Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,762 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
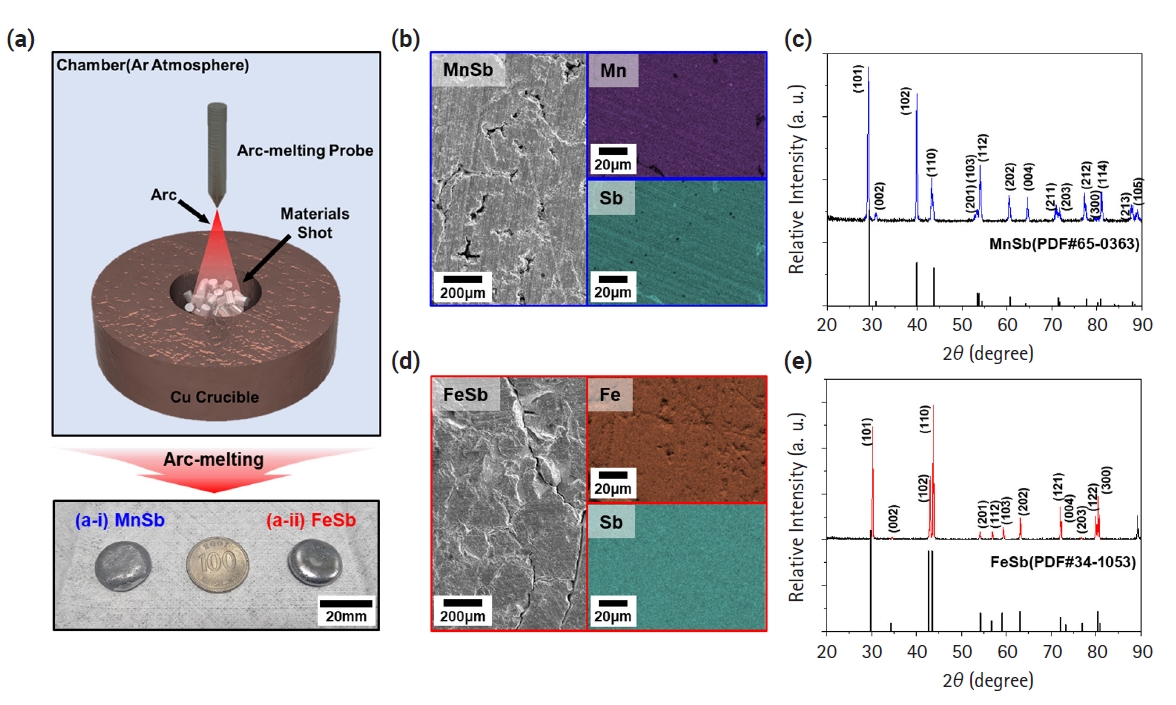
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Spark Plasma Sintered p-Type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 Compound via Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Induced Reduction of Lattice Thermal Conductivity
- Soo-Ho Jung, Ye Jin Woo, Kyung Tae Kim, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):123-129. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.123
- 1,601 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-temperature and high-pressure post-processing applied to sintered thermoelectric materials can create nanoscale defects, thereby enhancing their thermoelectric performance. Here, we investigate the effect of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) as a post-processing treatment on the thermoelectric properties of
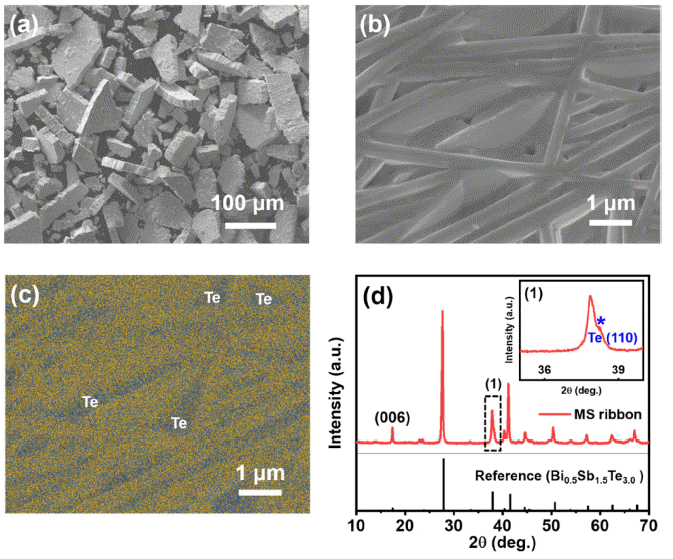
p -type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 compounds sintered via spark plasma sintering. The sample post-processed via HIP maintains its electronic transport properties despite the reduced microstructural texturing. Moreover, lattice thermal conductivity is significantly reduced owing to activated phonon scattering, which can be attributed to the nanoscale defects created during HIP, resulting in an ~18% increase in peakzT value, which reaches ~1.43 at 100°C. This study validates that HIP enhances the thermoelectric performance by controlling the thermal transport without having any detrimental effects on the electronic transport properties of thermoelectric materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 236. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
- [Korean]
- Effect of Morphological Control of Secondary Phase using Yb2O3 and Ca-Al-Si-O-based Glass on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN
- Dong Kyu Choi, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong Hun Yeo, Hyo Soon Shin, Dae Yong Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):498-502. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.498
- 845 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
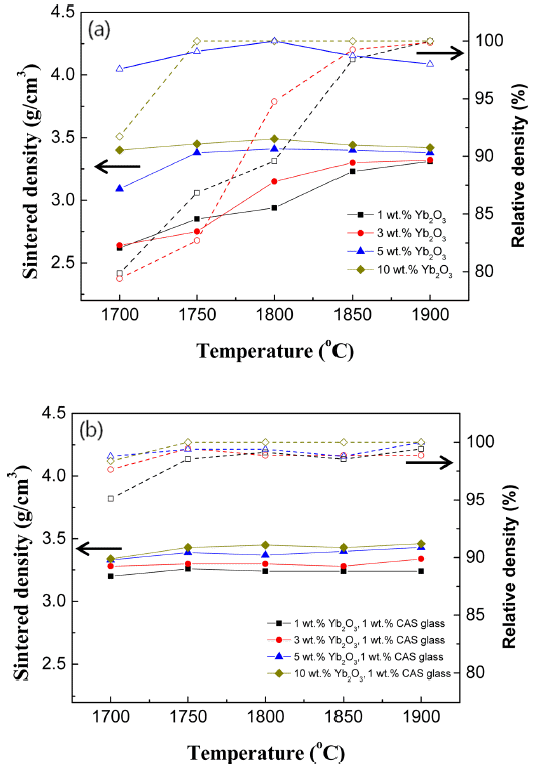
