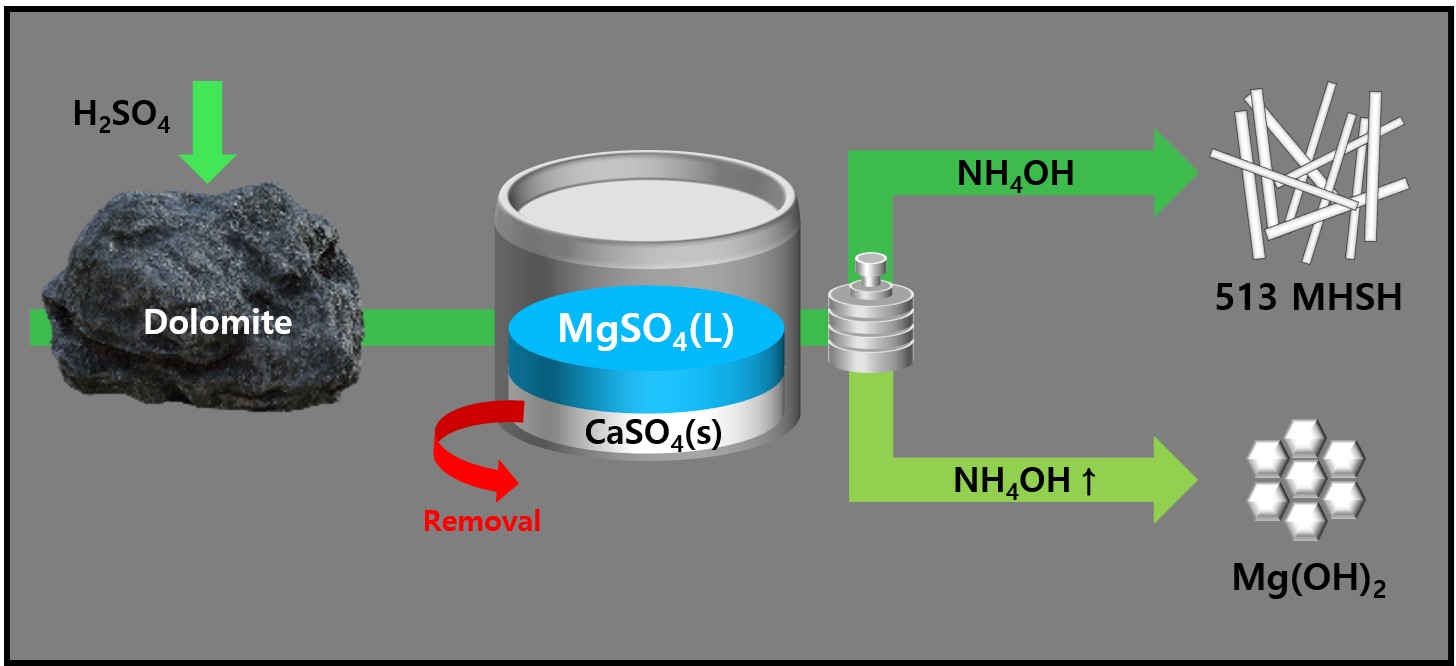
PDF - 513 magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) and Mg(OH)₂ were synthesized by controlling the pH and concentration using a domestic resource, dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), as the raw material. The MgSO₄ was extracted by treating dolomite with sulfuric acid under various conditions. Hexagonal plate-shaped Mg(OH)₂ and needle-like 513 MHSH were synthesized under the hydrothermal condition. The morphology of the synthesized materials was controlled by adjusting the pH (SO42-/OH- ratio) and hydrothermal reaction time. As the pH of the solution increased, the formation of plate-like structures became dominant, whereas lower pH values (higher SO42- concentration) led to needle-like forms. The results of the 513 MHSH, which was synthesized using reagents and sea bittern, are consistent with the synthesis conditions, and we observed changes in the length and aspect ratio of the needle-shaped structure in response to adjusting the hydrothermal reaction time.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234
- 963 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
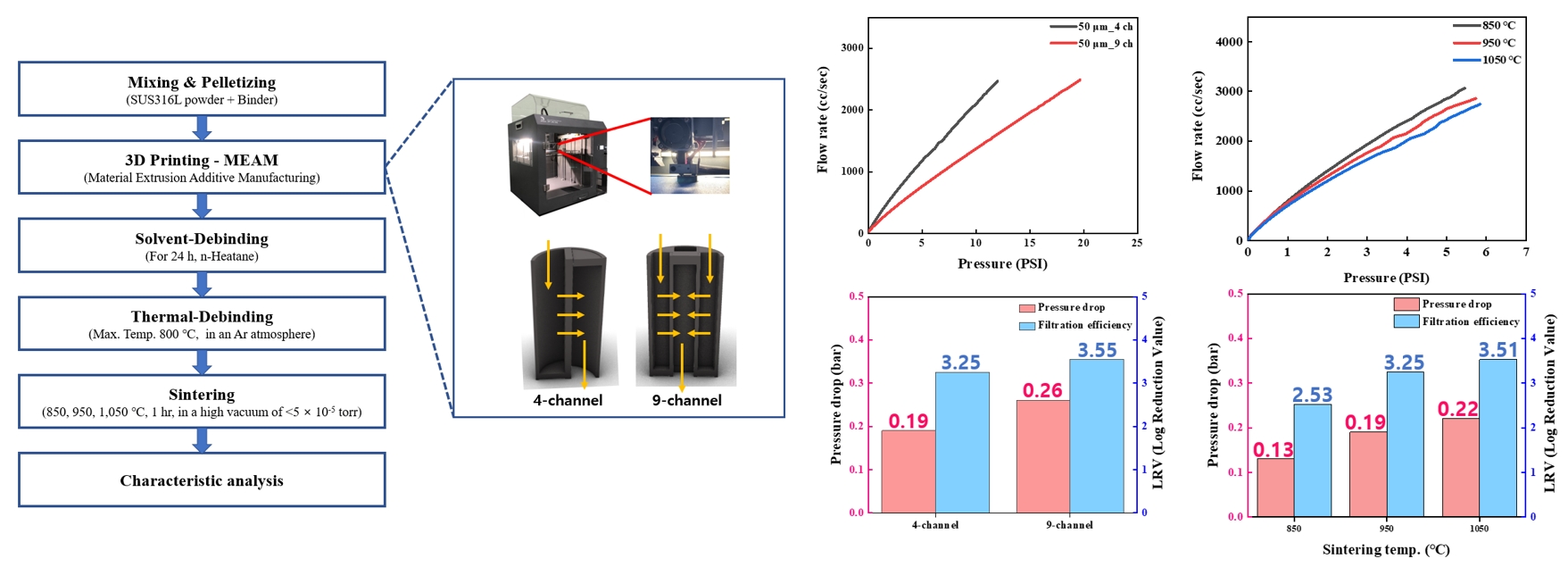
PDF - The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [English]
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):288-298. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00213

- 1,173 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective approach to fabricating near β-Ti alloys via in-situ alloying during laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF). A blend of non-spherical pure Ti, 3 wt.% Fe, and 0.1 wt.% SiO2 nanoparticles was used to induce β-phase stabilization and improve flowability. Twenty-five process conditions were evaluated across a volumetric energy density range of 31.75-214.30 J/mm3, achieving a maximum relative density of 99.21% at 89.29 J/mm3. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that the β-Ti phase was partially retained at room temperature, accompanied by lattice contraction in the α’-Ti structure, indicating successful Fe incorporation. Elemental mapping confirmed that the Fe distribution was homogeneous, without significant segregation. Compared to pure Ti, the Ti-3Fe sample exhibited a 49.2% increase in Vickers hardness and notable improvements in yield and ultimate tensile strengths. These results demonstrate the feasibility of in-situ alloying with low-cost elemental powders to produce high-performance near β-Ti alloys using L-PBF.
- [Korean]
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):330-343. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00136
- 1,093 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
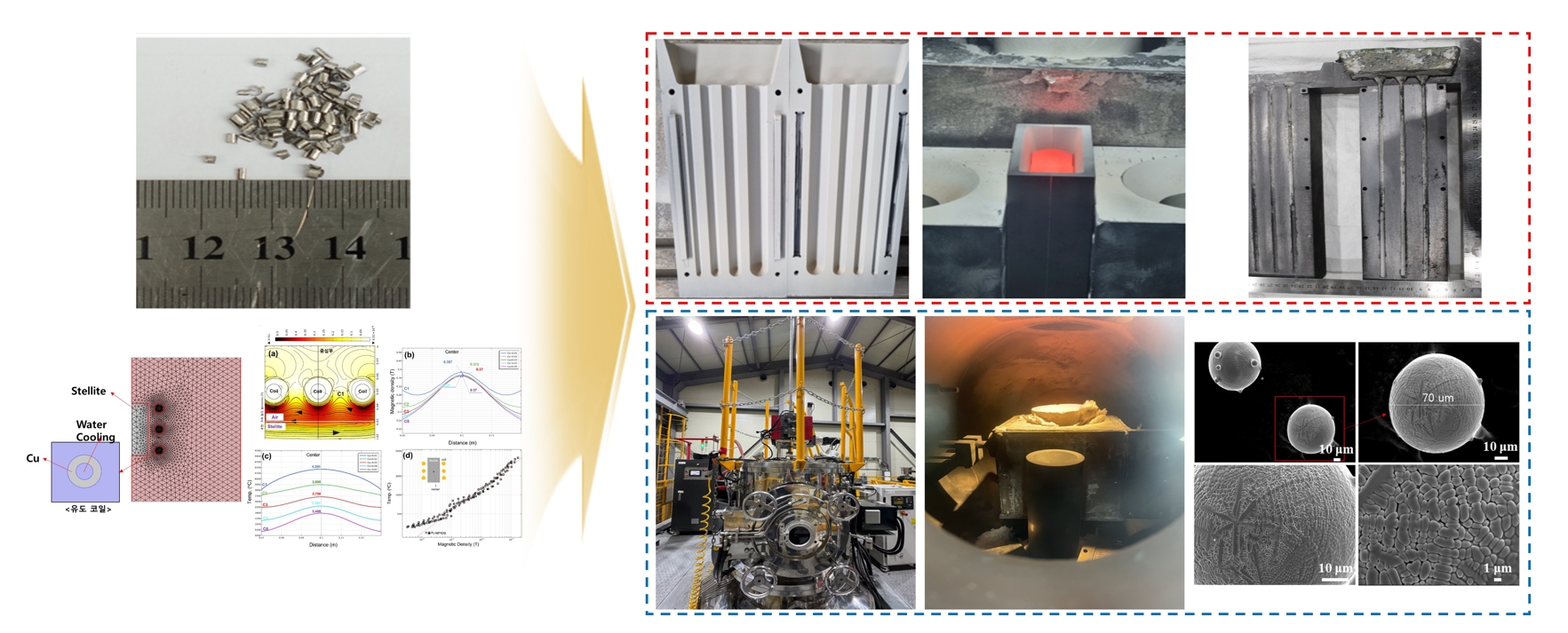
PDF - Co-Cr alloys are widely used in cutting tools and turbine components due to their high strength and resistance against wear and corrosion. However, scrap generated during hardfacing is often discarded due to impurities and oxidation, and research on its recycling remains limited. This study aimed to optimize the recycling process of Stellite 6 scrap to reduce waste and minimize costs while maintaining material quality. Melting, casting, and powdering processes were designed using HSC Chemistry, FactSage, and COMSOL Multiphysics, with optimization of key parameters such as the crucible material and temperature control. The recycled alloy and powder were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence analysis, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry, showing mechanical and chemical properties comparable to commercial Stellite 6. The Co and Cr contents were maintained, with a slight increase in Fe. These findings demonstrate the potential for producing high-quality recycled Stellite 6 materials, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metal resources in high-performance applications.
