Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Ti-Mn-Cu Alloys with Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
- Ye Jun Yun, Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):20-24. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.20
- 796 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
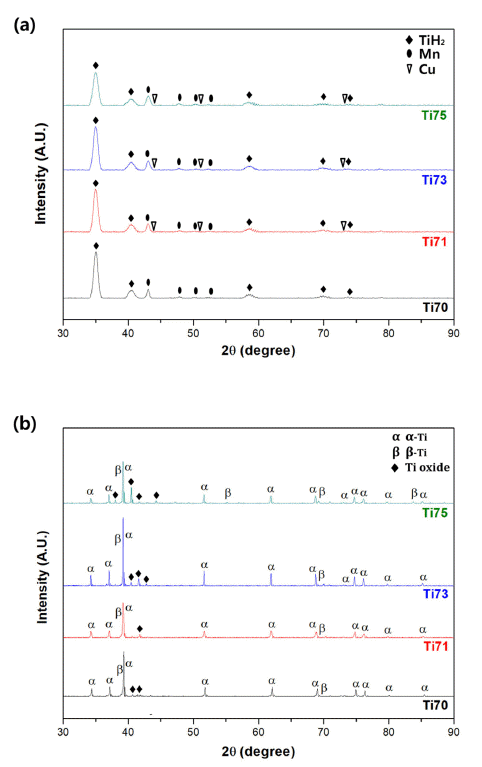
PDF Ti-based alloys are widely used in biomaterials owing to their excellent biocompatibility. In this study, Ti- Mn-Cu alloys are prepared by high-energy ball milling, magnetic pulsed compaction, and pressureless sintering. The microstructure and microhardness of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys with variation of the Cu addition and compaction pressure are analyzed. The correlation between the composition, compaction pressure, and density is investigated by measuring the green density and sintered density for samples with different compositions, subjected to various compaction pressures. For all compositions, it is confirmed that the green density increases proportionally as the compaction pressure increases, but the sintered density decreases owing to gas formation from the pyrolysis of TiH2 powders and reduction of oxides on the surface of the starting powders during the sintering process. In addition, an increase in the amount of Cu addition changes the volume fractions of the α-Ti and β-Ti phases, and the microstructure of the alloys with different compositions also changes. It is demonstrated that these changes in the phase volume fraction and microstructure are closely related to the mechanical properties of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys.
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of High-entropy Alloys
- Pureunsol Park, Ho Joon Lee, Youngjun Jo, Bonseung Gu, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):515-527. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.515
- 5,532 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
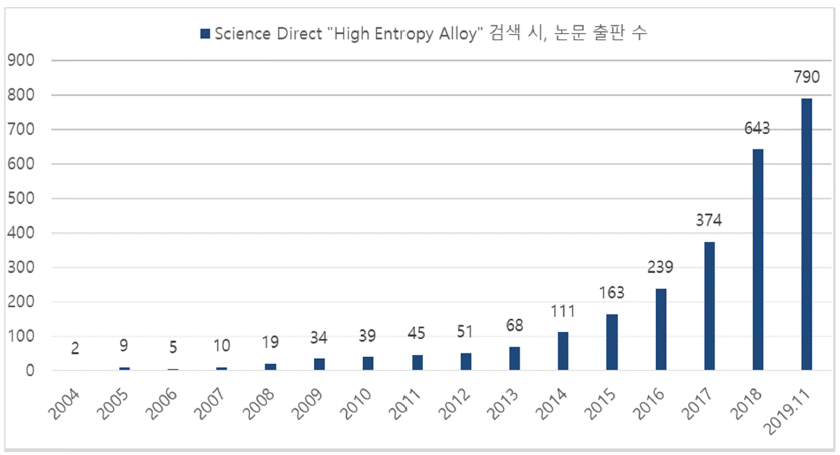
PDF High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are generally defined as solid solutions containing at least 5 constituent elements with concentrations between 5 and 35 atomic percent without the formation of intermetallic compounds. Currently, HEAs receive great attention as promising candidate materials for extreme environments due to their potentially desirable properties that result from their unique structural properties. In this review paper, we aim to introduce HEAs and explain their properties and related research by classifying them into three main categories, namely, mechanical properties, thermal properties, and electrochemical properties. Due to the high demand for structural materials in extreme environments, the mechanical properties of HEAs including strength, hardness, ductility, fatigue, and wear resistance are mainly described. Thermal and electrochemical properties, essential for the application of these alloys as structural materials, are also described.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
Jungsu Bin, Hyunbae Gee, Taesung Park, UiJun Go, Jeoung Han Kim, Youn-Seoung Lee
Current Applied Physics.2024; 59: 85. CrossRef - Sintering Behavior and Mechanical Property of Transition Metal Carbide-Based Cermets by Spark Plasma Sintering
Jeong-Han Lee, Hyun-Kuk Park, Sung-Kil Hong
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(1): 44. CrossRef
- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Alloys with Improved Fracture Toughness through the Dispersion of Lanthanum Oxide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):208-213. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.208
- 802 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
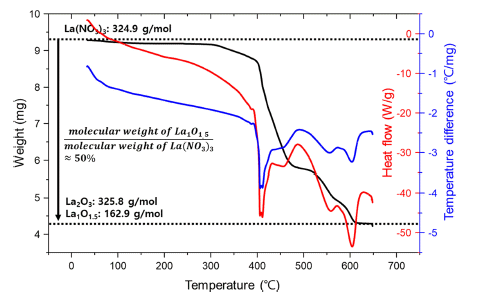
PDF In this study, lanthanum oxide (La2O3) dispersed molybdenum (Mo–La2O3) alloys are fabricated using lanthanum nitrate solution and nanosized Mo particles produced by hydrogen reduction of molybdenum oxide. The effect of La2O3 dispersion in a Mo matrix on the fracture toughness at room temperature is demonstrated through the formation behavior of La2O3 from the precursor and three-point bending test using a single-edge notched bend specimen. The relative density of the Mo–0.3La2O3 specimen sintered by pressureless sintering is approximately 99%, and La2O3 with a size of hundreds of nanometers is uniformly distributed in the Mo matrix. It is also confirmed that the fracture toughness is 19.46 MPa·m1/2, an improvement of approximately 40% over the fracture toughness of 13.50 MPa·m1/2 on a pure-Mo specimen without La2O3, and this difference in the fracture toughness occurs because of the changes in fracture mode of the Mo matrix caused by the dispersion of La2O3.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering property of micro/nano core-shell molybdenum powder synthesized by mechanochemical process
Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Won Hee Lee, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 119: 106532. CrossRef - Novel design of Mo-Si-B + La2O3 powder with multi-shell structure for ideal microstructure and enhanced mechanical property
Wonjune Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jongmin Byun
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 120: 106611. CrossRef
- Sintering property of micro/nano core-shell molybdenum powder synthesized by mechanochemical process
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of the Mo-Si-B Alloys as Next Generation Ultra-high-temperature Alloys
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):156-165. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.156

- 1,441 View
- 25 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Over the last decade, the next generation’s ultra-high-temperature materials as an alternative to Nickel-based superalloys have been highlighted. Ultra-high-temperature materials based on refractory metals are one of several potential candidates. In particular, molybdenum alloys with small amounts of silicon and boron (Mo-Si-B alloys) have superior properties at high temperature. However, research related to Mo-Si-B alloys were mainly conducted by several developed countries but garnered little interest in Korea. Therefore, in this review paper, we introduce the development history of Mo-Si-B alloys briefly and discuss the properties, particularly the mechanical and oxidation properties of Mo-Si-B alloys. We also introduce the latest research trends of Mo-Si-B alloys based on the research paper. Finally, for domestic research related to this field, we explain why Mo-Si-B alloys should be developed and suggest the potential directions for Mo-Si-B alloys research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef - Preparation and Structure of Chromium Coatings Doped with Diamond Nanoparticles Deposited Directly on a Monolithic Composite of Molybdenum and Aluminum
V. P. Petkov, M. K. Aleksandrova, R. V. Valov, V. P. Korzhov, V. M. Kiiko, I. S. Zheltyakova
Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces.2023; 59(3): 396. CrossRef - A Review of Mo-Si Intermetallic Compounds as Ultrahigh-Temperature Materials
Liang Jiang, Bin Zheng, Changsong Wu, Pengxiang Li, Tong Xue, Jiandong Wu, Fenglan Han, Yuhong Chen
Processes.2022; 10(9): 1772. CrossRef - Heat-Resistant Molybdenum Borosilicate Alloys Hardened with Titanium Carbides: Mo–Si–B–TiC (Survey)
I. L. Svetlov, O. G. Ospennikova, M. I. Karpov, Yu. V. Artemenko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2021; 12(4): 866. CrossRef
- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
- [Korean]
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
- Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101
- 964 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
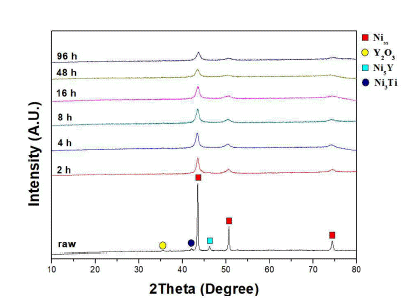
PDF Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402
- 458 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
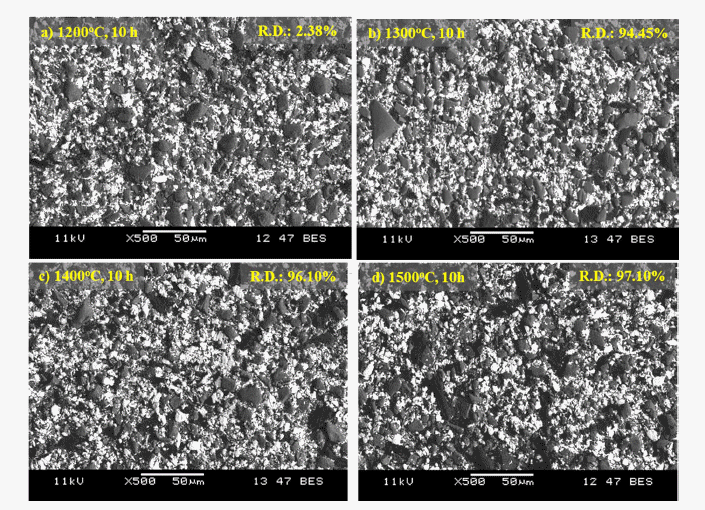
PDF Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Electric Contact Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Ta-Cu Composite
- Won Ju, Young Do Kim, Jae Jin Sim, Sang-Hoon Choi, Soong Keun Hyun, Kyoung Mook Lim, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):377-383. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.377
- 1,116 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
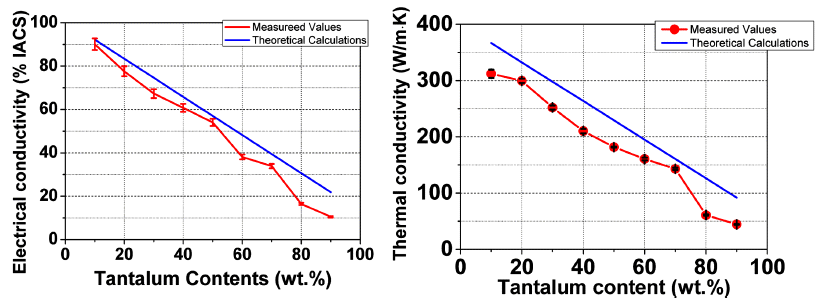
PDF Microstructure, electric, and thermal properties of the Ta-Cu composite is evaluated for the application in electric contact materials. This material has the potential to be used in a medium for a high current range of current conditions, replacing Ag-MO, W, and WC containing materials. The optimized SPS process conditions are a temperature of 900°C for a 5 min holding time under a 30 MPa mechanical pressure. Comparative research is carried out for the calculated and actual values of the thermal and electric properties. The range of actual thermal and electric properties of the Ta-Cu composite are 50~300W/mk and 10~90 %IACS, respectively, according to the compositional change of the 90 to 10 wt% Ta-Cu system. The results related to the electric contact properties, suggest that less than 50 wt% of Ta compositions are possible in applications of electric contact materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, K. Shimizu, T.V. Pastukhova, I. Petryshynets, A.M. Zusin, E.V. Kudinova, B.V. Efremenko
Vacuum.2021; 185: 110031. CrossRef
- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
- [Korean]
- Status of ITU-T International Standard Development on Rare Metal Recycling
- Mi Hye Lee, Won Jung Choi, Seok-Jun Seo, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):325-330. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.325
- 1,013 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
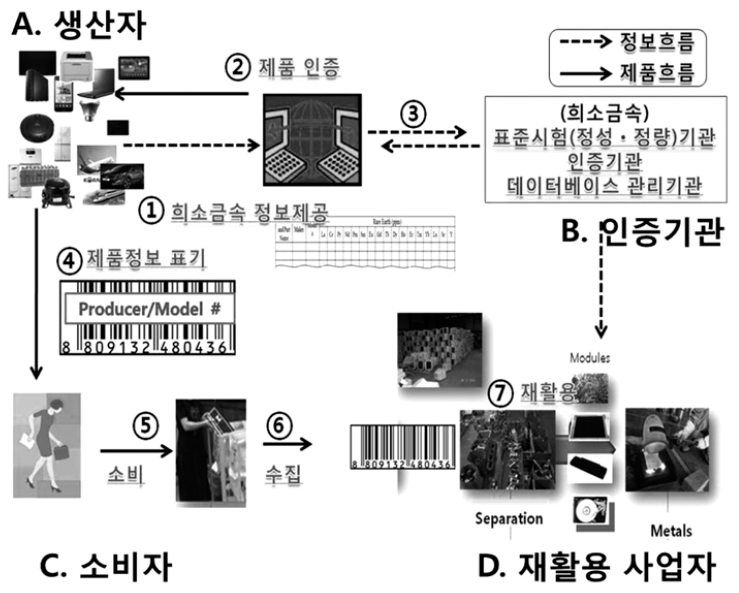
PDF Owing to increasing demand of rare metals present in ICT products, it is necessary to promote the rare metal recycling industry from an environmental viewpoint and to prevent climate change. Despite the fact that information for toxic substances is partly indicated, a legal basis and an international standard indicating usage of rare metals is insufficient. In order to address this issue, a newly created study group of environment and climate change at the ITU (International Telecommunication Union) is doing research to develop methodologies for recycling rare metals from ICT products in an eco-friendly way. Under this group, the Republic of Korea has established two international