PDF We investigate the effects of Yb2O3 and calcium aluminosilicate (CAS) glass as sintering additives on the sintering behavior of AlN. The AlN specimens are sintered at temperatures between 1700°C and 1900°C for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the Yb2O3 content is low (within 3 wt.%), an isolated shape of secondary phase is observed at the AlN grain boundary. In contrast, when 3 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added, a continuous secondary phase is formed at the AlN grain boundary. The thermal conductivity decreases when the CAS glass is added, but the sintering density does not decrease. In particular, when 10 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added to AlN, the flexural strength is the highest, at 463 MPa. These results are considered to be influenced by changes in the microstructure of the secondary phase of AlN.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Sintering Additives on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN by Pressureless Sintering
- Jin Uk Hwang, So Youn Mun, Sang Yong Nam, Hwan Soo Dow
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):395-404. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.395
- 2,253 View
- 53 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
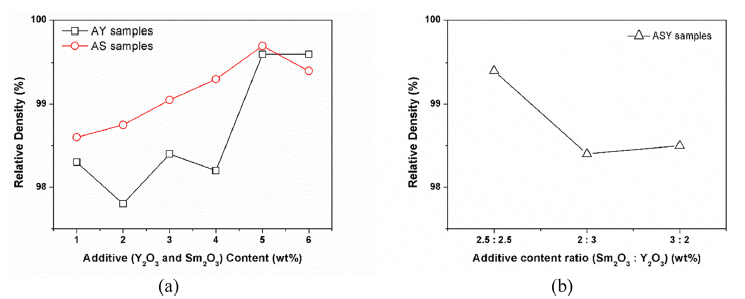
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) has excellent electrical insulation property, high thermal conductivity, and a low thermal expansion coefficient; therefore, it is widely used as a heat sink, heat-conductive filler, and heat dissipation substrate. However, it is well known that the AlN-based materials have disadvantages such as low sinterability and poor mechanical properties. In this study, the effects of addition of various amounts (1-6 wt.%) of sintering additives Y2O3 and Sm2O3 on the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples pressureless sintered at 1850°C in an N2 atmosphere for a holding time of 2 h are examined. All AlN samples exhibit relative densities of more than 97%. It showed that the higher thermal conductivity as the Y2O3 content increased than the Sm2O3 additive, whereas all AlN samples exhibited higher mechanical properties as Sm2O3 content increased. The formation of secondary phases by reaction of Y2O3, Sm2O3 with oxygen from AlN lattice influenced the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples due to the reaction of the oxygen contents in AlN lattice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
Liang Wang, Wei-Ming Guo, Peng-Fei Sheng, Li-Fu Lin, Xiao Zong, Shang-Hua Wu