- [English]
- Enhanced Compressive Strength of Fired Iron Ore Pellets: Effects of Blending Fine and Coarse Particle Concentrates
- Ngo Quoc Dung, Tran Xuan Hai, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Nguyen Quang Tung, Arvind Barsiwal, Nguyen Hoang Viet
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):315-329. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00129
- 1,826 View
- 70 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
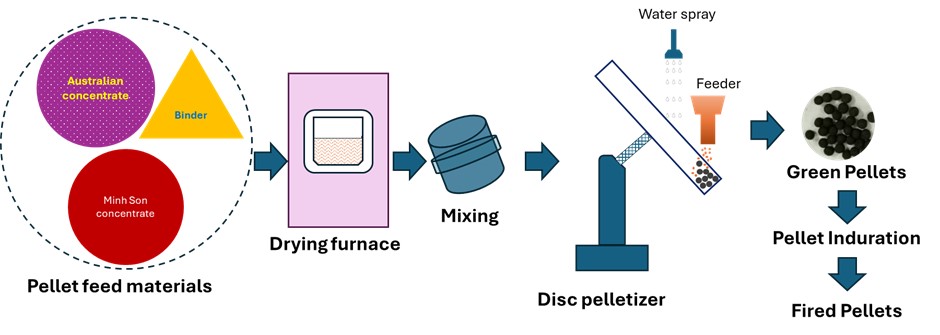
PDF - This study investigated the effects of oxidative firing parameters and raw material characteristics on the pelletization of Australian and Minh Son (Vietnam) iron ore concentrates. The influence of firing temperature (1050°C–1150°C) and holding time (15–120 min) on pellet compressive strength was examined, focusing on microstructural changes during consolidation. Green pellets were prepared using controlled particle size distributions and bentonite as a binder. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analyses revealed that grain boundary diffusion, liquid phase formation, and densification significantly improved mechanical strength. X-ray diffraction confirmed the complete oxidation of magnetite to hematite at elevated temperatures, a critical transformation for metallurgical performance. Optimal firing conditions for both single and blended ore compositions yielded compressive strengths above 250 kgf/pellet, satisfying the requirements for blast furnace applications. These results provide valuable guidance for improving pellet production, promoting the efficient utilization of diverse ore types, and enhancing the overall performance of ironmaking operations.
- [English]
- Laser Processing of an Al0.1CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy + Cu Composite Powders via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Kwangtae Son, Ji-Woon Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Somayeh Pasebani
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):277-287. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00101

- 1,114 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined process–structure relationships in laser powder bed fusion of Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi + Cu composites, focusing on densification, elemental distribution, and solidification cracking. Mechanically mixed Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi and Cu powders were processed across a range of laser powers (100–250 W) and scan speeds (200–800 mm/s). Increased volumetric energy density (VED) improved densification, with a plateau near 200 J/mm³ yielding ~96% relative density; however, this value was still below application-grade thresholds. At low VED, insufficient thermal input and short melt pool residence times promoted Cu segregation, while higher VED facilitated improved elemental mixing. Elemental mapping showed partial co-segregation of Ni with Cu at low energies. Solidification cracks were observed across all processing conditions. In high VED regimes, cracking exhibited a minimal correlation with segregation behavior and was primarily attributed to steep thermal gradients, solidification shrinkage, and residual stress accumulation. In contrast, at low VED, pronounced Cu segregation appeared to exacerbate cracking through localized thermal and mechanical mismatch.
- [English]
- The Effect of Aluminum Powder Size on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Foam
- Seunghyeok Choi, Sungjin Kim, Tae-Young Ahn, Yu-Song Choi, Jae-Gil Jung, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):232-243. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00157

- 1,378 View
- 54 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we analyzed the structural and mechanical properties of aluminum foams fabricated using aluminum powders of varying sizes and mixtures. The effects of sintering and pore structure at each size on the integrity and mechanical properties of the foams were investigated. Structural characteristics were examined using scanning electron microscopy and micro–computed tomography, while mechanical properties were evaluated through compression testing. The experimental results demonstrated that smaller powder sizes improved foam integrity, reduced porosity and pore size, and resulted in thinner cell walls. In combination, these effects increased compressive strength as the powder size decreased. The findings of this study contribute to the understanding and improvement of the mechanical properties of aluminum foams and highlight their potential for use in a wide range of applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
Xinwei Yang, Qian Peng, Changke Chen, Qingcui Liu, Yudai Huang
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2026; 12(1): 727. CrossRef
- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
- [Korean]
- Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
- Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):202-211. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00150

- 784 View
- 51 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study introduces a machine learning approach for designing new aluminum alloys tailored for directed energy deposition additive manufacturing, achieving an optimal balance between hardness and conductivity. Utilizing a comprehensive database of powder compositions, process parameters, and material properties, predictive models—including an artificial neural network and a gradient boosting regression model, were developed. Additionally, a variational autoencoder was employed to model input data distributions and generate novel process data for aluminum-based powders. The similarity between the generated data and the experimental data was evaluated using K-nearest neighbor classification and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding, with accuracy and the F1-score as metrics. The results demonstrated a close alignment, with nearly 90% accuracy, in numerical metrics and data distribution patterns. This work highlights the potential of machine learning to extend beyond multi-property prediction, enabling the generation of innovative process data for material design.
- [English]
- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
- Si Eun Jung, Ji Woong Shin, Ye Jin Han, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):179-190. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00094

- 4,763 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Area-selective atomic layer deposition (AS-ALD) is a bottom-up process that selectively deposits thin films onto specific areas of a wafer surface. The surface reactions of AS-ALD are controlled by blocking the adsorption of precursors using inhibitors such as self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) or small molecule inhibitors. To increase selectivity during the AS-ALD process, the design of both the inhibitor and the precursor is crucial. Both inhibitors and precursors vary in reactivity and size, and surface reactions are blocked through interactions between precursor molecules and surface functional groups. However, challenges in the conventional SAM-based AS-ALD method include thermal instability and potential damage to substrates during the removal of residual SAMs after the process. To address these issues, recent studies have proposed alternative inhibitors and process design strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
Hojeong Yoon, Saima Sadiq, Junhyeok Park, Kyungwon Kwak, Minhaeng Cho
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.2026; 17(4): 1119. CrossRef
- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
- [Korean]
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):244-253. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00087

- 1,094 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely utilized in aerospace and medical sectors due to its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its low machinability makes it difficult to manufacture complex-shaped products. Advancements in additive manufacturing have focused on producing high-performance, complex components using the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process, which is a specialized technique for customized geometries. The LPBF process exposes materials to extreme thermal conditions and rapid cooling rates, leading to residual stresses within the parts. These stresses are intensified by variations in the thermal history across regions of the component. These variations result in differences in microstructure and mechanical properties, causing distortion. Although support structure design has been researched to minimize residual stress, few studies have conducted quantitative analyses of stress variations due to different support designs. This study investigated changes in the residual stress and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated using LPBF, focusing on support structure design.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):254-261. Published online June 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00059

- 666 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) incorporating low-melting-point elements (Mg and Al) and high-melting-point elements (Ti, Cr, and V) were fabricated via mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Sintering temperatures were varied to investigate phase behavior and microstructural evolution. X-ray diffraction was used to identify phase structures, scanning electron microscopy to analyze microstructures, X-ray fluorescence to determine elemental composition, and a gas pycnometer to measure density. Micro-Vickers hardness testing was conducted to evaluate mechanical properties. Mechanical-alloyed HEAs exhibited a body-centered cubic (BCC) phase and lamellar structures with element-enriched regions. Sintering introduced additional BCC and Laves phases, while higher temperatures promoted Mg liquid-phase sintering, increasing density and hardness. This study highlights the effects of sintering on HEAs containing elements with differing melting points to optimize their properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [Korean]
- Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):131-137. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00080
- 1,139 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
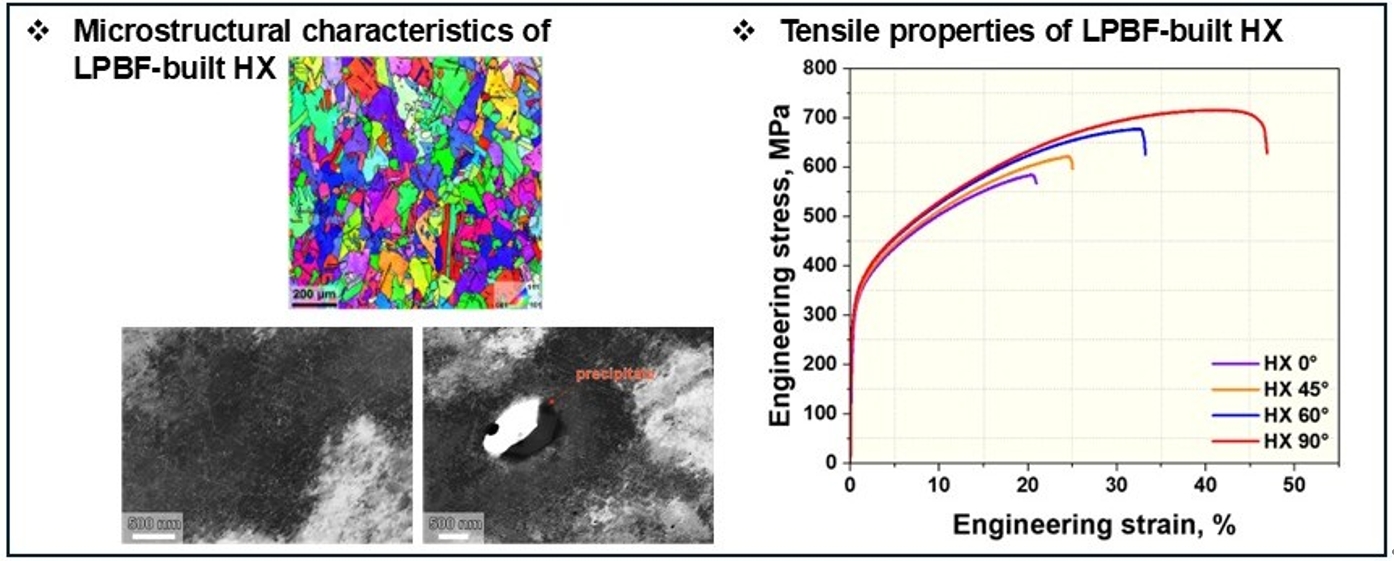
PDF - In this study, the effect of build orientation on the mechanical properties of Hastelloy X fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process was investigated. Initial microstructural analysis revealed an equiaxed grain structure with random crystallographic orientation and annealing twins. Intragranular precipitates identified as Cr-rich M23C6 and Mo-rich M6C carbides were observed, along with a dense dislocation network and localized dislocation accumulation around the carbides. Mechanical testing showed negligible variation in yield strength with respect to build orientation; however, both ultimate tensile strength and elongation exhibited a clear increasing trend with higher build angles. Notably, the specimen built at 90° exhibited approximately 22% higher tensile strength and more than twice the elongation compared to the 0° specimen.