standards related to rare metals present in ICT products. The first is ‘Release of rare metal information for ICT products (ITU-T L.1100)’ and the other is ‘Quantitative and qualitative analysis methods for rare metals (ITU-T L.1101)’. A new proposal for recommending the provision of rare metal information through a label by manufacturers and consumer/recycling businesses has been approved recently and is supposed to be published later in 2016. Moreover, these recommendations are also being extended to IEC, ISO and other standardization organizations and a strategy to reinforce the ability for domestic standardization is being established in accordance with industrial requirements. This will promote efficient recycling of rare metals from ICT products and will help improve the domestic supply of rare metals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The State of Affairs of ‘Rare Metal Industry’ in Korea
Jae Hong Shin, Lee Ro Woon, Kyoung Tae Park
Kompleksnoe Ispolʹzovanie Mineralʹnogo syrʹâ/Complex Use of Mineral Resources/Mineraldik Shikisattardy Keshendi Paidalanu.2024; 330(3): 43. CrossRef - Russian Mineral Market Flow and Economic Direction for Securing Stable Resources
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bin Lee, Kyoung Mook Lim, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 345. CrossRef - Trends and Implications of International Standardization for Rare Earths
Sardar Farhat Abbas, Sang-Hyun lee, Bin Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 165. CrossRef
- The State of Affairs of ‘Rare Metal Industry’ in Korea
- [Korean]
- Optical Characteristics of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot with Precursor Flow Rate Synthesized by using Microreactor
- Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Won Ju, Han Wook Seo, Yong-Ho Choa, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):91-94. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.91
- 1,239 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
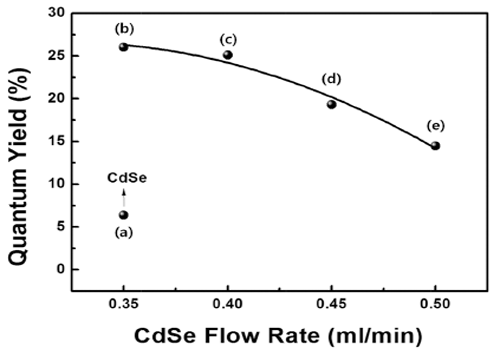
PDF High-quality colloidal CdSe/ZnS (core/shell) is synthesized using a continuous microreactor. The particle size of the synthesized quantum dots (QDs) is a function of the precursor flow rate; as the precursor flow rate increases, the size of the QDs decreases and the band gap energy increases. The photoluminescence properties are found to depend strongly on the flow rate of the CdSe precursor owing to the change in the core size. In addition, a gradual shift in the maximum luminescent wave (λmax) to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) is found owing to the decrease in the QD size in accordance with the quantum confinement effect. The ZnS shell decreases the surface defect concentration of CdSe. It also lowers the thermal energy dissipation by increasing the concentration of recombination. Thus, a relatively high emission and quantum yield occur because of an increase in the optical energy emitted at equal concentration. In addition, the maximum quantum yield is derived for process conditions of 0.35 ml/min and is related to the optimum thickness of the shell material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantum materials made in microfluidics - critical review and perspective
M. Wojnicki, V. Hessel
Chemical Engineering Journal.2022; 438: 135616. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef
- Quantum materials made in microfluidics - critical review and perspective
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