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2023; 43(3): 862. CrossRef
- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
- [Korean]
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):494-500. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.494
- 1,449 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
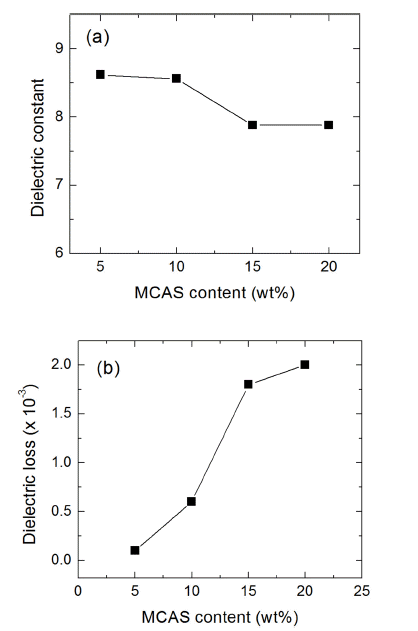
PDF In this study, the effect of the content of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (MCAS) glass additives on the properties of AlN ceramics is investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering for AlN compacts with MCAS contents varying between 5 and 20 wt% are carried out at temperatures ranging up to 1600°C. The results showed that the shrinkage of the AlN specimens increases with increasing MCAS content, and that full densification can be obtained irrespective of the MCAS content. Moreover, properties of the AlN-MCAS specimens such as microhardness, thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss are analyzed. Microhardness and thermal conductivity decrease with increasing MCAS content. An acceptable candidate for AlN application is obtained: an AlN-MCAS composite with a thermal conductivity over 70 W/m·K and a dielectric loss tangent (tan δ) below 0.6 × 10−3, with up to 10 wt% MCAS content.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of PbTe Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering of Nano Powders
- Eun-Young Jun, Ho-Young Kim, Cham Kim, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):384-389. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.384
- 1,151 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
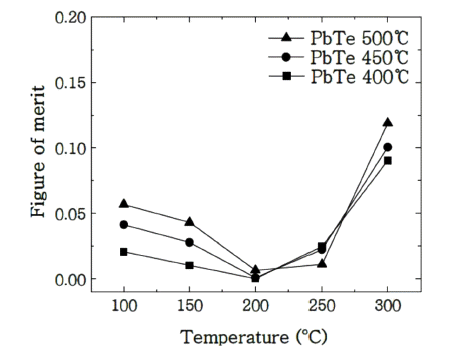
PDF Nanoparticles of PbTe are prepared via chemical reaction of the equimolar aqueous solutions of Pb(CH3COO)2 and Te at 120°C. The size of the obtained particles is 100 nm after calcination in a hydrogen atmosphere. Dense specimens for the thermoelectric characterization are produced by spark plasma sintering of prepared powders at 400°C to 500°C under 80 MPa for 5 min. The relative densities of the prepared specimens reach approximately 97% and are identified as cubic based on X-ray diffraction analyses. The thermoelectric properties are evaluated between 100°C and 300°C via electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity. Compared with PbTe ingot, the reduction of the thermal conductivities by more than 30% is verified via phonon scattering at the grain boundaries, which thus contributes to the increase in the figure of merit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