- [English]
- Ultra-Low-Temperature (4.2 K) Tensile Properties and Deformation Mechanism of Stainless Steel 304L Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seung-Min Jeon, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00066

- 1,927 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the ultra-low-temperature (4.2 K) tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of stainless steel 304L manufactured via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). The tensile properties of LPBF 304L were compared to those of conventional 304L to assess its suitability for cryogenic applications. The results revealed that LPBF 304L exhibited a significantly higher yield strength but lower ultimate tensile strength and elongation than conventional 304L at 4.2 K. The temperature dependence of the yield strength also favored LPBF 304L. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that LPBF 304L features a high density of dislocation cells and nano-inclusions, contributing to its greater strength. Furthermore, strain-induced martensitic transformation was observed as a key deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures, where austenite transformed into both hexagonal-closed packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite. Notably, BCC martensite nucleation occurred within a single HCP band. These findings provide critical insights into the mechanical behavior of LPBF 304L at cryogenic temperatures and its potential for applications in extreme environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Heechan Jung, Min Young Sung, Young-Kyun Kim, Jaimyun Jung, Yoona Lee, Namhyun Kang, Kyung Tae Kim, Young-Sang Na, Seok Su Sohn, Jeong Min Park
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 950: 149460. CrossRef - Twinning- and transformation-induced high cryogenic strength and ductility of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Experiment and MD simulation
Yuze Wu, Zhide Li, Charlie Kong, M.W. Fu, Hailiang Yu
International Journal of Plasticity.2026; 196: 104553. CrossRef - Understanding the unique appearance behavior of shear bands during tensile deformation of α-brass at 4.2 K
Seon-Keun Oh, Sang-Hun Shim, Young-Kyun Kim, Young-Sang Na
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 945: 148989. CrossRef
- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cellulose Fiber Density Variation on Energy Harvesting Performance in a Hydrovoltaic Generator
- Seung-Hwan Lee, So Hyun Baek, Hyun-Woo Lee, Yongbum Kwon, Kanghyuk Lee, Kee-Ryung Park, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Ji Young Park, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):113-121. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00052

- 1,284 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Energy harvesting has become a crucial technology for sustainable energy solutions; in particular, the utilization of ambient water movement in hydrovoltaic generators has emerged as a promising approach. However, optimizing performance requires an understanding of structural factors affecting energy harvesting, particularly capillary effects. This study aimed to improve hydrovoltaic generator performance by adjusting internal fiber density, which influences water transport and ion mobility. Using cold isostatic pressing, cellulose acetate (CA) loading in a urethane mold was varied to optimize internal density. As CA loading increased, the fiber arrangement became denser, narrowing capillary pathways and reducing proton mobility. While open-circuit voltage (VOC) remained stable, short-circuit current (ISC) decreased with higher CA mass. The sample with a loading of 0.3 g exhibited the highest energy harvesting efficiency, achieving ISC = 107.2 μA, VOC = 0.15 V, and power (P) = 16.7 μW. This study provides insights into methods of improving hydrovoltaic generator efficiency through internal structural modifications.
- [English]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Laser Powder Bed Fusion-Processed 316L Stainless Steel
- Rae Eon Kim, Yeon Taek Choi, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00017

- 2,271 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Metal additive manufacturing (AM) facilitates the production of complex geometries with enhanced functionality. Among various AM techniques, laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is distinguished by its precision and exceptional mechanical properties achieved via laser fusion deposition. Recent advancements in AM have focused on combining LPBF with post-processing methods such as cold rolling, high-pressure torsion, and forming processes. Therefore, understanding the forming behavior of LPBF-processed materials is essential for industrial adoption. This study investigates the stretch-flangeability of LPBF-fabricated 316L stainless steel, emphasizing its anisotropic microstructure and mechanical properties. Hole expansion tests were employed to assess stretch-flangeability in comparison to wrought 316L stainless steel. The results demonstrate that LPBF-processed samples exhibit significant anisotropic behavior, demonstrating the influence of microstructural evolution on formability. These findings contribute valuable insights into optimizing LPBF materials for industrial forming applications.
- [Korean]
- Friction Stir Spot Welding Characteristics of Dissimilar Materials of Aluminum-Based Damping Composites and Steel Plates
- Si-Seon Park, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):43-49. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00010
- 671 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
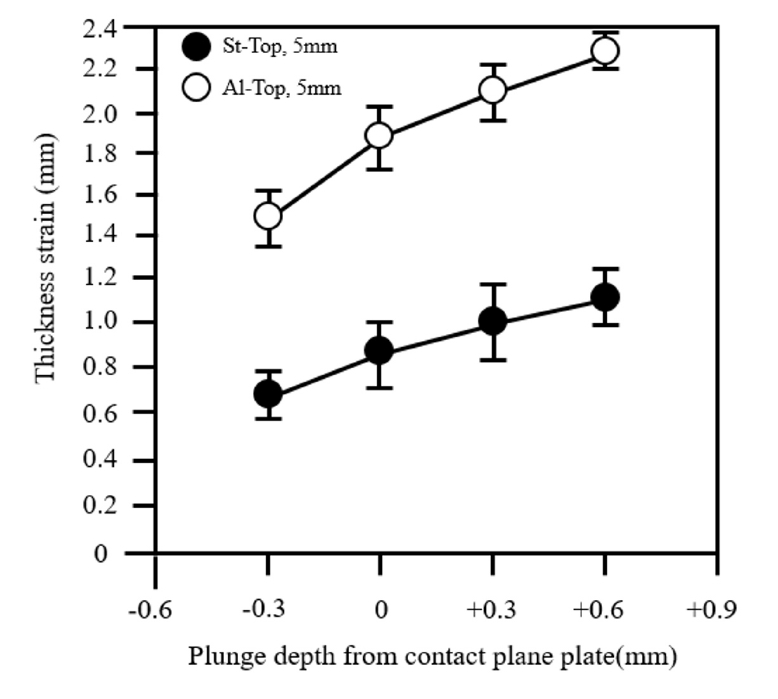
PDF - Friction Stir Spot Welding (FSSW) is a solid-state welding technology that is rapidly growing in the automotive industry. Achieving superior welding characteristics requires the proper selection of tool geometry and process conditions. In this study, FSSW was performed on dissimilar materials comprising AA5052-HO/hot-melt aluminum alloy sheets and Steel Plate Cold Rolled for Deep Drawing Use(SPCUD) steel sheets. The effects of tool geometry, plate arrangement, and tool plunge depth on the welding process were investigated. At the joint interface between the aluminum alloy and the steel sheet, new intermetallic compounds (IMCs) were observed. As the plunge depth increased, thicker and more continuous IMC layers were formed. However, excessive plunge depth led to discontinuous layers and cracking defects. An analysis of the IMCs revealed a correlation between the IMC thickness and the shear tensile load. Furthermore, compared to the conventional Al-Top arrangement, the St-Top arrangement exhibited reduced deformation and superior shear tensile load values. These findings indicate that plate arrangement significantly influences the mechanical properties of the joint.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Hatch Spacing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SA508 Gr.3 Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Yuanjiu Huang, Ho Jin Ryu, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):50-58. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00479
- 1,167 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
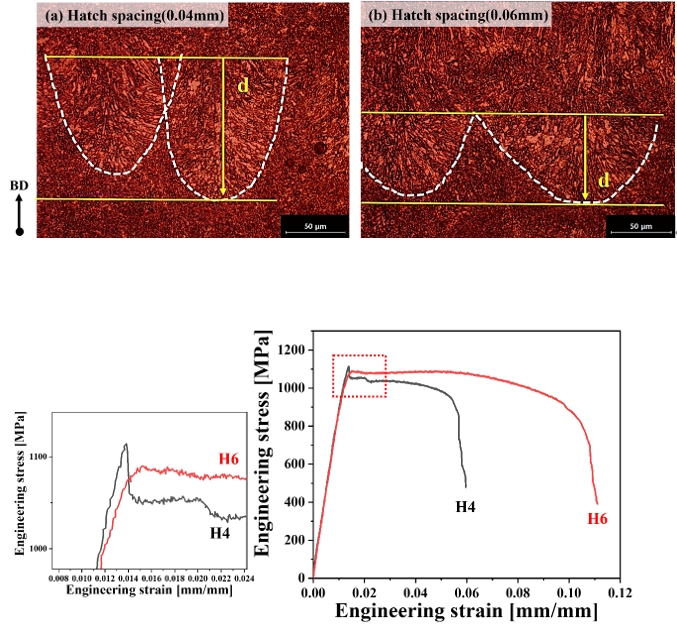
PDF - This study investigated the effect of the hatch spacing parameter on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SA508 Gr.3 steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) for a nuclear pressure vessel. Materials were prepared with varying hatch spacing (0.04 mm [H4] and 0.06 mm [H6]). The H4 exhibited finer and more uniformly distributed grains, while the H6 showed less porosity and a lower defect fraction. The yield strength of the H4 material was higher than that of the H6 material, but there was a smaller difference between the materials in tensile strength. The measured elongation was 5.65% for the H4 material and 10.41% for the H6 material, showing a significantly higher value for H6. An explanation for this is that although the H4 material had a microstructure of small and uniform grains, it contained larger and more numerous pore defects than the H6 material, facilitating stress concentration and the initiation of microcracks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low temperature mechanical behavior of in-situ oxide containing 304L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
Kwangtae Son, Seung-Min Jeon, Brian K. Paul, Young-Sang Na, Kijoon Lee, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2025; 234: 319. CrossRef
- Extremely low temperature mechanical behavior of in-situ oxide containing 304L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
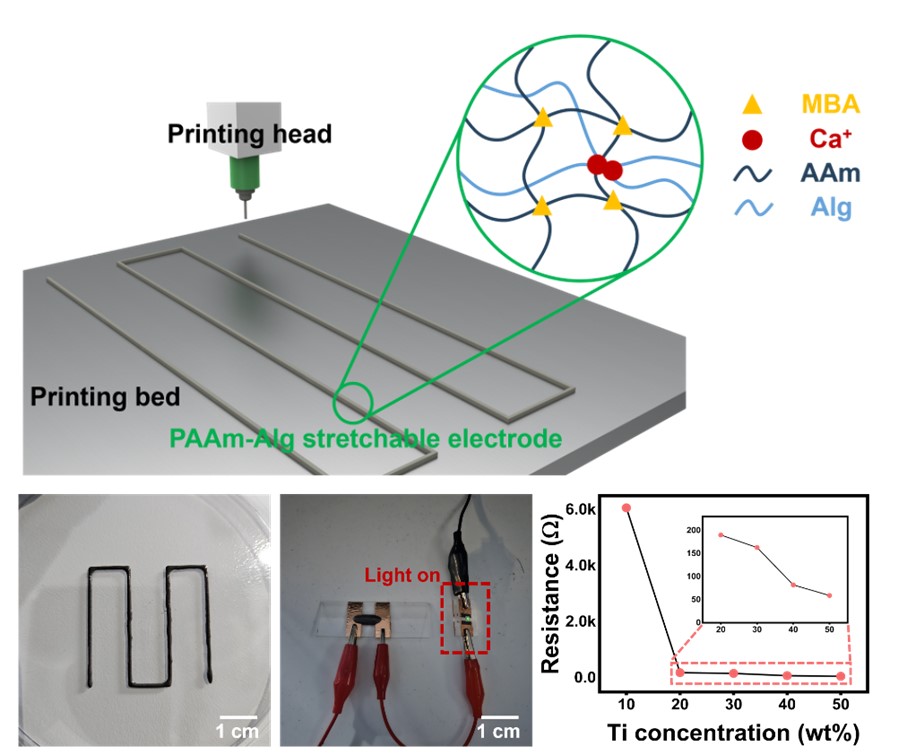
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
- Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
- 847 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
- [Korean]
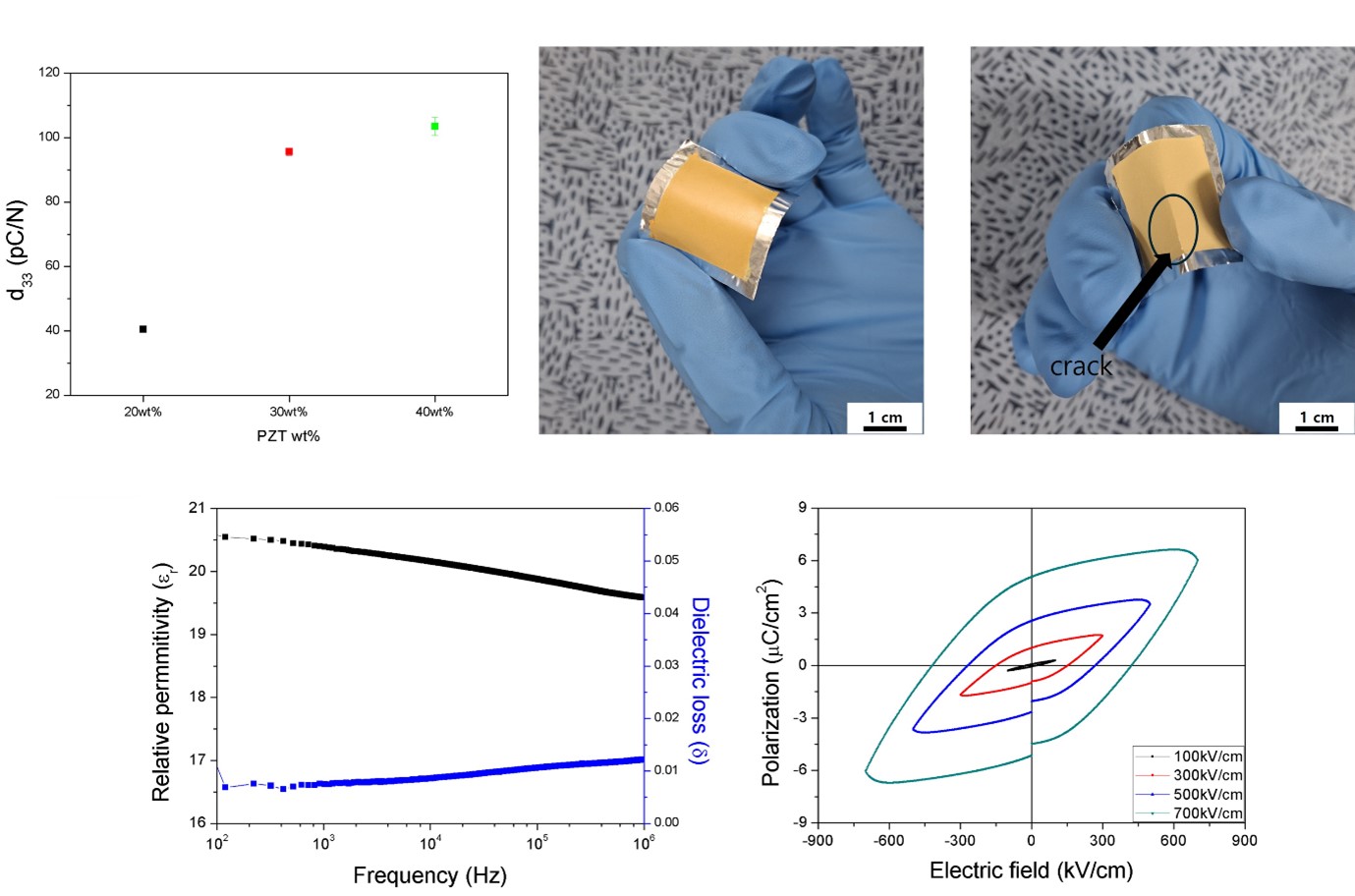
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00444
- 977 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Piezoelectric composites have attracted significant research interest as sustainable power sources for electronic devices due to their high mechanical stability and electrical output characteristics. This study investigated the optimal processing conditions for fabricating a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester based on Pb(Zr,Ti)O₃ (PZT) powder and a polyimide (PI) matrix composite. Various parameters, including the optimal mixing ratio of PI/PZT, ultrasonic treatment, homogenization, vacuum oven, and UV/O₃ treatment, were optimized to achieve a uniform piezoelectric composite. A PZT content of 30 wt% and 20 minutes of homogenization were identified as the most effective conditions for increasing the uniformity of the composite. The optimized composite exhibited a high piezoelectric coefficient, a typical P-E hysteresis loop, and dielectric properties, exhibiting a voltage output that adjusts in response to variations in the applied touch force. This study provides foundational data for the uniform fabrication of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters and next-generation miniaturized electronic devices.
Critical Review
- [English]
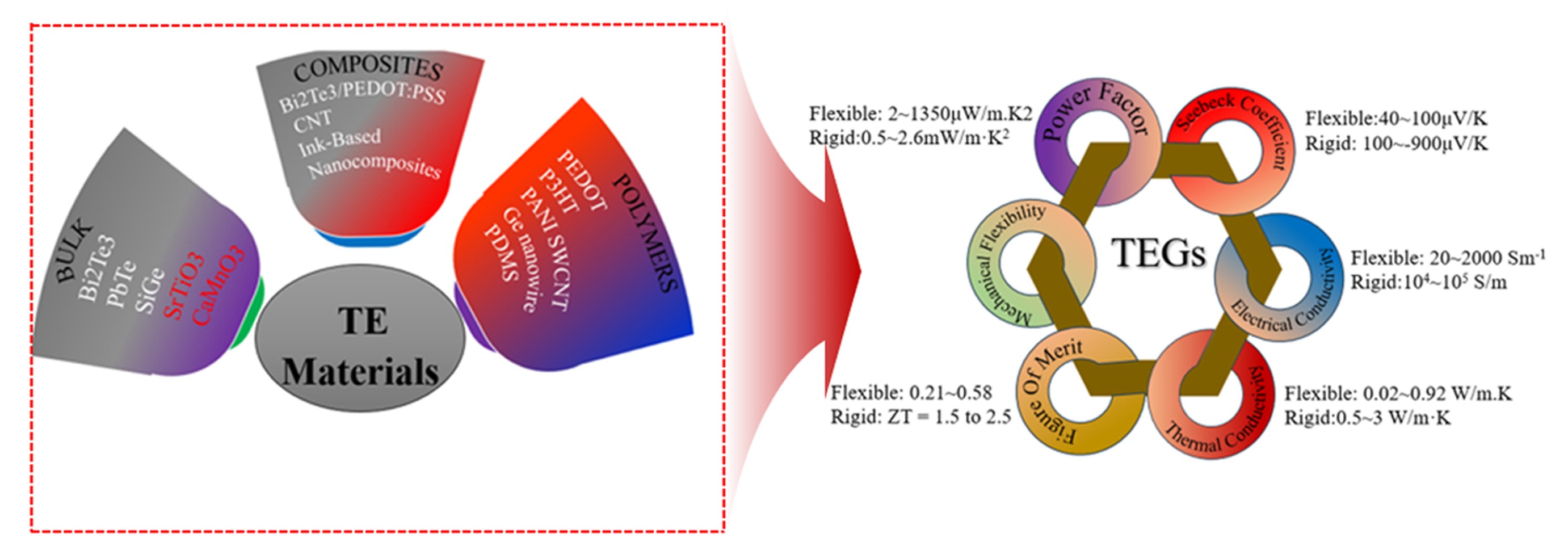
- Recent Advances in Thermoelectric Materials and Devices: Improving Power Generation Performance
- Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):1-15. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00395
- 9,762 View
- 216 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermoelectric materials have been the focus of extensive research interest in recent years due to their potential in clean power generation from waste heat. Their conversion efficiency is primarily reflected by the dimensionless figure of merit, with higher values indicating better performance. There is a pressing need to discover materials that increase output power and improve performance, from the material level to device fabrication. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent advancements, such as Bi2Te3-based nanostructures that reduce thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical conductivity, GeTe-based high entropy alloys that utilize multiple elements for improved thermoelectric properties, porous metal-organic frameworks offering tunable structures, and organic/hybrid films that present low-cost, flexible solutions. Innovations in thermoelectric generator designs, such as asymmetrical geometries, segmented modules, and flexible devices, have further contributed to increased efficiency and output power. Together, these developments are paving the way for more effective thermoelectric technologies in sustainable energy generation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mathematical and simulation modeling of photovoltaic systems utilizing thermoelectric modules for effective thermal management
Muhammad Sohaib Tahir, Xue Dong, Muhammad Mansoor Khan
Results in Engineering.2025; 27: 106344. CrossRef - Summary of Publications in the Special Issue: Advances in Corrosion Resistant Coatings
Yong X. Gan
Coatings.2025; 15(11): 1350. CrossRef - Standard Reference Thermoelectric Modules Based on Metallic Combinations and Geometric Design
EunA Koo, Hanhwi Jang, SuDong Park, Sang Hyun Park, Sae-byul Kang
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10273. CrossRef - Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 529. CrossRef
- Mathematical and simulation modeling of photovoltaic systems utilizing thermoelectric modules for effective thermal management
Research Articles
- [English]
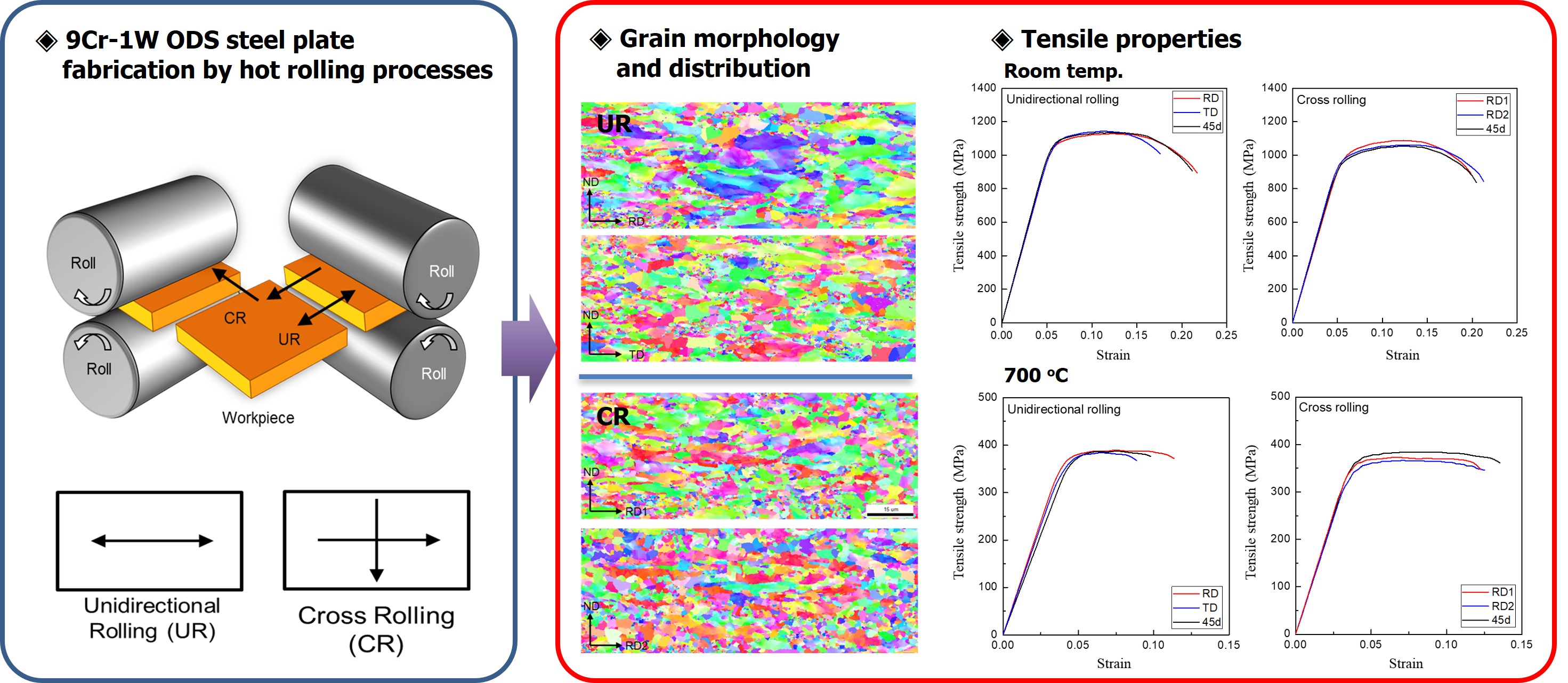
- Effect of the Cross-rolling Process on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-1W ODS Steel
- Bu-An Kim, Sanghoon Noh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00332
- 1,025 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study employed a cross-rolling process to fabricate oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel plates and investigated their microstructures and mechanical properties. The 9Cr-1W ODS ferritic steel was fabricated using mechanical alloying and hot isostatic pressing. The hot cross-rolling process produced thick ODS ferritic steel plates with a well-extended rectangular shape. The working direction greatly affected the grain structure and crystal texture of the ODS ferritic steel. Cross-rolled plates showed fine micro-grains with random crystal orientation, while unidirectionally rolled plates exhibited a strong orientation with larger, elongated grains. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a uniform distribution of nano-oxide particles in both rolling methods, with no major differences. Tensile tests of the ODS ferritic steel plates showed that the unidirectional rolled plates had anisotropic elongation, while cross-rolled plates exhibited isotropic behavior with uniform elongation. Cross-rolling produced finer, more uniform grains, reducing anisotropy and improving mechanical properties, making it ideal for manufacturing wide ODS steel components.