Ho-Jeong Kim, Il-Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(6): 422. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanocrystals and Their Application to Thermally Conductive Composites
- Jae-Yong Jung, Yang-Do Kim, Pyung-Woo Shin, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):414-419. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.414

- 1,496 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Much attention has been paid to thermally conductive materials for efficient heat dissipation of electronic devices to maintain their functionality and to support lifetime span. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which has a high thermal conductivity, is one of the most suitable materials for thermally conductive composites. In this study, we synthesize h-BN nanocrystals by pyrolysis of cost-effective precursors, boric acid, and melamine. Through pyrolysis at 900°C and subsequent annealing at 1500°C, h-BN nanoparticles with diameters of ~80 nm are synthesized. We demonstrate that the addition of small amounts of Eu-containing salts during the preparation of melamine borate precursors significantly enhanced the crystallinity of h-BN. In particular, addition of Eu assists the growth of h-BN nanoplatelets with diameters up to ~200 nm. Polymer composites containing both spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) and Eu-doped h-BN nanoparticles (4 vol%) show an enhanced thermal conductivity (λ ~ 1.72W/mK), which is larger than the thermal conductivity of polymer composites containing spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) as the sole fillers (λ ~ 1.48W/mK).
- [Korean]
- Investigation on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Telluride Matrix Composites by Addition of Graphene Oxide Powders
- Kyung Tae Kim, Taesik Min, Dong Won Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):263-269. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.263
- 782 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
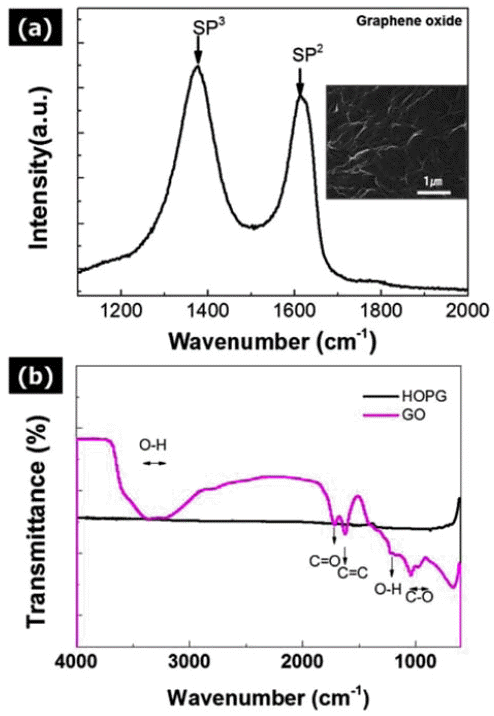