- [English]
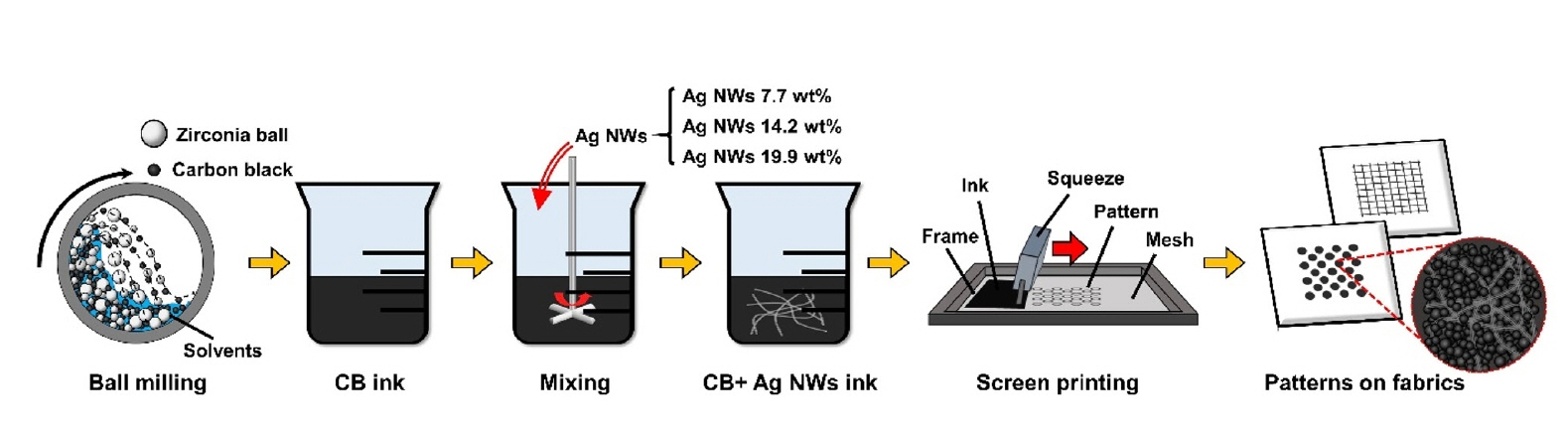
- Design of Conductive Inks Containing Carbon Black and Silver Nanowires for Patternable Screen-Printing on Fabrics
- Seokhwan Kim, Geumseong Lee, Jinwoo Park, Dahye Shin, Ki-Il Park, Kyoung Jin Jung, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):500-507. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00409
- 1,989 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study developed conductive inks composed of carbon black (CB) and silver nanowires (Ag NWs) for cost-effective screen-printing on fabrics. The Ag NW density within the CB matrix was precisely controlled, achieving tunable electrical conductivity with minimal Ag NW usage. The resulting inks were successfully patterned into shapes such as square grids and circles on textile surfaces, demonstrating excellent conductivity and fidelity. Adding 19.9 wt% Ag NWs reduced sheet resistance by ~92% compared to CB-only inks, highlighting the effectiveness and potential of this hybrid approach for cost-effective, high-performance textile-based electronics. The one-dimensional morphology of Ag NWs facilitated the formation of conductive percolation networks, creating efficient electron pathways within the CB matrix even at low loadings. This work advances the field of CB-based conductive inks and provides a scalable and practical method for producing functional, patterned electronic textiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
Nahid Islam, Manisha Das, Bashir Ahmed Johan, Syed Shaheen Shah, Atif Saeed Alzahrani, Md. Abdul Aziz
ACS Applied Electronic Materials.2025; 7(16): 7503. CrossRef
- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381
- 1,484 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [Korean]
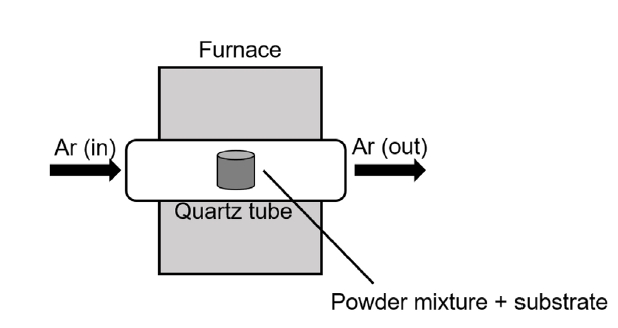
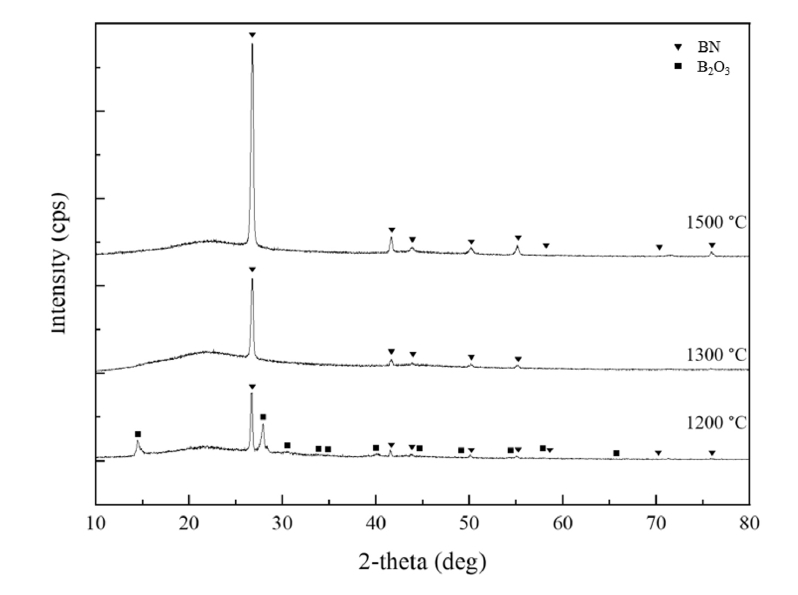
- Fabrication of SiCf/SiC Composites with a BN Interphase Prepared by the Wet Method
- Kyung Ho Kim, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):530-536. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00339
- 981 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective wet chemical coating process for fabricating a boron nitride (BN) interphase on silicon carbide (SiC) fibers, increasing the oxidation resistance and performance of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Using urea as a precursor, optimal nitriding conditions were determined by adjusting the composition, concentration, and immersion time. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed distinct BN phase formation at 1300°C and 1500°C, while a mixture of BN and B₂O₃ was observed at 1200°C. HF treatment improved coating uniformity by removing SiO₂ layers formed during the de-sizing process. Optimization of the boric acid-to-urea molar ratio resulted in a uniform, 130-nm-thick BN layer. This study demonstrates that the wet coating process offers a viable and economical alternative to chemical vapor deposition for fabricating high-performance BN interphases in SiCf/SiC composites that are suitable for high-temperature applications.
Critical Reviews
- [English]
- Advances in Powder Metallurgy for High-Entropy Alloys
- Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Hansung Lee, K. Raja Rao, Man Mohan, Reliance Jain, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):480-492. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00297
- 5,026 View
- 169 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a revolutionary class of materials characterized by their multi-principal element compositions and exceptional mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy, a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process, offers significant advantages for the development of HEAs, including precise control over their composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties. This review explores innovative approaches integrating powder metallurgy techniques in the synthesis and optimization of HEAs. Key advances in powder production, sintering methods, and additive manufacturing are examined, highlighting their roles in improving the performance, advancement, and applicability of HEAs. The review also discusses the mechanical properties, potential industrial applications, and future trends in the field, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of HEA development using powder metallurgy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
Leonardo Baylón García, José Manuel Mendoza Duarte, Ivanovich Estrada Guel, Audel Santos Beltrán, Hansel Manuel Medrano Prieto, Gustavo Rodríguez Cabriales, Enrique Rocha Rangel, José Luis Hernández Rivera, Roberto Martínez Sánchez, Alfredo Martínez Garcí
Coatings.2026; 16(3): 275. CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Latest Advancements and Mechanistic Insights into High-Entropy Alloys: Design, Properties and Applications
Anthoula Poulia, Alexander E. Karantzalis
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5616. CrossRef
- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
- [English]
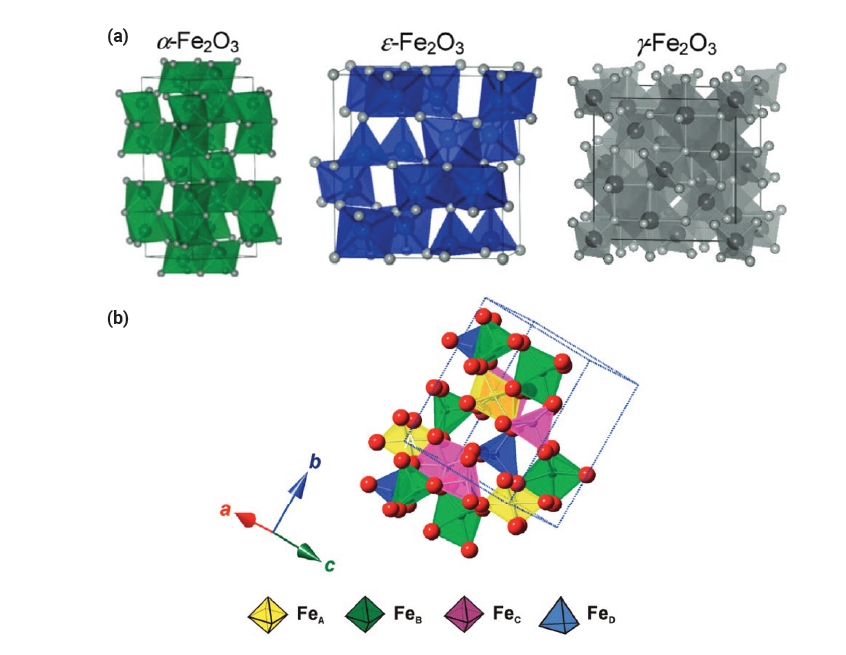
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290
- 3,513 View
- 91 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Research Articles
- [English]
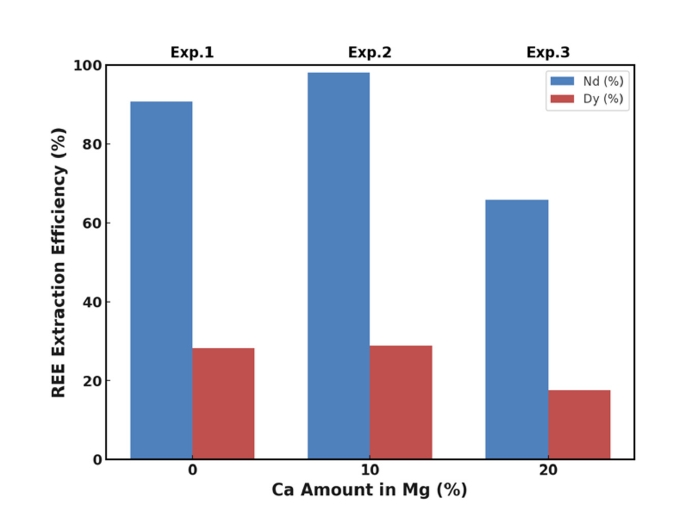
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283
- 1,694 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [English]
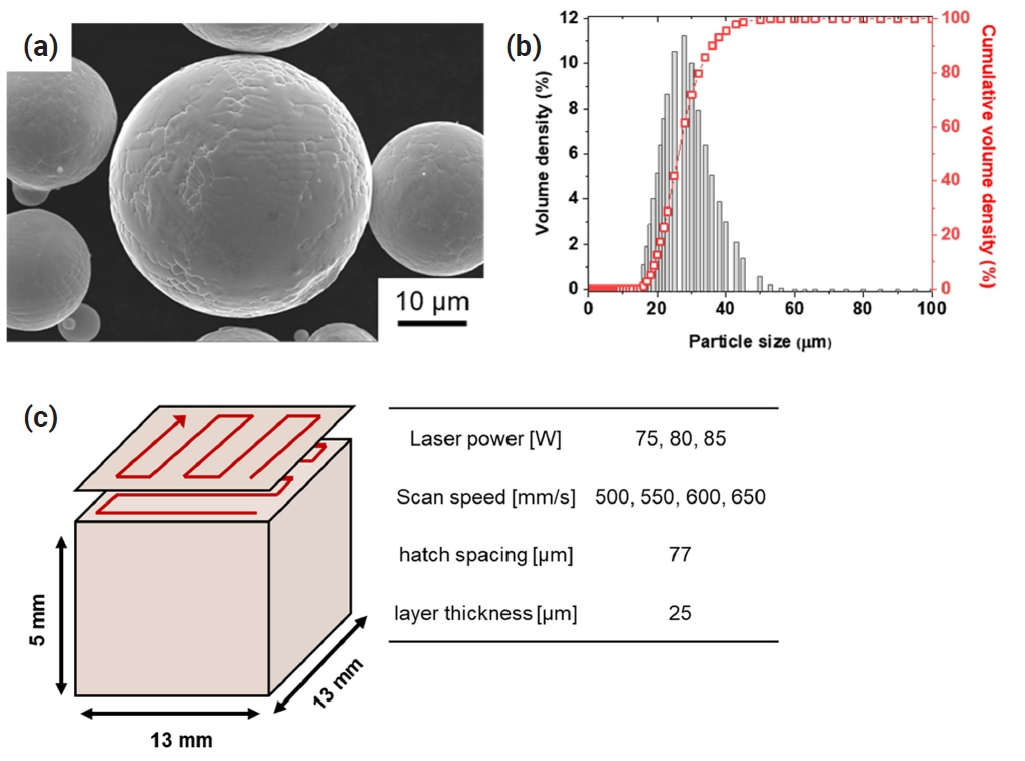
- Hot-Cracking Behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 Medium-Entropy Alloys Manufactured via Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungjin Nam, Heechan Jung, Haeum Park, Chahee Jung, Jeong Min Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):537-545. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00262
- 1,413 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Additive manufacturing makes it possible to improve the mechanical properties of alloys through segregation engineering of specific alloying elements into the dislocation cell structure. In this study, we investigated the mechanical and microstructural characteristics of CoNi-based medium-entropy alloys (MEAs), including the refractory alloying element Mo with a large atomic radius, manufactured via laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF). In an analysis of the printability depending on the processing parameters, we achieved a high compressive yield strength up to 653 MPa in L-PBF for (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs. However, severe residual stress remained at high-angle grain boundaries, and a brittle µ phase was precipitated at Mo-segregated dislocation cells. These resulted in hot-cracking behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs during L-PBF. These findings highlight the need for further research to adjust the Mo content and processing techniques to mitigate cracking behaviors in L-PBF-manufactured (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [English]
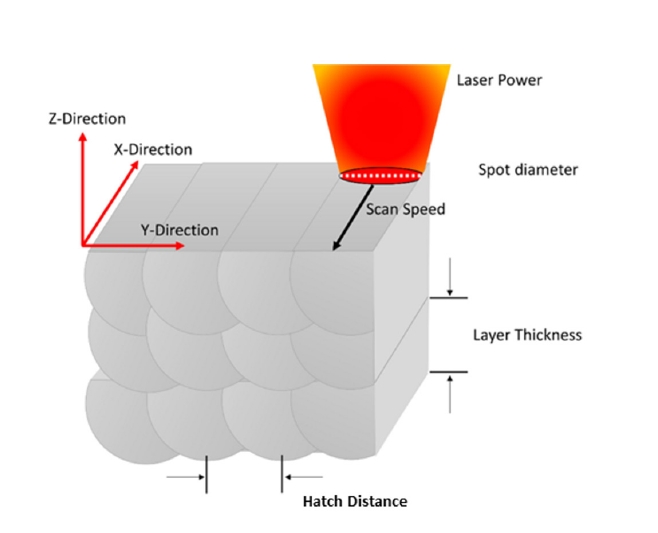
- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
- Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00325
- 2,193 View
- 65 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The AlSi10Mg alloy has garnered significant attention for its application in laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF), due to its lightweight properties and good printability using L-PBF. However, the low production speed of the L-PBF process is the main bottleneck in the industrial commercialization of L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy parts. Furthermore, while L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy exhibits excellent mechanical properties, the properties are often over-specified compared to the target properties of parts traditionally fabricated by casting. To accelerate production speed in L-PBF, this study investigated the effects of process parameters on the build rate and mechanical properties of the AlSi10Mg alloy. Guidelines are proposed for high-speed additive manufacturing of the AlSi10Mg alloy for use in automotive parts. The results show a significant increase in the build rate, exceeding the conventional build rate by a factor of 3.6 times or more, while the L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy met the specifications for automotive prototype parts. This strategy can be expected to offer significant cost advantages while maintaining acceptable mechanical properties of topology-optimized parts used in the automobile industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - Lightweight Design of a Connecting Rod Using Lattice-Structure Parameter Optimisation: A Test Case for L-PBF
Michele Amicarelli, Michele Trovato, Paolo Cicconi
Machines.2025; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
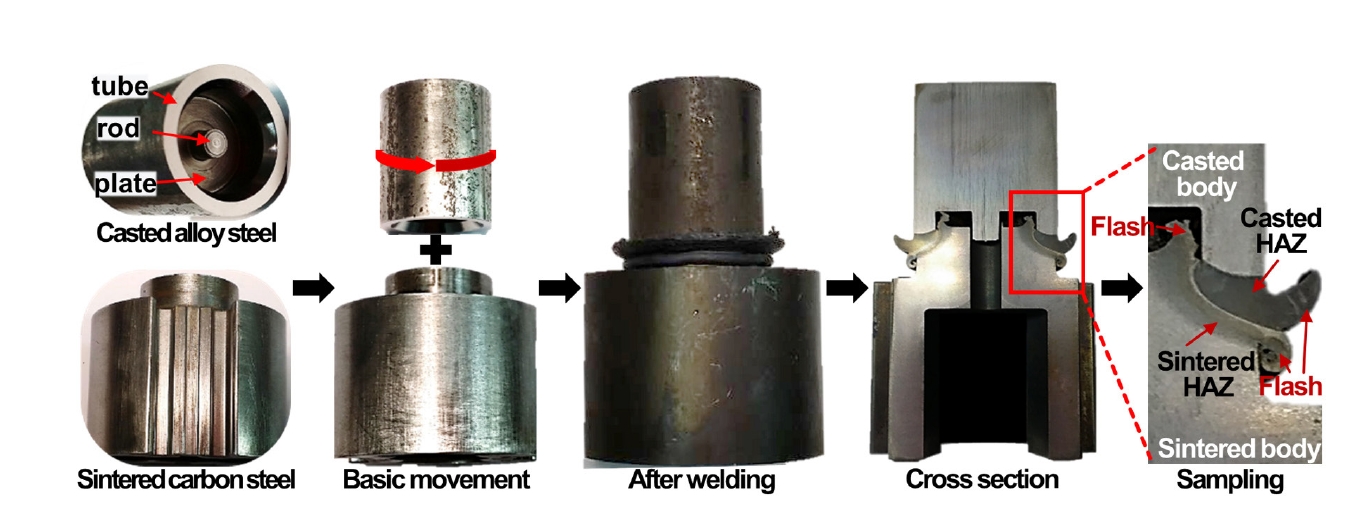
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):414-421. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00311
- 923 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Friction welding, which uses heat and plastic flow to join metals, is expanding across industries due to its ability to weld heterogeneous alloys and simple process. However, process research is essential for materials with complex geometries, and limited research has been conducted on friction welding between cast and sintered metals. This study analyzed the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of the joint by controlling the rotational speed and friction pressure, which affect the removal of the heat-affected zone in friction welding of casted SCM440 and sintered F-05-140. Hardness mapping and microstructure observations with material transition were performed to investigate the correlation between phase behavior and welding conditions. These results are anticipated to reduce costs and improve the mechanical properties of key mobility components.
- [Korean]
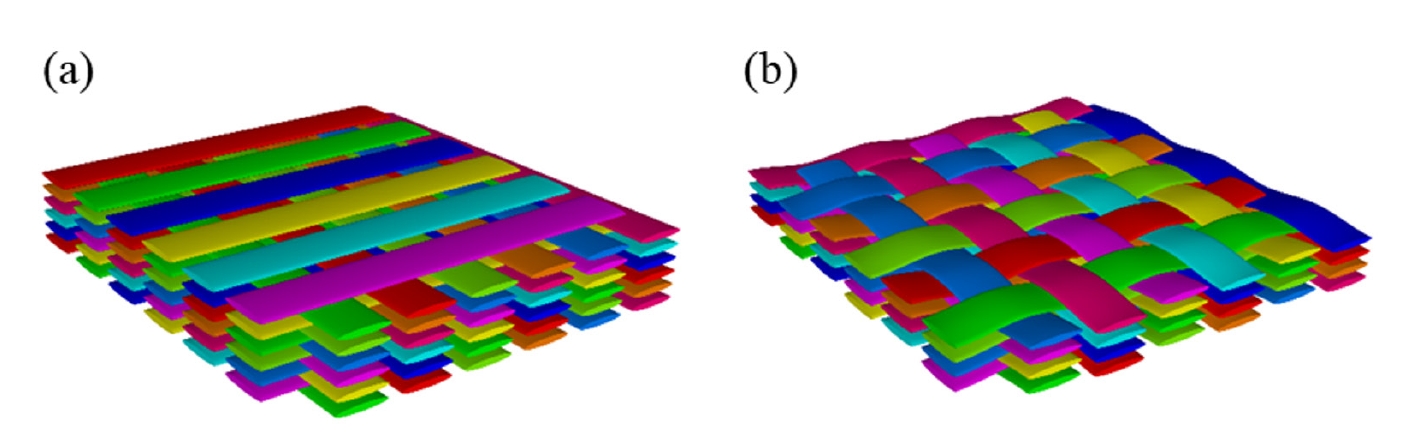
- Inter-laminar Strength of NITE-SiC/SiC Composites With Various Fiber Reinforcing Architecture
- Jong-il Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):437-444. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00248
- 893 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The mechanical performance of SiC/SiC composites is significantly influenced by the architecture of fiber reinforcement. Among the various fabrication methods, the nano-powder infiltration transition/eutectic (NITE) process is a promising technique that is capable of achieving a dense and stoichiometric SiC matrix. The reinforcement architecture, such as cross-ply (CP) or woven prepreg (WP), is determined during the preform stage of the NITE process, which is crucial in determining the mechanical properties of SiC/SiC composites. In this study, the tensile test and double notch shear (DNS) test were conducted using NITE-SiC/SiC composites to investigate the effect of the fiber reinforcing architecture on the fracture mechanism of SiC/SiC composites. The tensile strength and maximum shear strength of both CP and WP specimens were nearly identical. However, other mechanical properties, particularly those of CP specimens, exhibited significant variability. A comparison of fracture surfaces and load-displacement curve analyses from the DNS tests revealed that the cross points of the longitudinal or transverse fibers act as obstacles to both deformation and crack propagation. These obstacles were found to be more densely distributed in WP specimens than in CP specimens. The variability observed in the mechanical properties of CP specimens is likely due to size effects caused by the sparser distribution of these obstacles compared to the WP specimens.