PDF Graphene oxide (GO) powder processed by Hummer's method is mixed with p-type Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by a high-energy ball milling process. The synthesized GO-dispersed p-type Bi2Te3 composite powder has a composition of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 (BSbT), and the powder is consolidated into composites with different contents of GO powder by using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. It is found that the addition of GO powder significantly decreases the thermal conductivity of the pure BSbT material through active phonon scattering at the newly formed interfaces. In addition, the electrical properties of the GO/BSbT composites are degraded by the addition of GO powder except in the case of the 0.1 wt% GO/BSbT composite. It is found that defects on the surface of GO powder hinder the electrical transport properties. As a result, the maximum thermoelectric performance (ZT value of 0.91) is achieved from the 0.1% GO/BSbT composite at 398 K. These results indicate that introducing GO powder into thermoelectric materials is a promising method to achieve enhanced thermoelectric performance due to the reduction in thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
Hua‐Lu Zhuang, Jincheng Yu, Jing‐Feng Li
Small Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - The role of edge-oxidized graphene to improve the thermopower of p-type bismuth telluride-based thick films
Young Min Cho, Kyung Tae Kim, Gi Seung Lee, Soo Hyung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 476: 533. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef
- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
- [Korean]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Behavior and Heat Dissipation Characteristics of the Aluminum Matrix Composite Materials with the Contents of Graphite
- Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Sungwook Joo, Sanghwui Hong, Jihoon Mun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):195-201. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.195
- 1,018 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
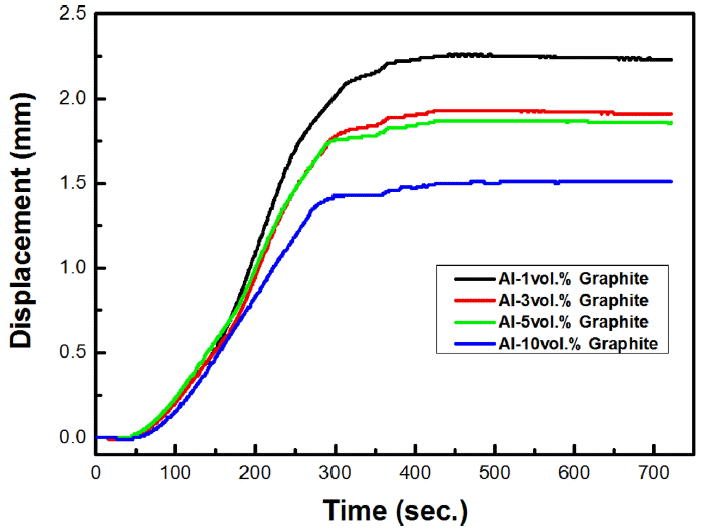
PDF Composite materials consisting of pure aluminum matrix reinforced with different amounts of graphite particles are successfully fabricated by mechanical ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) processes. The shrinkage rates of the composite powders vary with the amount of graphite particles and the lowest shrinkage value is observed for the composite