- [English]
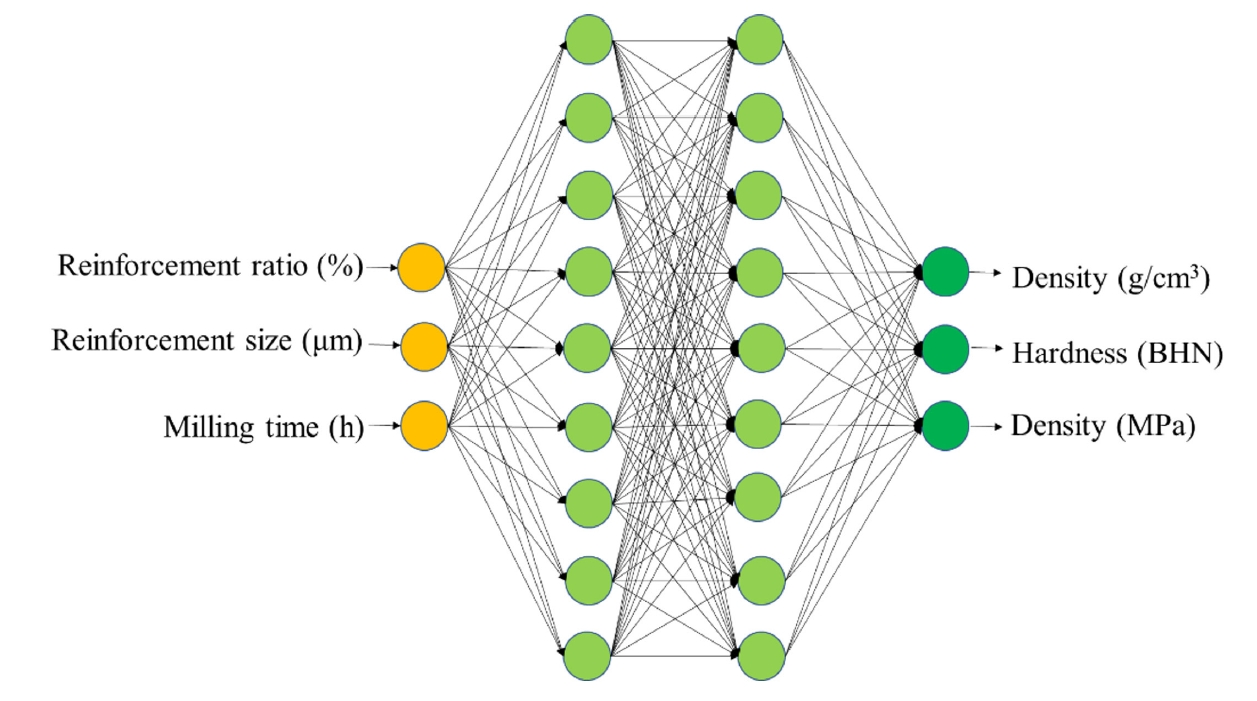
- Machine Learning Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C Composites
- Maurya A. K., Narayana P. L., Wang X.-S., Reddy N. S.
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):382-389. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00234
- 1,562 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Aluminum-based composites are in high demand in industrial fields due to their light weight, high electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Due to its unique advantages for composite fabrication, powder metallurgy is a crucial player in meeting this demand. However, the size and weight fraction of the reinforcement significantly influence the components' quality and performance. Understanding the correlation of these variables is crucial for building high-quality components. This study, therefore, investigated the correlations among various parameters—namely, milling time, reinforcement ratio, and size—that affect the composite’s physical and mechanical properties. An artificial neural network model was developed and showed the ability to correlate the processing parameters with the density, hardness, and tensile strength of Al2024-B4C composites. The predicted index of relative importance suggests that the milling time has the most substantial effect on fabricated components. This practical insight can be directly applied in the fabrication of high-quality Al2024-B4C composites.
Critical Review
- [English]
- Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
- Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):365-373. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00213
- 2,836 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review examines the microstructural and mechanical properties of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by wrought processing and powder metallurgy (PM), specifically laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and hot isostatic pressing. Wrought methods, such as forging and rolling, create equiaxed alpha (α) and beta (β) grain structures with balanced properties, which are ideal for fatigue resistance. In contrast, PM methods, particularly LPBF, often yield a martensitic α′ structure with high microhardness, enabling complex geometries but requiring post-processing to improve its properties and reduce stress. The study evaluated the effects of processing parameters on grain size, phase distribution, and material characteristics, guiding the choice of fabrication techniques for optimizing Ti-6Al-4V performance in aerospace, biomedical, and automotive applications. The analysis emphasizes tailored processing to meet advanced engineering demands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef
- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Conditions on the Microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo High-Entropy Alloy
- Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Junho Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):406-413. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00185

- 1,292 View
- 40 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We investigated the microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering under different sintering temperatures (1000–1100°C) and times (1–600 s). All sintered alloys consisted of a single face-centered cubic phase. As the sintering time or temperature increased, the grains of the sintered alloys became partially coarse. The formation of Cr7C3 carbide occurred on the surface of the sintered alloys due to carbon diffusion from the graphite crucible. The depth of the layer containing Cr7C3 carbides increased to ~110 μm under severe sintering conditions (1100°C, 60 s). A molten zone was observed on the surface of the alloys sintered at higher temperatures (>1060°C) due to severe carbon diffusion that reduced the melting point of the alloy. The porosity of the sintered alloys decreased with increasing time at 1000°C, but increased at higher temperatures above 1060°C due to melting-induced porosity formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Microstructure and mechanical properties of oxide-dispersion-strengthened CrMnFeCoNiC0.2O0.2 high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering
Sang-Hwa Lee, Seonghyun Park, Ka Ram Lim, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 947: 149284. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
- Jong Hoon Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):336-341. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00241
- 1,236 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
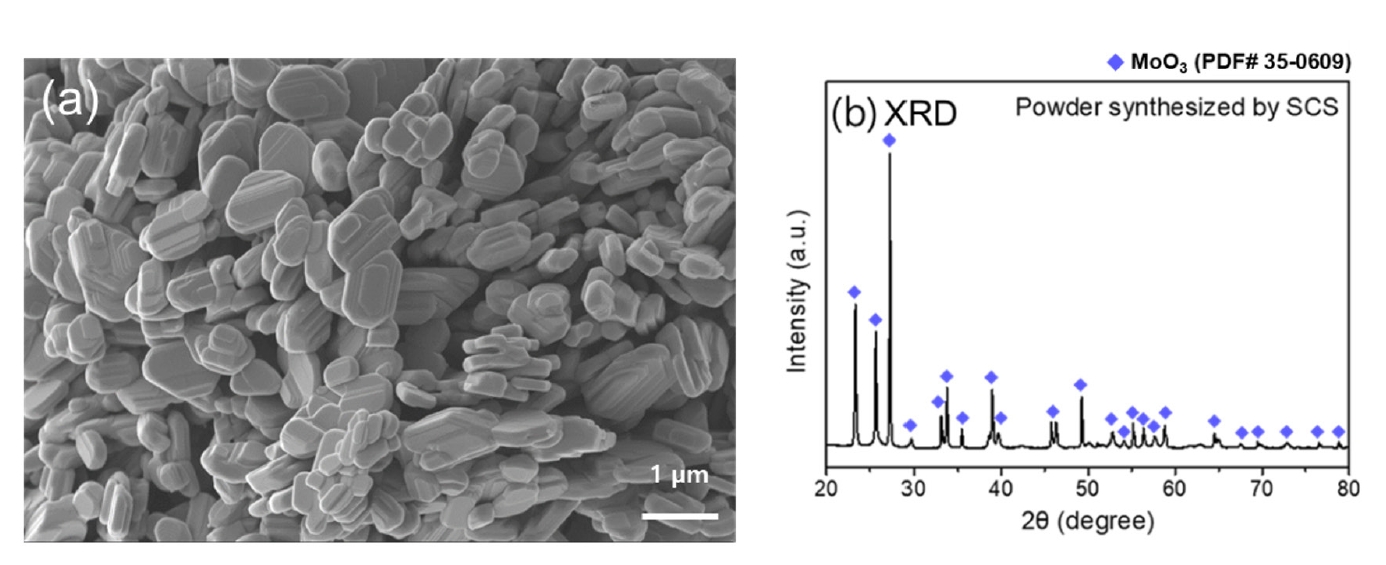
PDF - Molybdenum, valued for its high melting point and exceptional physical and chemical properties, is studied in diverse fields such as electronics, petrochemicals, and aviation. Among molybdenum oxides, molybdenum dioxide stands out for its higher electrical conductivity than other transition metal oxides due to its structural characteristics, exhibiting metallic properties. It is applied as pellets to gas sensors, semiconductors, and secondary batteries for its properties. Thus, research on molybdenum dioxide compaction and pressureless sintering is necessary, yet research on pressureless sintering is currently insufficient. This study synthesized MoO₃ powder via solution combustion synthesis and reduced it using the 3% hydrogen/argon gas mixture to investigate the effect of reduction temperature on the powder. Additionally, the reduced powder was compacted and subjected to pressureless sintering with temperature as a variable. The density and the microstructure of brown parts were analyzed and discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
Mohammed M. Alkhabet, Saad H. Girei, Ammar H. Farhan, Fatimah F. Hashim, Jaafar A. Jaafar, Husam K. Salih, Manar F. Abbood, Mohd H. Yaacob
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing.2025; 200: 110021. CrossRef
- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 3D Aligned h-BN based Polymer Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Battery Housing
- Kiho Song, Hyunseung Song, Sang In Lee, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):329-335. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00220
- 1,395 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
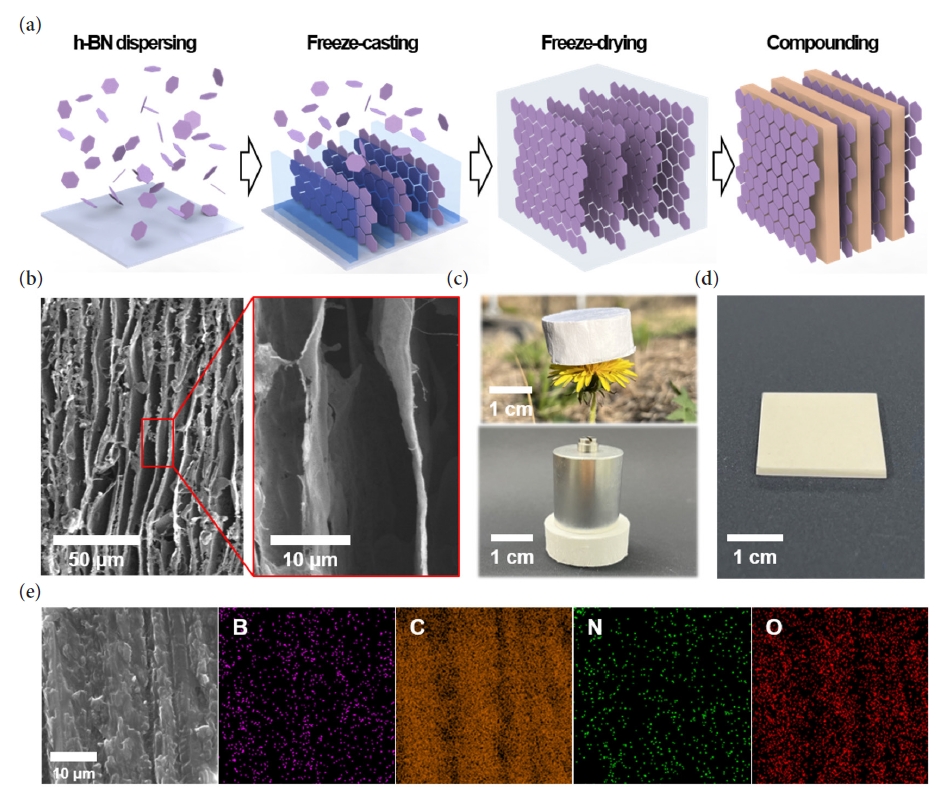
Supplementary Material - As the demand for electric vehicles increases, the stability of batteries has become one of the most significant issues. The battery housing, which protects the battery from external stimuli such as vibration, shock, and heat, is the crucial element in resolving safety problems. Conventional metal battery housings are being converted into polymer composites due to their lightweight and improved corrosion resistance to moisture. The transition to polymer composites requires high mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability. In this paper, we proposes a high-strength nanocomposite made by infiltrating epoxy into a 3D aligned h-BN structure. The developed 3D aligned h-BN/epoxy composite not only exhibits a high compressive strength (108 MPa) but also demonstrates excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, with a stable electrical resistivity at 200 °C and a low thermal expansion coefficient (11.46ⅹppm/℃), respectively.
- [Korean]
- Microstructural Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Direct Energy Deposition
- Juho Kim, Seoyeon Jeon, Hwajin Park, Taeyoel Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):302-307. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00157
- 1,561 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study explored the process-structure-property (PSP) relationships in Ti-6Al-4V alloys fabricated through direct energy deposition (DED) additive manufacturing. A systematic investigation was conducted to clarify how process variables—specifically, manipulating the cooling rate and energy input by adjusting the laser power and scan speed during the DED process—influenced the phase fractions, pore structures, and the resultant mechanical properties of the samples under various processing conditions. Significant links were found between the controlled process parameters and the structural and mechanical characteristics of the produced alloys. The findings of this research provide foundational knowledge that will drive the development of more effective and precise control strategies in additive manufacturing, thereby improving the performance and reliability of produced materials. This, in turn, promises to make significant contributions to both the advancement of additive manufacturing technologies and their applications in critical sectors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural and tribological performance of Ti6Al4V alloy modified by laser surface texturing
Bryan Ivan Quintanar-Abarca, Dulce Viridiana Melo-Máximo, Lizbeth Melo-Máximo, Esmeralda Uribe-Lam, Erika García-López
Journal of Materials Science.2026; 61(2): 1309. CrossRef - Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 202. CrossRef
- Microstructural and tribological performance of Ti6Al4V alloy modified by laser surface texturing
- [Korean]
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
- 2,125 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
- [Korean]
- Study on the Elemental Diffusion Distance of a Pure Nickel Layer Additively Manufactured on 316H Stainless Steel
- UiJun Ko, Won Chan Lee, Gi Seung Shin, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):220-225. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00164
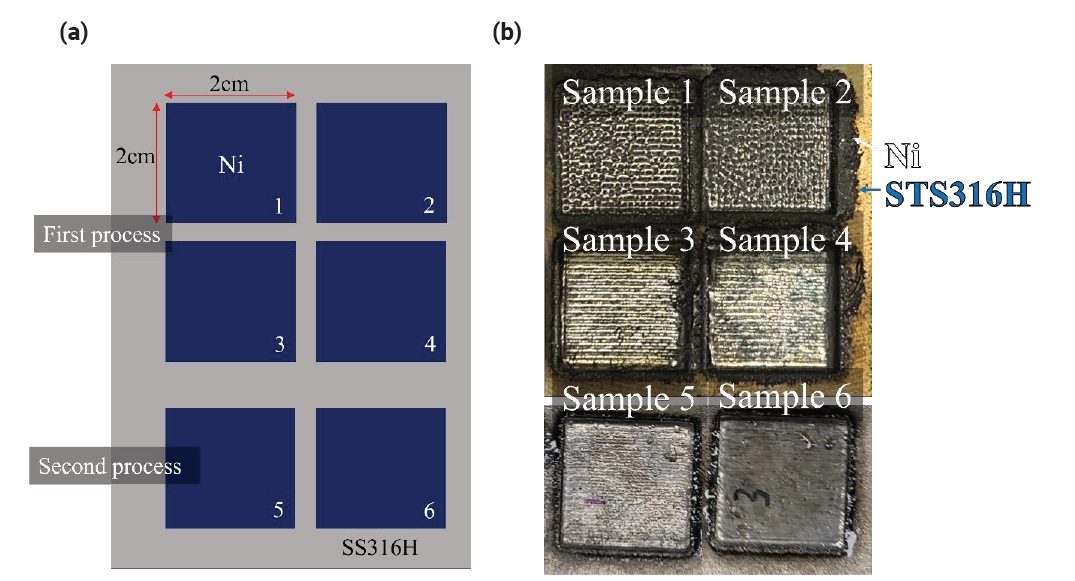
- 1,578 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Molten salt reactors represent a promising advancement in nuclear technology due to their potential for enhanced safety, higher efficiency, and reduced nuclear waste. However, the development of structural materials that can survive under severe corrosion environments is crucial. In the present work, pure Ni was deposited on the surface of 316H stainless steel using a directed energy deposition (DED) process. This study aimed to fabricate pure Ni alloy layers on an STS316H alloy substrate. It was observed that low laser power during the deposition of pure Ni on the STS316H substrate could induce stacking defects such as surface irregularities and internal voids, which were confirmed through photographic and SEM analyses. Additionally, the diffusion of Fe and Cr elements from the STS316H substrate into the Ni layers was observed to decrease with increasing Ni deposition height. Analysis of the composition of Cr and Fe components within the Ni deposition structures allows for the prediction of properties such as the corrosion resistance of Ni.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
Won Chan Lee, Jin Woong Park, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 342. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef - Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Pure Ni Coatings on a Type 316H Stainless Steel Substrate via High-Velocity Oxy-fuel and Directed Energy Deposition Processes
Won Chan Lee, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 309. CrossRef
- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
- [Korean]
- Comparison and Characterization of Silodosin-loaded Solid Dispersions Prepared by Various Solid Dispersion Preparation Methods
- Su Man Lee, Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):263-271. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00143
- 1,589 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study focused on improving the solubility of silodosin, a drug poorly soluble in water, by utilizing solid dispersions. Three types of dispersions were examined and compared against the drug powder: surface-attached (SA), solvent-wetted (SW), and solvent-evaporated (SE). Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was identified as the most effective polymer in enhancing solubility. These dispersions were prepared using spray-drying techniques with silodosin and PVA as the polymer, employing solvents such as water, ethanol, and a water-acetone mix. The physicochemical properties and solubility of the dispersions were evaluated. The surface-attached dispersions featured the polymer on a crystalline drug surface, the solvent-wetted dispersions had the amorphous drug on the polymer, and the solvent-evaporated dispersions produced nearly round particles with both components amorphous. Testing revealed that the order of improved solubility was: solvent-evaporated, solvent-wetted, and surface-attached. The results demonstrated that the preparation method of the solid dispersions significantly impacted their physicochemical properties and solubility enhancement.
- [English]
- Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):243-254. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00059
- 2,235 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been reported to have better properties than conventional materials; however, they are more expensive due to the high cost of their main components. Therefore, research is needed to reduce manufacturing costs. In this study, CoCrFeMnNi HEAs were prepared using metal injection molding (MIM), which is a powder metallurgy process that involves less material waste than machining process. Although the MIM-processed samples were in the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, porosity remained after sintering at 1200°C, 1250°C, and 1275°C. In this study, the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process, which considers both temperature (1150°C) and pressure (150 MPa), was adopted to improve the quality of the MIM samples. Although the hardness of the HIP-treated samples decreased slightly and the Mn composition was significantly reduced, the process effectively eliminated many pores that remained after the 1275°C MIM process. The HIP process can improve the quality of the alloy.
- [Korean]
- TiO2 Thin Film Coating on an Nb-Si–Based Superalloy via Atomic Layer Deposition
- Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):255-262. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00052
- 2,054 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nano-oxide dispersion–strengthened (ODS) superalloys have attracted attention because of their outstanding mechanical reinforcement mechanism. Dispersed oxides increase the material’s strength by preventing grain growth and recrystallization, as well as increasing creep resistance. In this research, atomic layer deposition (ALD) was applied to synthesize an ODS alloy. It is useful to coat conformal thin films even on complex matrix shapes, such as nanorods or powders. We coated an Nb-Si–based superalloy with TiO2 thin film by using rotary-reactor type thermal ALD. TiO2 was grown by controlling the deposition recipe, reactor temperature, N2 flow rate, and rotor speed. We could confirm the formation of uniform TiO2 film on the surface of the superalloy. This process was successfully applied to the synthesis of an ODS alloy, which could be a new field of ALD applications.
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,781 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [Korean]
- Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Stellite 6 Alloy prepared by Directed Energy Deposition
- Joowon Suh, Jae Hyeon Koh, Young-Bum Chun, Young Do Kim, Jinsung Jang, Suk Hoon Kang, Heung Nam Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):152-162. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00066

- 1,750 View
- 39 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The directed energy deposited (DED) alloys show higher hardness values than the welded alloys due to the finer microstructure following the high cooling rate. However, defects such as microcracks, pores, and the residual stress are remained within the DED alloy. These defects deteriorate the wear behavior so post-processing such as heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are applied to DED alloys to reduce the defects. HIP was chosen in this study because the high pressure and temperature uniformly reduced the defects. The HIP is processed at 1150oC under 100 MPa for 4 hours. After HIP, microcracks are disappeared and porosity is reduced by 86.9%. Carbides are spherodized due to the interdiffusion of Cr and C between the dendrite and interdendrite region. After HIP, the nanohardness (GPa) of carbides increased from 11.1 to 12, and the Co matrix decreased from 8.8 to 7.9. Vickers hardness (HV) decreased by 18.9 % after HIP. The dislocation density (10-2/m2) decreased from 7.34 to 0.34 and the residual stress (MPa) changed from tensile 79 to a compressive -246 by HIP. This study indicates that HIP is effective in reducing defects, and the HIP DED Stellite 6 exhibits a higher HV than welded Stellite 6.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 330. CrossRef
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024

- 1,190 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