with the highest amount of graphite particles. The current slopes of time increase with increase in the amount of graphite particles whereas the current slopes of temperature show the opposite trend. The highest thermal conductivity is achieved for the composite with the least amount of graphite particles. Therefore, the thermal properties of the composite materials can be controlled by controlling the amount of the graphite particles during the SPS process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Properties of Cu-Graphite Materials by a Spark Plasma Sintering Method
Min-hyeok Yang, Bum-soon Park, Hyoung-seok Moon, Jae-cheol Park, Hyun-kuk Park
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(6): 411. CrossRef - Effect of processing parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of aluminum–carbon nanotube composites produced by spark plasma sintering
B. Sadeghi, M. Shamanian, P. Cavaliere, F. Ashrafizadeh
International Journal of Materials Research.2018; 109(10): 900. CrossRef
- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Properties of Cu-Graphite Materials by a Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- [Korean]
- Thermal Properties of Diamond Aligned Electroless Ni Plating Layer/Oxygen Free Cu Substrates
- Da-Woon Jeong, Song-Yi Kim, Kyoung-Tae Park, Seok-Jun Seo, Taek Soo Kim, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):134-137. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.134
- 1,008 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
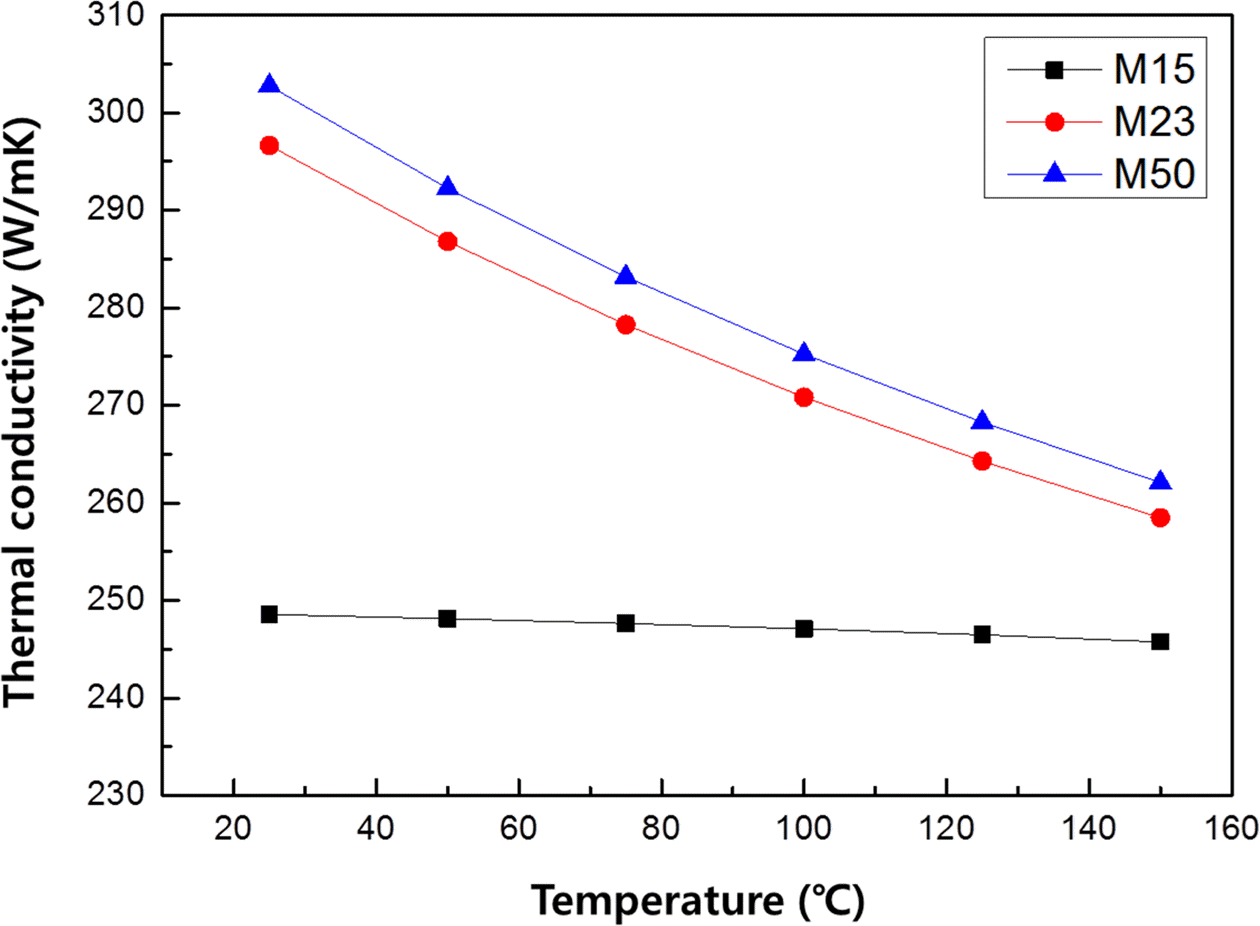
PDF The monolayer engineering diamond particles are aligned on the oxygen free Cu plates with electroless Ni plating layer. The mean diamond particle sizes of 15, 23 and 50 μm are used as thermal conductivity pathway for fabricating metal/carbon multi-layer composite material systems. Interconnected void structure of irregular shaped diamond particles allow dense electroless Ni plating layer on Cu plate and fixing them with 37-43% Ni thickness of their mean diameter. The thermal conductivity decrease with increasing measurement temperature up to 150°C in all diamond size conditions. When the diamond particle size is increased from 15 μm to 50 μm (Max. 304 W/mK at room temperature) tended to increase thermal conductivity, because the volume fraction of diamond is increased inside plating layer.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


